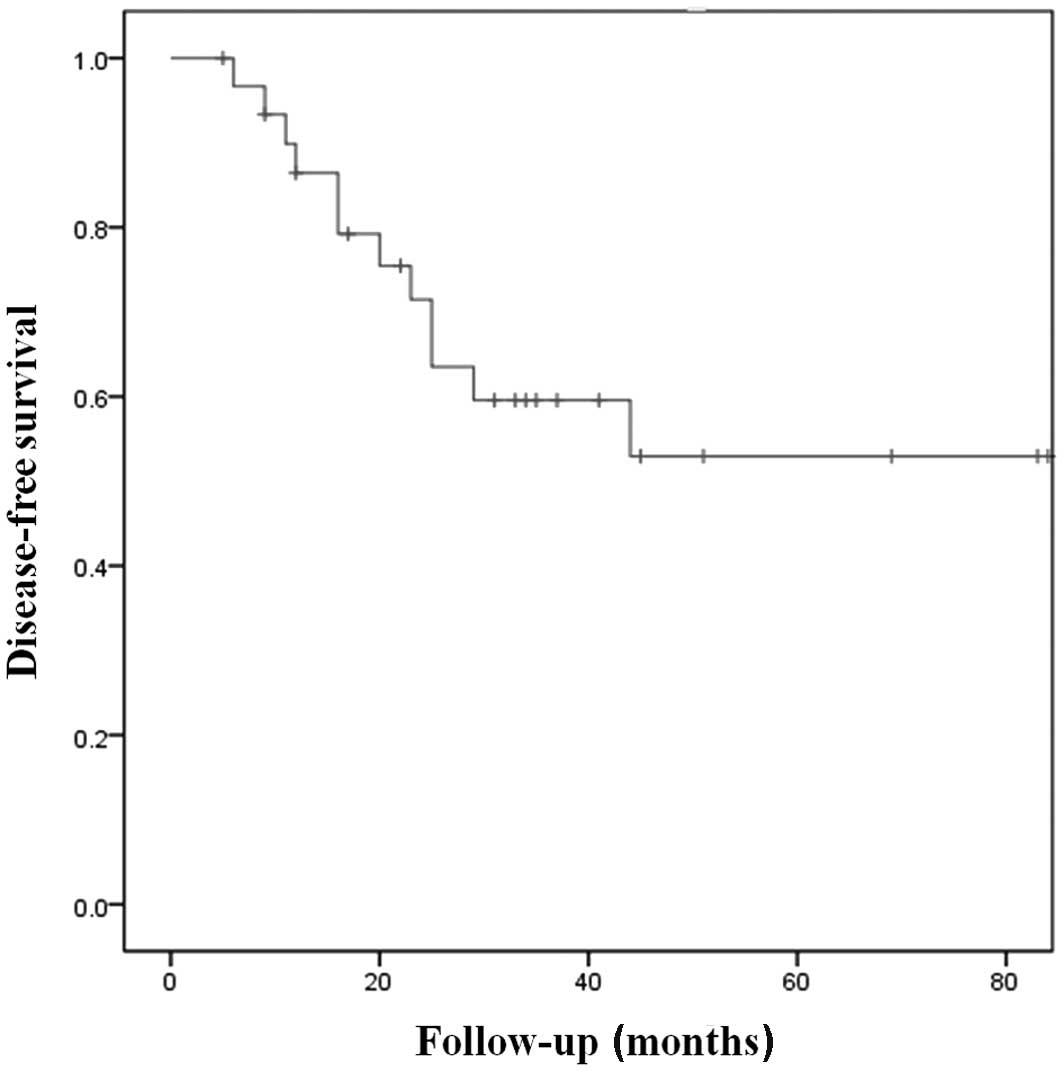
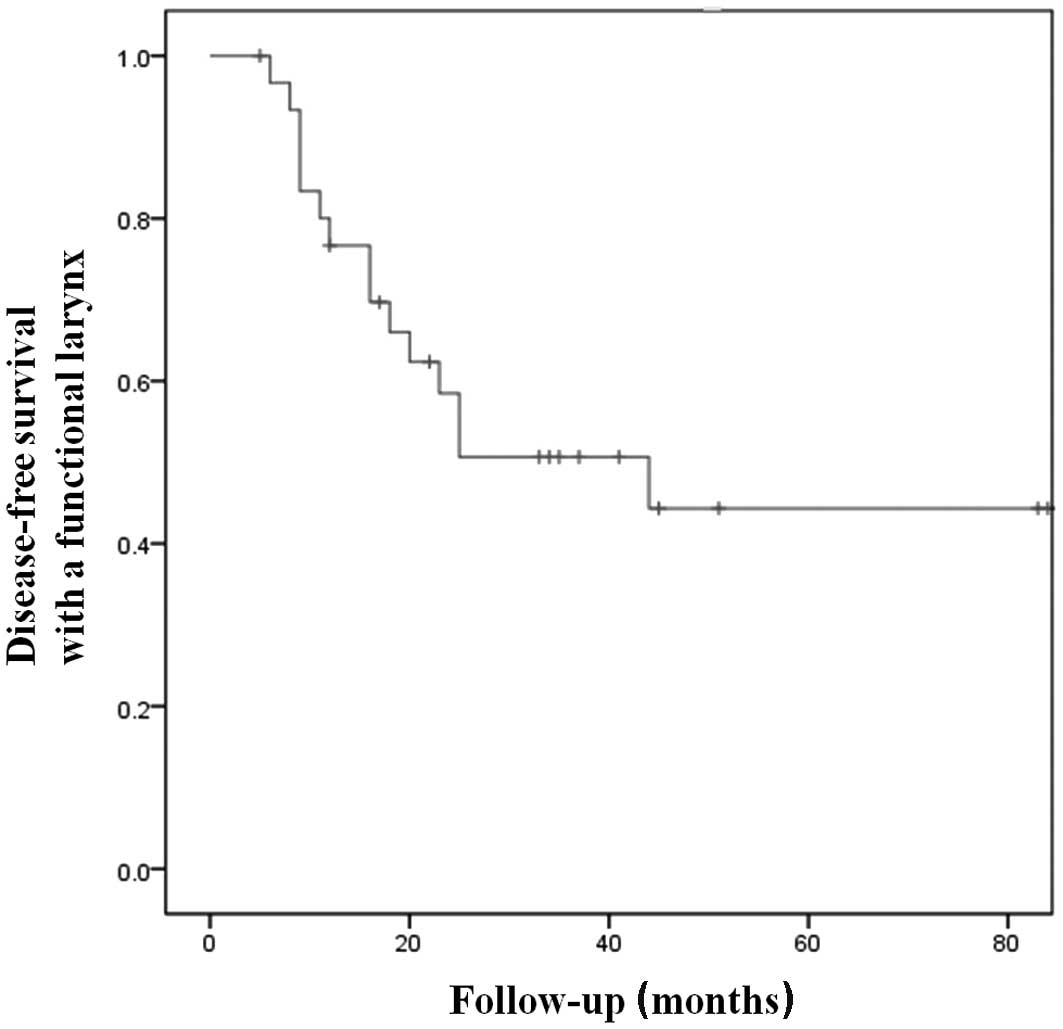
|
1.
|
Kim JG, Sohn SK, Kim DH, et al: Phase II
study of concurrent chemoradiotherapy with capecitabine and
cisplatin in patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma
of the head and neck. Br J Cancer. 93:1117–1121. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Brizel DM, Albers ME, Fisher SR, et al:
Hyperfractionated irradiation with or without concurrent
chemotherapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer. N Engl J
Med. 338:1798–1804. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Pignon JP, Bourhis J, Domenge C and
Designé L: Chemotherapy added to locoregional treatment for head
and neck squamous-cell carcinoma: three meta-analyses of updated
individual data. MACH-NC Collaborative Group. Meta-Analysis of
Chemotherapy on Head and Neck Cancer. Lancet. 355:949–955. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Forastiere AA, Goepfert H, Maor M, et al:
Concurrent chemotherapy and radiotherapy for organ preservation in
advanced laryngeal cancer. N Engl J Med. 349:2091–2098. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Rodriguez CP, Adelstein DJ, Rybicki LA, et
al: Clinical predictors of larynx preservation after multiagent
concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Head Neck. 30:1535–1542. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Clavel M, Vermorken JB, Cognetti F, et al:
Randomized comparison of cisplatin, methotrexate, bleomycin and
vincristine (CABO) versus cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil (CF) versus
cisplatin (C) in recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of
the head and neck. A phase III study of the EORTC Head and Neck
Cancer Cooperative Group. Ann Oncol. 5:521–526. 1994.
