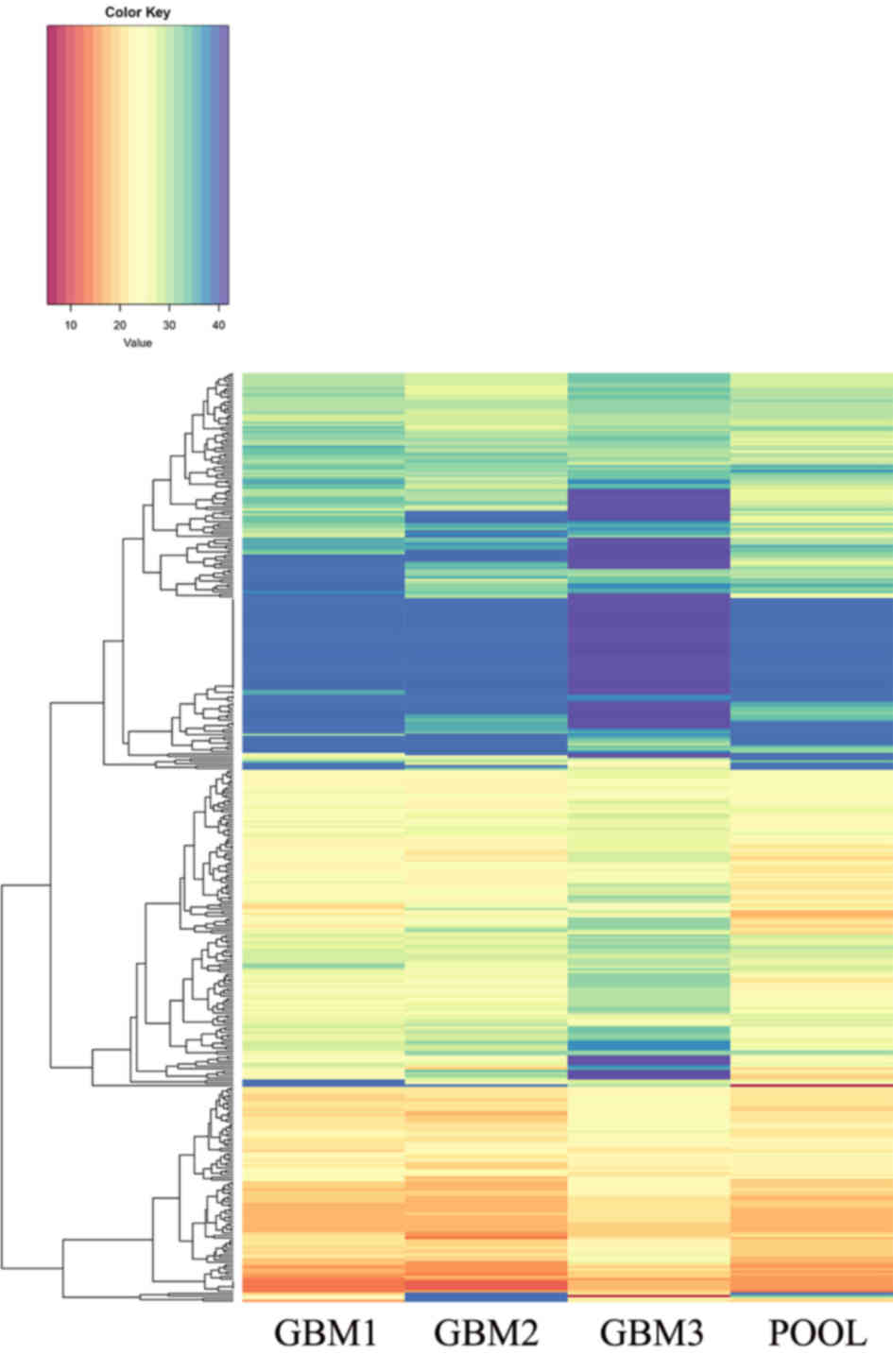
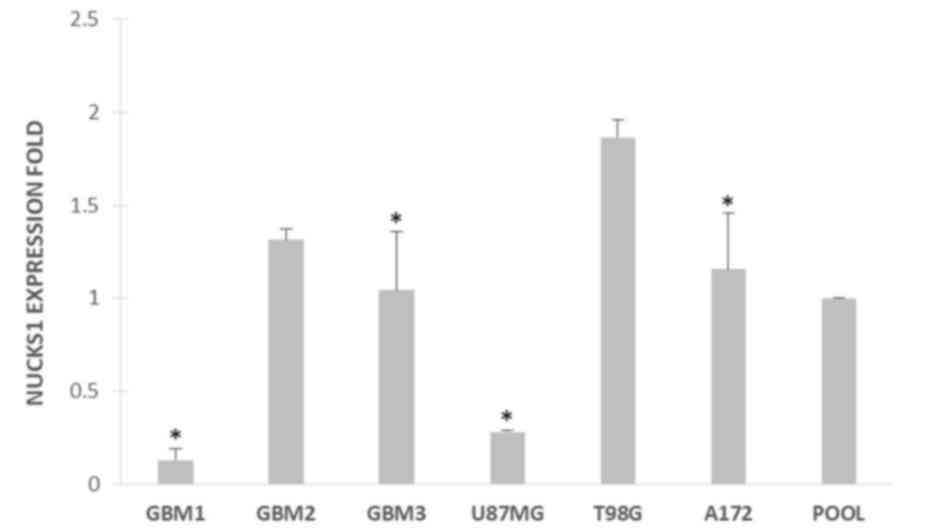
|
1
|
Pollack IF, Hamilton RL, James CD,
Finkelstein SD, Burnham J, Yates AJ, Holmes EJ, Zhou T and Finlay
JL: Children's Oncology Group: Rarity of PTEN deletions and EGFR
amplification in malignant gliomas of childhood: Results from the
Children's Cancer Group 945 cohort. J Neurosurg. 105 Suppl
5:S418–S424. 2006.
|
|
2
|
Pollack IF, Finkelstein SD, Woods J,
Burnham J, Holmes EJ, Hamilton RL, Yates AJ, Boyett JM, Finlay JL
and Sposto R: Children's Cancer Group: Expression of p53 and
prognosis in children with malignant gliomas. N Engl J Med.
346:420–427. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pollack IF, Boyett JM, Yates AJ, Burger
PC, Gilles FH, Davis RL and Finlay JL: Children's Cancer Group: The
influence of central review on outcome associations in childhood
malignant gliomas: Results from the CCG-945 experience. Neuro
Oncol. 5:197–207. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ganigi PM, Santosh V, Anandh B,
Chandramouli BA and Sastry Kolluri VR: Expression of p53, EGFR, pRb
and bcl-2 proteins in pediatric glioblastoma multiforme: A study of
54 patients. Pediatr Neurosurg. 41:292–299. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nakamura M, Shimada K, Ishida E, Higuchi
T, Nakase H, Sakaki T and Konishi N: Molecular pathogenesis of
