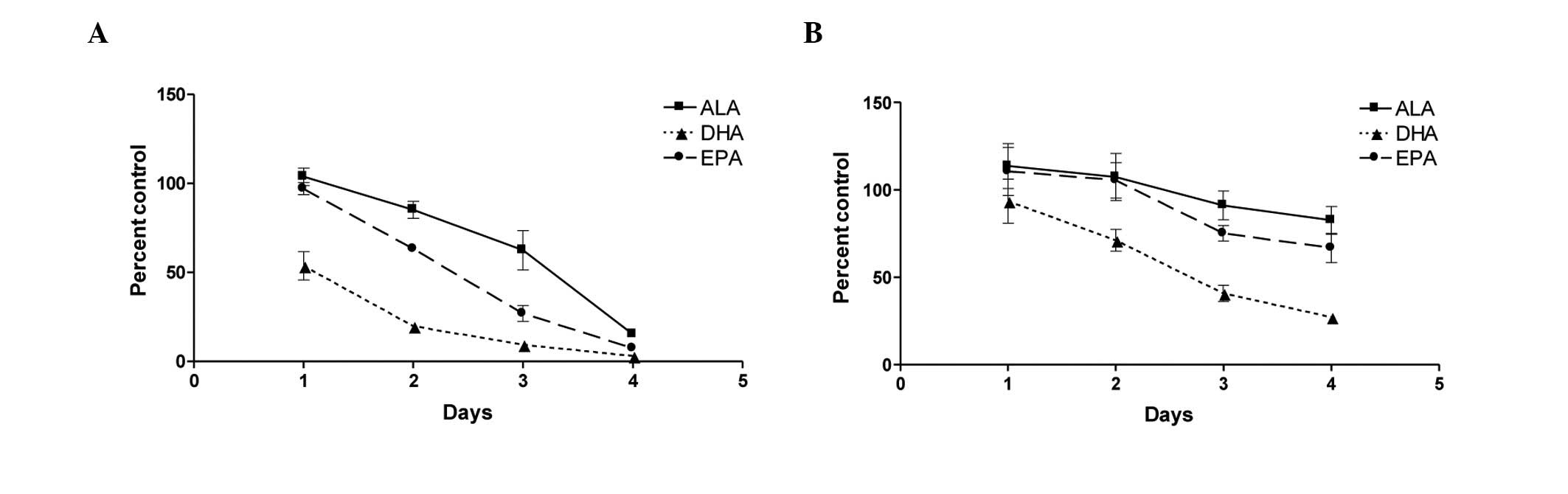
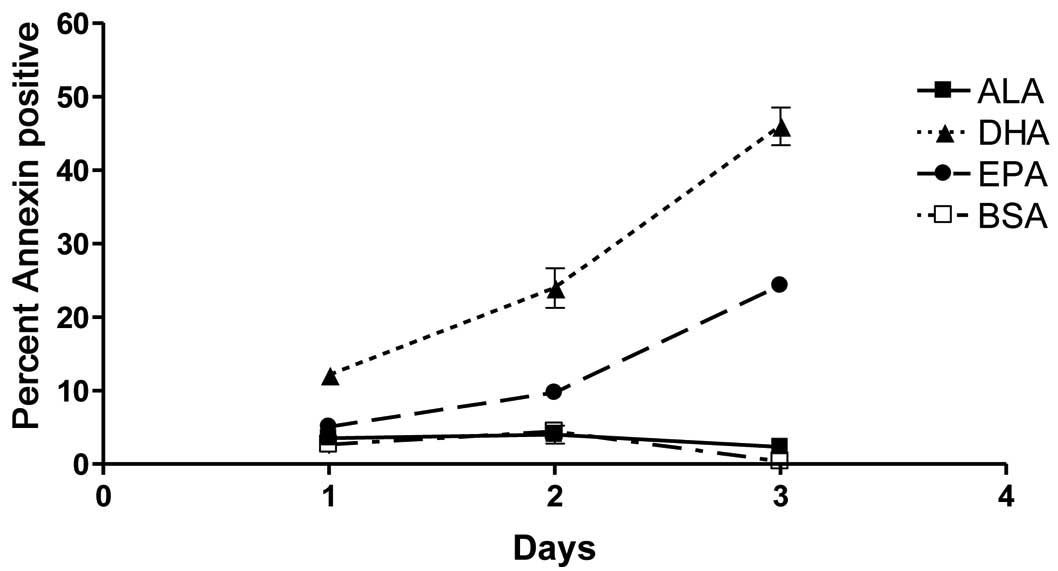
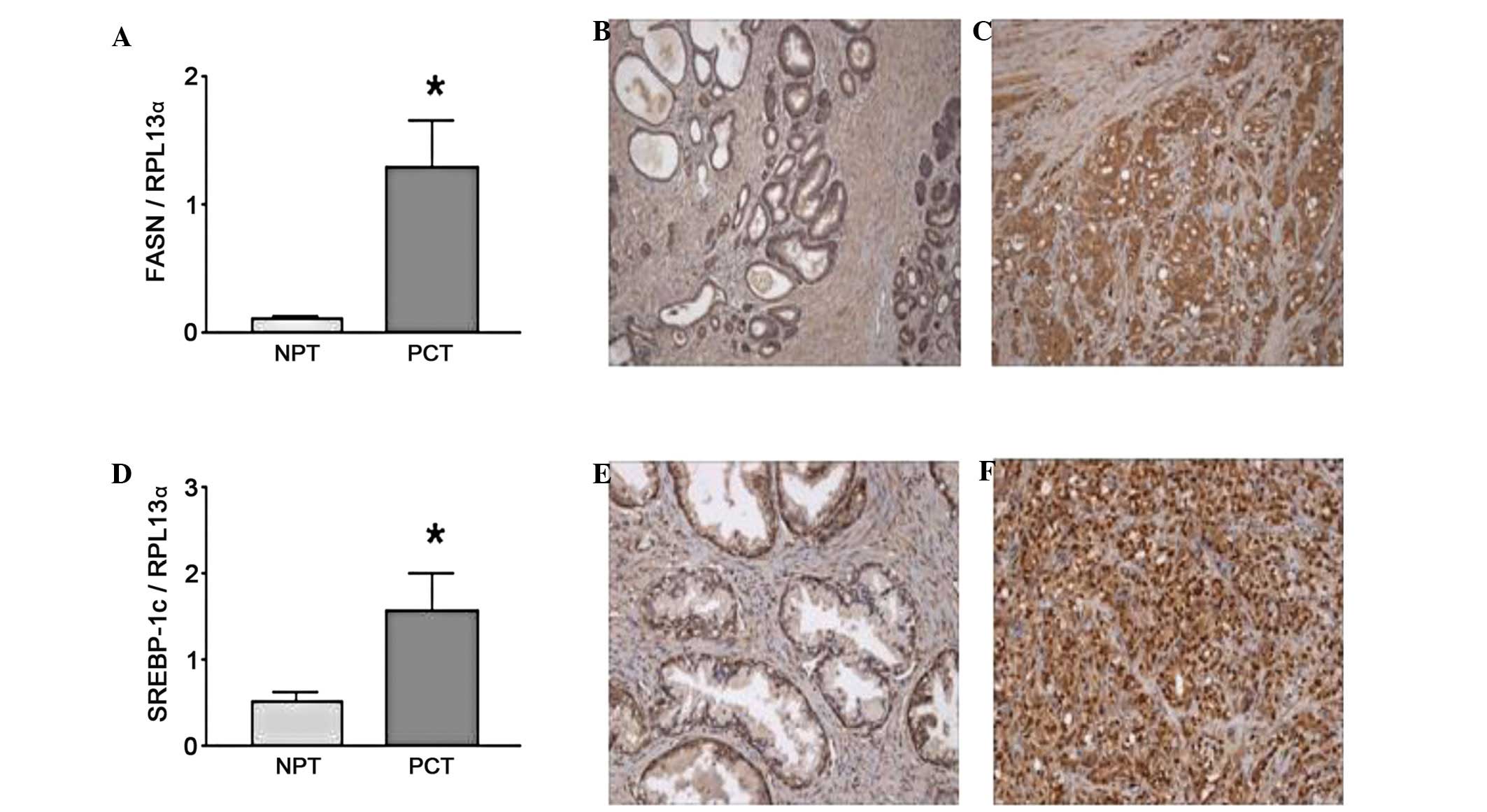
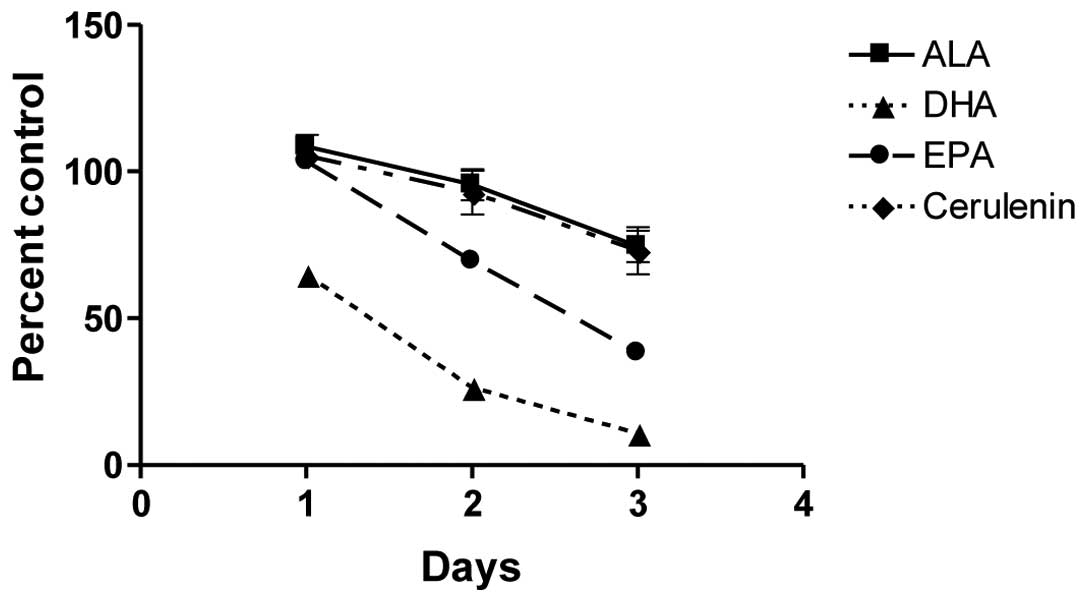
|
1.
|
Rambeaud JJ: Intermittent complete
androgen blockade in meta-static prostate cancer. Eur Urol.
35(Suppl 1): 32–36. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Harris KA and Reese DM: Treatment options
in hormone-refractory prostate cancer: current and future
approaches. Drugs. 61:2177–2192. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Chan JM, Gann PH and Giovannucci EL: Role
of diet in prostate cancer development and progression. J Clin
Oncol. 23:8152–8160. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
King IB, Kristal AR, Schaffer S,
Thornquist M and Goodman GE: Serum trans-fatty acids are associated
with risk of prostate cancer in beta-Carotene and Retinol Efficacy
Trial. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 14:988–992. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Haaland CM, Heaphy CM, Butler KS, Fischer
EG, Griffith JK and Bisoffi M: Differential gene expression in
tumor adjacent histologically normal prostatic tissue indicates
field cancerization. Int J Oncol. 35:537–546. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Baron A, Migita T, Tang D and Loda M:
Fatty acid synthase: a metabolic oncogene in prostate cancer? J
Cell Biochem. 91:47–53. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Di Nunzio M, van Deursen D, Verhoeven AJ
and Bordoni A: n-3 and n-6 Polyunsaturated fatty acids suppress
sterol regulatory element binding protein activity and increase
flow of non-esterified cholesterol in HepG2 cells. Br J Nutr.
103:161–167. 2010.
|
|
8.
|
Worgall TS, Sturley SL, Seo T, Osborne TF
and Deckelbaum RJ: Polyunsaturated fatty acids decrease expression
of promoters with sterol regulatory elements by decreasing levels
of mature sterol regulatory element-binding protein. J Biol Chem.
