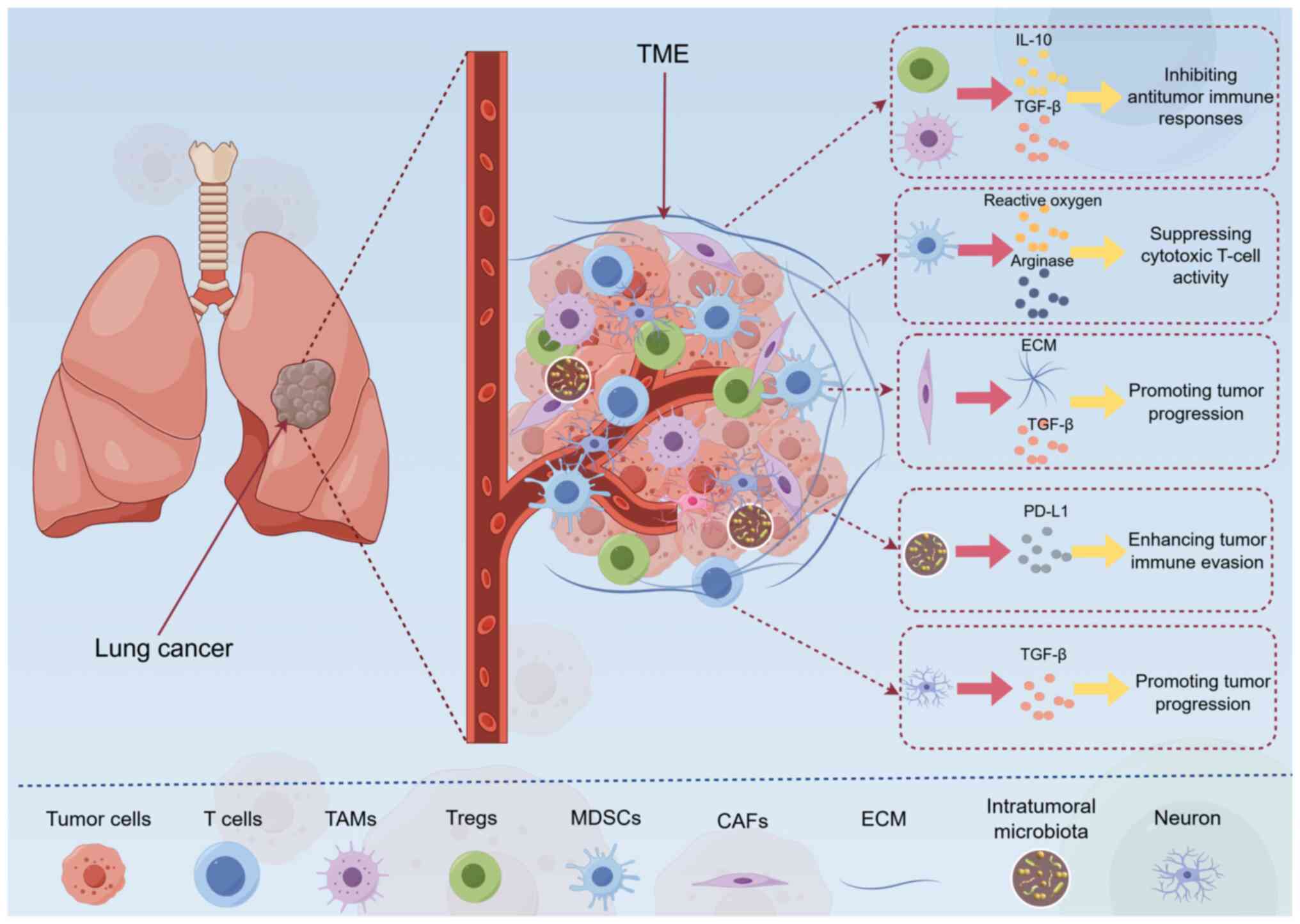
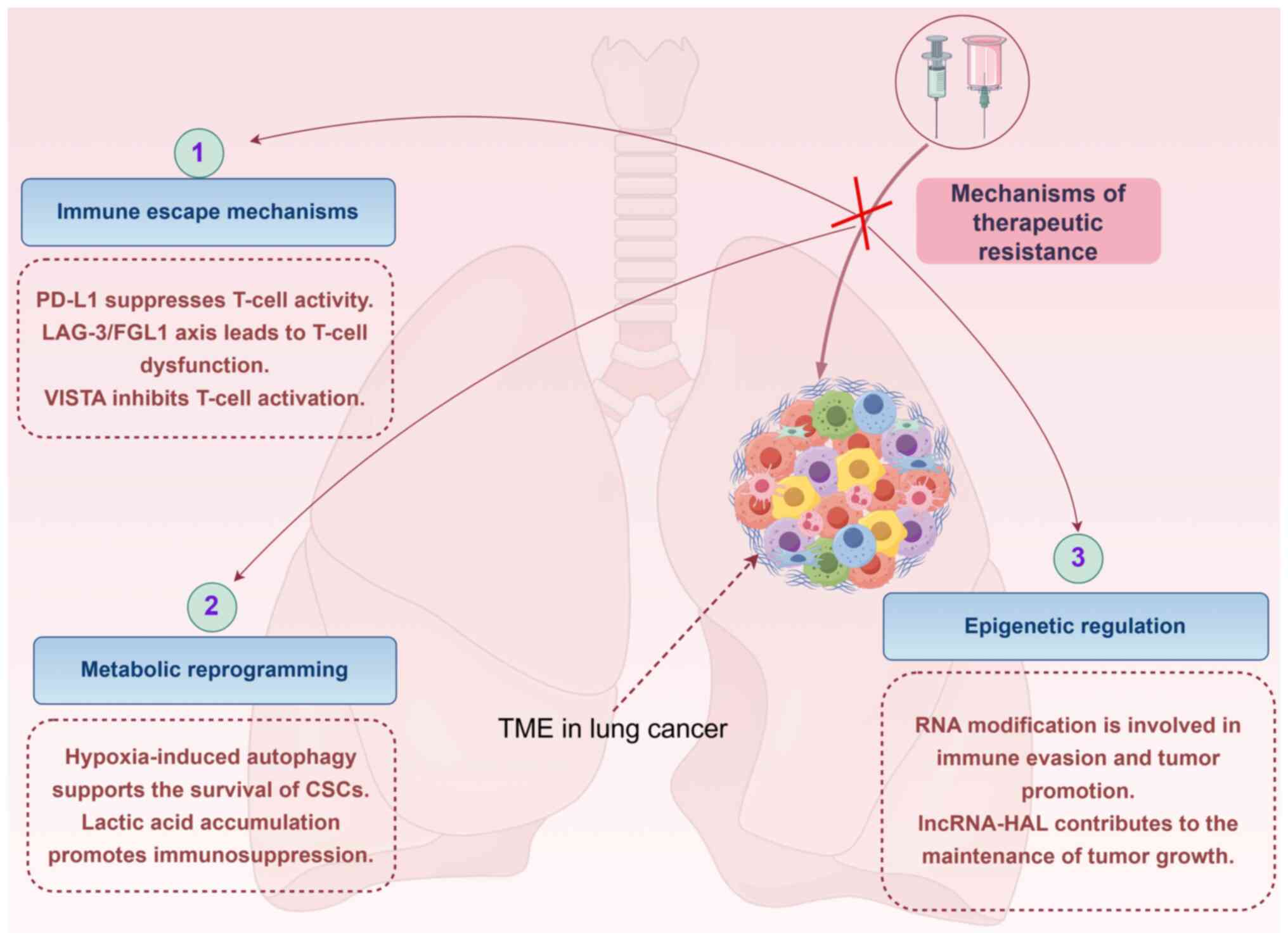
|
1
|
Wéber A, Morgan E, Vignat J, Laversanne M,
Pizzato M, Rumgay H, Singh D, Nagy P, Kenessey I, Soerjomataram I
and Bray F: Lung cancer mortality in the wake of the changing
smoking epidemic: A descriptive study of the global burden in 2020
and 2040. BMJ Open. 13:e0653032023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Oxnard GR, Arcila ME, Sima CS, Riely GJ,
Chmielecki J, Kris MG, Pao W, Ladanyi M and Miller VA: Acquired
resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant lung
cancer: Distinct natural history of patients with tumors harboring
the T790M mutation. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1616–1622. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Miyata H, Shigeto H, Ikeya T, Ashizawa T,
Iizuka A, Kikuchi Y, Maeda C, Kanematsu A, Yamashita K, Urakami K,
et al: Localization of epidermal growth factor receptor-mutations
using PNA: DNA probes in clinical specimens from patients with
non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep. 15:113142025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Son B, Lee S, Youn H, Kim E, Kim W and
Youn B: The role of tumor microenvironment in therapeutic
resistance. Oncotarget. 8:3933–3945. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Yu H, Zhang W, Xu XR and Chen S: Drug
resistance related genes in lung adenocarcinoma predict patient
prognosis and influence the tumor microenvironment. Sci Rep.
13:96822023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Skoulidis F, Li BT, Dy GK, Price TJ,
Falchook GS, Wolf J, Italiano A, Schuler M, Borghaei H, Barlesi F,
et al: Sotorasib for lung cancers with KRAS p.G12C mutation. N Engl
