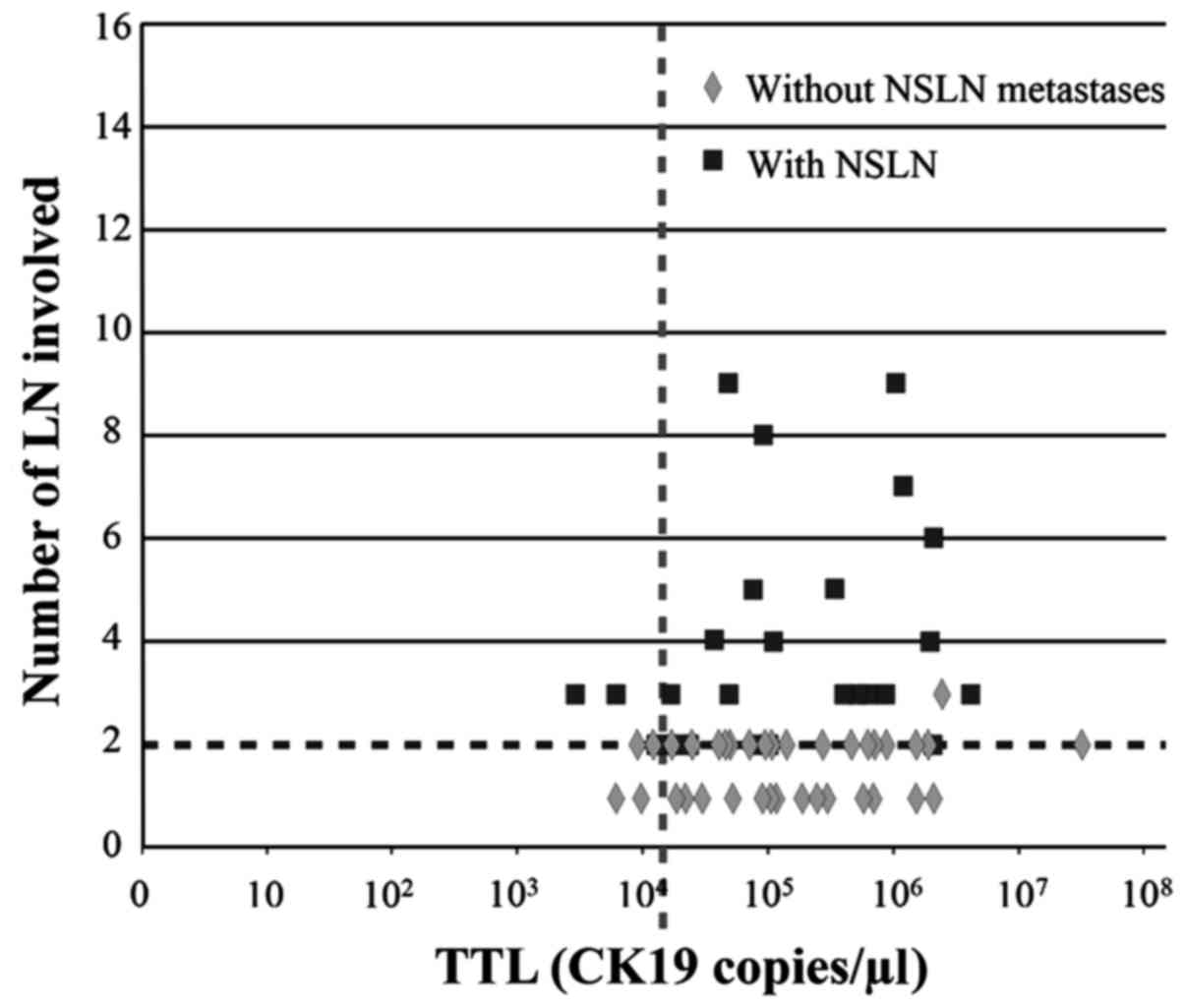
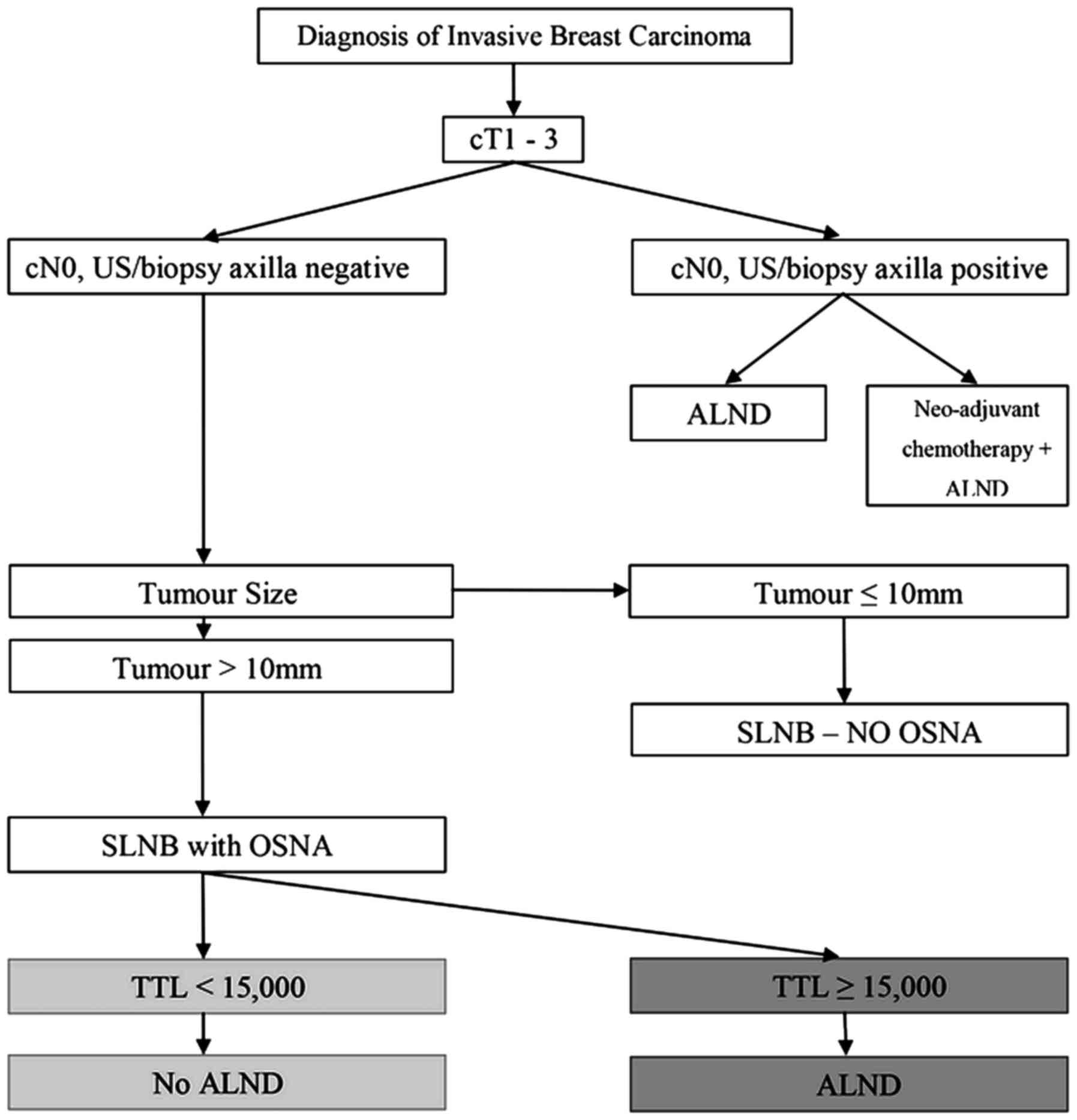
|
1
|
Krag DN, Anderson SJ, Julian TB, Brown AM,
Harlow SP, Costantino JP, Ashikaga T, Weaver DL, Mamounas EP,
Jalovec LM, et al: Sentinel-lymph-node resection compared with
conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in clinically
node-negative patients with breast cancer: Overall survival
findings from the NSABP B-32 randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet
Oncol. 11:927–933. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Galimberti V, Cole BF, Zurrida S, Viale G,
Luini A, Veronesi P, Baratella P, Chifu C, Sargenti M, Intra M, et
al: Axillary dissection versus no axillary dissection in patients
with sentinel-node micrometastases (IBCSG 23–01): A phase 3
randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 14:297–305. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Giuliano AE, Hunt KK, Ballman KV, Beitsch
PD, Whitworth PW, Blumencranz PW, Leitch AM, Saha S, McCall LM and
Morrow M: Axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection in women
with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: A
randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 305:569–575. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lyman GH, Temin S, Edge SB, Newman LA,
Turner RR, Weaver DL, Benson AB III, Bosserman LD, Burstein HJ,
Cody H III, et al: Sentinel lymph node biopsy for patients with
early-stage breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology
clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 32:1365–1383.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tsujimoto M, Nakabayashi K, Yoshidome K,
Kaneko T, Iwase T, Akiyama F, Kato Y, Tsuda H, Ueda S, Sato K, et
al: One-step nucleic acid amplification for intraoperative
detection of lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients. Clin
