Introduction
Crizotinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that has
antitumor activity against anaplastic lymphoma kinase
(ALK)-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
(1). However, crizotinib-associated
interstitial lung disease (ILD) has been reported as an infrequent
but potentially fatal complication (2,3).
Alectinib is a novel oral ALK inhibitor with high
potency and selectivity for ALK, which displays promising antitumor
activity in NSCLC. Alectinib has shown promising activity in
patients with crizotinib-resistant disease and has been generally
well-tolerated in clinical trials (4,5). The
safety of alectinib for patients who develop crizotinib-induced ILD
has not been determined. We herein describe a case of
ALK-positive NSCLC successfully treated with alectinib after
developing crizotinib-induced ILD.
Case report
A 63-year-old Japanese man with a 25 pack-year
smoking history presented with a 4-month history of cough. The
patient was diagnosed with advanced lung adenocarcinoma (cT4N3M1b),
with bone, brain and multiple lymph node metastases (Fig. 1A). Fluorescence in situ
hybridization analysis revealed the presence of ALK gene
rearrangement. Crizotinib (250 mg twice daily) was administered as
first-line chemotherapy. On day 27, the patient developed
high-grade fever and exertional dyspnea. Chest computed tomography
(CT) revealed a decrease in tumor size; however, there was new
extensive bilateral ground-glass opacity (GGO) and airspace
consolidation with traction bronchiectasis (Fig. 1B). With the patient on oxygen at a
flow rate of 5 l/min via a mask, the arterial blood gas analysis
revealed a PaO2 of 48.5 mmHg. Although the chest CT
revealed bilateral pleural effusions, there was no evidence of left
heart failure. There were also no signs of infection. Based on
these findings, crizotinib-induced ILD was suspected. Crizotinib
was discontinued immediately, and methylprednisolone pulse therapy
(1 g/day for 3 days) followed by oral prednisolone (PSL) at a dose
of 65 mg/day was initiated. Given that the patient's symptoms and
radiological findings improved, the PSL dose was gradually tapered.
Ten weeks after crizotinib was discontinued, the PSL dose was
decreased to 25 mg/day. The chest CT showed no recurrence of ILD,
but the primary lesion had regrown (Fig.
1C). After discussing the risk of ILD exacerbation and
obtaining the patient's informed consent, alectinib (300 mg twice
daily) was initiated. After 2 weeks, the primary lesion had
decreased in size, without any exacerbation of the ILD. The patient
received continuous alectinib treatment, with neither disease
progression nor recurrence of ILD for more than 4 months, without
the need for steroid therapy (Fig.
1D).
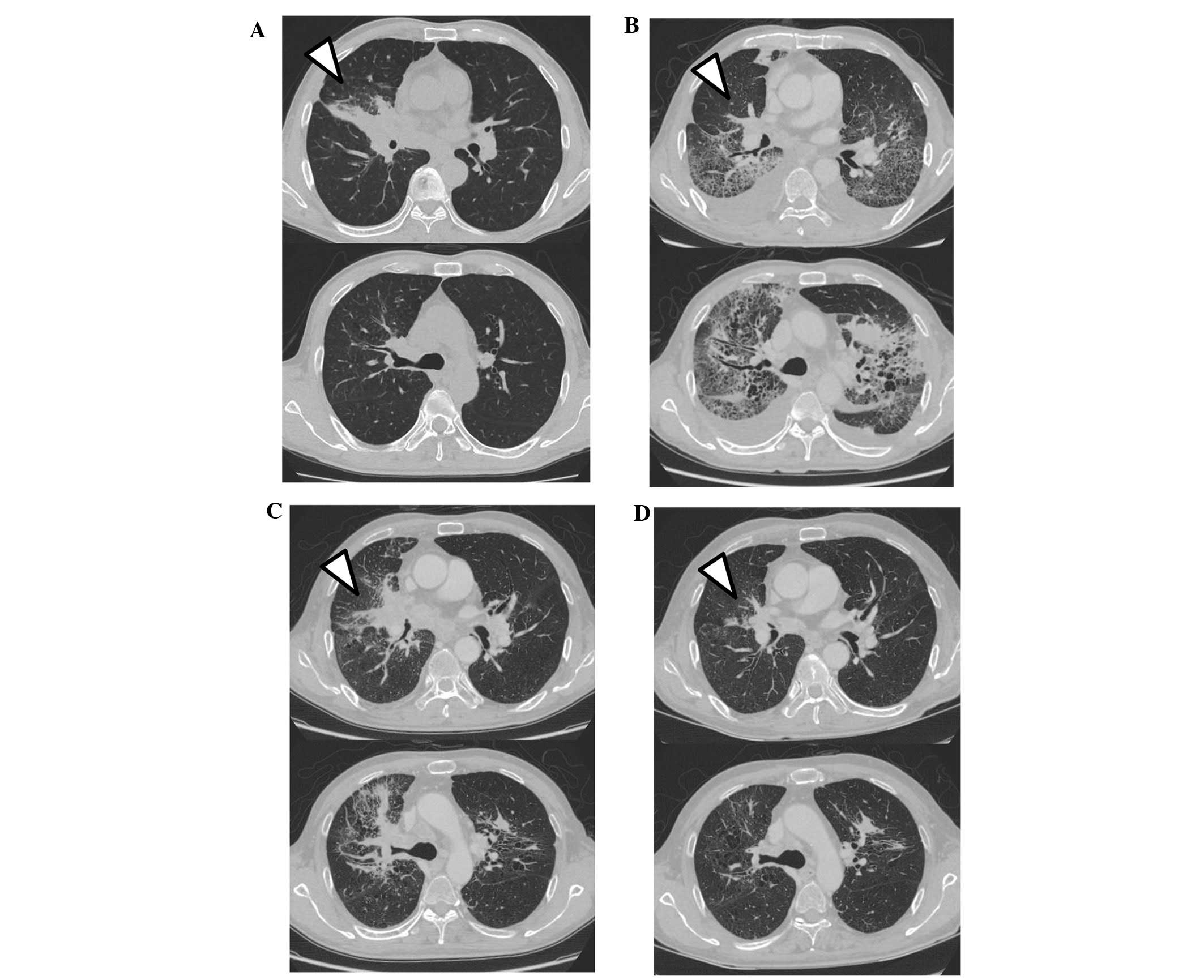 | Figure 1.(A) Prior to treatment with
crizotinib, chest CT revealed a mass in the middle lobe of the
right lung. (B) One month after initiation of crizotinib, the chest
CT revealed a decrease in the size of the tumor, but there was
extensive bilateral GGO, airspace consolidation with traction
bronchiectasis, and bilateral pleural effusion. (C) After treatment
with prednisolone and discontinuation of crizotinib, the chest CT
showed improvement of ILD, but also regrowth of the tumor. (D) Four
months after initiation of alectinib, CT showed good response
without recurrence of ILD. The tumor location is indicated by the
arrowheads. CT, computed tomography; GGO, ground-glass opacity;
ILD, interstitial lung disease. |
Discussion
Treatment with the first-generation ALK inhibitor
crizotinib is associated with a risk of ILD development. ILD, which
may be severe and occasionally fatal (2,3), develops
in 2% of the cases. Crizotinib-induced ILD may present with at
least two types of radiological findings, namely as the ‘diffuse
alveolar damage (DAD) pattern’ and the ‘hypersensitivity pneumonia
(HP) pattern’ (6). The DAD pattern is
severe and fatal in most cases. Chest CT shows a rapid, bilateral