J Med. 384:2371–2381. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Said SS and Ibrahim WN: Cancer resistance
to immunotherapy: Comprehensive insights with future perspectives.
Pharmaceutics. 15:11432023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Glaviano A, Lau HS, Carter LM, Lee EHC,
Lam HY, Okina E, Tan DJJ, Tan W, Ang HL, Carbone D, et al:
Harnessing the tumor microenvironment: Targeted cancer therapies
through modulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Hematol
Oncol. 18:62025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tian Y, Yang Y, He L, Yu X, Zhou H and
Wang J: Exploring the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer to
develop a prognostic model and predict immunotherapy responses. Sci
Rep. 15:125692025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tan Z, Xue H, Sun Y, Zhang C, Song Y and
Qi Y: The role of tumor inflammatory microenvironment in lung
cancer. Front Pharmacol. 12:6886252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Y, Liang J, Zhang Y and Guo Q: Drug
resistance and tumor immune microenvironment: An overview of
current understandings (Review). Int J Oncol. 65:962024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Heydenreich B, Bellinghausen I, Lorenz S,
Henmar H, Strand D, Würtzen PA and Saloga J: Reduced in vitro
T-cell responses induced by glutaraldehyde-modified allergen
extracts are caused mainly by retarded internalization of dendritic
cells. Immunology. 136:208–217. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mai Z, Lin Y, Lin P, Zhao X and Cui L:
Modulating extracellular matrix stiffness: A strategic approach to
boost cancer immunotherapy. Cell Death Dis. 15:3072024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen K, Luo L, Li Y and Yang G:
Reprogramming the immune microenvironment in lung cancer. Volume.