Cancer Res. 13:4807–4816. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Di Filippo F, Giannarelli D, Bouteille C,
Bernet L, Cano R, Cunnick G and Sapino A: Elaboration of a nomogram
to predict non sentinel node status in breast cancer patients with
positive sentinel node, intraoperatively assessed with one step
nucleic acid amplification method. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
34:1362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Peg V, Espinosa-Bravo M, Vieites B,
Vilardell F, Antúnez JR, de Salas MS, Delgado-Sánchez JJ, Pinto W,
Gozalbo F, Petit A, et al: Intraoperative molecular analysis of
total tumor load in sentinel lymph node: A new predictor of
axillary status in early breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 139:87–93. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
NHS Cancer Screening Programmes/Royal
College of Pathologists: Pathology Reporting of Breast Disease.
NHSBSP publication no. 58. 2005 http://www.cancerscreening.nhs.uk/breastscreen/publications/nhsbsp58.htmlAccessed.
May 21–2016.
|
|
9
|
Mansel RE, MacNeill F, Horgan K, Goyal A,
Britten A, Townson J, Clarke D, Newcombe RG, Keshtgar M Guildford
Breast Surgeons, et al: Results of a national training programme in
sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer. Br J Surg.
100:654–661. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Koca B, Kuru B, Ozen N, Yoruker S and Bek
Y: A breast cancer nomogram for prediction of non-sentinel node
metastasis-validation of fourteen existing models. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:1481–1488. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Glechner A, Wöckel A, Gartlehner G, Thaler
K, Strobelberger M, Griebler U and Kreienberg R: Sentinel lymph
node dissection only versus complete axillary lymph node dissection
