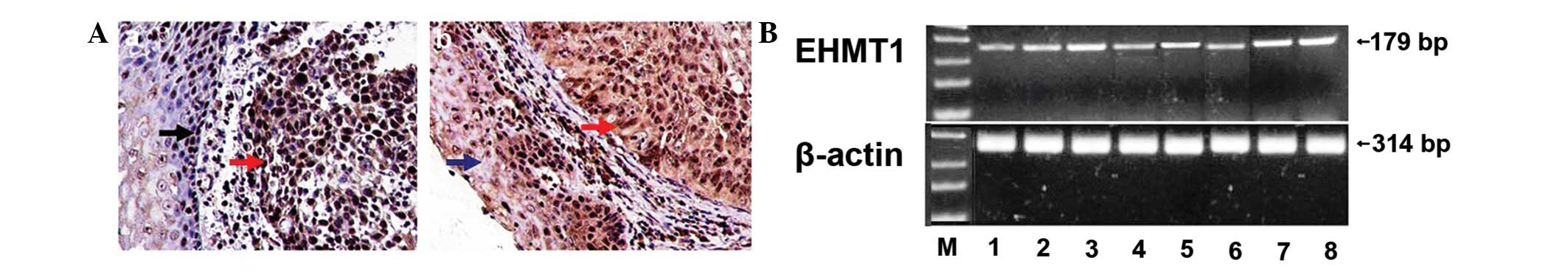
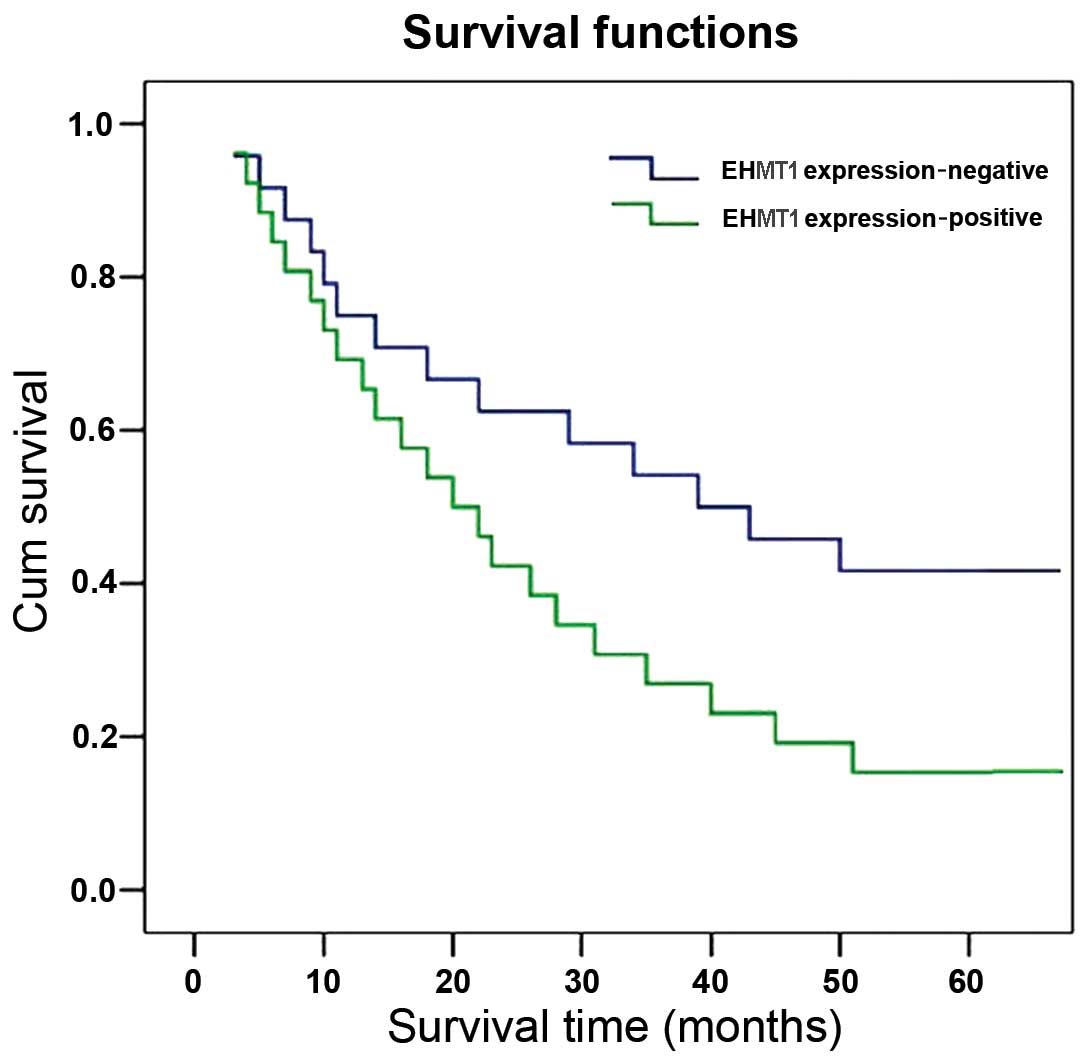
|
1.
