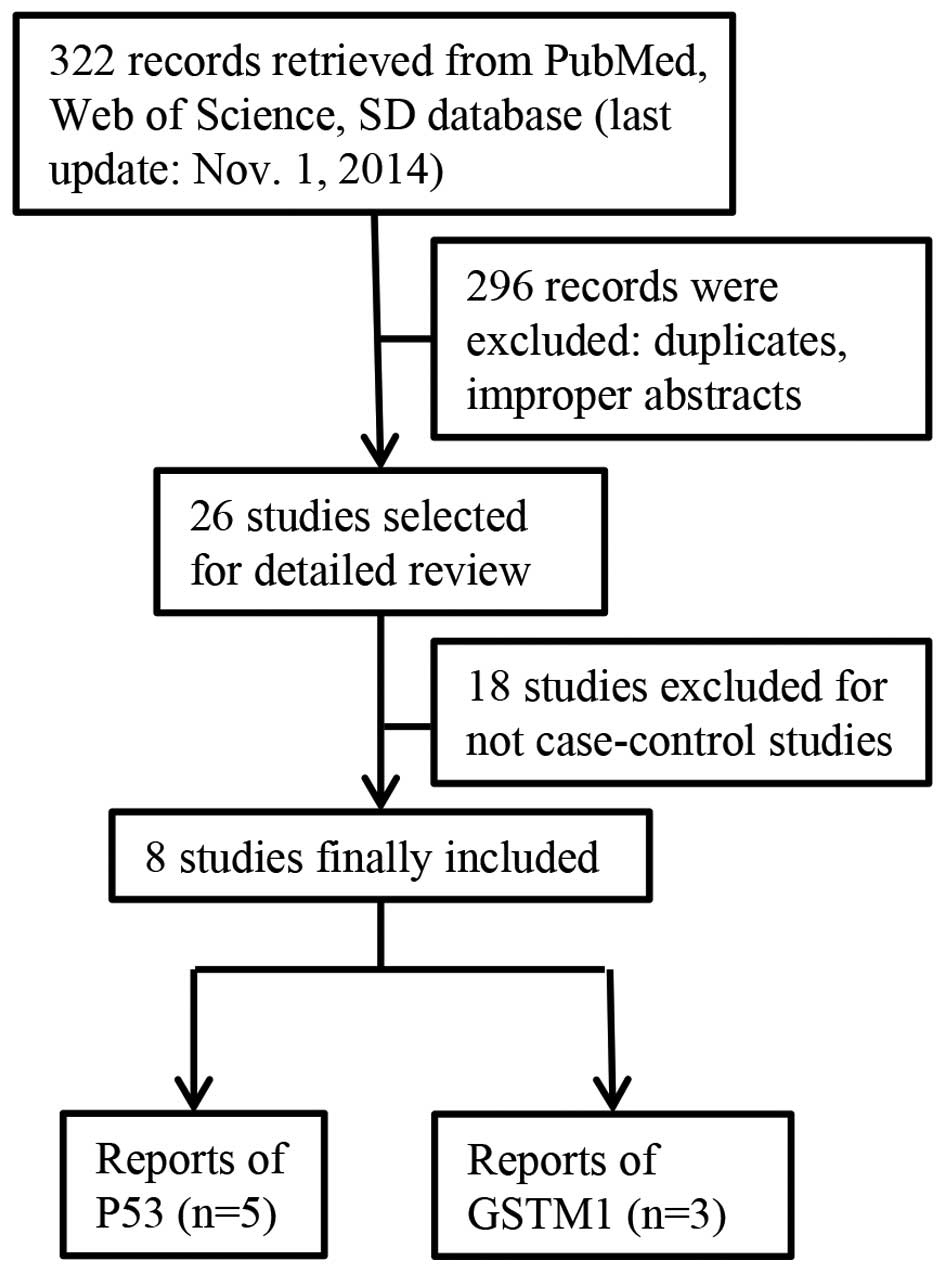
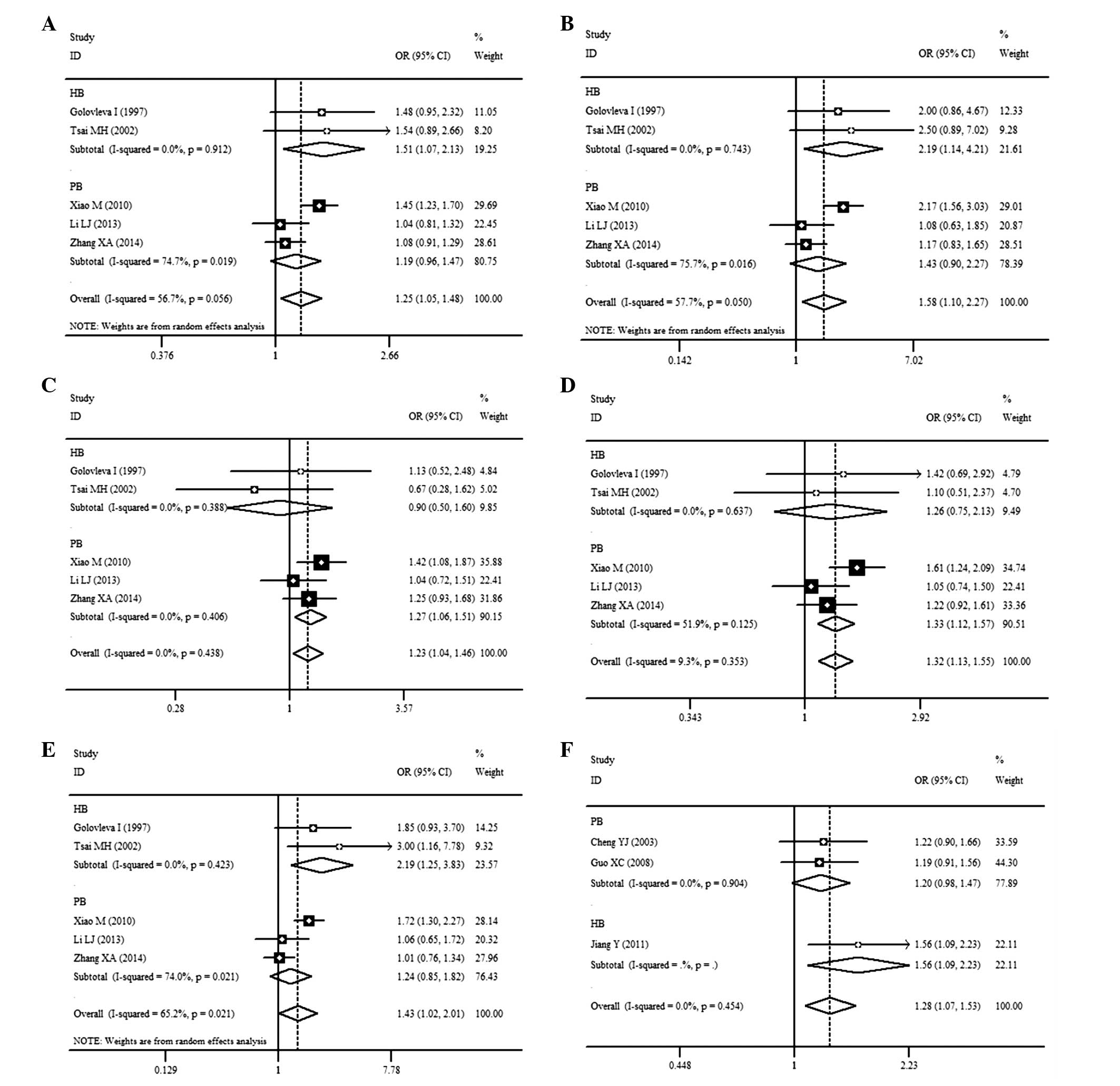
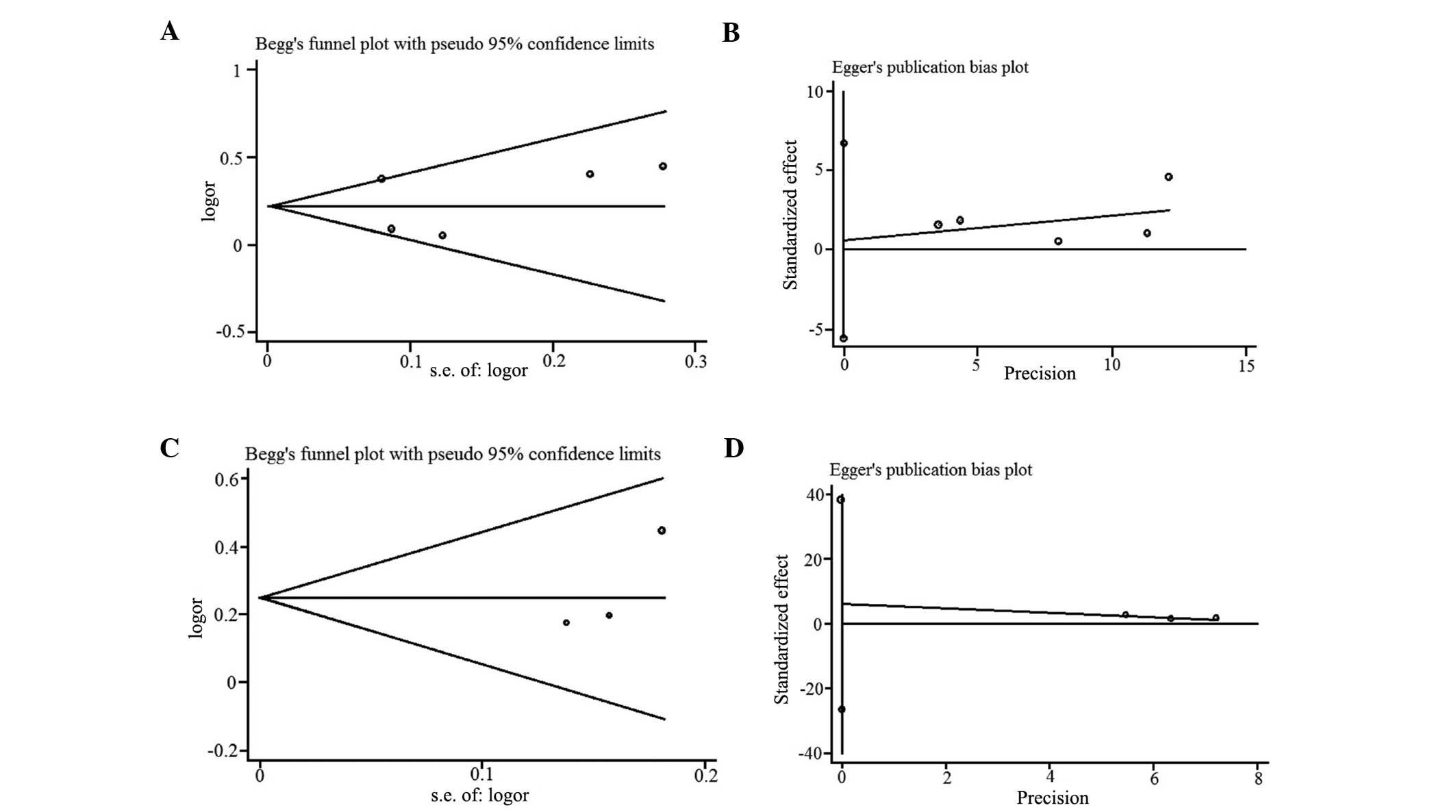
|
1
|
Lee AW, Ng WT, Chan YH, Sze H, Chan C and
Lam TH: The battle against nasopharyngeal cancer. Radiother Oncol.
104:272–278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bei JX, Li Y, Jia WH, Feng BJ, Zhou G,
Chen LZ, Feng QS, Low HQ, Zhang H, He F, et al: A genome-wide
association study of nasopharyngeal carcinoma identifies three new
susceptibility loci. Nat Genet. 42:599–603. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chang CM, Yu KJ, Mbulaiteye SM, Hildesheim
A and Bhatia K: The extent of genetic diversity of Epstein-Barr
virus and its geographic and disease patterns, A need for
reappraisal. Virus Res. 143:209–221. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cho WC: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: M
olecular biomarker discovery and progress. Mol Cancer. 6:12007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Horikawa T, Yoshizaki T, Kondo S, Furukawa
M, Kaizaki Y and Pagano JS: Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane
protein 1 induces snail and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 104:1160–1167.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hildesheim A and Wang CP: Genetic
predisposition factors and nasopharyngeal carcinoma risk: A review
of epidemiological association studies 2000-2011: Rosetta Stone for
NPC: Genetics, viral infection and other environmental factors.
