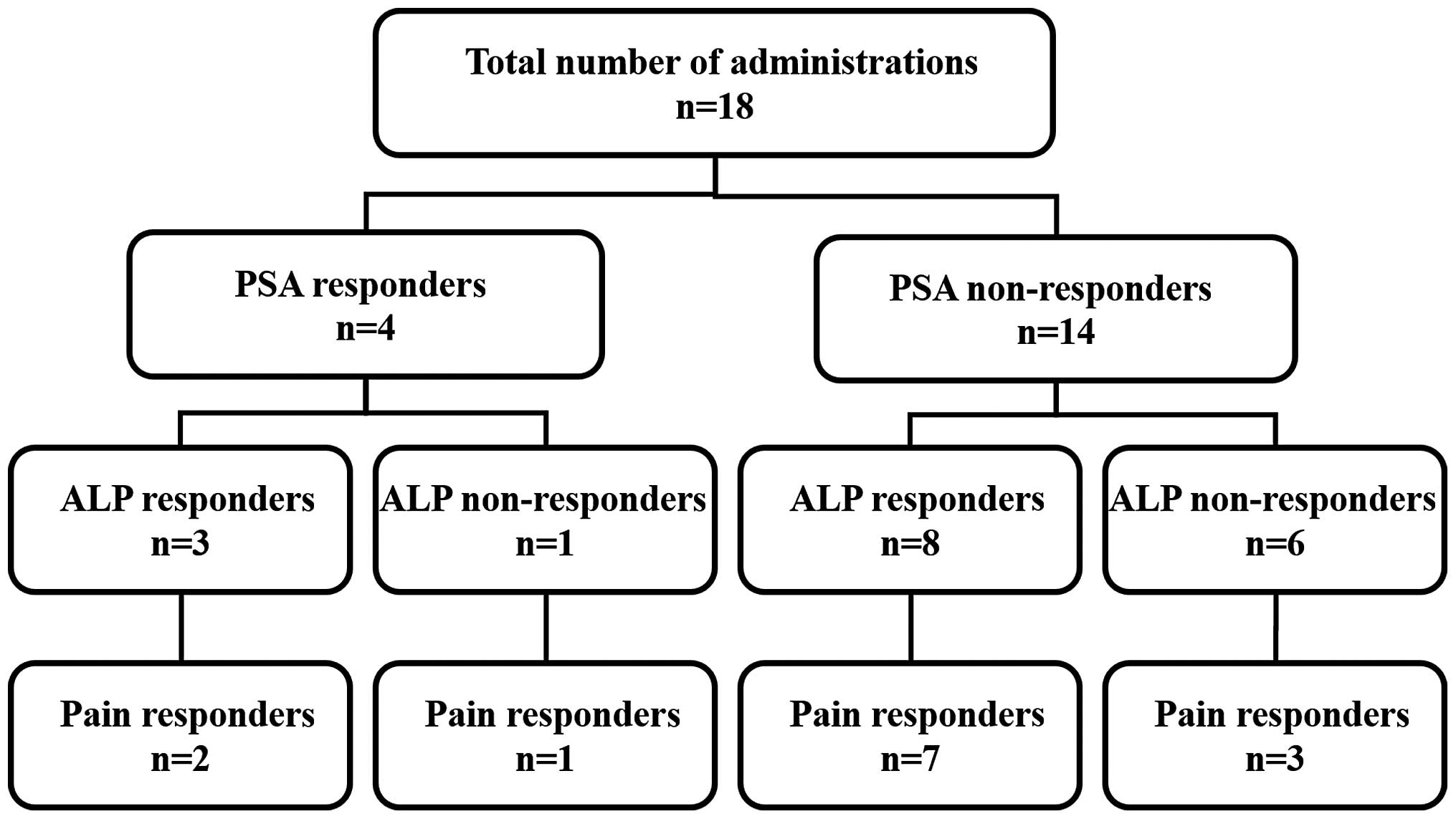
|
1
|
Coleman RE: Metastatic bone disease:
clinical features, pathophysiology and treatment strategies. Cancer
Treat Rev. 27:165–176. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Coleman RE: Skeletal complications of
malignancy. Cancer. 80 8 Suppl:1588–1594. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zekri J, Ahmed N, Coleman RE and Hancock
BW: The skeletal metastatic complications of renal cell carcinoma.