|
Thallinger CM, Kiesewetter B, Raderer M
and Hejna M: Pre- and postoperative treatment modalities for
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 11:4609–4627.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Tachibana M, Ueda J, Fukuda M, Takeda N,
Ohta T, Iwanari H, Sakihama T, Kodama T, Hamakubo T and Shinkai Y:
Histone methyltransferases G9a and GLP form heteromeric complexes
and are both crucial for methylation of euchromatin at H3-K9. Genes
Dev. 19:815–826. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Collins R and Cheng X: A case study in
cross-talk: the histone lysine methyltransferases G9a and GLP.
Nucleic Acids Res. 38:3503–3511. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Chin HG, Esteve PO, Pradhan M, Benner J,
Patnaik D, Carey MF and Pradhan S: Automethylation of G9a and its
implication in wider substrate specificity and HP1 binding. Nucleic
Acids Res. 35:7313–7323. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Rathert P, Dhayalan A, Murakami M, Zhang
X, Tamas R, Jurkowska R, Komatsu Y, Shinkai Y, Cheng X and Jeltsch
A: Protein lysine methyltransferase G9a acts on non-histone
targets. Nat Chem Biol. 4:344–346. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Pless O, Kowenz-Leutz E, Knoblich M,
Lausen J, Beyermann M, Walsh MJ and Leutz A: G9a-mediated lysine
methylation alters the function of CCAAT/enhancer-binding
protein-beta. J Biol Chem. 283:26357–26363. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Fritsch L, Robin P, Mathieu JR, et al: A
subset of the histone H3 lysine 9 methyltransferases Suv39h1, G9a,
GLP, and SETDB1 participate in a multimeric complex. Mol Cell.
37:46–56. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Sampath SC, Marazzi I, Yap KL, Sampath SC,
Krutchinsky AN, Mecklenbrauker I, Viale A, Rudensky E, Zhou MM,
Chait BT and Tarakhovsky A: Methylation of a histone mimic within
the histone methyltransferase G9a regulates protein complex
assembly. Mol Cell. 27:596–608. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Lee SH, Kim J, Kim WH and Lee YM: Hypoxic
silencing of tumor suppressor RUNX3 by histone modification in
gastric cancer cells. Oncogene. 28:184–194. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Purcell DJ, Khalid O, Ou CY, et al:
Recruitment of coregulator G9a by Runx2 for selective enhancement
or suppression of transcription. J Cell Biochem. 113:2406–2414.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Purcell DJ, Jeong KW, Bittencourt D, et
al: A distinct mechanism for co-activator versus corepressor
function by histone methytransferase G9a in transcriptional
regulation. J Biol Chem. 286:41963–41971. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Bird A: Methylation talk between histones
and DNA. Science. 294:2113–2115. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Tamaru H, Zhang X, McMillen D, et al:
Trimethylated lysine 9 of histone H3 is a mark for DNA methylation
in Neurospora crassa. Nat Genet. 34:75–79. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Jackson JP, Lindroth AM, Cao X and
Jacobsen SE: Control of CpNpG DNA methylation by the KRYPTONITE
histone H3 methyltransferase. Nature. 416:556–560. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Ikegami K, Iwatani M, Suzuki M, et al:
Genome-wide and locus-specific DNA hypomethylation in G9a deficient
mouse embryonic stem cells. Gene Cells. 12:1–11. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Chen L, Li Z, Zwolinska AK, et al: MDM2
recruitment of lysine methyltransferases regulates p53
transcriptional output. EMBO J. 29:2538–2552. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Candelaria M, de la Cruz-Hernandez E,
Taja-Chayeb L, et al: DNA methylation-independent reversion of
gemcitabine resistance by hydralazine in cervical cancer cells.
PloS One. 7:e291812010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Ibrahim AE, Arends MJ, Silva AL, Wyllie
AH, Greger L, Ito Y, Vowler SL, Huang TH, Tavare S and Murrell A:
Sequential DNA methylation changes are associated with DNMT2B
over-expression in colorectal neoplastic progression. Gut.
60:499–508. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Schwartzman J, Mongoue-Tchokote S, Gibbs
A, et al: A DNA methylation microarray-based study identifies ERG
as a gene commonly methylated in prostate cancer. Epigenetics.
6:1248–1256. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Jelinek J, Gharibyan V, Estecio MR, et al:
Aberrant DNA methylation is associated with disease progression,
resistance to imatinib and shortened survival in chronic
myelogenous leukemia. PloS One. 6:e221102011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|