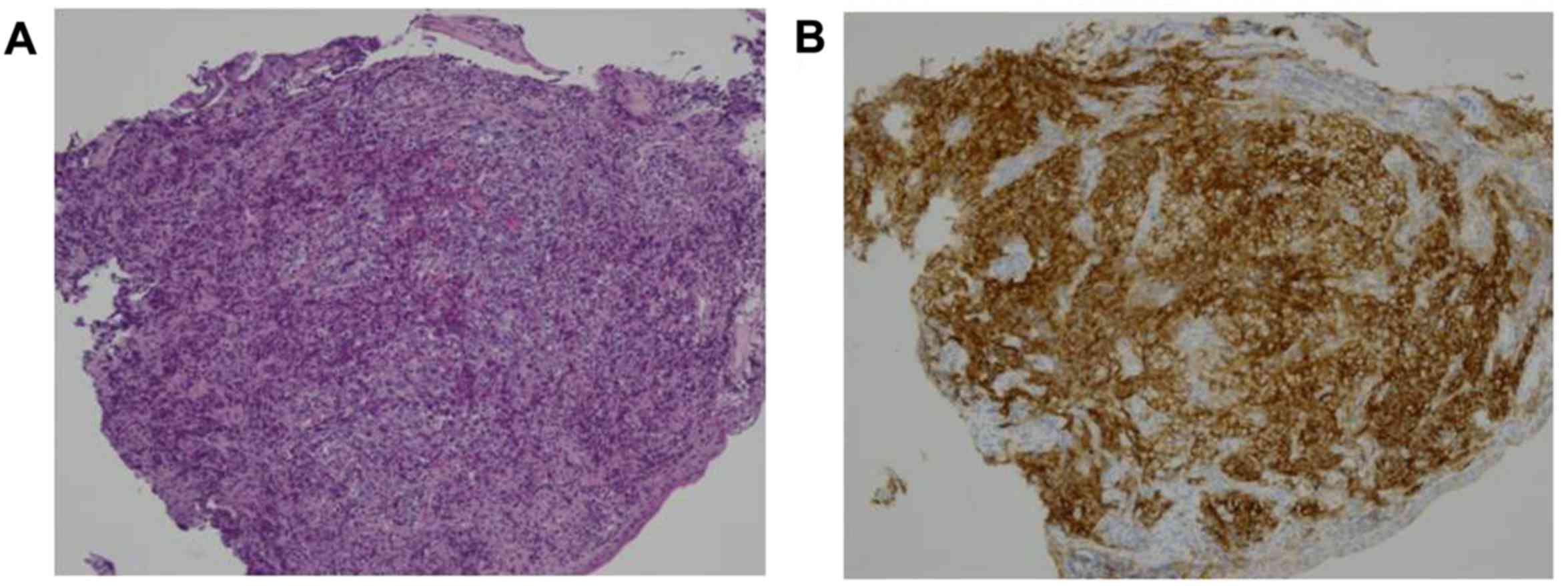
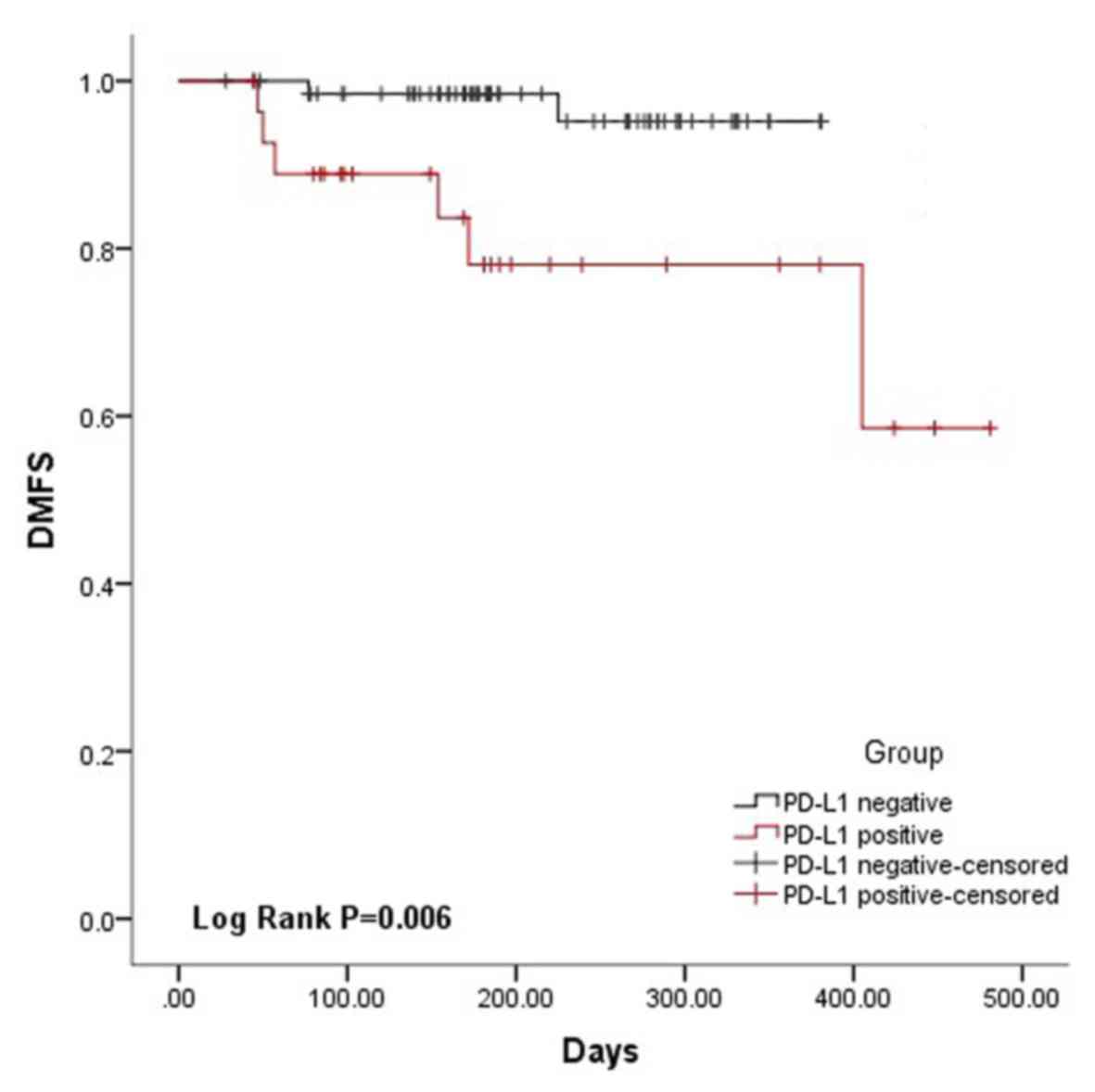
|
1
|
Chang ET and Adami HO: The enigmatic
epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark
Prev. 15:1765–1777. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lee AW, Ma BB, Ng WT and Chan AT:
Management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Current practice and future
perspective. J Clin Oncol. 33:3356–3364. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chua MLK, Wee JTS, Hui EP and Chan ATC:
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 387:1012–1024. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Seliger B, Marincola FM, Ferrone S and
Abken H: The complex role of B7 molecules in tumor immunology.
Trends Mol Med. 14:550–559. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
del Rio ML, Buhler L, Gibbons C, Tian J
and Rodriguez-Barbosa JI: PD-1/PD-L1, PD-1/PD-L2, and other
co-inhibitory signaling pathways in transplantation. Transpl Int.
21:1015–1028. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Day CL, Kaufmann DE, Kiepiela P, Brown JA,
Moodley ES, Reddy S, Mackey EW, Miller JD, Leslie AJ, DePierres C,
et al: PD-1 expression on HIV-specific T cells is associated with
T-cell exhaustion and disease progression. Nature. 443:350–354.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Balar AV and Weber JS: PD-1 and PD-L1
antibodies in cancer: Current status and future directions. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 66:551–564. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin X, Gudgeon NH, Hui EP, Jia H, Qun X,
