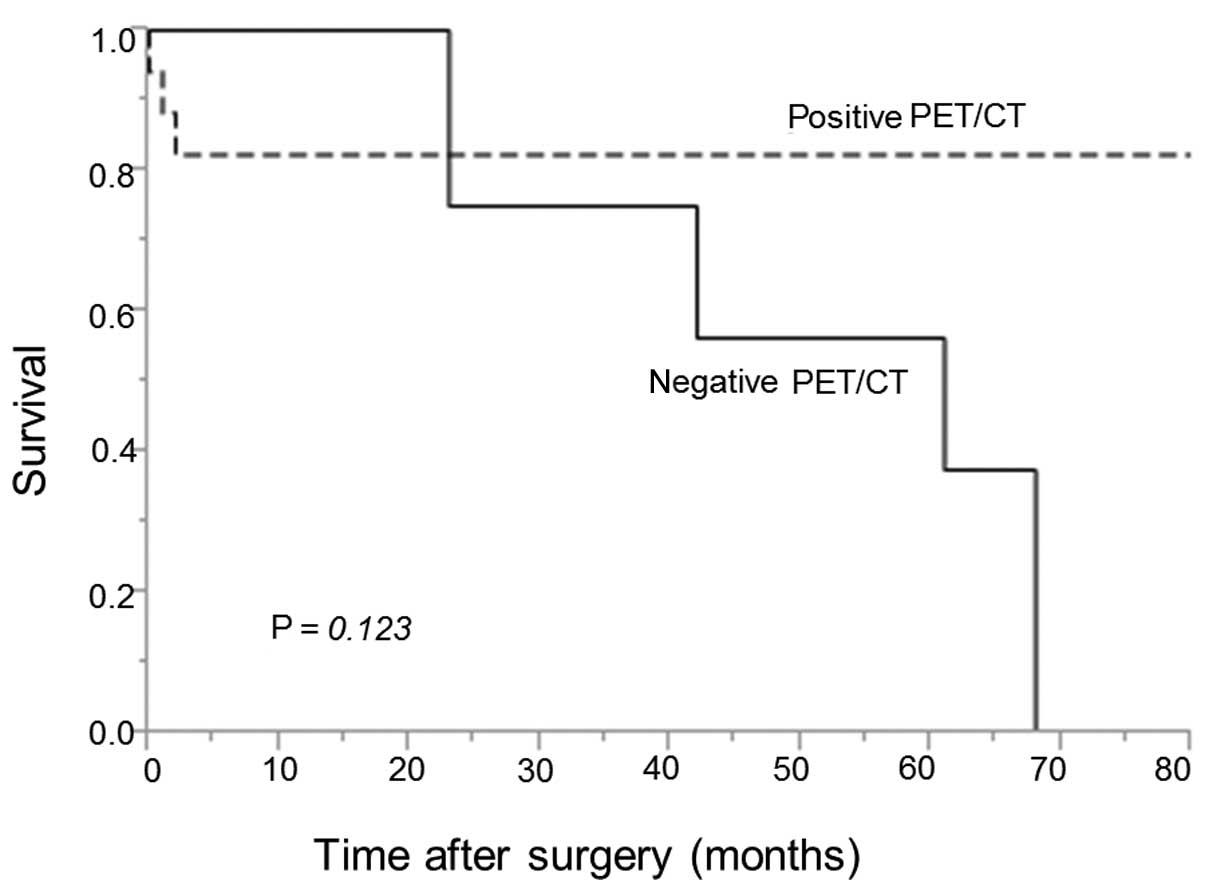
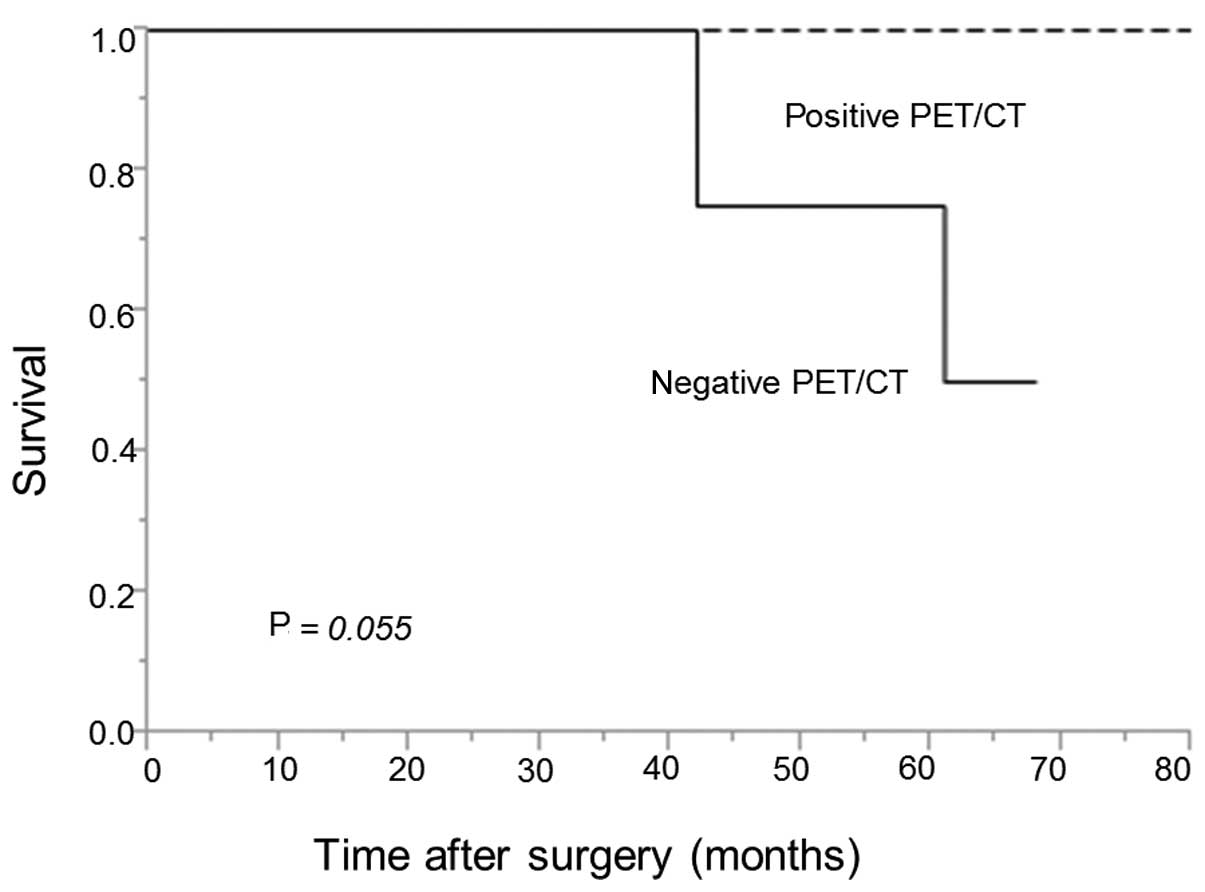
|
1
|
Mountain CF: Revisions in the
international system for staging lung cancer. Chest. 111:1710–1717.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rusch VW, Crowley J, Giroux DJ, Goldstraw
P, Im JG, Tsuboi M, Tsuchiya R and Vansteenkiste JInternational
Staging Committee; Cancer Research and Biostatistics; Observers to
the Committee; Participating Institutions: The IASLC Lung Cancer
Staging Project: proposals for the revision of the N descriptors in
the forthcoming seventh edition of the TNM classification for lung
cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2:603–612. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Watanabe S, Asamura H, Suzuki K and
Tsuchiya R: Problems in diagnosis and surgical management of
clinical N1 non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg.
79:1682–1685. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hishida T, Yoshida J, Nishimura M,
Nishiwaki Y and Nagai K: Problems in the current diagnostic
standards of clinical N1 non-small cell lung cancer. Thorax.
