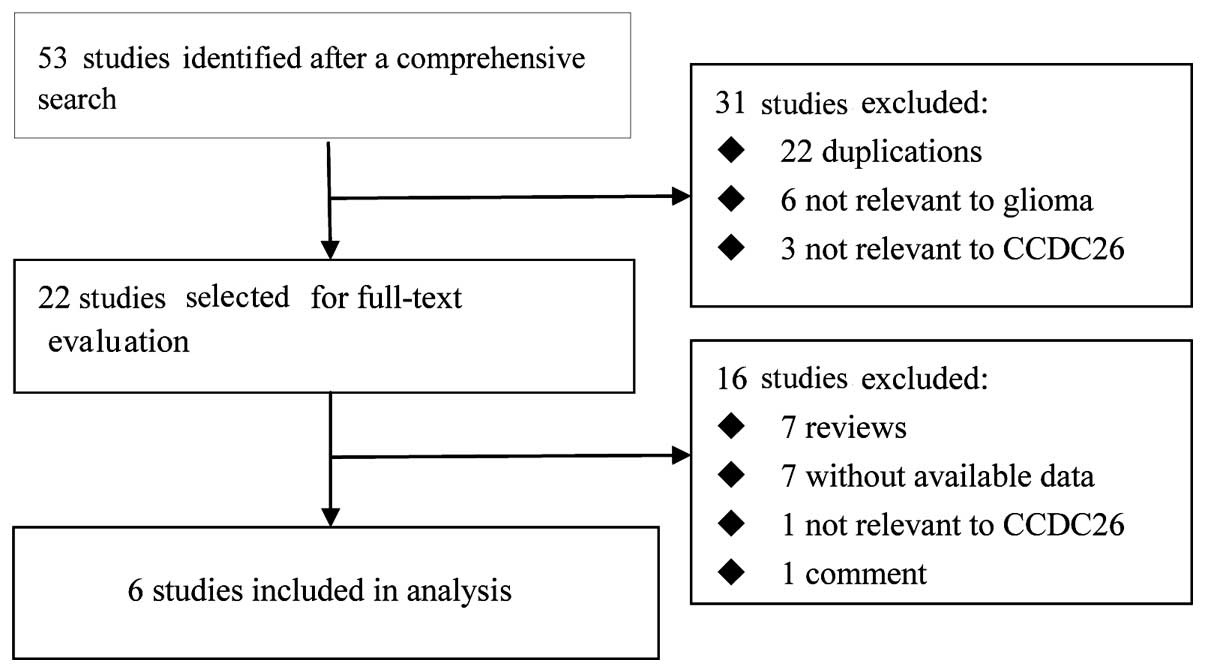
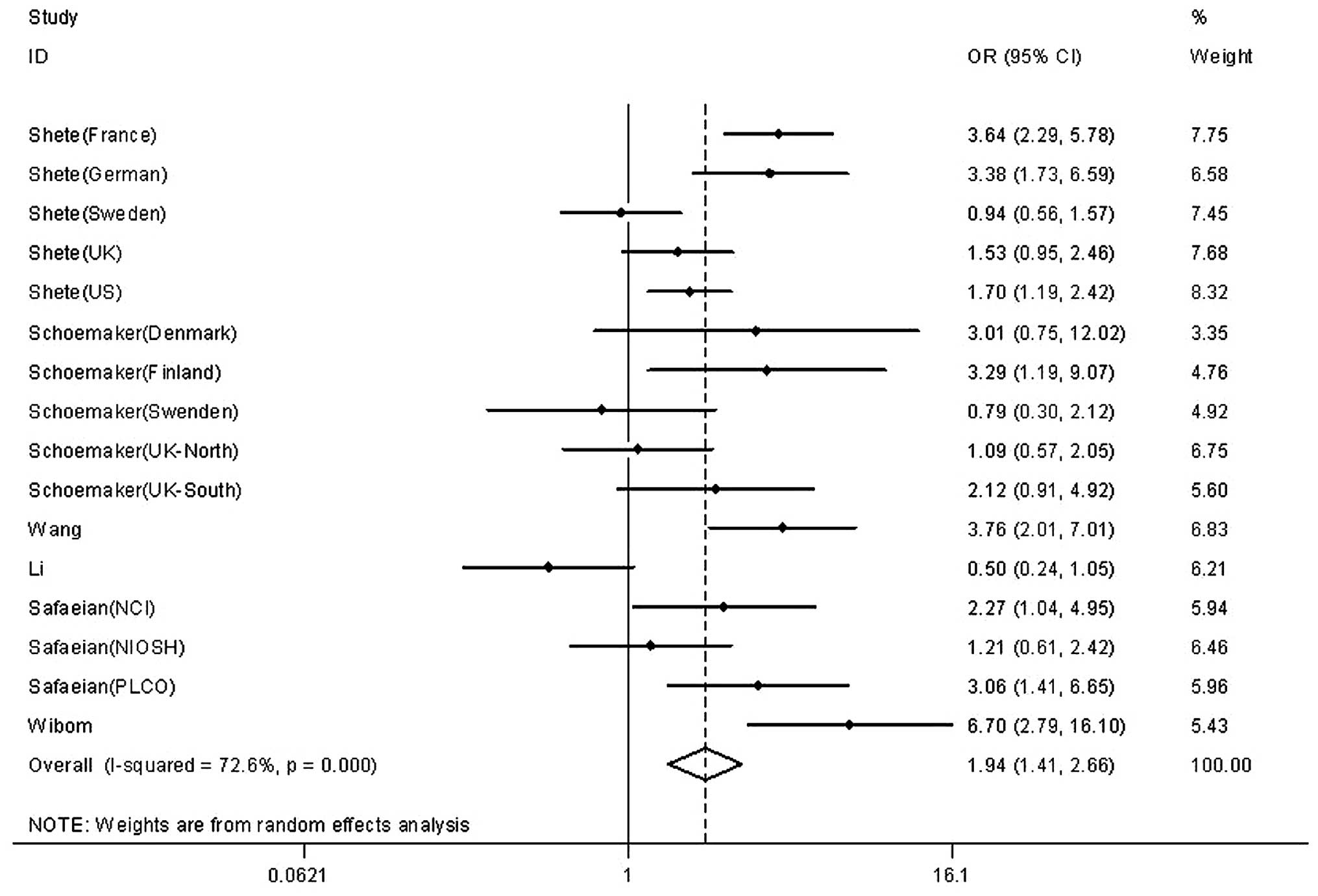
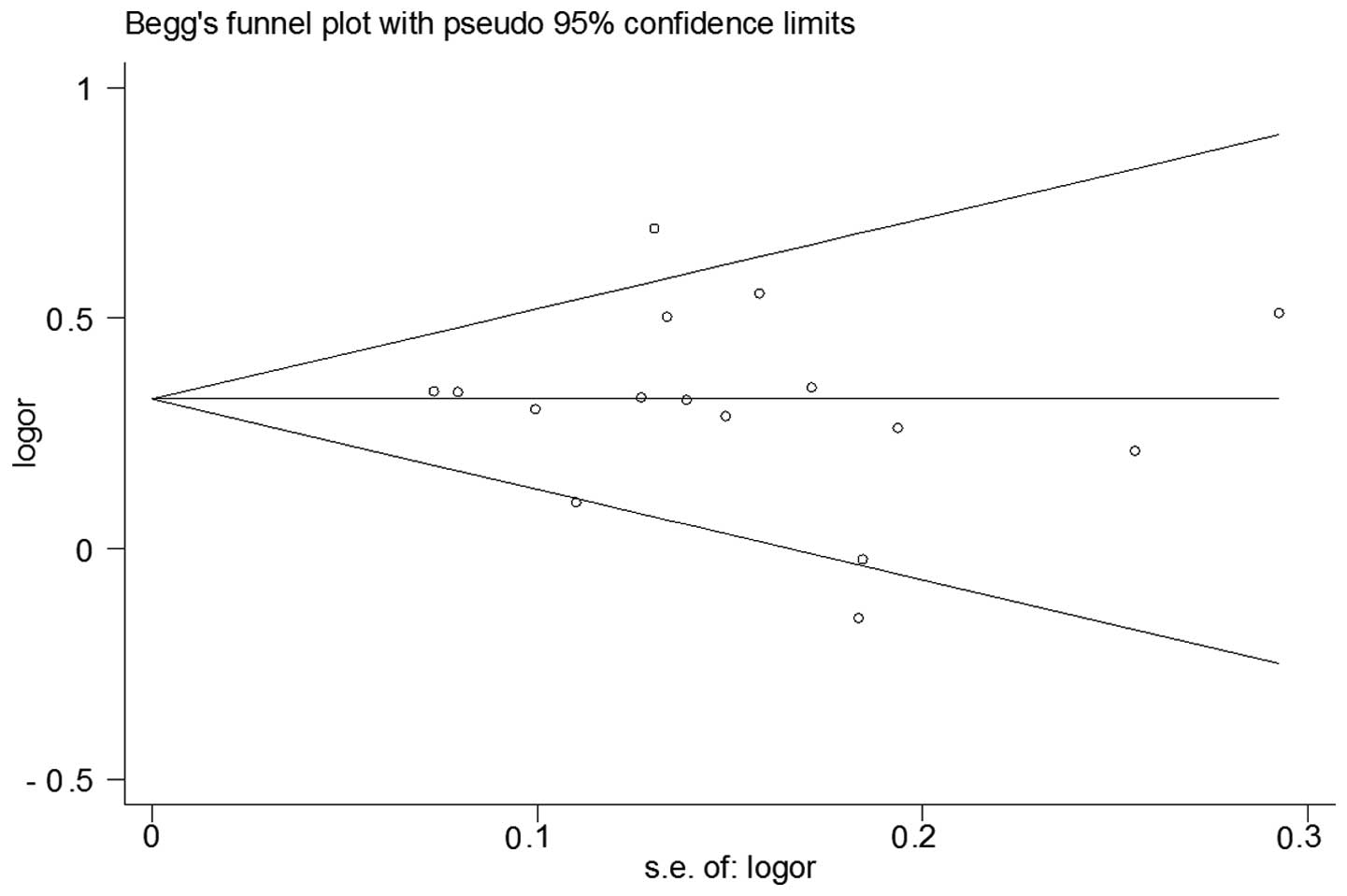
|
1
|
Ahmed R, Oborski MJ, Hwang M, Lieberman FS
and Mountz JM: Malignant gliomas: Current perspectives in
diagnosis, treatment and early response assessment using advanced
quantitative imaging methods. Cancer Manag Res. 6:149–170.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bondy ML, Scheurer ME, Malmer B,
Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Davis FG, Il'yasova D, Kruchko C, McCarthy BJ,
Rajaraman P, Schwartzbaum JA, et al: Brain Tumor Epidemiology
Consortium: Brain tumor epidemiology: Consensus from the Brain
Tumor Epidemiology Consortium. Cancer. 113(7 Suppl): S1953–S1968.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhao W, Bian Y, Zhu W, Zou P and Tang G:
Regulator of telomere elongation helicase 1 (RTEL1) rs6010620
polymorphism contribute to increased risk of glioma. Tumour Biol.