pediatric astrocytic tumors. Neuro Oncol. 9:113–123. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ohgaki H, Dessen P, Jourde B, Horstmann S,
Nishikawa T, Di Patre PL, Burkhard C, Schüler D, Probst-Hensch NM,
Maiorka PC, et al: Genetic pathways to glioblastoma: A
population-based study. Cancer Res. 64:6892–6899. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Di Sapio A, Morra I, Pradotto L, Guido M,
Schiffer D and Mauro A: Molecular genetic changes in a series of
neuroepithelial tumors of childhood. J Neurooncol. 59:117–122.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bredel M, Pollack IF, Hamilton RL and
James CD: Epidermal growth factor receptor expression and gene
amplification in high-grade non-brainstem gliomas of childhood.
Clin Cancer Res. 5:1786–1792. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kraus JA, Felsberg J, Tonn JC,
Reifenberger G and Pietsch T: Molecular genetic analysis of the
TP53, PTEN, CDKN2A, EGFR, CDK4 and MDM2 tumour-associated genes in
supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumours and glioblastomas
of childhood. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 28:325–333. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Visone R and Croce CM: MiRNAs and cancer.
Am J Pathol. 174:1131–1138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Munoz JL, Walker ND, Scotto KW and
Rameshwar P: Temozolomide competes for P-glycoprotein and
contributes to chemoresistance in glioblastoma cells. Cancer Lett.