16:16848892025.
|
|
16
|
Chandra R, Ehab J, Hauptmann E, Gunturu
NS, Karalis JD, Kent DO, Heid CA, Reznik SI, Sarkaria IS, Huang H,
et al: The current state of tumor Microenvironment-specific
therapies for Non-small cell lung cancer. Cancers (Basel).
17:17322025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
He ZN, Zhang CY, Zhao YW, He SL, Li Y, Shi
BL, Hu JQ, Qi RZ and Hua BJ: Regulation of T cells by
myeloid-derived suppressor cells: Emerging immunosuppressor in lung
cancer. Discov Oncol. 14:1852023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lim JU, Lee E, Lee SY, Cho HJ, Ahn DH,
Hwang Y, Choi JY, Yeo CD, Park CK and Kim SJ: Current literature
review on the tumor immune micro-environment, its heterogeneity and
future perspectives in treatment of advanced non-small cell lung
cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 12:857–876. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Genova C, Dellepiane C, Carrega P,
Sommariva S, Ferlazzo G, Pronzato P, Gangemi R, Filaci G, Coco S
and Croce M: Therapeutic implications of tumor microenvironment in
lung cancer: Focus on immune checkpoint blockade. Front Immunol.
12:7994552021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Cao Q, Li C, Li Y, Kong X, Wang S and Ma
J: Tumor microenvironment and drug resistance in lung
adenocarcinoma: Molecular mechanisms, prognostic implications, and
therapeutic strategies. Discov Oncol. 16:2382025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chu X, Tian Y and Lv C: Decoding the
spatiotemporal heterogeneity of Tumor-associated macrophages. Mol
Cancer. 23:1502024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mei S, Zhang H, Hirz T, Jeffries NE, Xu Y,
Baryawno N, Wu S, Wu CL, Patnaik A, Saylor PJ, et al: Single-cell
and spatial transcriptomics reveal a Tumor-associated macrophage
subpopulation that mediates prostate cancer progression and
metastasis. Mol Cancer Res. 23:653–665. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ashrafi A, Akter Z, Modareszadeh P,
Modareszadeh P, Berisha E, Alemi PS, Chacon Castro MDC, Deese AR
and Zhang L: Current landscape of therapeutic resistance in lung
cancer and promising strategies to overcome resistance. Cancers
(Basel). 14:45622022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guo T and Xu J: Cancer-associated
fibroblasts: A versatile mediator in tumor progression, metastasis,
and targeted therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 43:1095–1116. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu C, Gu J, Gu H, Zhang X, Zhang X and Ji
R: The recent advances of cancer associated fibroblasts in cancer
progression and therapy. Front Oncol. 12:10088432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Papavassiliou KA, Sofianidi AA, Gogou VA
and Papavassiliou AG: Drugging the tumor microenvironment epigenome
for therapeutic interventions in NSCLC. J Cancer. 16:1832–1835.
2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tong L, Jiménez-Cortegana C, Tay AHM,
Wickström S, Galluzzi L and Lundqvist A: NK cells and solid tumors:
Therapeutic potential and persisting obstacles. Mol Cancer.
21:2062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu J, Wu M, Yang Y, Wang Z, He S, Tian X
and Wang H: γδ T cells and the PD-1/PD-L1 axis: A love-hate
relationship in the tumor microenvironment. J Transl Med.
22:5532024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Mancini A, Gentile MT, Pentimalli F,
Cortellino S, Grieco M and Giordano A: Multiple aspects of matrix
stiffness in cancer progression. Front Oncol. 14:14066442024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Henke E, Nandigama R and Ergün S:
Extracellular matrix in the tumor microenvironment and its impact
on cancer therapy. Front Mol Biosci. 6:1602019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Marrugal Á, Ojeda L, Paz-Ares L,
Molina-Pinelo S and Ferrer I: Proteomic-based approaches for the
study of cytokines in lung cancer. Dis Markers. 2016:21386272016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang A, Miao K, Sun H and Deng CX: Tumor
heterogeneity reshapes the tumor microenvironment to influence drug
resistance. Int J Biol Sci. 18:3019–3033. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li X, Shang S, Wu M, Song Q and Chen D:
Gut microbial metabolites in lung cancer development and
immunotherapy: Novel insights into gut-lung axis. Cancer Lett.
598:2170962024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li J, Shi B, Ren X, Hu J, Li Y, He S,
Zhang G, Maolan A, Sun T, Qi X, et al: Lung-intestinal axis,
Shuangshen granules attenuate lung metastasis by regulating the
intestinal microbiota and related metabolites. Phytomedicine.
132:1558312024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ankudavicius V, Nikitina D, Lukosevicius
R, Tilinde D, Salteniene V, Poskiene L, Miliauskas S, Skieceviciene
J, Zemaitis M and Kupcinskas J: Detailed characterization of the
Lung-gut microbiome axis reveals the link between PD-L1 and the
microbiome in Non-Small-cell lung cancer patients. Int J Mol Sci.
25:23232024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dong Q, Chen ES, Zhao C and Jin C:
Host-Microbiome interaction in lung cancer. Front Immunol.