Semin Cancer Biol. 22:107–116. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Su CK and Wang CC: Prognostic value of
Chinese race in nasopharyngeal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 54:752–758. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qin HD, Shugart YY, Bei JX, Pan QH, Chen
L, Feng QS, Chen LZ, Huang W, Liu JJ, Jorgensen TJ, et al:
Comprehensive pathway-based association study of DNA repair gene
variants and the risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res.
71:3000–3008. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Levine AJ and Oren M: The first 30 years
of p53: Growing ever more complex. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:749–758. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Goodsell DS: The molecular perspective:
p53 tumor suppressor. Oncologist. 4:138–139. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hickman ES and Helin K: The p53 tumor
suppressor protein. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 17:179–211. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiang P, Liu J, Zeng X, Li W and Tang J:
Association of TP53 codon 72 polymorphism with cervical cancer risk
in Chinese women. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 197:174–178. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xiong X, Wang M, Wang L, Liu J, Zhao X,
Tian Z and Wang J: Risk of MDM2 SNP309 alone or in combination with
the p53 codon 72 polymorphism in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res.
33:1454–1458. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hayes JD and Pulford DJ: The glutathione
S-transferase supergene family: Regulation of GST and the
contribution of the isoenzymes to cancer chemoprotection and drug
resistance. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 30:445–600. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Parl FF: Glutathione S-reansferase
genotypes and cancer risk. Cancer Lett. 221:123–129. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Scheneider J, Bernges U, Philipp M and
Woitowitz HJ: GSTM1, GSTT1 and GSTP1 polymorphism and lung cancer
risk in relation to tobacco smoking. Cancer Lett. 208:65–74. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Thakkinstian A, McEvoy M, Minelli C,
Gibson P, Hancox B, Duffy D, Thompson J, Hall I, Kaufman J, Leung
TF, et al: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the association
between {beta}2-adrenoceptor polymorphisms and asthma: A HuGE
review. Am J Epidemiol. 162:201–211. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Higgins JP and Thompson SG: Quantifying
heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 21:1539–1558. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ.
327:557–560. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
DerSimonian R and Laird N: Meta-analysis
in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 7:177–188. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mantel N and Haenszel W: Statistical
aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of
disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 22:719–748. 1959.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Egger M, Smith Davey G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Stuck AE, Rubenstein LZ and Wieland D:
Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test.
Histopathology. BMJ. 316:470–471. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Duval S and Tweedie R: Trim and fill: A
simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for
publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics. 56:455–463. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Golovleva I, Birgander R, Själander A,
Lundgren E and Beckman L: Interferon-alpha and p53 alleles involved
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 18:645–647. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tsai MH, Lin CD, Hsieh YY, Chang FC, Tsai
FJ, Chen WC and Tsai CH: Prognostic significance of the proline
form of p53 codon 72 polymorphism in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Laryngoscope. 112:116–119. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xiao M, Zhang L, Zhu X, Huang J, Jiang H,
Hu S and Liu Y: Genetic polymorphisms of MDM2 and TP53 genes are
associated with risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in a Chinese
population. BMC Cancer. 10:1472010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li L, Wu J, Sima X, Bai P, Deng W, Deng X,
Zhang L and Gao L: Interactions of miR-34b/c and TP-53
polymorphisms on the risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Tumor Biol.