63:526–531. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miyasaka Y, Suzuki K, Takamochi K,
Matsunaga T and Oh S: The maximum standardized uptake value of
fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography of the primary
tumour is a good predictor of pathological nodal involvement in
clinical N0 non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.
44:83–87. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Steinert HC, Hauser M, Allemann F, Engel
H, Berthold T, von Schulthess GK and Weder W: Non-small cell lung
cancer: Nodal staging with FDG PET versus CT with correlative lymph
node mapping and sampling. Radiology. 202:441–446. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vansteenkiste JF, Stroobants SG, De Leyn
PR, Dupont PJ, Verschakelen JA, Nackaerts KL and Mortelmans
LALeuven Lung Cancer Group: Mediastinal lymph node staging with
FDG-PET scan in patients with potentially operable non-small cell
lung cancer: A prospective analysis of 50 cases. Chest.
112:1480–1486. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vansteenkiste JF, Stroobants SG, Dupont
PJ, De Leyn PR, De Wever WF, Verbeken EK, Nuyts JL, Maes FP and
Bogaert JG: FDG-PET scan in potentially operable non-small cell
lung cancer: Do anatometabolic PET-CT fusion images improve the
localisation of regional lymph node metastases? The Leuven Lung
Cancer Group. Eur J Nucl Med. 25:1495–1501. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hellwig D, Graeter TP, Ukena D, Groeschel
A, Sybrecht GW, Schaefers HJ and Kirsch CM: 18F-FDG PET
for mediastinal staging of lung cancer: Which SUV threshold makes
sense? J Nucl Med. 48:1761–1766. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Carrillo SA, Daniel VC, Hall N, Hitchcock
CL, Ross P Jr and Kassis ES: Fusion positron emission/computed
tomography underestimates the presence of hilar nodal metastases in
patients with resected non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg.
93:1621–1624. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rusch VW, Asamura H, Watanabe H, Giroux
DJ, Rami-Porta R and Goldstraw PMembers of IASLC Staging Committee:
The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: a proposal for a new
international lymph node map in the forthcoming seventh edition of
the TNM classification for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 4:568–577.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Detterbeck FC, Boffa DJ and Tanoue LT: The
new lung cancer staging system. Chest. 136:260–271. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vansteenkiste JF, Stroobants SG, Dupont
PJ, De Leyn PR, Verbeken EK, Deneffe GJ, Mortelmans LA and Demedts
MGLeuven Lung Cancer Group: Prognostic importance of the
standardized uptake value on
18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-glucose-positron emission tomography
scan in non-small-cell lung cancer: An analysis of 125 cases. J
Clin Oncol. 17:3201–3206. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fischer B, Lassen U, Mortensen J, Larsen
S, Loft A, Bertelsen A, Ravn J, Clementsen P, Høgholm A, Larsen K,
et al: Preoperative staging of lung cancer with combined PET-CT. N
Engl J Med. 361:32–39. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Silvestri GA, Gould MK, Margolis ML,
Tanoue LT, McCrory D, Toloza E and Detterbeck FAmerican College of
Chest Physicians: Noninvasive staging of non-small cell lung
cancer: ACCP evidenced-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd
edition). Chest. 132 (Suppl 3):178S–201S. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ernst A, Eberhardt R, Krasnik M and Herth
FJ: Efficacy of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial
needle aspiration of hilar lymph nodes for diagnosing and staging
cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 4:947–950. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shin S, Kim HK, Choi YS, Kim K, Kim J and
Shim YM: Prognosis of unexpected and expected pathologic N1
non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 96:969–975;
discussion. 975–976. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moreno AC, Morgensztern D, Boffa DJ,
Decker RH, Yu JB, Detterbeck FC, Wang Z, Rose MG and Kim AW:
Treating locally advanced disease: An analysis of very large, hilar
lymph node positive non-small cell lung cancer using the National
Cancer Data Base. Ann Thorac Surg. 97:1149–1155. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Watanabe S, Asamura H, Suzuki K and
Tsuchiya R: Recent results of postoperative mortality for surgical
resections in lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 78:999–1002;
discussion. 1002–1003. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|