12:6798292021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hunt PJ, Andújar FN, Silverman DA and Amit
M: Mini-review: Trophic interactions between cancer cells and
primary afferent neurons. Neurosci Lett. 746:1356582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hernandez S, Serrano AG and Solis Soto LM:
The role of nerve fibers in the tumor Immune microenvironment of
solid tumors. Adv Biol (Weinh). 6:22000462022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Li X, Peng X, Yang S, Wei S, Fan Q, Liu J,
Yang L and Li H: Targeting tumor innervation: Premises, promises,
and challenges. Cell Death Discov. 8:1312022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang Y, Ye WL, Zhang RN, He XS, Wang JR,
Liu YX, Wang Y, Yang XM, Zhang YJ and Gan WJ: The role of TGF-β
signaling pathways in cancer and its potential as a therapeutic
target. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021:66752082021.
|
|
41
|
Jiang C, Zhang N, Hu X and Wang H:
Tumor-associated exosomes promote lung cancer metastasis through
multiple mechanisms. Mol Cancer. 20:1172021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang J, Xu J, Wang W, Zhang B, Yu X and
Shi S: Epigenetic regulation in the tumor microenvironment:
Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 8:2102023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yu W, Hua Y, Qiu H, Hao J, Zou K, Li Z, Hu
S, Guo P, Chen M, Sui S, et al: PD-L1 promotes tumor growth and
progression by activating WIP and β-catenin signaling pathways and
predicts poor prognosis in lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 11:5062020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Xiao K, Zhang S, Peng Q, Du Y, Yao X, Ng
II and Tang H: PD-L1 protects tumor-associated dendritic cells from
ferroptosis during immunogenic chemotherapy. Cell Rep.
43:1148682024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shi AP, Tang XY, Xiong YL, Zheng KF, Liu
YJ, Shi XG, Lv Y, Jiang T, Ma N and Zhao JB: Immune checkpoint LAG3
and its ligand FGL1 in cancer. Front Immunol. 12:7850912021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Villarroel-Espindola F, Yu X, Datar I,
Mani N, Sanmamed M, Velcheti V, Syrigos K, Toki M, Zhao H, Chen L,
et al: Spatially resolved and quantitative analysis of VISTA/PD-1H
as a novel immunotherapy target in human Non-small cell lung
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 24:1562–1573. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
47
|
Wang S, Wang J, Chen Z, Luo J, Guo W, Sun
L and Lin L: Targeting M2-like tumor-associated macrophages is a
potential therapeutic approach to overcome antitumor drug
resistance. NPJ Precis Oncol. 8:312024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li Y, Zhao L and Li XF: Hypoxia and the
tumor microenvironment. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
20:153303382110363042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zaarour RF, Azakir B, Hajam EY, Nawafleh
H, Zeinelabdin NA, Engelsen AST, Thiery J, Jamora C and Chouaib S:
Role of Hypoxia-mediated autophagy in tumor cell death and
survival. Cancers (Basel). 13:5332021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sasidharan Nair V, Saleh R, Toor SM,
Cyprian FS and Elkord E: Metabolic reprogramming of T regulatory
cells in the hypoxic tumor microenvironment. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 70:2103–2121. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li X, Yan X, Wang Y, Kaur B, Han H and Yu
J: The Notch signaling pathway: A potential target for cancer
immunotherapy. J Hematol Oncol. 16:452023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Luo H, Liu L, Liu X, Xie Y, Huang X, Yang
M, Shao C and Li D: Interleukin-33 (IL-33) promotes DNA
damage-resistance in lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 16:2742025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Boo SH and Kim YK: The emerging role of
RNA modifications in the regulation of mRNA stability. Exp Mol Med.
52:400–408. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Guo Y, Xie Y and Luo Y: The role of Long
Non-coding RNAs in the tumor immune microenvironment. Front
Immunol. 13:8510042022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jiang J, Lu Y, Zhang F, Huang J, Ren XL
and Zhang R: The emerging roles of long noncoding RNAs as hallmarks
of lung cancer. Front Oncol. 11:7615822021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Entezari M, Ghanbarirad M, Taheriazam A,
Sadrkhanloo M, Zabolian A, Goharrizi MASB, Hushmandi K, Aref AR,
Ashrafizadeh M, Zarrabi A, et al: Long non-coding RNAs and exosomal
lncRNAs: Potential functions in lung cancer progression, drug
resistance and tumor microenvironment remodeling. Biomed
Pharmacother. 150:1129632022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Tian Z, Cen L, Wei F, Dong J, Huang Y, Han
Y, Wang Z, Deng J and Jiang Y: EGFR mutations in non-small cell
lung cancer: Classification, characteristics and resistance to
third-generation EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (Review). Oncol
Lett. 30:3752025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Parente P, Parcesepe P, Covelli C,
Olivieri N, Remo A, Pancione M, Latiano TP, Graziano P, Maiello E
and Giordano G: Crosstalk between the tumor microenvironment and
immune system in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Potential
targets for new therapeutic approaches. Gastroenterol Res Pract.
2018:75306192018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Reichel D, Tripathi M and Perez JM:
Biological effects of nanoparticles on macrophage polarization in
the tumor microenvironment. Nanotheranostics. 3:66–88. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Coelho MA, Strauss ME, Watterson A, Cooper
S, Bhosle S, Illuzzi G, Karakoc E, Dinçer C, Vieira SF, Sharma M,
et al: Base editing screens define the genetic landscape of cancer
drug resistance mechanisms. Nature Genetics. 56:2479–2492. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wen Y, Zhu Y, Zhang C, Yang X, Gao Y, Li
M, Yang H, Liu T and Tang H: Chronic inflammation, cancer
development and immunotherapy. Front Pharmacol. 13:10401632022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Qian FF and Han BH: Mechanisms of
resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors and strategies to
reverse drug resistance in lung cancer. Chin Med J (Engl).