in early invasive breast cancer: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. 49:812–825. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Straver ME, Meijnen P, van Tienhoven G,
van de Velde CJ, Mansel RE, Bogaerts J, Demonty G, Duez N,
Cataliotti L, Klinkenbijl J, et al: Role of axillary clearance
after a tumor-positive sentinel node in the administration of
adjuvant therapy in early breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 28:731–737.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nadeem RM, Gudur LD and Saidan ZA: An
independent assessment of the 7 nomograms for predicting the
probability of additional axillary nodal metastases after positive
sentinel lymph node biopsy in a cohort of British patients with
breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 14:272–279. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Meretoja TJ, Audisio RA, Heikkilä PS, Bori
R, Sejben I, Regitnig P, Luschin-Ebengreuth G, Zgajnar J, Perhavec
A, Gazic B, et al: International multicenter tool to predict the
risk of four or more tumour-positive axillary lymph nodes in breast
cancer patients with sentinel node macrometastases. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 138:817–827. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Katz A, Smith BL, Golshan M, Niemierko A,
Kobayashi W, Raad RA, Kelada A, Rizk L, Wong JS, Bellon JR, et al:
Nomogram for the prediction of having four or more involved nodes
for sentinel lymph node-positive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
26:2093–2098. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chagpar AB, Scoggins CR, Martin RC II,
Cook EF, McCurry T, Mizuguchi N, Paris KJ, Carlson DJ, Laidley AL,
El-Eid SE, et al: Predicting patients at low probability of
requiring post-mastectomy radiation therapy. Ann Surg Oncol.