|
|
7.
|
Jacobs C: Head and neck cancer in 1994: a
change in the standard of care. J Natl Cancer Inst. 86:250–252.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Blum JL, Jones SE, Buzdar AU, et al:
Multicenter phase II study of capecitabine in paclitaxel-refractory
metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 17:485–493. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Hoff PM, Ansari R, Batist G, et al:
Comparison of oral capecitabine versus intravenous fluorouracil
plus leucovorin as first-line treatment in 605 patients with
metastatic colorectal cancer: results of a randomized phase III
study. J Clin Oncol. 19:2282–2292. 2001.
|
|
10.
|
Van Cutsem E, Twelves C, Cassidy J, et al:
Oral capecitabine compared with intravenous fluorouracil plus
leucovorin in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: results
of a large phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 19:4097–4106. 2001.
|
|
11.
|
World Health Organization: WHO Handbook
for Reporting Results of Cancer Treatment: World Health
Organization. Geneva, Switzerland: 1979
|
|
12.
|
Bussu F, Paludetti G, Almadori G, et al:
Comparison of total laryngectomy with surgical (cricohyoidopexy)
and nonsurgical organ-preservation modalities in advanced laryngeal
squamous cell carcinomas: a multicenter retrospective analysis.
Head Neck. 35:554–561. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Induction chemotherapy plus radiation
compared with surgery plus radiation in patients with advanced
laryngeal cancer. The Department of Veterans Affairs Laryngeal
Cancer Study Group. N Engl J Med. 324:1685–1690. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Lefebvre JL, Chevalier D, Luboinski B,
Kirkpatrick A, Collette L and Sahmoud T: Larynx preservation in
pyriform sinus cancer: preliminary results of a European
Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer phase III trial.
EORTC Head and Neck Cancer Cooperative Group. J Natl Cancer Inst.
88:890–899. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15.
|
Lefebvre JL, Rolland F, Tesselaar M, et
al: Phase 3 randomized trial on larynx preservation comparing
sequential vs. alternating chemotherapy and radiotherapy. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 101:142–152. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Veronesi A, Zagonel V, Tirelli U, et al:
High-dose versus low-dose cisplatin in advanced head and neck
squamous carcinoma: a randomized study. J Clin Oncol. 3:1105–1108.
1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Yoon TM, Lee JK, Cho JS, Lim SC and Chung
WK: Role of concurrent chemoradiation in laryngeal preservation for
supraglottic cancer. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 39:142–149.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Kubota A, Furukawa M, Hanamura H, Fujita Y
and Sugiyama M: Concurrent chemoradiotherapy for squamous cell
carcinoma of the oropharynx. Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho.
110:635–642. 2007.(In Japanese).
|
|
19.
|
Won YW, Park YH, Ahn MJ, Do IG, Ko YH and
Park K: A phase II study of combination chemotherapy with
capecitabine and cisplatin in patients with metastatic or recurrent
squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Ann Oncol.
22:417–423. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Pivot X, Chamorey E, Guardiola E, et al:
Phase I and pharmaco-kinetic study of the association of
capecitabine-cisplatin in head and neck cancer patients. Ann Oncol.
14:1578–1586. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Adelstein DJ, Li Y, Adams GL, et al: An
intergroup phase III comparison of standard radiation therapy and
two schedules of concurrent chemoradiotherapy in patients with
unresectable squamous cell head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol.
21:92–98. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Vokes EE, Kies MS, Haraf DJ, et al:
Concomitant chemoradio-therapy as primary therapy for
locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol.
18:1652–1661. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Schuller J, Cassidy J, Dumont E, et al:
Preferential activation of capecitabine in tumor following oral
administration to colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 45:291–297. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Sawada N, Ishikawa T, Sekiguchi F, Tanaka
Y and Ishitsuka H: X-ray irradiation induces thymidine
phosphorylase and enhances the efficacy of capecitabine (Xeloda) in
human cancer xenografts. Clin Cancer Res. 5:2948–2953.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Richard JM, Sancho-Garnier H, Pessey JJ,
et al: Randomized trial of induction chemotherapy in larynx
carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 34:224–228. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|