367:69–75. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun C, Li N, Yang Z, Zhou B, He Y, Weng D,
Fang Y, Wu P, Chen P, Yang X, et al: miR-9 regulation of BRCA1 and
ovarian cancer sensitivity to cisplatin and PARP inhibition. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 105:1750–1758. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shen R, Wang Y, Wang CX, Yin M, Liu HL,
Chen JP, Han JQ and Wang WB: MiRNA-155 mediates TAM resistance by
modulating SOCS6-STAT3 signalling pathway in breast cancer. Am J
Transl Res. 7:2115–2126. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dong Z, Ren L, Lin L and Li J, Huang Y and
Li J: Effect of microRNA-21 on multidrug resistance reversal in
A549/DDP human lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 11:682–690. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Blower PE, Chung JH, Verducci JS, Lin S,
Park JK, Dai Z, Liu CG, Schmittgen TD, Reinhold WC, Croce CM, et
al: MicroRNAs modulate the chemosensitivity of tumor cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 7:1–9. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
González-Gómez P, Sánchez P and Mira H:
MicroRNAs as regulators of neural stem cell-related pathways in
glioblastoma multiforme. Mol Neurobiol. 44:235–249. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Berindan-Neagoe I, Monroig Pdel C,
Pasculli B and Calin GA: MicroRNAome genome: A treasure for cancer
diagnosis and therapy. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:311–336. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rajewsky N and Socci ND: Computational
identification of microRNA targets. Dev Biol. 267:529–535. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hummel R, Maurer J and Haier J: MicroRNAs
in brain tumors: A new diagnostic and therapeutic perspective? Mol
Neurobiol. 44:223–234. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M
and Croce CM: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at
fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fabbri M, Ivan M, Cimmino A, Negrini M and
Calin GA: Regulatory mechanisms of microRNAs involvement in cancer.
Expert Opin Biol Ther. 7:1009–1019. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Møller HG, Rasmussen AP, Andersen HH,
Johnsen KB, Henriksen M and Duroux M: A systematic review of
microRNA in glioblastoma multiforme: Micro-modulators in the
mesenchymal mode of migration and invasion. Mol Neurobiol.
47:131–144. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shea A, Harish V, Afzal Z, Chijioke J,
Kedir H, Dusmatova S, Roy A, Ramalinga M, Harris B, Blancato J, et
al: MicroRNAs in glioblastoma multiforme pathogenesis and
therapeutics. Cancer Med. 5:1917–1946. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ahir BK, Ozer H, Engelhard HH and Lakka
SS: MicroRNAs in glioblastoma pathogenesis and therapy: A
comprehensive review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 120:22–33. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ciafrè SA, Galardi S, Mangiola A, Ferracin
M, Liu CG, Sabatino G, Negrini M, Maira G, Croce CM and Farace MG:
Extensive modulation of a set of microRNAs in primary glioblastoma.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 334:1351–1358. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM and Kosik KS:
MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells.
Cancer Res. 65:6029–6033. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Silber J, Lim DA, Petritsch C, Persson AI,
Maunakea AK, Yu M, Vandenberg SR, Ginzinger DG, James CD, Costello
JF, et al: miR-124 and miR-137 inhibit proliferation of
glioblastoma multiforme cells and induce differentiation of brain
tumor stem cells. BMC Med. 6:142008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Godlewski J, Nowicki MO, Bronisz A,
Williams S, Otsuki A, Nuovo G, Raychaudhury A, Newton HB, Chiocca
EA and Lawler S: Targeting of the Bmi-1 oncogene/stem cell renewal
factor by microRNA-128 inhibits glioma proliferation and
self-renewal. Cancer Res. 68:9125–9130. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lawler S and Chiocca EA: Emerging
functions of microRNAs in glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 92:297–306.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Birks DK, Barton VN, Donson AM, Handler
MH, Vibhakar R and Foreman NK: Survey of MicroRNA expression in
pediatric brain tumors. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 56:211–216. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Miele E, Buttarelli FR, Arcella A, Begalli
F, Garg N, Silvano M, Po A, Baldi C, Carissimo G, Antonelli M, et
al: High-throughput microRNA profiling of pediatric high-grade
gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 16:228–240. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Braunstein S, Raleigh D, Bindra R, Mueller
S and Haas-Kogan D: Pediatric high-grade glioma: Current molecular
landscape and therapeutic approaches. J Neurooncol. 134:541–549.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Massimino M, Gandola L, Luksch R,
Spreafico F, Riva D, Solero C, Giangaspero F, Locatelli F, Podda M,
Bozzi F, et al: Sequential chemotherapy, high-dose thiotepa,
circulating progenitor cell rescue and radiotherapy for childhood
high-grade glioma. Neuro Oncol. 7:41–48. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Biassoni V, Casanova M, Spreafico F,
Gandola L and Massimino M: A case of relapsing glioblastoma
multiforme responding to vinorelbine. J Neurooncol. 80:195–201.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dvinge H and Bertone P: HTqPCR:
High-throughput analysis and visualization of quantitative
real-time PCR data in R. Bioinformatics. 25:3325–3326. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
R Development Core Team R: A language and
environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical
Computing; Vienna, Austria: ISBN 3-900051-07-0. http://www.R-project.org2008
|
|
42
|
Enright AJ, John B, Gaul U, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: MicroRNA targets in drosophila. Genome Biol.
