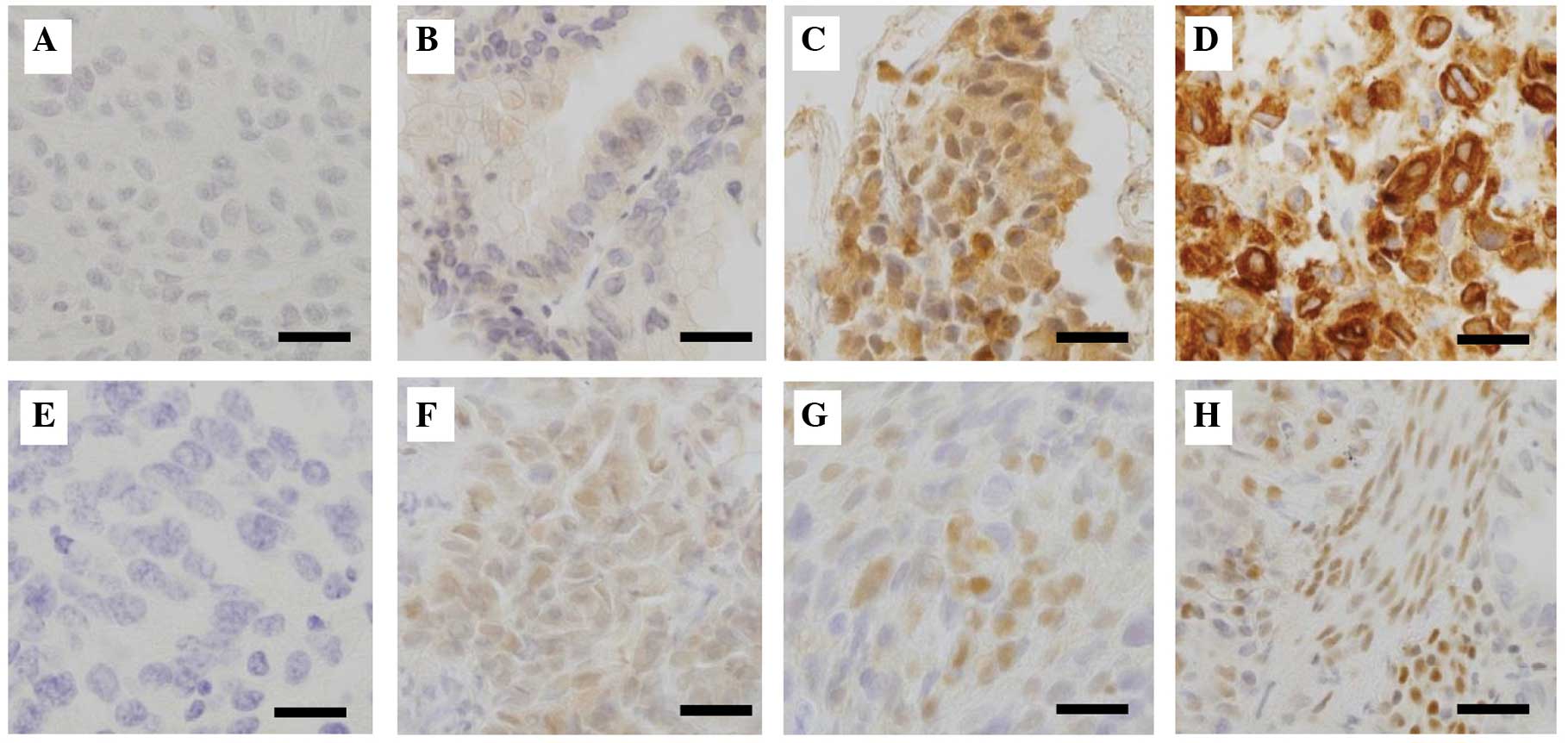
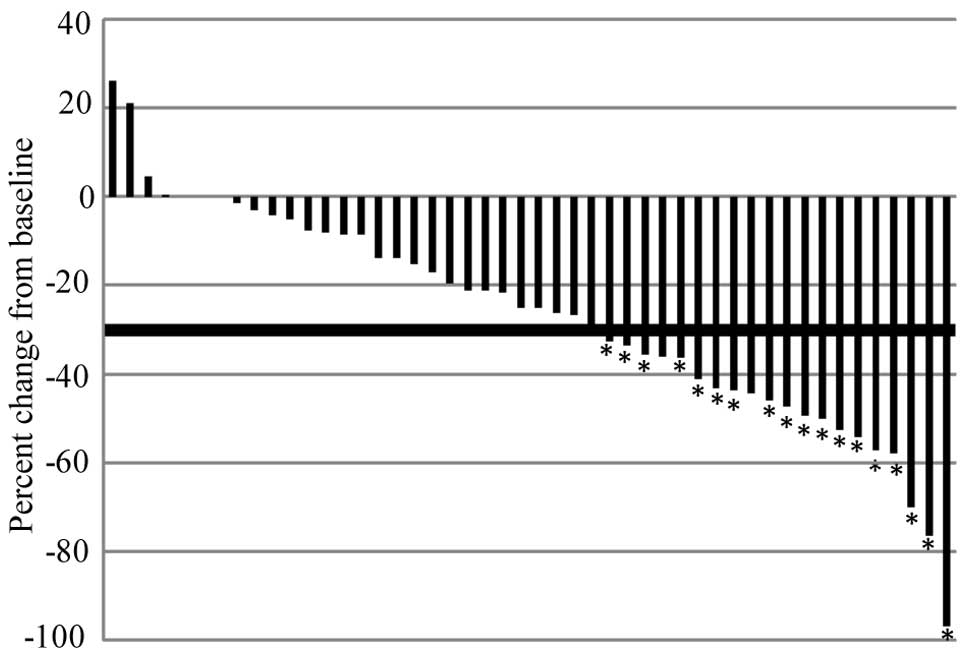
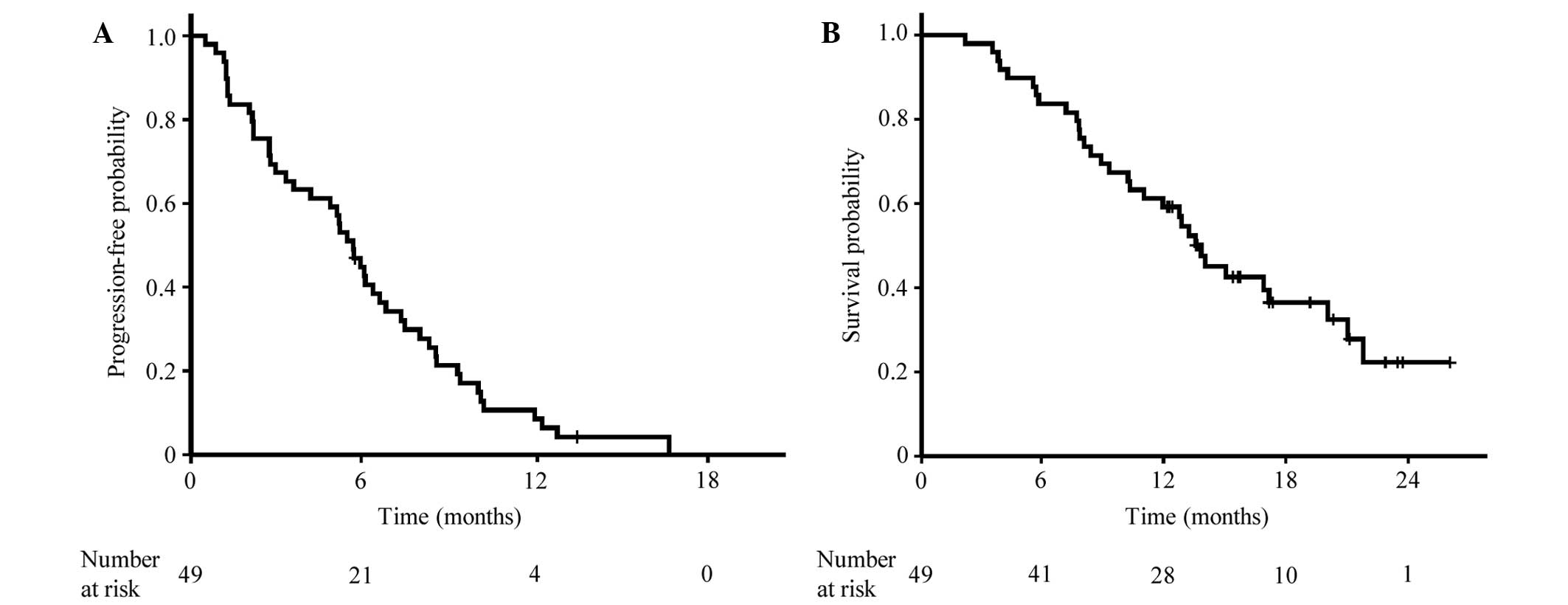
|
1
|
Castelao JE, Bart RD III, DiPerna CA,
Sievers EM and Bremner RM: Lung cancer and cyclooxygenase-2. Ann
Thorac Surg. 76:1327–1335. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wolff H, Saukkonen K, Anttila S,
Karjalainen A, Vainio H and Ristimaki A: Expression of
cyclooxygenase-2 in human lung carcinoma. Cancer Res. 58:4997–5001.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Achiwa H, Yatabe Y, Hida T, et al:
Prognostic significance of elevated cyclooxygenase 2 expression in
primary, resected lung adenocarcinomas. Clin Cancer Res.
5:1001–1005. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Khuri FR, Wu H, Lee JJ, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression is a marker of poor prognosis in
stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 7:861–867.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brabender J, Park J, Metzger R, et al:
Prognostic significance of cyclooxygenase 2 mRNA expression in
non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Surg. 235:440–443. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang H, Wang J and Zhao W: Cox-2 in
non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta.
