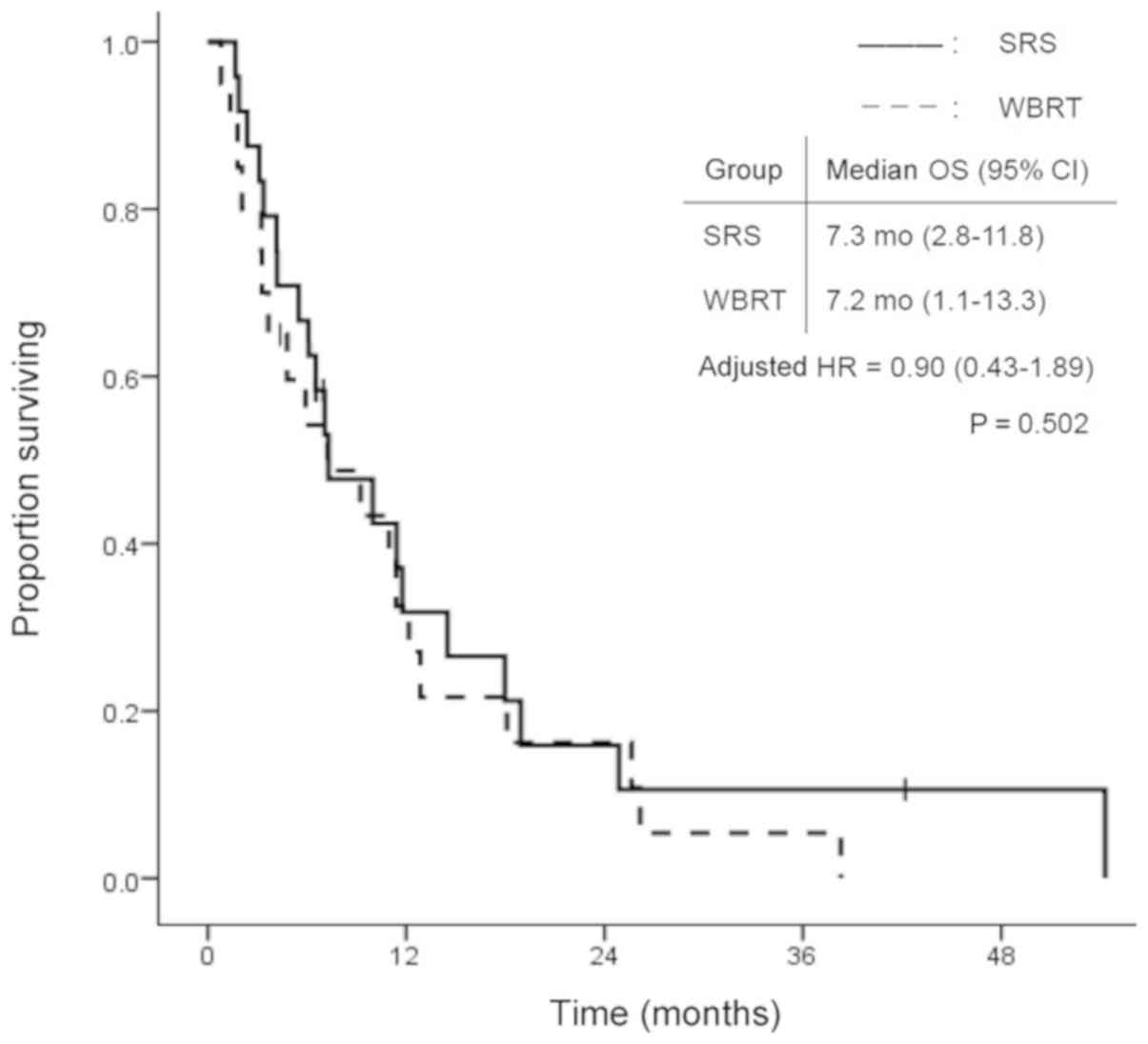
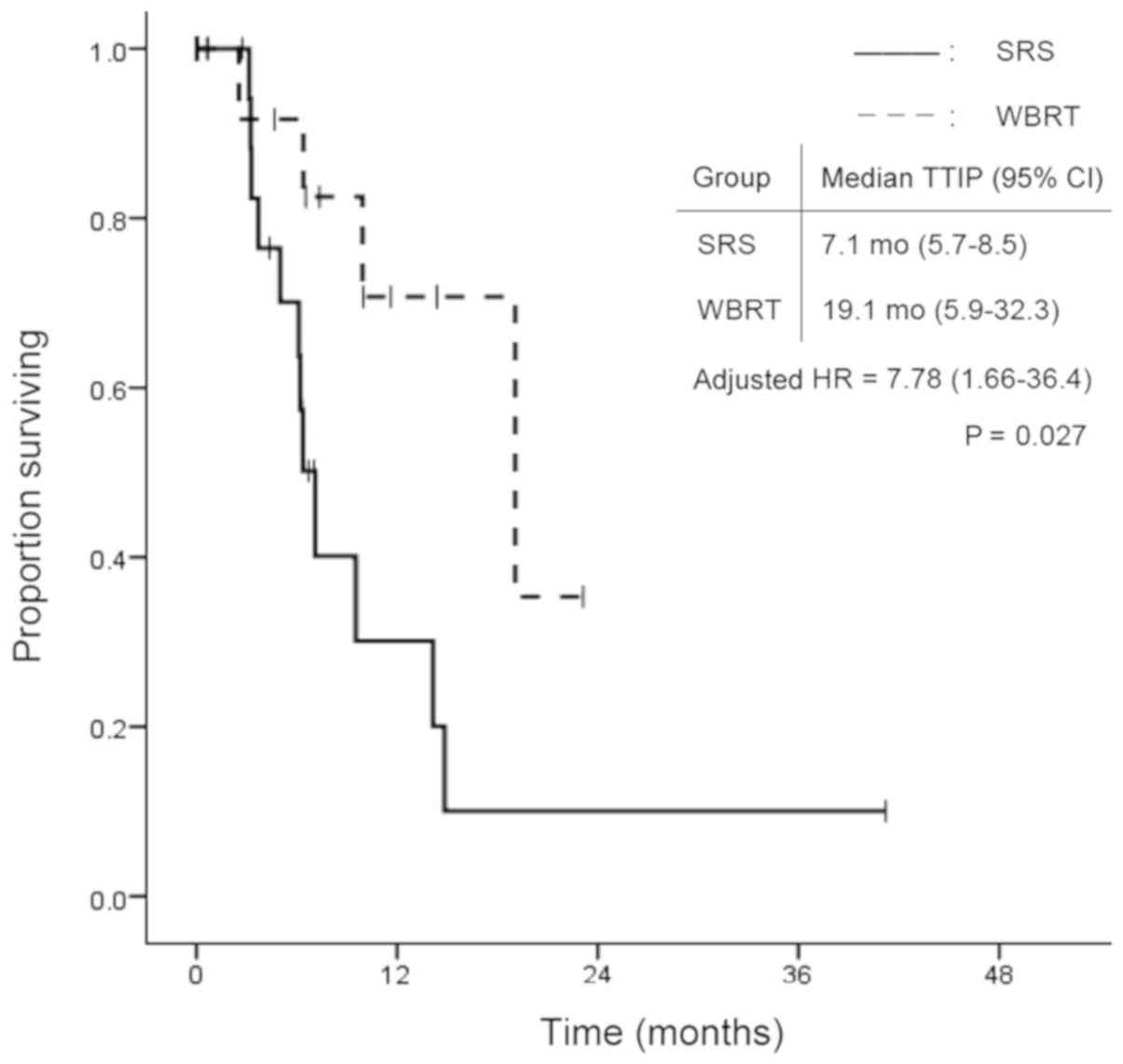
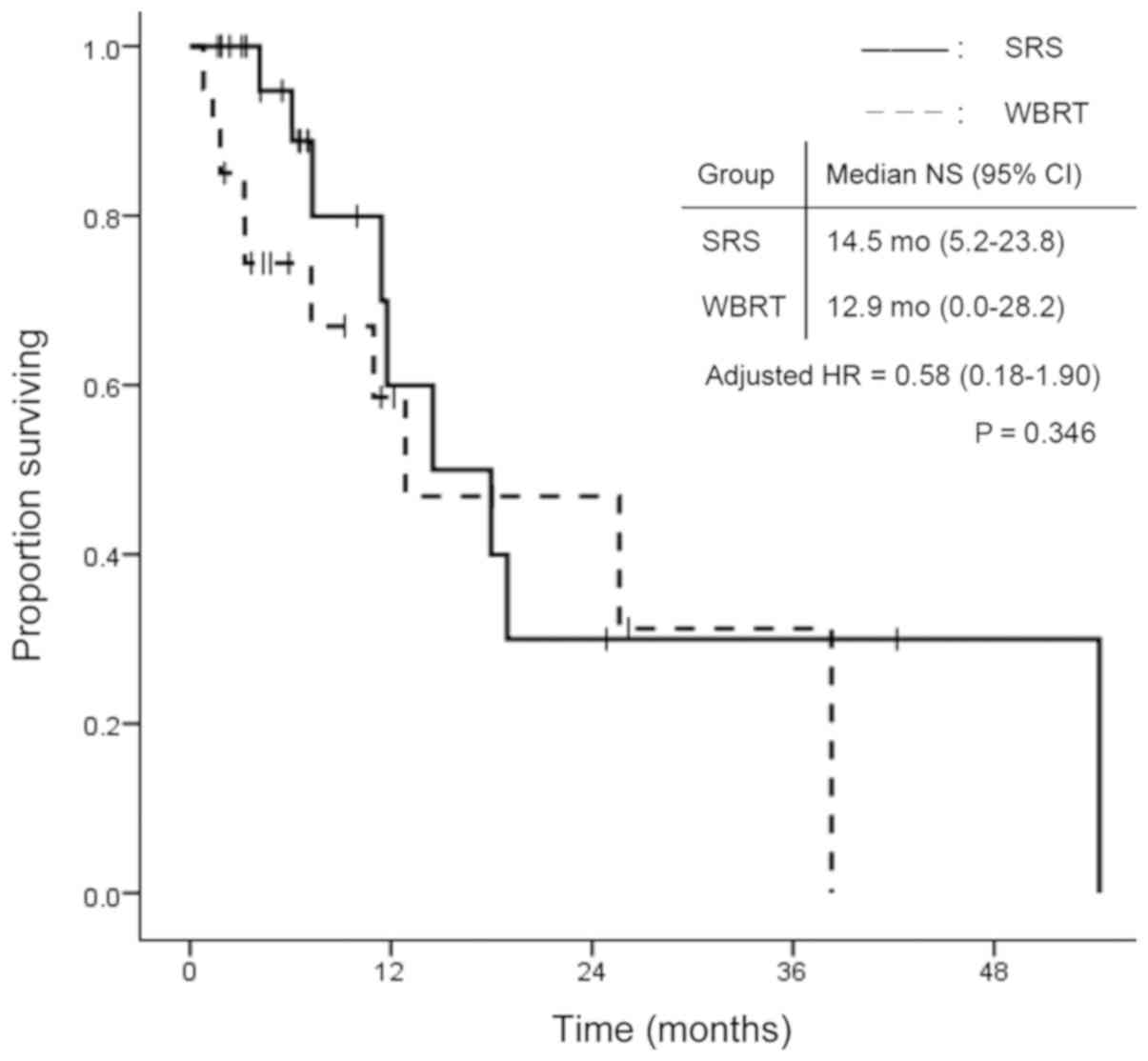
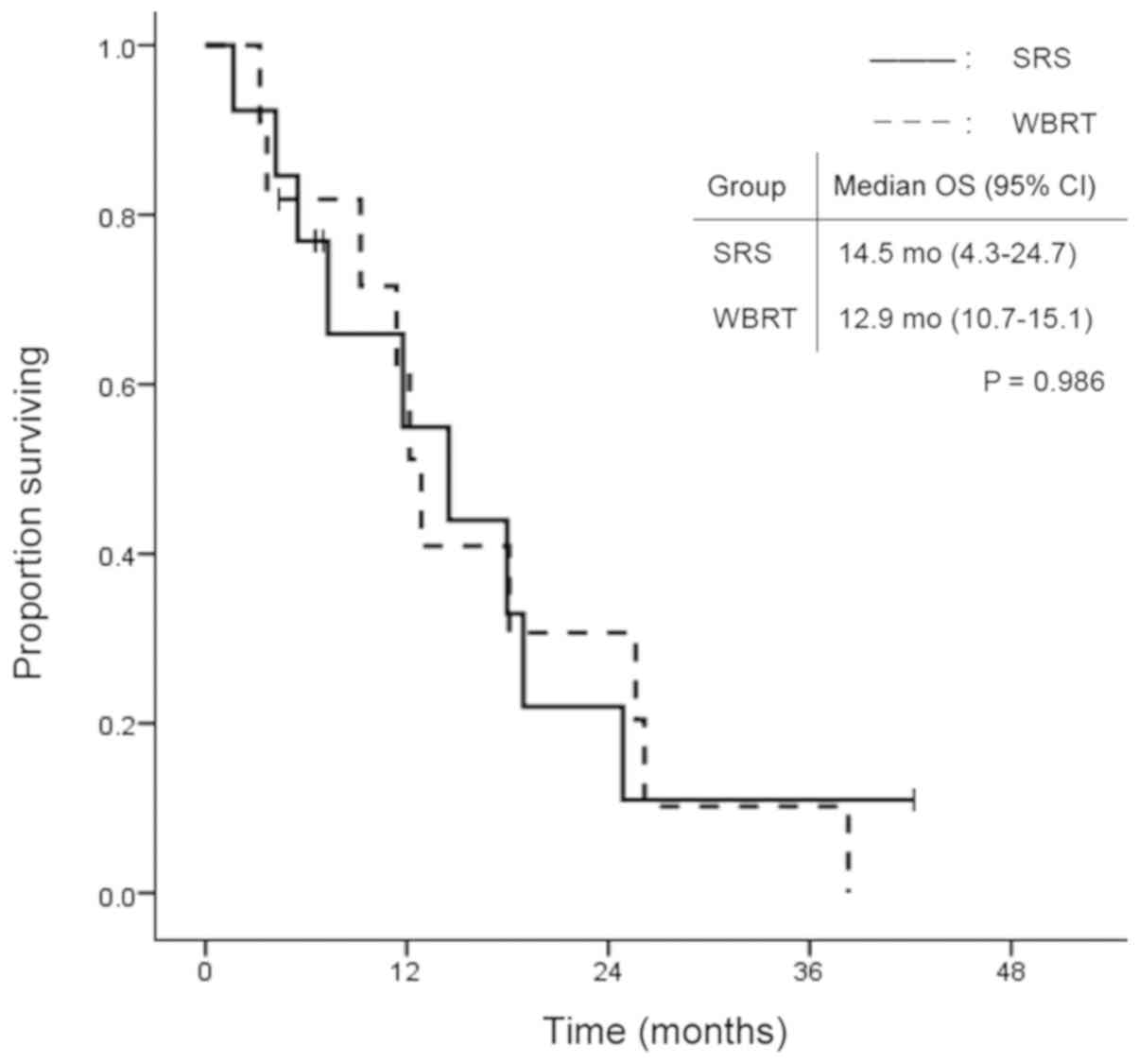
|
1
|
Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Sloan AE, Davis FG,
Vigneau FD, Lai P and Sawaya RE: Incidence proportions of brain
metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan
Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J Clin Oncol. 22:2865–2872.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shin DY, Na II, Kim CH, Park S, Baek H and
Yang SH: EGFR mutation and brain metastasis in pulmonary
adenocarcinomas. J Thoracic Oncol. 9:195–199. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zimm S, Wampler GL, Stablein D, Hazra T
and Young HF: Intracerebral metastases in solid-tumor patients:
natural history and results of treatment. Cancer. 48:384–394. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Borgelt B, Gelber R, Kramer S, Brady LW,
Chang CH, Davis LW, Perez CA and Hendrickson FR: The palliation of
brain metastases: final results of the first two studies by the
Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
6:1–9. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Halasz LM, Uno H, Hughes M, D'Amico T,
Dexter EU, Edge SB, Hayman JA, Niland JC, Otterson GA, Pisters KM,
et al: Comparative effectiveness of stereotactic radiosurgery
versus whole-brain radiation therapy for patients with brain
metastases from breast or non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer.