273:25537–25540. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Xu J, Nakamura MT, Cho HP and Clarke SD:
Sterol regulatory element binding protein-1 expression is
suppressed by dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids. A mechanism for
the coordinate suppression of lipogenic genes by polyunsaturated
fats. J Biol Chem. 274:23577–23583. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Nakatani T, Kim HJ, Kaburagi Y, Yasuda K
and Ezaki O: A low fish oil inhibits SREBP-1 proteolytic cascade,
while a high-fish-oil feeding decreases SREBP-1 mRNA in mice liver:
relationship to anti-obesity. J Lipid Res. 44:369–379. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Pizer ES, Pflug BR, Bova GS, Han WF, Udan
MS and Nelson JB: Increased fatty acid synthase as a therapeutic
target in androgen-independent prostate cancer progression.
Prostate. 47:102–110. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Pizer ES, Jackisch C, Wood FD, Pasternack
GR, Davidson NE and Kuhajda FP: Inhibition of fatty acid synthesis
induces programmed cell death in human breast cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 56:2745–2747. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Menendez JA and Lupu R: Fatty acid
synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nat
Rev Cancer. 7:763–777. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Neumann F: Pharmacology and clinical use
of antiandrogens: a short review. Ir J Med Sci. 151:61–70. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Gaillard-Moguilewsky M: Pharmacology of
antiandrogens and value of combining androgen suppression with
antiandrogen therapy. Urology. 37:5–12. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Feldman BJ and Feldman D: The development
of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 1:34–45.
2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Lin WW and Karin M: A cytokine-mediated
link between innate immunity, inflammation, and cancer. J Clin
Invest. 117:1175–1183. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Cansino Alcaide JR, Vera San Martin R,
Rodriguez de Bethencourt Codes F, Bouraoui Y, Rodriguez Berriguete
G, Oueslati R, Perez-Utrilla M, De la Pena Barthel J, Paniagua
Gomez-Alvarez R and Royuela Garcia M: Prostatic specific antigen
(PS), pro-inflammatory cytokines, and prostatic pathology (benign
prostatic hyperplasia and cancer). Relationship with malignancy.
Arch Esp Urol. 62:359–366. 2009.(In Spanish).
|
|
19.
|
Bouraoui Y, Ricote M, Garcia-Tunon I,
Rodriguez-Berriguete G, Touffehi M, Rais NB, Fraile B, Paniagua R,
Oueslati R and Royuela M: Pro-inflammatory cytokines and
prostate-specific antigen in hyperplasia and human prostate cancer.
Cancer Detect Prev. 32:23–32. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Lu Y, Cai Z, Xiao G, Keller ET, Mizokami
A, Yao Z, Roodman GD and Zhang J: Monocyte chemotactic protein-1
mediates prostate cancer-induced bone resorption. Cancer Res.
67:3646–3653. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Lu Y, Cai Z, Galson DL, Xiao G, Liu Y,
George DE, Melhem MF, Yao Z and Zhang J: Monocyte chemotactic
protein-1 (MCP-1) acts as a paracrine and autocrine factor for
prostate cancer growth and invasion. Prostate. 66:1311–1318. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Shi CL, Yu CH, Zhang Y, Zhao D, Chang XH
and Wang WH: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 modulates invasion
and apoptosis of PC-3M prostate cancer cells via regulating
expression of VEGF, MMP9 and caspase-3. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
12:555–559. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Hsieh TC and Chiao JW: Growth modulation
of human prostatic cancer cells by interleukin-1 and interleukin-1
receptor antagonist. Cancer Lett. 95:119–123. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Giri D, Ozen M and Ittmann M:
Interleukin-6 is an autocrine growth factor in human prostate
cancer. Am J Pathol. 159:2159–2165. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Shariat SF, Andrews B, Kattan MW, Kim J,
Wheeler TM and Slawin KM: Plasma levels of interleukin-6 and its
soluble receptor are associated with prostate cancer progression
and metastasis. Urology. 58:1008–1015. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Kim SW, Kim JS, Papadopoulos J, Choi HJ,
He J, Maya M, Langley RR, Fan D, Fidler IJ and Kim SJ: Consistent
interactions between tumor cell IL-6 and macrophage TNF-α enhance
the growth of human prostate cancer cells in the bone of nude
mouse. Int Immunopharmacol. 11:862–872. 2011.
|
|
27.
|
Kyprianou N: Apoptosis: therapeutic
significance in the treatment of androgen-dependent and
androgen-independent prostate cancer. World J Urol. 12:299–303.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Raffo AJ, Perlman H, Chen MW, Day ML,
Streitman JS and Buttyan R: Overexpression of bcl-2 protects
prostate cancer cells from apoptosis in vitro and confers
resistance to androgen depletion in vivo. Cancer Res. 55:4438–4445.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Thompson MR, Xu D and Williams BR: ATF3
transcription factor and its emerging roles in immunity and cancer.