419:26–32. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhan P, Qian Q and Yu LK: Prognostic value
of COX-2 expression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a
systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thorac Dis. 5:40–47.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brown JR and DuBois RN: Cyclooxygenase as
a target in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10:4266s–4269s. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Katayose Y, Kim M, Rakkar AN, et al:
Promoting apoptosis: a novel activity associated with the
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27. Cancer Res. 57:5441–5445.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hommura F, Dosaka-Akita H, Mishina T, et
al: Prognostic significance of p27KIP1 protein and ki-67 growth
fraction in non-small cell lung cancers. Clin Cancer Res.
6:4073–4081. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grosch S, Tegeder I, Niederberger E,
Brautigam L and Geisslinger G: COX-2 independent induction of cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis in colon cancer cells by the selective
COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib. FASEB J. 15:2742–2744. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gligorov J and Lotz JP: Preclinical
pharmacology of the taxanes: implications of the differences.
Oncologist. 9(Suppl 2): 3–8. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Haldar S, Basu A and Croce CM: Bcl2 is the
guardian of microtubule integrity. Cancer Res. 57:229–233.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Subbaramaiah K, Marmo TP, Dixon DA and
Dannenberg AJ: Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA stability by
taxanes: evidence for involvement of p38, MAPKAPK-2, and HuR. J
Biol Chem. 278:37637–37647. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Millward MJ, Boyer MJ, Lehnert M, et al:
Docetaxel and carboplatin is an active regimen in advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase II study in Caucasian and Asian
patients. Ann Oncol. 14:449–454. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang X, Hunt JL, Landsittel DP, et al:
Correlation of protease-activated receptor-1 with differentiation
markers in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck and its
implication in lymph node metastasis. Clin Cancer Res.
10:8451–8459. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Muller S, Su L, Tighiouart M, et al:
Distinctive E-cadherin and epidermal growth factor receptor
expression in metastatic and nonmetastatic head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma: predictive and prognostic correlation. Cancer.