122:2091–2100. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Shuto T, Akabane
A, Higuchi Y, Kawagishi J, Yamanaka K, Sato Y, Jokura H, Yomo S, et
al: Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain
metastases (JLGK0901): a multi-institutional prospective
observational study. Lancet Oncol. 15:387–395. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chang WS, Kim HY, Chang JW, Park YG and
Chang JH: Analysis of radiosurgical results in patients with brain
metastases according to the number of brain lesions: is
stereotactic radiosurgery effective for multiple brain metastases?
J Neurosurg. 113 (Suppl):73–78. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Grandhi R, Kondziolka D, Panczykowski D,
Monaco EA III, Kano H, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC and Lunsford LD:
Stereotactic radiosurgery using the Leksell Gamma Knife Perfexion
unit in the management of patients with 10 or more brain
metastases. J Neurosurg. 117:237–245. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim CH, Im YS, Nam DH, Park K, Kim JH and
Lee JI: Gamma knife radiosurgery for ten or more brain metastases.
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 44:358–363. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rava P, Leonard K, Sioshansi S, Curran B,
Wazer DE, Cosgrove GR, Norén G and Hepel JT: Survival among
patients with 10 or more brain metastases treated with stereotactic
radiosurgery. J Neurosurg. 119:457–462. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yamamoto M, Kawabe T, Sato Y, Higuchi Y,
Nariai T, Watanabe S and Kasuya H: Stereotactic radiosurgery for
patients with multiple brain metastases: a case-matched study
comparing treatment results for patients with 2–9 versus 10 or more
tumors. J Neurosurg. 121 Suppl:16–25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z,
Shanley R, Luo X, Sneed PK, Chao ST, Weil RJ, Suh J, et al: Summary
report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile
diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with
brain metastases. J Clin Oncol. 30:419–425. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sperduto PW, Yang TJ, Beal K, Pan H, Brown
PD, Bangdiwala A, Shanley R, Yeh N, Gaspar LE, Braunstein S, et al:
Estimating survival in patients with lung cancer and brain
metastases: an update of the Graded Prognostic Assessment for lung
cancer using molecular markers (Lung-molGPA). JAMA Oncol.
