Spandidos Publications style
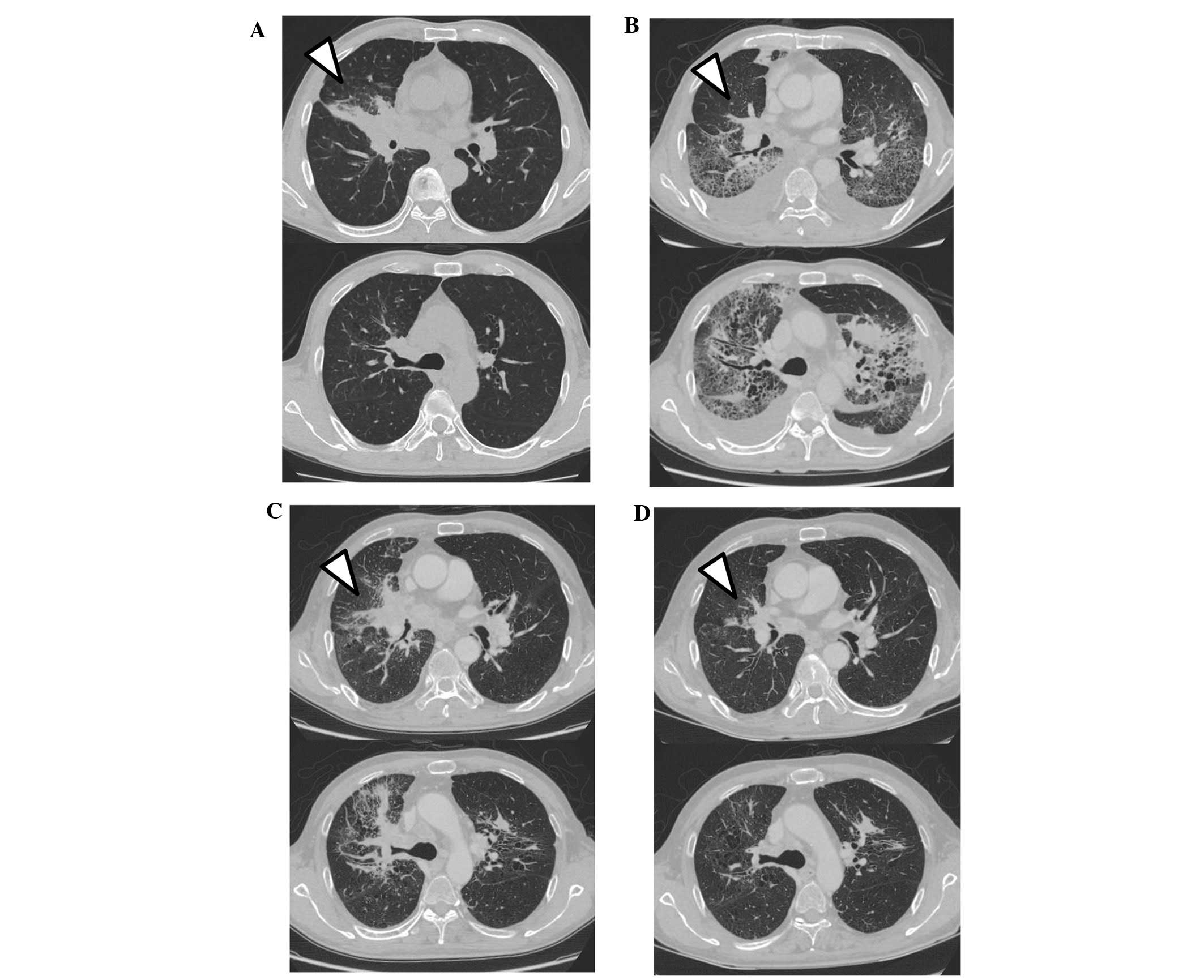
Nukaga S, Naoki K, Kamo T, Masuzawa K, Yasuda H, Soejima K and Betsuyaku T: Alectinib as a treatment option following recovery from crizotinib‑induced interstitial lung disease in patients with
anaplastic lymphoma kinase‑positive advanced non‑small‑cell lung cancer. Mol Clin Oncol 4: 1085-1087, 2016.
APA
Nukaga, S., Naoki, K., Kamo, T., Masuzawa, K., Yasuda, H., Soejima, K., & Betsuyaku, T. (2016). Alectinib as a treatment option following recovery from crizotinib‑induced interstitial lung disease in patients with
anaplastic lymphoma kinase‑positive advanced non‑small‑cell lung cancer. Molecular and Clinical Oncology, 4, 1085-1087. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2016.838
MLA
Nukaga, S., Naoki, K., Kamo, T., Masuzawa, K., Yasuda, H., Soejima, K., Betsuyaku, T."Alectinib as a treatment option following recovery from crizotinib‑induced interstitial lung disease in patients with
anaplastic lymphoma kinase‑positive advanced non‑small‑cell lung cancer". Molecular and Clinical Oncology 4.6 (2016): 1085-1087.
Chicago
Nukaga, S., Naoki, K., Kamo, T., Masuzawa, K., Yasuda, H., Soejima, K., Betsuyaku, T."Alectinib as a treatment option following recovery from crizotinib‑induced interstitial lung disease in patients with
anaplastic lymphoma kinase‑positive advanced non‑small‑cell lung cancer". Molecular and Clinical Oncology 4, no. 6 (2016): 1085-1087. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2016.838