Int J Oncol. 19:379–382. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sciuto R, Festa A, Rea S, Pasqualoni R,
Bergomi S, Petrilli G and Maini CL: Effects of low-dose cisplatin
on 89Sr therapy for painful bone metastases from
prostate cancer: a randomized clinical trial. J Nucl Med. 43:79–86.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bolger JJ, Dearnaley DP, Kirk D, et al:
Strontium-89 (Metastron) versus external beam radiotherapy in
patients with painful bone metastases secondary to prostatic
cancer: preliminary report of a multicenter trial. UK Metastron
Investigators Group. Semin Oncol. 20:32–33. 1993.
|
|
6
|
Blake GM, Zivanovic MA, Blaquiere RM, Fine
DR, McEwan AJ and Ackery DM: Strontium-89 therapy: measurement of
absorbed dose to skeletal metastases. J Nucl Med. 29:549–557.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pecher C: Biological investigations with
radioactive calcium and strontium: preliminary report on the use of
radioactive strontium in the treatment of metastatic bone cancer.
Univ Calif Publ Pharmacol. 2:1117–1149. 1942.
|
|
8
|
Lewington VJ, McEwan AJ, Ackery DM, et al:
A prospective, randomised double-blind crossover study to examine
the efficacy of strontium-89 in pain palliation in patients with
advanced prostate cancer metastatic to bone. Eur J Cancer.
27:954–958. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Porter AT, McEwan AJ, Powe JE, et al:
Results of a randomized phase-III trial to evaluate the efficacy of
strontium-89 adjuvant to local field external beam irradiation in
the management of endocrine resistant metastatic prostate cancer.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 25:805–813. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
McEwan AJ, Amyotte GA, McGowan DG,
MacGillivray JA and Porter AT: A retrospective analysis of the cost
effectiveness of treatment with Metastron
(89Sr-chloride) in patients with prostate cancer
metastatic to bone. Nucl Med Commun. 15:499–504. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Malmberg I, Persson U, Ask A, Tennvall J
and Abrahamsson PA: Painful bone metastases in hormone-refractory
prostate cancer: economic costs of strontium-89 and/or external
radiotherapy. Urology. 50:747–753. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kimura Y, Hamamoto K, Furudate M, et al:
Effectiveness of the radioactive strontium (89Sr) chloride agent,
SMS.2P for pain palliation in patients with metastatic bone tumor
in phase III multicenter clinical trial. Jpn J Nucl Med.
33:1347–1358. 1996.(In Japanese).
|
|
13
|
Finlay IG, Mason MD and Shelley M:
Radioisotopes for the palliation of metastatic bone cancer: a
systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 6:392–400. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kraeber-Bodéré F, Campion L, Rousseau C,
Bourdin S, Chatal JF and Resche I: Treatment of bone metastases of
prostate cancer with strontium-89 chloride: efficacy in relation to
the degree of bone involvement. Eur J Nucl Med. 27:1487–1493.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McEwan AJ: Use of radionuclides for the
palliation of bone metastases. Semin Radiat Oncol. 10:103–114.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Serafini AN: Therapy of metastatic bone
pain. J Nucl Med. 42:895–906. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lewington VJ: Bone-seeking radionuclides
for therapy. J Nucl Med. 46 Suppl 1:38S–47S. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Windsor PM: Predictors of response to
strontium-89 (Metastron) in skeletal metastases from prostate
cancer: report of a single centre's 10-year experience. Clin Oncol
(R Coll Radiol). 13:219–227. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Laing AH, Ackery DM, Bayly RJ, et al:
Strontium-89 chloride for pain palliation in prostatic skeletal
malignancy. Br J Radiol. 64:816–822. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Turner SL, Gruenewald S, Spry N and Gebski
VMetastron Users Group: Less pain does equal better quality of life
following strontium-89 therapy for metastatic prostate cancer. Br J
Cancer. 84:297–302. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rogers CL, Speiser BL, Ram PC, et al:
Efficacy and toxicity of intravenous strontium-89 for symptomatic
osseous metastasis. Brachyther Int. 4:133–142. 1998.
|
|
22
|
Lee CK, Aeppli DM, Unger J, Boudreau RJ
and Levitt SH: Strontium-89 chloride (Metastron) for palliative
treatment of bony metastases. The University of Minnesota
experience. Am J Clin Oncol. 19:102–107. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fosså SD, Paus E, Lochoff M, Backe SM and
Aas M: 89Strontium in bone metastases from hormone
resistant prostate cancer: palliation effect and biochemical
changes. Br J Cancer. 66:177–180. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|