3:827–831. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Serizawa T, Higuchi Y, Yamamoto M,
Matsunaga S, Nagano O, Sato Y, Aoyagi K, Yomo S, Koiso T, Hasegawa
T, et al: Comparison of treatment results between 3- and 2-stage
Gamma Knife radiosurgery for large brain metastases: a
retrospective multi-institutional study. J Neurosurg. Sep
1–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hasegawa T, Kato T, Yamamoto T, Iizuka H,
Nishikawa T, Ito H and Kato N: Multisession gamma knife surgery for
large brain metastases. J Neurooncol. 131:517–524. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW, Dempsey
RJ, Maruyama Y, Kryscio RJ, Markesbery WR, Macdonald JS and Young
B: A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single
metastases to the brain. N Engl J Med. 322:494–500. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hunter GK, Suh JH, Reuther AM, Vogelbaum
MA, Barnett GH, Angelov L, Weil RJ, Neyman G and Chao ST: Treatment
of five or more brain metastases with stereotactic radiosurgery.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 83:1394–1398. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Raldow AC, Chiang VL, Knisely JP and Yu
JB: Survival and intracranial control of patients with 5 or more
brain metastases treated with gamma knife stereotactic
radiosurgery. Am J Clin Oncol. 36:486–490. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamamoto M, Kawabe T, Sato Y, Higuchi Y,
Nariai T, Barfod BE, Kasuya H and Urakawa Y: A case-matched study
of stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain
metastases: comparing treatment results for 1–4 vs ≥ 5 tumors:
clinical article. J Neurosurg. 118:1258–1268. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sahgal A, Ruschin M, Ma L, Verbakel W,
Larson D and Brown PD: Stereotactic radiosurgery alone for multiple
brain metastases? A review of clinical and technical issues. Neuro
Oncol. 19 Suppl 2:ii2–ii15. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brown PD, Jaeckle K, Ballman KV, Farace E,
Cerhan JH, Anderson SK, Carrero XW, Barker FG II, Deming R, Burri
SH, et al: Effect of radiosurgery alone vs radiosurgery with whole
brain radiation therapy on cognitive function in patients with 1 to
3 brain metastases: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 316:401–409.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, Allen PK,
Lang FF, Kornguth DG, Arbuckle RB, Swint JM, Shiu AS, Maor MH, et
al: Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with
radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: A
randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:1037–1044. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Crossen JR, Garwood D, Glatstein E and
Neuwelt EA: Neurobehavioral sequelae of cranial irradiation in
adults: a review of radiation-induced encephalopathy. J Clin Oncol.
12:627–642. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Habets EJ, Dirven L, Wiggenraad RG,
Verbeek-de Kanter A, Lycklama À, Nijeholt GJ, Zwinkels H, Klein M
and Taphoorn MJ: Neurocognitive functioning and health-related
quality of life in patients treated with stereotactic radiotherapy
for brain metastases: a prospective study. Neuro Oncol. 18:435–444.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Soffietti R, Kocher M, Abacioglu UM, Villa
S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, Fariselli L, Tzuk-Shina T, Kortmann RD,
Carrie C, et al: A European Organisation for Research and Treatment
of Cancer phase III trial of adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy
versus observation in patients with one to three brain metastases
from solid tumors after surgical resection or radiosurgery:
quality-of-life results. J Clin Oncol. 31:65–72. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M, Nakagawa K,
Toyoda T, Hatano K, Kenjyo M, Oya N, Hirota S, Shioura H, et al:
Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs
stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases:
a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 295:2483–2491. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U, Villà
S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, Fariselli L, Tzuk-Shina T, Kortmann RD,
Carrie C, et al: Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus
observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to
three cerebral metastases: Results of the EORTC 22952–26001 study.
J Clin Oncol. 29:134–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Magnuson WJ, Lester-Coll NH, Wu AJ, Yang
TJ, Lockney NA, Gerber NK, Beal K, Amini A, Patil T, Kavanagh BD,
et al: Management of brain metastases in tyrosine kinase
inhibitor-naïve epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant
non-small-cell lung cancer: a retrospective multi-institutional
analysis. J Clin Oncol. 35:1070–1077. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lorenzoni J, Devriendt D, Massager N,
David P, Ruíz S, Vanderlinden B, Van Houtte P, Brotchi J and
Levivier M: Radiosurgery for treatment of brain metastases:
estimation of patient eligibility using three stratification
systems. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 60:218–224. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang T, Min W, Li Y, Yue Z, Wu C and Zhou
C: Radiotherapy plus EGFR TKIs in non-small cell lung cancer
patients with brain metastases: An update meta-analysis. Cancer
Med. 5:1055–1065. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Luo S, Chen L, Chen X and Xie X:
Evaluation on efficacy and safety of tyrosine kinase inhibitors
plus radiotherapy in NSCLC patients with brain metastases.
Oncotarget. 6:16725–16734. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim DY, Lee KW, Yun T, Kim DW, Kim TY, Heo
DS, Bang YJ and Kim NK: Efficacy of platinum-based chemotherapy
after cranial radiation in patients with brain metastasis from
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 14:207–211. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|