14:670–677. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rivers AK, Griffith KA, Hunt KK, Degnim
AC, Sabel MS, Diehl KM, Cimmino VM, Chang AE, Lucas PC and Newman
LA: Clinicopathologic features associated with having four or more
metastatic axillary nodes in breast cancer patients with a positive
sentinel lymph node. Ann Surg Oncol. 13:36–44. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kubota M, Komoike Y, Hamada M, Shinzaki W,
Azumi T, Hashimoto Y, Imoto S, Takeyama Y and Okuno K: One-step
nucleic acid amplification assay for intraoperative prediction of
advanced axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer patients
with sentinel node metastasis. Mol Clin Oncol. 4:173–178. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Piñero-Madrona A, Ruiz-Merino G, Bernet L,
Miguel-Martínez B, Vicente-García F, Viguri-Díaz MA and
Giménez-Climent J: Tumoral load quantification of positive sentinel
lymph nodes in breast cancer to predict more than two involved
nodes. Breast. 23:859–864. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Intraoperative tests (RD-100i OSNA system
and Metasin test) for detecting sentinel lymph node metastases in
breast cancer. NICE diagnostics guidance 8. August;2013 http://www.nice.org.uk/dg8Accessed. May
21–2016.
|
|
21
|
Raia-Barjat T, Trombert B, Khaddage A,
Douchet C, Seffert P, Peoc'h M, Falk AT, Magné N and Chauleur C:
OSNA (one-step nucleic acid amplification) sentinel lymph node
intraoperative molecular analysis in breast cancer: A cost-benefit
analysis. Med Oncol. 31:3222014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Brambilla T, Fiamengo B, Tinterri C,
Testori A, Grassi MM, Sciarra A, Abbate T, Gatzemeier W, Roncalli M
and Di Tommaso L: One-step nucleic acid amplification in breast
cancer sentinel lymph node: A single institutional experience and a
short review. Front Med (Lausanne). 2:372015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Espinosa-Bravo M, Sansano I, Pérez-Hoyos
S, Ramos M, Sancho M, Xercavins J, Rubio IT and Peg V: Prediction
of non-sentinel lymph node metastasis in early breast cancer by
assessing total tumoral load in the sentinel lymph node by
molecular assay. Eur J Surg Oncol. 39:766–773. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ohi Y, Umekita Y, Sagara Y, Rai Y,
Yotsumoto D, Matsukata A, Baba S, Tamada S, Matsuyama Y, Ando M, et
al: Whole sentinel lymph node analysis by a molecular assay
predicts axillary node status in breast cancer. Br J Cancer.
107:1239–1243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Osako T, Iwase T, Kimura K, Horii R and
Akiyama F: Sentinel node tumour burden quantified based on
cytokeratin 19 mRNA copy number predicts non-sentinel node
metastases in breast cancer: Molecular whole-node analysis of all
removed nodes. Eur J Cancer. 49:1187–1195. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Giuliano A, Ballman K, McCall L, Beitsch
P, Whitworth PW, Blumencranz P, Leitch AM, Saha S, Morrow M and
Hunt KK: Locoregional recurrence after sentinel lymph node
dissection with or without axillary dissection in patients with
sentinel lymph node metastases: Long-term Follow-up From the
American College of Surgeons Oncology Group (Alliance) ACOSOG Z0011
Randomized Trial. Ann Surg. 264:413–420. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Peg V, Sansano I, Vieites B, Bernet L,
Cano R, Córdoba A, Sancho M, Martín MD, Vilardell F, Cazorla A, et
al: Role of total tumour load of sentinel lymph node on survival in
early breast cancer patients. Breast. 33:8–13. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Goyal A, Newcombe RG and Mansel RE:
Axillary Lymphatic Mapping Against Nodal Axillary Clearance
(ALMANAC) Trialists Group: Clinical relevance of multiple sentinel
nodes in patients with breast cancer. Br J Surg. 92:438–442. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fujisue M, Nishimura R, Okumura Y, Tashima
R, Nishiyama Y, Osako T, Toyozumi Y and Arima N: Clinical
significance of CK19 negative breast cancer. Cancers (Basel).