133:2444–2455. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Bagchi S, Yuan R and Engleman EG: Immune
checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of cancer: Clinical impact
and mechanisms of response and resistance. Annu Rev Pathol.
16:223–249. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Zhang M and Zhang B: Extracellular matrix
stiffness: Mechanisms in tumor progression and therapeutic
potential in cancer. Exp Hematol Oncol. 14:542025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Benvenuto M and Focaccetti C: Tumor
microenvironment: Cellular interaction and metabolic adaptations.
Int J Mol Sci. 25:36422024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Utsumi T, Mizuta H, Seto Y, Uchibori K,
Nishio M, Okamoto I and Katayama R: AXL-Mediated drug resistance in
ALK-rearranged NSCLC enhanced by GAS6 from macrophages and MMP11
positive fibroblasts. Cancer Sci. 116:1034–1047. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Peyraud F, Guégan JP, Rey C, Lara O, Odin
O, Del Castillo M, Vanhersecke L, Coindre JM, Clot E, Brunet M, et
al: Spatially resolved transcriptomics reveal the determinants of
primary resistance to immunotherapy in NSCLC with mature tertiary
lymphoid structures. Cell Rep Med. 6:1019342025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Nishinakamura H, Shinya S, Irie T,
Sakihama S, Naito T, Watanabe K, Sugiyama D, Tamiya M, Yoshida T,
Hase T, et al: Coactivation of innate immune suppressive cells
induces acquired resistance against combined TLR agonism and PD-1
blockade. Sci Transl Med. 17:adk31602025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Gandhi L, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S,
Esteban E, Felip E, De Angelis F, Domine M, Clingan P, Hochmair MJ,
Powell SF, et al: Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic
non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 378:2078–2092. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Cheng M and Hu S: Lung-resident γδ T cells
and their roles in lung diseases. Immunology. 51:375–384. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Subhi-Issa N, Tovar Manzano D, Pereiro
Rodriguez A, Sanchez Ramon S, Perez Segura P and Ocaña A: γδ T
cells: Game changers in immune cell therapy for cancer. Cancers
(Basel). 17:10632025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Lv J, Liu Z, Ren X, Song S, Zhang Y and
Wang Y: γδT cells, a key subset of T cell for cancer immunotherapy.
Front Immunol. 16:15621882025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Jin C, Lagoudas GK, Zhao C, Bullman S,
Bhutkar A, Hu B, Ameh S, Sandel D, Liang XS, Mazzilli S, et al:
Commensal microbiota promote lung cancer development via γδ T
cells. Cell. 176:998–1013.e16. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Dhodapkar MV and Dhodapkar KM:
Tissue-resident memory-like T cells in tumor immunity: Clinical
implications. Semin Immunol. 49:1014152020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hofmann M, Thimme R and Schamel WW: PD-1
and LAG-3: Synergistic fostering of T cell exhaustion. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 9:2912024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ducimetière L, Vermeer M and Tugues S: The
interplay between innate lymphoid cells and the tumor
microenvironment. Front Immunol. 10:28952019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Yuan X, Rasul F, Nashan B and Sun C:
Innate lymphoid cells and cancer: Role in tumor progression and
inhibition. Eur J Immunol. 51:2188–2205. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Ebid N, Sharaky M, Elkhoely A, El Morsy EM
and Saad SY: Cross-talk signaling between non-small cell lung
cancer cell lines and fibroblasts attenuates the cytotoxic effect
of cisplatin. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 39:e702012025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zhang Q, Luo Y, Qian B, Cao X, Xu C, Guo
K, Wan R, Jiang Y, Wang T, Mei Z, et al: A systematic pan-cancer
analysis identifies LDHA as a novel predictor for immunological,
prognostic, and immunotherapy resistance. Aging (Albany NY).
16:8000–8018. 2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Wang Z, Yan N, Sheng H, Xiao Y, Sun J and
Cao C: Single-cell transcriptomic analysis reveals an
immunosuppressive network between POSTN CAFs and ACKR1 ECs in
TKI-resistant lung cancer. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 21:65–78.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
81
|
Wang Y, Meraz IM, Qudratullah M, Kotagiri
S, Han Y, Xi Y, Wang J and Lissanu Y: SMARCA4 mutation induces
tumor cell-intrinsic defects in enhancer landscape and resistance
to immunotherapy. bioRxiv. Jun 22–2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Huang H, Zhu X, Yu Y, Li Z, Yang Y, Xia L
and Lu S: EGFR mutations induce the suppression of CD8+ T cell and
anti-PD-1 resistance via ERK1/2-p90RSK-TGF-β axis in non-small cell
lung cancer. J Transl Med. 22:6532024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Kobayashi N, Katakura S, Fukuda N,
Somekawa K, Kaneko A and Kaneko T: The impact of bevacizumab and
miR200c on EMT and EGFR-TKI resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer
organoids. Genes (Basel). 15:16242024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Tan J, Zhu L, Shi J, Zhang J, Kuang J, Guo
Q, Zhu X, Chen Y, Zhou C and Gao X: Evaluation of drug resistance
for EGFR-TKIs in lung cancer via multicellular lung-on-a-chip. Eur
J Pharm Sci. 199:1068052024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Pan X, Qian H, Sun Z, Yi Q, Liu Y, Lan G,
Chen J and Wang G: Investigating the role of disulfidptosis related
genes in radiotherapy resistance of lung adenocarcinoma. Front Med
(Lausanne). 11:14730802024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Han R, Guo H, Shi J, Zhao S, Jia Y, Liu X,
Liu Y, Cheng L, Zhao C, Li X and Zhou C: Osimertinib in combination
with anti-angiogenesis therapy presents a promising option for
osimertinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Med.