5:R12003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene
Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
The Gene Ontology Consortium: Expansion of
the gene ontology knowledgebase and resources. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:D331–D338. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M, Sato Y
and Morishima K: KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways,
diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:D353–D361. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Kawashima M, Furumichi
M and Tanabe M: KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein
annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:D457–D462. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Whitfield ML, Sherlock G, Saldanha AJ,
Murray JI, Ball CA, Alexander KE, Matese JC, Perou CM, Hurt MM,
Brown PO and Botstein D: Identification of genes periodically
expressed in the human cell cycle and their expression in tumors.
Mol Biol Cell. 13:1977–2000. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Drosos Y, Kouloukoussa M, Østvold AC,
Grundt K, Goutas N, Vlachodimitropoulos D, Havaki S, Kollia P,
Kittas C, Marinos E and Aleporou-Marinou V: NUCKS overexpression in
breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 9:192009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Walaas SI, Ostvold AC and Laland SG:
Phosphorylation of P1, a high mobility group-like protein,
catalyzed by casein kinase II protein kinase C, cyclic
AMP-dependent protein kinase and calcium/calmodulin-dependent
protein kinase II. FEBS Lett. 258:106–108. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ostvold AC, Norum JH, Mathiesen S, Wanvik
B, Sefland I and Grundt K: Molecular cloning of a mammalian nuclear
phosphoprotein NUCKS, which serves as a substrate for Cdk1 in vivo.
Eur J Biochem. 268:2430–2440. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Meijer L, Ostvold AC, Walass SI, Lund T
and Laland SG: High-mobility-group proteins P1, I and Y as
substrates of the M-phase-specific p34cdc2/cyclincdc13 kinase. Eur
J Biochem. 196:557–567. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Parplys AC, Zhao W, Sharma N, Groesser T,
Liang F, Maranon DG, Leung SG, Grundt K, Dray E, Idate R, et al:
NUCKS1 is a novel RAD51AP1 paralog important for homologous
recombination and genome stability. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:9817–9834. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kikuchi A, Ishikawa T, Mogushi K, Ishiguro
M, Iida S, Mizushima H, Uetake H, Tanaka H and Sugihara K:
Identification of NUCKS1 as a colorectal cancer prognostic marker
through integrated expression and copy number analysis. Int J
Cancer. 132:2295–2302. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Gu L, Xia B, Zhong L, Ma Y, Liu L, Yang L
and Lou G: NUCKS1 overexpression is a novel biomarker for
recurrence-free survival in cervical squamous cell carcinoma.
Tumour Biol. 35:7831–7836. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cheong JY, Kim YB, Woo JH, Kim DK, Yeo M,
Yang SJ, Yang KS, Soon SK, Wang HJ, Kim BW, et al: Identification
of NUCKS1 as a putative oncogene and immunodiagnostic marker of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Gene. 584:47–53. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Balcárková J, Urbánková H, Scudla V,
Holzerová M, Bacovský J, Indrák K and Jarosová M: Gain of
chromosome arm 1q in patients in relapse and progression of
multiple myeloma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 192:68–72. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Szponar A, Zubakov D, Pawlak J, Jauch A
and Kovacs G: Three genetic developmental stages of papillary renal
cell tumors: Duplication of chromosome 1q marks fatal progression.