5:1–11. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vilardell F, Novell A, Martin J, Santacana
M, Velasco A, Díez-Castro MJ, Cuevas D, Panadés MJ, González S,
Llombart A, et al: Importance of assessing CK19 immunostaining in
core biopsies in patients subjected to sentinel node study by OSNA.
Virchows Arch. 460:569–575. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tamaki Y: One-step nucleic acid
amplification assay (OSNA) for sentinel lymph node biopsy. Breast
Cancer. 22:230–234. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Alvarenga CA, Paravidino PI, Alvarenga M,
Dufloth R, Gomes M, Zeferino LC and Schmitt F: Expression of CK19
in invasive breast carcinomas of special histological types:
Implications for the use of one-step nucleic acid amplification. J
Clin Pathol. 64:493–497. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pegolo E, Puppin C, Gerometta A, Damante
G, Puglisi F and Di Loreto C: One-step nucleic acid amplification
(OSNA) for intraoperative evaluation of sentinel lymph node status
in breast cancer: A comparative study between CK19 protein
expression and CK19 mRNA level in primary tumors and lymph node
metastasis. Virchows Arch. 463:7–15. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shah-Khan M and Boughey JC: Evolution of
axillary node staging in breast cancer: Clinical implications of
the ACOSOG Z0011 trial. Cancer Control. 19:267–276. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kohrt HE, Olshen RA, Bermas HR, Goodson
WH, Wood DJ, Henry S, Rouse RV, Bailey L, Philben VJ, Dirbas FM, et
al: New models and online calculator for predicting non-sentinel
lymph node status in sentinel node positive breast cancer patients.
BMC Cancer. 8:662008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Goyal A, Newcombe RG, Chhabra A and Mansel
RE: ALMANAC Trialists Group: Factors affecting failed localisation
and false-negative rates of sentinel node biopsy in breast
cancer--results of the ALMANAC validation phase. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 99:203–208. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bergkvist L, de Boniface J, Jönsson PE,
Ingvar C, Liljegren G and Frisell J: Swedish Society of Breast
Surgeons: Axillary recurrence rate after negative sentinel node
biopsy in breast cancer: Three year follow-up of the Swedish
multicenter cohort study. Ann Surg. 247:150–156. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mansel RE, Fallowfield L, Kissin M, Goyal
A, Newcombe RG, Dixon JM, Yiangou C, Horgan K, Bundred N, Monypenny
I, et al: Randomized multicenter trial of sentinel node biopsy
versus standard axillary treatment in operable breast cancer: The
ALMANAC trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 98:599–609. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Langer I, Guller U, Berclaz G, Koechli OR,
Schaer G, Fehr MK, Hess T, Oertli D, Bronz L, Schnarwyler B, et al:
Morbidity of sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLN) alone versus SLN and
completion axillary lymph node dissection after breast cancer
surgery: A prospective Swiss multicenter study on 659 patients. Ann
Surg. 245:452–461. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Martín-Sánchez E, Pernaut-Leza E, Mendaza
S, Cordoba A, Vicente-Garcia F, Monreal-Santesteban I, Vizcaino JP,
De Cerio MJ, Perez-Janices N, Blanco-Luquin I, et al: Gene promoter
hypermethylation is found in sentinel lymph nodes of breast cancer
patients, in samples identified as positive by one-step nucleic
acid amplification of cytokeratin 19 mRNA. Virchows Arch.
469:51–59. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|