Taylor GS, Barnardo MC, Lin CK, Rickinson AB and Chan AT: CD4 and
CD8 T cell responses to tumour-associated Epstein-Barr virus
antigens in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 57:963–975. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lo YM, Chan LY, Lo KW, Leung SF, Zhang J,
Chan AT, Lee JC, Hjelm NM, Johnson PJ and Huang DP: Quantitative
analysis of cell-free Epstein-Barr virus DNA in plasma of patients
with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 59:1188–1191.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li J, Huang ZF, Xiong G, Mo HY, Qiu F, Mai
HQ, Chen QY, He J, Chen SP, Zheng LM, et al: Distribution,
characterization, and induction of CD8+regulatory T
cells and IL-17-producing CD8+T cells in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. J Transl Med. 9:1892011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin DC, Meng X, Hazawa M, Nagata Y, Varela
AM, Xu L, Sato Y, Liu LZ, Ding LW, Sharma A, et al: The genomic
landscape of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nat Genet. 46:866–871. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Tesniere A,
Obeid M, Ortiz C, Criollo A, Mignot G, Maiuri MC, Ullrich E,
Saulnier P, et al: Toll-like receptor 4-dependent contribution of
the immune system to anticancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Nat
Med. 13:1050–1059. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen L and Flies DB: Molecular mechanisms
of T cell co-stimulation and co-inhibition. Nat Rev Immunol.