22:1742024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Shen A, Sun Y, Wang G, Meng X, Ren X, Wan
Q, Lv Q, Wang X, Ni J, Li M, et al: An adaptable nanoprobe
integrated with quantitative T1-Mapping MRI for accurate
differential diagnosis of Multidrug-resistant lung cancer. Adv
Healthc Mater. 12:e23006842023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Lu J, Li J, Lin Z, Li H, Lou L, Ding W,
Ouyang S, Wu Y, Wen Y, Chen X, et al: Reprogramming of TAMs via the
STAT3/CD47-SIRPα axis promotes acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs in
lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 564:2162052023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Yuan Y: Spatial heterogeneity in the tumor
microenvironment. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 6:a0265832016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Wang Y, Liu B, Min Q, Yang X, Yan S, Ma Y,
Li S, Fan J, Wang Y, Dong B, et al: Spatial transcriptomics
delineates molecular features and cellular plasticity in lung
adenocarcinoma progression. Cell Discovery. 9:962023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zhang JT, Zhang J, Wang SR, Yan LX, Qin J,
Yin K, Chu XP, Wang MM, Hong HZ, Lv ZY, et al: Spatial
downregulation of CD74 signatures may drive invasive component
development in part-solid lung adenocarcinoma. iScience.
26:1076992023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhang J, Song C, Tian Y and Yang X:
Single-cell RNA sequencing in lung cancer: Revealing phenotype
shaping of stromal cells in the microenvironment. Front Immunol.
12:8020802021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Joo MS, Pyo KH, Chung JM and Cho BC:
Artificial intelligence-based non-small cell lung cancer
transcriptome RNA-sequence analysis technology selection guide.
Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 11:10819502023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Xie L, Xie D, Du Z, Xue S, Wang K, Yu X,
Liu X, Peng Q and Fang C: A novel therapeutic outlook:
Classification, applications and challenges of inhalable
micron/nanoparticle drug delivery systems in lung cancer (Review).
Int J Oncol. 64:382024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Hu M and Huang L: Strategies targeting
tumor immune and stromal microenvironment and their clinical
relevance. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 183:1141372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Qian W, Zhao M, Wang R and Li H:
Fibrinogen-like protein 1 (FGL1): The next immune checkpoint
target. J Hematol Oncol. 14:1472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Wang J, Sanmamed MF, Datar I, Su TT, Ji L,
Sun J, Chen L, Chen Y, Zhu G, Yin W, et al: Fibrinogen-like Protein
1 Is a Major Immune Inhibitory Ligand of LAG-3. Cell.
176:334–347.e12. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Miao L, Wang Y, Lin CM, Xiong Y, Chen N,
Zhang L, Kim WY and Huang L: Nanoparticle modulation of the tumor
microenvironment enhances therapeutic efficacy of cisplatin. J
Control Release. 217:27–41. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Runa F, Hamalian S, Meade K, Shisgal P,
Gray PC and Kelber JA: Tumor microenvironment heterogeneity:
Challenges and opportunities. Curr Mol Biol Rep. 3:218–229. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Guan XY, Guan XL and Jiao ZY: Improving
therapeutic resistance: Beginning with targeting the tumor
microenvironment. J Chemother. 34:492–516. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Lu J and Ramirez RA: The role of
checkpoint inhibition in Non-small cell lung cancer. Ochsner J.
17:379–387. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Reck M, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG,
Hui R, Csőszi T, Fülöp A, Gottfried M, Peled N, Tafreshi A, Cuffe
S, et al: Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive
Non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 375:1823–1833. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Hellmann MD, Paz-Ares L, Bernabe Caro R,
Zurawski B, Kim SW, Carcereny Costa E, Park K, Alexandru A,
Lupinacci L, de la Mora Jimenez E, et al: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab
in advanced Non-Small-Cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med.
381:2020–2031. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Forde PM, Chaft JE, Smith KN, Anagnostou
V, Cottrell TR, Hellmann MD, Zahurak M, Yang SC, Jones DR,
Broderick S, et al: Neoadjuvant PD-1 blockade in resectable lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 378:1976–1986. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Niemeijer AN, Leung D, Huisman MC, Bahce
I, Hoekstra OS, van Dongen GAMS, Boellaard R, Du S, Hayes W, Smith
R, et al: Whole body PD-1 and PD-L1 positron emission tomography in
patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Commun. 9:46642018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Zhang Y, Zhou H and Zhang L: Which is the
optimal immunotherapy for advanced squamous non-small-cell lung
cancer in combination with chemotherapy: Anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1? J
Immunother Cancer. 6:1352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Bozorgmehr F, Hommertgen A, Krisam J,
Lasitschka F, Kuon J, Maenz M, Huber PE, König L, Kieser M, Debus
J, et al: Fostering efficacy of anti-PD-1-treatment: Nivolumab plus
radiotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer-study protocol
of the FORCE trial. BMC Cancer. 19:10742019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Zhao S, Ren S, Jiang T, Zhu B, Li X, Zhao
C, Jia Y, Shi J, Zhang L, Liu X, et al: Low-Dose apatinib optimizes
tumor microenvironment and potentiates antitumor effect of
PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 7:630–643.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Leighl NB, Redman MW, Rizvi N, Hirsch FR,
Mack PC, Schwartz LH, Wade JL, Irvin WJ, Reddy SC, Crawford J, et
al: Phase II study of durvalumab plus tremelimumab as therapy for
patients with previously treated anti-PD-1/PD-L1 resistant stage IV
squamous cell lung cancer (Lung-MAP substudy S1400F, NCT03373760).