Int J Cancer. 124:2071–2076. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Giunti L, Pantaleo M, Sardi I, Provenzano
A, Magi A, Cardellicchio S, Castiglione F, Tattini L, Novara F,
Buccoliero AM, et al: Genome-wide copy number analysis in pediatric
glioblastoma multiforme. Am J Cancer Res. 4:293–303.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Faria C, Miguéns J, Antunes JL, Salgado D,
Nunes S, Barroso C, Martins Mdo C, Nunes VM and Roque L: Pediatric
brain tumors: Genetics and clinical outcome. J Neurosurg Pediatr.
5:263–270. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hirose Y, Aldape K, Bollen A, James CD,
Brat D, Lamborn K, Berger M and Feuerstein BG: Chromosomal
abnormalities subdivide ependymal tumors into clinically relevant
groups. Am J Pathol. 158:1137–1143. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Lo KC, Ma C, Bundy BN, Pomeroy SL,
Eberhart CG and Cowell JK: Gain of 1q is a potential univariate
negative prognostic marker for survival in medulloblastoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 13:7022–7028. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Shen H, Wang L, Ge X, Jiang CF, Shi ZM, Li
DM, Liu WT, Yu X and Shu YQ: MicroRNA-137 inhibits tumor growth and
sensitizes chemosensitivity to paclitaxel and cisplatin in lung
cancer. Oncotarget. 7:20728–20742. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yang Y, Li F, Saha MN, Abdi J, Qiu L and
Chang H: miR-137 and miR-197 induce apoptosis and suppress
tumorigenicity by targeting MCL-1 in multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer
Res. 21:2399–2411. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Liu LL, Lu SX, Li M, Li LZ, Fu J, Hu W,
Yang YZ, Luo RZ, Zhang CZ and Yun JP: FoxD3-regulated microRNA-137
suppresses tumour growth and metastasis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma by targeting AKT2. Oncotarget. 5:5113–5124. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Chen DL, Wang DS, Wu WJ, Zeng ZL, Luo HY,
Qiu MZ, Ren C, Zhang DS, Wang ZQ, Wang FH, et al: Overexpression of
paxillin induced by miR-137 suppression promotes tumor progression
and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 34:803–811.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhu X, Li Y, Shen H, Li H, Long L, Hui L
and Xu W: miR-137 inhibits the proliferation of lung cancer cells
by targeting Cdc42 and Cdk6. FEBS Lett. 587:73–81. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Chen L, Wang X, Wang H, Li Y, Yan W, Han
L, Zhang K, Zhang J, Wang Y, Feng Y, et al: miR-137 is frequently
down-regulated in glioblastoma and is a negative regulator of
Cox-2. Eur J Cancer. 48:3104–3111. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Bier A, Giladi N, Kronfeld N, Lee HK,
Cazacu S, Finniss S, Xiang C, Poisson L, deCarvalho AC, Slavin S,
et al: MicroRNA-137 is downregulated in glioblastoma and inhibits
the stemness of glioma stem cells by targeting RTVP-1. Oncotarget.
4:665–676. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Giunti L, da Ros M, Vinci S, Gelmini S,
Iorio AL, Buccoliero AM, Cardellicchio S, Castiglione F, Genitori
L, de Martino M, et al: Anti-miR21 oligonucleotide enhances
chemosensitivity of T98G cell line to doxorubicin by inducing
apoptosis. Am J Cancer Res. 5:231–242. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Li D, Shan W, Fang Y, Wang P and Li J:
miR-137 acts as a tumor suppressor via inhibiting CXCL12 in human
glioblastoma. Oncotarget. 8:101262–101270. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Chen W, Ye L, Wen D and Chen F: miR-490-5p
inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and
invasion by directly regulating ROBO1. Pathol Oncol Res. Sep
19–2017.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
74
|
Xu B, Xu T, Liu H, Min Q, Wang S and Song
Q: miR-490-5p suppresses cell proliferation and invasion by
targeting BUB1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Pharmacology.