13:227–242. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lim DY, Tanaka Y, Iwasaki M, Gittis AG, Su
HP, Mikami B, Okazaki T, Honjo T, Minato N and Garboczi DN: The
PD-1/PD-L1 complex resembles the antigen-binding Fv domains of
antibodies and T cell receptors. Proe Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:3011–3016. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chang DY, Song SH, You S, Lee J, Kim J,
Racanelli V, Son H and Shin EC: Programmed death-1 (PD-1)-dependent
functional impairment of CD4(+T cells in recurrent
genital papilloma. Clin Exp Med. 14:305–313. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Muenst S, Schaerli AR, Gao F, Däster S,
Trella E, Droeser RA, Muraro MG, Zajac P, Zanetti R, Gillanders WE,
et al: Expression of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) is
associated with poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 146:15–24. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Frigola X, Inman BA, Lohse CM, Krco CJ,
Cheville JC, Houston TR, Leibovich B, Blute ML, Dong H and Kwon ED:
Identification of a soluble form of B7-H1 that retains
immunosuppressive activity and is associated with aggressive renal
cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1915–1923. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Maine CJ, Aziz NH, Chatterjee J, Hayford
C, Brewig N, Whilding L, George AJ and Ghaem-Maghami S: Programmed
death ligand-1 over-expression correlates with malignancy and
contributes to immune regulation in ovarian cancer. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 63:215–224. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Azuma K, Ota K, Kawahara A, Hattori S,
Iwama E, Harada T, Matsumoto K, Takayama K, Takamori S, Kage M, et
al: Association of PD-L1 overexpression with activating EGFR
mutations in surgically resected nonsmall-cell lung cancer. Ann
Oncol. 25:1935–1940. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peng H, Zhong BL, Li YM, Wang GM and Chen
YY: Expression and significance of costimulatory molecule PD-L1 in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Trop Med. 12:1367–1368. 2012.
|
|
21
|
Shi SJ, Wang LJ, Wang GD, Guo ZY, Wei M,
Meng YL, Yang AG and Wen WH: B7-H1 expression is associated with
poor prognosis in colorectal carcinoma and regulates the
proliferation and invasion of HCT116 colorectal cancer cells. PLoS
One. 8:e760122013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nomi T, Sho M, Akahori T, Hamada K, Kubo
A, Kanehiro H, Nakamura S, Enomoto K, Yagita H, Azuma M and
Nakajima Y: Clinical significance and therapeutic potential of the
programmed death-1 ligand/programmed death-1 pathway in human
pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2151–2157. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li YF, Ding JW, Liao LM, Zhang ZL, Liao
SS, Wu Y, Zhou DY, Liu AW and Huang L: Expression of programmed
death ligand-1 predicts poor outcome in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Mol Clin Oncol. 7:378–382. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Song Y, Xiao H, Yang Z, Geng M, Ma J, Ren
Y, Liu Y and Wang G: The predictive value of pre- and
post-induction chemotherapy plasma EBV DNA level and tumor volume
for the radiosensitivity of locally advanced nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. EXCLI J. 16:1268–1275. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR,
Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD,
Sosman JA, Atkins MB, et al: Safety, activity, and immune
correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med.
366:2443–2454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hamid O, Robert C, Daud A, Hodi FS, Hwu
WJ, Kefford R, Wolchok JD, Hersey P, Joseph RW, Weber JS, et al:
Safety and tumor responses with lambrolizumab (anti-PD-1) in
melanoma. N Engl J Med. 369:134–144. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQ, Hwu WJ,
Topalian SL, Hwu P, Drake CG, Camacho LH, Kauh J, Odunsi K, et al:
Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with
advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:2455–2465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|