J Mol Med (Berl). 87:1053–1060. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Chen BP, Liang G, Whelan J and Hai T: ATF3
and ATF3 delta Zip. Transcriptional repression versus activation by
alternatively spliced isoforms. J Biol Chem. 3:15819–15826.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Huang X, Li X and Guo B: KLF6 induces
apoptosis in prostate cancer cells through up-regulation of ATF3. J
Biol Chem. 283:29795–29801. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Terry PD, Rohan TE and Wolk A: Intakes of
fish and marine fatty acids and the risks of cancers of the breast
and prostate and of other hormone-related cancers: a review of the
epidemiologic evidence. Am J Clin Nutr. 77:532–543. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Friedrichs W, Ruparel SB, Marciniak RA and
DeGraffenried L: Omega-3 fatty acid inhibition of prostate cancer
progression to hormone independence is associated with suppression
of mTOR signaling and androgen receptor expression. Nutr Cancer.
63:771–777. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
De Stefani E, Deneo-Pellegrini H, Boffetta
P, Ronco A and Mendilaharsu M: Alpha-linolenic acid and risk of
prostate cancer: a case-control study in Uruguay. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 9:335–338. 2000.
|
|
35.
|
Leitzmann MF, Stampfer MJ, Michaud DS,
Augustsson K, Colditz GC, Willett WC and Giovannucci EL: Dietary
intake of n-3 and n-6 fatty acids and the risk of prostate cancer.
Am J Clin Nutr. 80:204–216. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Migita T, Ruiz S, Fornari A, Fiorentino M,
Priolo C, Zadra G, Inazuka F, Grisanzio C, Palescandolo E, Shin E,
et al: Fatty acid synthase: a metabolic enzyme and candidate
oncogene in prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 101:519–532. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Rossi S, Graner E, Febbo P, Weinstein L,
Bhattacharya N, Onody T, Bubley G, Balk S and Loda M: Fatty acid
synthase expression defines distinct molecular signatures in
prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 1:707–715. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Gillies PJ, Bhatia SK, Belcher LA, Hannon
DB, Thompson JT and Vanden Heuvel JP: Regulation of inflammatory
and lipid metabolism genes by eicosapentaenoic acid-rich oil. J
Lipid Res. 53:1679–1689. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Pawlosky RJ, Hibbeln JR and Salem N Jr:
Compartmental analyses of plasma n-3 essential fatty acids among
male and female smokers and nonsmokers. J Lipid Res. 48:935–943.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Harper CR, Edwards MJ, DeFilippis AP and
Jacobson TA: Flaxseed oil increases the plasma concentrations of
cardioprotective (n-3) fatty acids in humans. J Nutr. 136:83–87.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Harvei S, Bjerve KS, Tretli S, Jellum E,
Robsahm TE and Vatten L: Prediagnostic level of fatty acids in
serum phospholipids: omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids and the risk
of prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 71:545–551. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Schonberg SA, Lundemo AG, Fladvad T,
Holmgren K, Bremseth H, Nilsen A, Gederaas O, Tvedt KE, Egeberg KW
and Krokan HE: Closely related colon cancer cell lines display
different sensitivity to polyunsaturated fatty acids, accumulate
different lipid classes and downregulate sterol regulatory
element-binding protein 1. FEBS J. 273:2749–2765. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43.
|
Cavazos DA, Price RS, Apte SS and
deGraffenried LA: Docosahexaenoic acid selectively induces human
prostate cancer cell sensitivity to oxidative stress through
modulation of NF-κB. Prostate. 71:1420–1428. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|