100:269–282. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Tang B, Liu C, Zhang QM and Ni M:
Decreased expression of miR-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical
significance. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:246–251.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Li J, Feng Q, Wei X and Yu Y: MicroRNA-490
regulates lung cancer metastasis by targeting poly r(C)-binding
protein 1. Tumour Biol. 37:15221–15228. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Tian J, Xu YY, Li L and Hao Q: miR-490-3p
sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin by directly targeting
ABCC2. Am J Transl Res. 9:1127–1138. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Wu X, Yan L, Liu Y, Xian W, Wang L and
Ding X: MicroRNA-448 suppresses osteosarcoma cell proliferation and
invasion through targeting EPHA7. PLoS One. 12:e01755532017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zhu H, Zhou X, Ma C, Chang H, Li H, Liu F
and Lu J: Low expression of miR-448 induces EMT and promotes
invasion by regulating ROCK2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 36:487–498. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Lv Y, Lei Y, Hu Y, Ding W, Zhang C and
Fang C: miR-448 negatively regulates ovarian cancer cell growth and
metastasis by targeting CXCL12. Clin Transl Oncol. 17:903–909.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Bamodu OA, Huang WC, Lee WH, Wu A, Wang
LS, Hsiao M, Yeh CT and Chao TY: Aberrant KDM5B expression promotes
aggressive breast cancer through MALAT1 overexpression and
downregulation of hsa-miR-448. BMC Cancer. 16:1602016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Correia NC, Melão A, Póvoa V, Sarmento L,
Gómez de Cedrón M, Malumbres M, Enguita FJ and Barata JT: microRNAs
regulate TAL1 expression in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Oncotarget. 7:8268–8281. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Powrózek T, Krawczyk P, Kowalski DM,
Kuźnar-Kamińska B, Winiarczyk K, Olszyna-Serementa M,
Batura-Gabryel H and Milanowski J: Application of plasma
circulating microRNA-448, 506, 4316, and 4478 analysis for
non-invasive diagnosis of lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:2049–2055.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Hara N, Kikuchi M, Miyashita A, Hatsuta H,
Saito Y, Kasuga K, Murayama S, Ikeuchi T and Kuwano R: Serum
microRNA miR-501-3p as a potential biomarker related to the
progression of Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol Commun.
5:102017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Ling Q, Xu X, Ye P, Xie H, Gao F, Hu Q,
Liu Z, Wei X, Röder C, Trauzold A, et al: The prognostic relevance
of primary tumor location in patients undergoing resection for
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:15159–15167. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Jiang X, Wang W, Yang Y, Du L, Yang X,
Wang L, Zheng G, Duan W, Wang R, Zhang X, et al: Identification of
circulating microRNA signatures as potential noninvasive biomarkers
for prediction and prognosis of lymph node metastasis in gastric
cancer. Oncotarget. 8:65132–65142. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Huang Y, Liao D, Pan L, Ye R, Li X, Wang
S, Ye C and Chen L: Expressions of miRNAs in papillary thyroid
carcinoma and their associations with the BRAFV600E mutation. Eur J
Endocrinol. 168:675–681. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Paydas S, Acikalin A, Ergin M, Celik H,
Yavuz B and Tanriverdi K: Micro-RNA (miRNA) profile in Hodgkin
lymphoma: Association between clinical and pathological variables.
Med Oncol. 33:342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Bao L, Lv L, Feng J, Chen Y, Wang X, Han S
and Zhao H: miR-876-5p suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition
of lung cancer by directly down-regulating bone morphogenetic
protein 4. J Biosci. 42:671–681. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Riemenschneider MJ, Jeuken JW, Wesseling P
and Reifenberger G: Molecular diagnostics of gliomas: State of the
art. Acta Neuropathol. 120:567–584. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Conway C, Beswick S, Elliott F, Chang YM,
Randerson-Moor J, Harland M, Affleck P, Marsden J, Sanders DS, Boon
A, et al: Deletion at chromosome arm 9p in relation to BRAF/NRAS
mutations and prognostic significance for primary melanoma. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 49:425–438. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Giunti L, da Ros M, Vinci S, Gelmini S,
Iorio AL, Buccoliero AM, Cardellicchio S, Castiglione F, Genitori
L, de Martino M, et al: Anti-miR21 oligonucleotide enhances
chemosensitivity of T98G cell line to doxorubicin by inducing
apoptosis. Am J Cancer Res. 5:231–242. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|