and widespread development of GGO. The HP pattern is less severe
and may not be associated with a definitive need for crizotinib
withdrawal. Chest CT shows a predominant GGO pattern, which is
localized and faint. Some cases of successful crizotinib
retreatment after crizotinib-induced ILD have been reported, but
they all had the non-DAD pattern (6,7).
Retreatment with crizotinib should be avoided in patients with the
DAD pattern, as the mortality rate of such patients is very
high.
While crizotinib is a multitargeted inhibitor of the
ALK, MET, and ROS1 receptor tyrosine kinases (8,9), alectinib
is highly selective for ALK. The high selectivity for ALK may
contribute to its reduced toxicity compared with crizotinib
(4). We were able to successfully
treat our patient, who had developed a crizotinib-induced DAD
pattern of ILD, with alectinib. Therefore, alectinib may be
considered as an alternative agent in cases of crizotinib-induced
ILD, irrespective of the pattern of ILD, i.e., a DAD or non-DAD
pattern, with careful observation.
References
|
1
|
Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, Shaw AT,
Solomon B, Maki RG, Ou SH, Dezube BJ, Jänne PA, Costa DB, et al:
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1693–1703. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shaw AT, Kim DW, Nakagawa K, Seto T, Crinó
L, Ahn MJ, De Pas T, Besse B, Solomon BJ, Blackhall F, et al:
Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 368:2385–2394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tamiya A, Okamoto I, Miyazaki M, Shimizu
S, Kitaichi M and Nakagawa K: Severe acute interstitial lung
disease after crizotinib therapy in a patient with
EML4-ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol.
31:e15–e17. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Seto T, Kiura K, Nishio M, Nakagawa K,
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Hida T, Yamamoto N, Yoshioka H, Harada M, et
al: CH5424802 (RO5424802) for patients with ALK-rearranged advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer (AF-001JP study): A single-arm,
open-label, phase 1–2 study. Lancet Oncol. 14:590–598. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gadgeel SM, Gandhi L, Riely GJ, Chiappori
AA, West HL, Azada MC, Morcos PN, Lee RM, Garcia L, Yu L, et al:
Safety and activity of alectinib against systemic disease and brain
metastases in patients with crizotinib resistant ALK-rearranged
non-small-cell lung cancer (AF-002JG): Results from the
dose-finding portion of a phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol.
15:1119–1128. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Créquit P, Wislez M, Fleury Feith J,
Rozensztajn N, Jabot L, Friard S, Lavole A, Gounant V, Fillon J,
Antoine M and Cadranel J: Crizotinib associated with ground-glass
opacity predominant pattern interstitial lung disease: A
retrospective observational cohort study with a systematic
literature review. J Thorac Oncol. 10:1148–1155. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yanagisawa S, Inoue A, Koarai A, Ono M,
Tamai T and Ichinose M: Successful crizotinib retreatment after
crizotinib-induced interstitial lung disease. J Thorac Oncol.
8:e73–e74. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Christensen JG, Zou HY, Arango ME, Li Q,
Lee JH, McDonnell SR, Yamazaki S, Alton GR, Mroczkowski B and Los
G: Cytoreductive antitumor activity of PF-2341066, a novel
inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase and c-Met, in experimental
models of anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Mol Cancer Ther.
6:3314–3322. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bergethon K, Shaw AT, Ou SH, Katayama R,
Lovly CM, McDonald NT, Massion PP, Siwak-Tapp C, Gonzalez A, Fang
R, et al: ROS1 rearrangements define a unique molecular class of
lung cancers. J Clin Oncol. 30:863–870. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|