34:1919–1923. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhang XA, Chen X, Zhai Y, Cui Y, Cao P,
Zhang H, Wu Z, Li P, Yu L, Xia X, et al: Combined effects of
genetic variants of the PTEN, AKT1, MDM2 and p53 genes on the risk
of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One. 9:e921352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cheng YJ, Chien YC, Hildesheim A, Hsu MM,
Chen IH, Chuang J, Chang J, Ma YD, Luo CT, Hsu WL, et al: No
association between genetic polymorphisms of CYP1A1, GSTM1, GSTT1,
GSTP1, NAT2 and nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Taiwan. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 12:179–180. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guo XC, O'Brien SJ, Zeng Y, Nelson GW and
Winkler CA: GSTM1 and GSTT1 gene deletions and the risk for
nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Han Chinese. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 17:1760–1763. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jiang Y, Li N, Dong P, Zhang N, Sun Y, Han
M, Wen J and Chen M: Polymorphisms in GSTM1, GSTT1 and GSTP1 and
nasopharyngeal cancer in the east of China, A case-control study.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:3097–3100. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hu S, Zhou G, Zhang L, Jiang H and Xiao M:
The effects of functional polymorphisms in the TGFβ1 gene on
nasopharyngeal carcinoma susceptibility. Otolaryngol Head Neck
Surg. 146:579–584. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ben Chaaben A, Busson M, Douik H,
Boukouaci W, Mamoghli T, Chaouch L, Harzallah L, Dorra S, Fortier
C, Ghanem A, et al: Association of IL-12p40+1188A/C polymorphism
with nasopharyngeal cancer risk and tumor extension. Tissue
Antigens. 78:148–151. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chang KW, Lin SC, Mangold KA, Jean MS,
Yuan TC, Lin SN and Chang CS: Alterations of adenomatous polyposis
Coli (APC) gene in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oral
Maxillofac Surg. 29:223–226. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rosenthal AN, Ryan A, Al-Jehani RM, Storey
A, Harwood CA and Jacobs IJ: P53 codon 72 polymorphism and risk of
cervical cancer in UK. Lancet. 352:871–872. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang NM, Tsai CH, Yeh KT, Chen SJ and
Chang JG: P53 codon 72Arg polymorphism is not a risk factor for
carcinogenesis in the Chinese. Int J Mol Med. 4:249–252. 1995.
|
|
38
|
Zhuo W, Wang Y, Zhuo X, Zhu Y, Wang W, Zhu
B, Li D and Chen Z: CYP1A1 and GSTM1 polymorphisms and oral cancer
risk, Association studies via evidence-based meta-analyses. Cancer
Invest. 27:86–95. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gao LB, Pan XM, Li LJ, Liang WB, Bai P,
Rao L, Su XW, Wang T, Zhou B, Wei YG, et al: Null genotypes of
GSTM1 and GSTT1 contribute to risk of cervical neoplasia: An
evidence-based meta-analysis. PLoS One. 6:e201572011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
White DL, Li D, Nurgalieva Z and El-Serag
HB: Genetic variants of glutathione S-transferase as possible risk
factors for hepatocellular carcinoma A HuGE systematic review and
meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol. 167:377–389. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhou XL, Cai L, Xiang ZL, Zhou WL, Wang Y
and Zhang XY: TP53 codon 72 polymorphism contributes to
nasopharyngeal cancer susceptibility, A meta-analysis. Arch Med
Res. 40:299–305. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ren WH, Jiang DK, Pei Y, Wang SQ, Yang XM
and Yu L: Meta-analysis of associations between the TP53 Arg72Pro
polymorphism with risk of head and neck carcinomas based on
case-control studies. Genet Mol Res. 13:103–114. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cai K, Wang Y, Zhao X and Bao X:
Association between the P53 codon 72 polymorphism and
nasopharyngeal cancer risk. Tumor Biol. 35:1891–1897. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zhou X, Cai L, Xiang Z, Li Q and Zhang X:
GSTM1 and GSTT1 polymorphisms and nasopharyngeal cancer risk, An
evidence-based meta-analysis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 28:462009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sun ZF, Zhang J, Xu HM, Wang GL and Dong
P: Association between GSTM1 polymorphism and nasopharyngeal cancer
susceptibility, A meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:5817–5821. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wei Y, Zhou T, Lin H, Sun M, Wang D, Li H
and Li B: Significant associations between GSTM1/GSTT1
polymorphisms and nasopharyngeal cancer risk. Tumor Biol.
34:887–894. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Murthy AK, Kumar V and Suresh KP:
Meta-analysis of GSTM1 and GSTT1 polymorphisms and risk of
nasopharyngeal cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:1697–1701. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|