113:97–107. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Belani CP, Einzig A, Bonomi P, et al:
Multicenter phase II trial of docetaxel and carboplatin in patients
with stage IIIB and IV non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol.
11:673–678. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jahanzeb M, Sarna G, Hirsch R, et al:
Docetaxel and carboplatin as first-line therapy in advanced
non-small cell lung carcinoma: a phase II study. Anticancer Res.
24:1239–1242. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schuette W, Nagel S, von Weikersthal LF,
et al: Randomized phase III trial of docetaxel plus carboplatin
with or without levofloxacin prophylaxis in elderly patients with
advanced non-small cell lung cancer: the APRONTA trial. J Thorac
Oncol. 6:2090–2096. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Groen HJ, Sietsma H, Vincent A, et al:
Randomized, placebo-controlled phase III study of docetaxel plus
carboplatin with celecoxib and cyclooxygenase-2 expression as a
biomarker for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer:
the NVALT-4 study. J Clin Oncol. 29:4320–4326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Koch A, Bergman B, Holmberg E, et al;
Swedish Lung Cancer Study Group. Effect of celecoxib on survival in
patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a double blind
randomised clinical phase III trial (CYCLUS study) by the Swedish
Lung Cancer Study Group. Eur J Cancer. 47:1546–1555. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Edelman MJ, Watson D, Wang X, et al:
Eicosanoid modulation in advanced lung cancer: cyclooxygenase-2
expression is a positive predictive factor for
celecoxib+chemotherapy - Cancer and Leukemia Group B Trial 30203. J
Clin Oncol. 26:848–855. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang Z, Duan J, Guo Q, et al: A phase II
clinical trial of celecoxib combined with platinum-based
chemotherapy in the treatment of patients with advanced NSCLC as
first-line treatment. Chin J Lung Cancer. 11:425–430. 2008.(In
Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Mendes RT, Stanczyk CP, Sordi R, Otuki MF,
dos Santos FA and Fernandes D: Selective inhibition of
cyclooxygenase-2: risks and benefits. Rev Bras Reumatol.
52:767–782. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Matsui Y, Amano H, Ito Y, et al:
Thromboxane A2receptor signaling facilitates tumor
colonization through P-selectin-mediated interaction of tumor cells
with platelets and endothelial cells. Cancer Sci. 103:700–707.
2012.
|
|
27
|
Honn KV: Inhibition of tumor cell
metastasis by modulation of the vascular prostacyclin/thromboxane
A2 system. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1:103–114. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang ZL, Fan ZQ, Jiang HD and Qu JM:
Selective Cox-2 inhibitor celecoxib induces epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in human lung cancer cells via activating MEK-ERK
signaling. Carcinogenesis. 34:638–646. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kozak KR, Milne GL, Bentzen SM and Yock
TI: Elevation of prostaglandin E2 in lung cancer patients with
digital clubbing. J Thorac Oncol. 7:1877–1878. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sorenson S, Fohlin H, Lindgren A, et al:
Predictive role of plasma vascular endothelial growth factor for
the effect of celecoxib in advanced non-small cell lung cancer
treated with chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer. 49:115–120. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al:
Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor
underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to
gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 350:2129–2139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, et al:
Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 448:561–566. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cebola I and Peinado MA: Epigenetic
deregulation of the COX pathway in cancer. Prog Lipid Res.
51:301–313. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
de Maat MF, van de Velde CJ, Umetani N, et
al: Epigenetic silencing of cyclooxygenase-2 affects clinical
outcome in gastric cancer. J Clin Oncol. 25:4887–4894.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Suzuki R, Yamamoto M, Saka H, et al: A
phase II study of carboplatin and paclitacel with meloxicam. Lung
Cancer. 63:72–76. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
O’Donnell PH and Dolan ME: Cancer
pharmacoethnicity: ethnic differences in susceptibility to the
effects of chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 15:4806–4814.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|