J Immunother Cancer. 9:e0029732021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Ott PA, Hu-Lieskovan S, Chmielowski B,
Govindan R, Naing A, Bhardwaj N, Margolin K, Awad MM, Hellmann MD,
Lin JJ, et al: A Phase Ib Trial of Personalized Neoantigen Therapy
Plus Anti-PD-1 in Patients with Advanced Melanoma, Non-small Cell
Lung Cancer, or Bladder Cancer. Cell. 183:347–362.e24. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Awad MM, Govindan R, Balogh KN, Spigel DR,
Garon EB, Bushway ME, Poran A, Sheen JH, Kohler V, Esaulova E, et
al: Personalized neoantigen vaccine NEO-PV-01 with chemotherapy and
anti-PD-1 as first-line treatment for non-squamous non-small cell
lung cancer. Cancer Cell. 40:1010–1026.e11. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Li JH, Tian F, Qiu CS, Chen WJ, Xu DX,
Yang LQ and Li RJ: Relevant studies on effect of Fuzheng Sanjie
recipe in regulating immune microenvironment remodeling of TAMs in
Lewis lung cancer mice. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 40:1161–1165.
2015.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Gao J, Bi L, Jiang YC, Yang Y, Li BY and
Chen WP: Effect of water extract of ginseng on biological
bechaviors of lung cancer A549 cells and the expression of F-actin
in Co-culture system of TAMs and A549 cells. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi
Jie He Za Zhi. 37:345–350. 2017.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Wen X, Wang Y, Su C, You Y, Jiang Z, Zhu D
and Fan Q: Integrating Multi-omics technologies with traditional
Chinese medicine to enhance cancer research and treatment. QJM. Apr
29–2025.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Li Y, Cao F, Li M, Li P, Yu Y, Xiang L, Xu
T, Lei J, Tai YY, Zhu J, et al: Hydroxychloroquine induced lung
cancer suppression by enhancing chemo-sensitization and promoting
the transition of M2-TAMs to M1-like macrophages. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 37:2592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Sarnaik AA, Hwu P, Mulé JJ and
Pilon-Thomas S: Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes: A new hope. Cancer
Cell. 42:1315–1318. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Stachowiak M, Becker WJ, Olkhanud PB,
Moreno PA, Markowicz S, Berzofsky JA and Sarnowska E: Cancer cells
accelerate exhaustion of persistently activated mouse CD4+ T cells.
Oncoimmunology. 14:25213922025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
118
|
Stachowiak M, Becker WJ, Olkhanud PB,
Moreno PA, Markowicz S, Berzofsky JA and Sarnowska E: Mechanisms
underlying immunosuppression by regulatory cells. Front Immunol.
15:13281932024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Mastelic-Gavillet B, Navarro Rodrigo B,
Décombaz L, Wang H, Ercolano G, Ahmed R, Lozano LE, Ianaro A, Derré
L, Valerio M, et al: Adenosine mediates functional and metabolic
suppression of peripheral and tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells. J
Immunother Cancer. 7:2572019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
120
|
Sumitomo R, Huang CL, Fujita M, Cho H and
Date H: Differential expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 is associated
with the tumor microenvironment of TILs and M2 TAMs and tumor
differentiation in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep.
47:732022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
121
|
Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Ding Y, Fang Y, Wang P,
Chu W, Jin Z, Yang X, Wang J, Lou J and Qian Q: Phase I clinical
trial of EGFR-specific CAR-T cells generated by the piggyBac
transposon system in advanced relapsed/refractory non-small cell
lung cancer patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 147:3725–3734. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Sterner RC and Sterner RM: CAR-T cell
therapy: Current limitations and potential strategies. Blood Cancer
J. 11:692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Labanieh L and Mackall CL: CAR immune
cells: Design principles, resistance and the next generation.
Nature. 614:635–648. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Kong Q, Zhu H, Gong W, Deng X, Liu B and
Dong J: Modified Bushen Yiqi formula enhances antitumor immunity by
reducing the chemotactic recruitment of M2-TAMs and PMN-MDSCs in
Lewis lung cancer-bearing mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 319:1171832024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Chen C, Hou J, Yu S, Li W, Wang X, Sun H,
Qin T, Claret FX, Guo H and Liu Z: Role of cancer-associated
fibroblasts in the resistance to antitumor therapy, and their
potential therapeutic mechanisms in non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncol Lett. 21:4132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Feng H, Cao B, Peng X and Wei Q:
Cancer-associated fibroblasts strengthen cell proliferation and
EGFR TKIs resistance through aryl hydrocarbon receptor dependent
signals in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 22:7642022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Li F, Zhao S, Cui Y, Guo T, Qiang J, Xie
Q, Yu W, Guo W, Deng W, Gu C and Wu T: α1,6-Fucosyltransferase
(FUT8) regulates the cancer-promoting capacity of cancer-associated
fibroblasts (CAFs) by modifying EGFR core fucosylation (CF) in
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Am J Cancer Res. 10:816–837.