35:5259–5266. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu Y, Tong X, Tang LL, Zhou K, Zhong CH
and Jiang S: Associations between the rs6010620 polymorphism in
RTEL1 and risk of glioma: A meta-analysis of 20,711 participants.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:7163–7167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kayani MA, Khan S, Baig RM and Mahjabeen
I: Association of RAD 51 135 G/C, 172 G/T and XRCC3 Thr241Met gene
polymorphisms with increased risk of head and neck cancer. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:10457–10462. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Du SL, Geng TT, Feng T, Chen CP, Jin TB
and Chen C: The RTEL1 rs6010620 polymorphism and glioma risk: A
meta-analysis based on 12 case-control studies. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 15:10175–10179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liang HJ, Yan YL, Liu ZM, Chen X, Peng QL,
Wang J, Mo CJ, Sui JZ, Wu JR, Zhai LM, et al: Association of XRCC3
Thr241Met polymorphisms and gliomas risk: Evidence from a
meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:4243–4247. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wibom C, Späth F, Dahlin AM, Langseth H,
Hovig E, Rajaraman P, Johannesen TB, Andersson U and Melin B:
Investigation of established genetic risk variants for glioma in
pre-diagnostic samples from a population-based nested case-control
study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 24:810–816. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Das A, Banik NL and Ray SK:
Differentiation decreased telomerase activity in rat glioblastoma
C6 cells and increased sensitivity to IFN-gamma and taxol for
apoptosis. Neurochem Res. 32:2167–2183. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Safaeian M, Rajaraman P, Hartge P, Yeager
M, Linet M, Butler MA, Ruder AM, Purdue MP, Hsing A, Beane-Freeman
L, et al: Joint effects between five identified risk variants,
allergy and autoimmune conditions on glioma risk. Cancer Causes
Control. 24:1885–1891. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li S, Jin T, Zhang J, Lou H, Yang B, Li Y,
Chen C and Zhang Y: Polymorphisms of TREH, IL4R and CCDC26 genes
associated with risk of glioma. Cancer Epidemiol. 36:283–287. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang SS, Hartge P, Yeager M, Carreón T,
Ruder AM, Linet M, Inskip PD, Black A, Hsing AW, Alavanja M, et al:
Joint associations between genetic variants and reproductive
factors in glioma risk among women. Am J Epidemiol. 174:901–908.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schoemaker MJ, Robertson L, Wigertz A,
Jones ME, Hosking FJ, Feychting M, Lönn S, McKinney PA, Hepworth
SJ, Muir KR, et al: Interaction between 5 genetic variants and
allergy in glioma risk. Am J Epidemiol. 171:1165–1173. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shete S, Hosking FJ, Robertson LB, Dobbins
SE, Sanson M, Malmer B, Simon M, Marie Y, Boisselier B, Delattre
JY, et al: Genome-wide association study identifies five
susceptibility loci for glioma. Nat Genet. 41:899–904. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
DerSimonian R and Laird N: Meta-analysis
in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 7:177–188. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Egger M, Smith Davey G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Farah P, Ondracek
A, Chen Y, Wolinsky Y, Stroup NE, Kruchko C and Barnholtz-Sloan JS:
CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central nervous system
tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2006–2010. Neuro Oncol.
15(Suppl 2): ii1–ii56. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gu J, Liu Y, Kyritsis AP and Bondy ML:
Molecular epidemiology of primary brain tumors. Neurotherapeutics.
6:427–435. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu Y, Shete S, Hosking FJ, Robertson LB,
Bondy ML and Houlston RS: New insights into susceptibility to
glioma. Arch Neurol. 67:275–278. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yin W, Rossin A, Clifford JL and
Gronemeyer H: Co-resistance to retinoic acid and TRAIL by insertion
mutagenesis into RAM. Oncogene. 25:3735–3744. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kiemeney LA, Thorlacius S, Sulem P, Geller
F, Aben KK, Stacey SN, Gudmundsson J, Jakobsdottir M, Bergthorsson
JT, Sigurdsson A, et al: Sequence variant on 8q24 confers
susceptibility to urinary bladder cancer. Nat Genet. 40:1307–1312.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tomlinson I, Webb E, Carvajal-Carmona L,
Broderick P, Kemp Z, Spain S, Penegar S, Chandler I, Gorman M, Wood
W, et al: A genome-wide association scan of tag SNPs identifies a
susceptibility variant for colorectal cancer at 8q24.21. Nat Genet.
39:984–988. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Easton DF, Pooley KA, Dunning AM, Pharoah
PD, Thompson D, Ballinger DG, Struewing JP, Morrison J, Field H,
Luben R, et al: Genome-wide association study identifies novel
breast cancer susceptibility loci. Nature. 447:1087–1093. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhu LX, Ho SC and Wong TK: Effectiveness
of health education programs on exercise behavior among patients
with heart disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Evid
Based Med. 6:265–301. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|