2020.
|
|
128
|
Yang F, Yan Y, Yang Y, Hong X, Wang M,
Yang Z, Liu B and Ye L: MiR-210 in exosomes derived from CAFs
promotes non-small cell lung cancer migration and invasion through
PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell Signal. 73:1096752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Chen Y, Zhu S, Yang L, Lu Y and Ye X:
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) regulate lung cancer malignant
progression by transferring SERPINE2 (PN1) via exosomes. Curr Mol
Med. 25:1025–1037. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Sun Y, Ying K, Sun J, Wang Y, Qiu L, Ji M,
Sun L and Chen J: PRRX1-OLR1 axis supports CAFs-mediated lung
cancer progression and immune suppression. Cancer Cell Int.
24:2472024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Wang H, Wu C, Wan S, Zhang H, Zhou S and
Liu G: Shikonin attenuates lung cancer cell adhesion to
extracellular matrix and metastasis by inhibiting integrin β1
expression and the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Toxicology.
308:104–112. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Wang H, Zhu Y, Zhao M, Wu C, Zhang P, Tang
L, Zhang H, Chen X, Yang Y and Liu G: miRNA-29c suppresses lung
cancer cell adhesion to extracellular matrix and metastasis by
targeting integrin β1 and matrix metalloproteinase2 (MMP2). PLoS
One. 8:e701922013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Bi HX, Shi HB, Zhang T and Cui G: PRDM14
promotes the migration of human non-small cell lung cancer through
extracellular matrix degradation in vitro. Chin Med J (Engl).
128:373–377. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Zhang T, Cui G, Yao YL, Guo Y, Wang QC, Li
XN and Feng WM: Inhibition of nonsmall cell lung cancer cell
migration by protein arginine methyltransferase 1-small hairpin RNA
through inhibiting Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, extracellular
matrix degradation, and src phosphorylation in vitro. Chin Med J
(Engl). 128:1202–1208. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Wang Y, Zhang T, Guo L, Ren T and Yang Y:
Stromal extracellular matrix is a microenvironmental cue promoting
resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer cells.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 106:96–106. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Shie WY, Chu PH, Kuo MY, Chen HW, Lin MT,
Su XJ, Hong YL and Chou HE: Acidosis promotes the metastatic
colonization of lung cancer via remodeling of the extracellular
matrix and vasculogenic mimicry. Int J Oncol. 63:1362023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Peláez R, Ochoa R, Pariente A,
Villanueva-Martínez Á, Pérez-Sala Á and Larráyoz IM: Sterculic acid
alters adhesion molecules expression and extracellular matrix
compounds to regulate migration of lung cancer cells. Cancers
(Basel). 13:43702021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Abdel-Hafez SM, Gallei M, Wagner S and
Schneider M: Inhalable nano-structured microparticles for
extracellular matrix modulation as a potential delivery system for
lung cancer. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 204:1145122024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Frezzetti D, Gallo M, Maiello MR,
D'Alessio A, Esposito C, Chicchinelli N, Normanno N and De Luca A:
VEGF as a potential target in lung cancer. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 21:959–966. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Villaruz LC and Socinski MA: The role of
Anti-angiogenesis in non-small-cell lung cancer: An update. Curr
Oncol Rep. 17:262015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Socinski MA, Nishio M, Jotte RM, Cappuzzo
F, Orlandi F, Stroyakovskiy D, Nogami N, Rodríguez-Abreu D,
Moro-Sibilot D, Thomas CA, et al: IMpower150 final overall survival
analyses for atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and chemotherapy in
First-line metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol.
16:1909–1924. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Qiang H, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Li J, Zhang L,
Du H, Ling X, Cao S, Zhou Y, Zhong R and Zhong H: Efficacy of
first-line chemotherapy combined with immunotherapy or
anti-angiogenic therapy in advanced KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung
cancer. Transl Oncol. 53:1023172025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Cai Q, Hu K, Dong S, Li X, Hu S, Deng W
and Ou W: Tumor cavitation in patients with non-small-cell lung
cancer receiving anti-angiogenic therapy with apatinib. Transl Lung
Cancer Res. 13:1708–1717. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Zhang X, Sun Q, Chen R, Zhao M, Cai F, Cui
Z and Jiang H: Efficacy and safety of combining anti-angiogenic
therapy, radiotherapy, and PD-1 inhibitors in patients with driver
gene-negative non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases: A
retrospective study. BMC Cancer. 24:14922024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Song JQ, Wang X, Zeng ZM, Liang PA, Zhong
CY and Liu AW: Efficacy of PD-1 Inhibitors combined with
anti-angiogenic therapy in driver gene mutation negative
non-small-cell lung cancer with brain metastases. Discov Med.
35:321–331. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Itatani Y, Kawada K, Yamamoto T and Sakai
Y: Resistance to Anti-angiogenic therapy in Cancer-alterations to
Anti-VEGF pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 19:12322018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Bergers G and Hanahan D: Modes of
resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:592–603.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Wu Y, Yan Y, Guo Y, Niu M, Zhou B, Zhang
J, Zhou P, Chu Q, Mei Q, Yi M and Wu K: Anti-TGF-β/PD-L1 bispecific
antibody synergizes with radiotherapy to enhance antitumor immunity
and mitigate radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Hematol Oncol.
18:242025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Huehls AM, Coupet TA and Sentman CL:
Bispecific T-cell engagers for cancer immunotherapy. Immunol Cell
Biol. 93:290–296. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Si Y, Pei X, Wang X, Han Q, Xu C and Zhang
B: An Anti-EGFR/anti-HER2 bispecific antibody with enhanced
antitumor activity against acquired Gefitinib-resistant NSCLC
cells. Protein Pept Lett. 28:1290–1297. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|