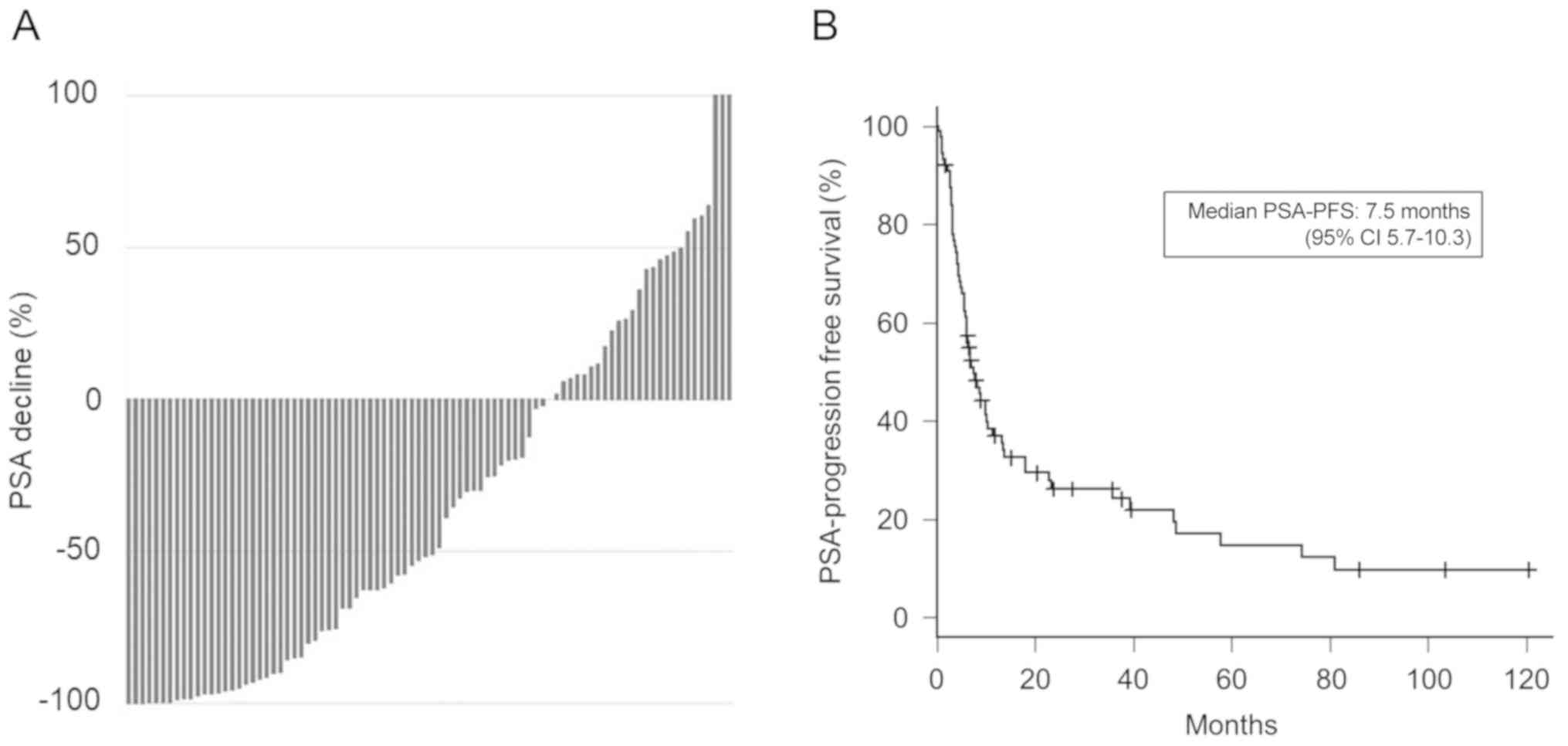
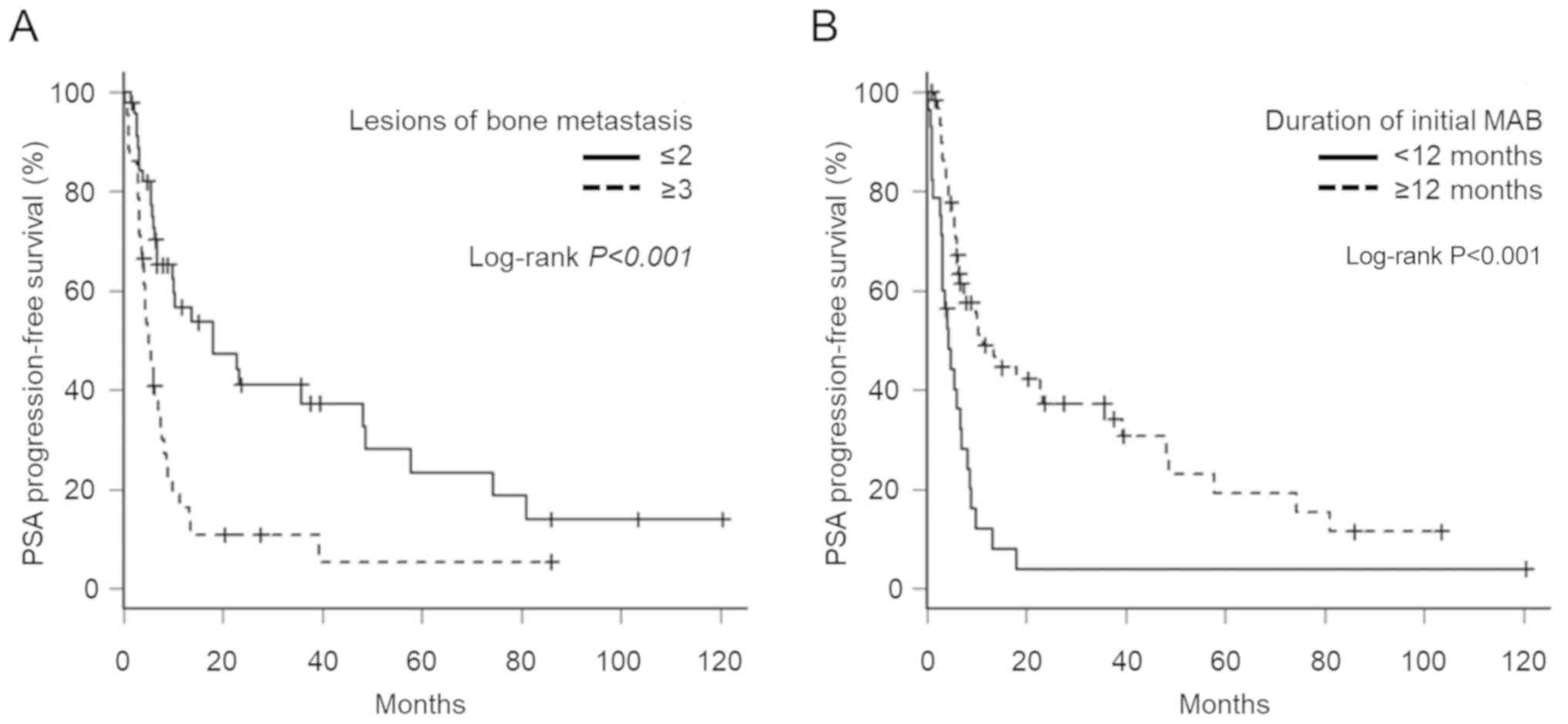
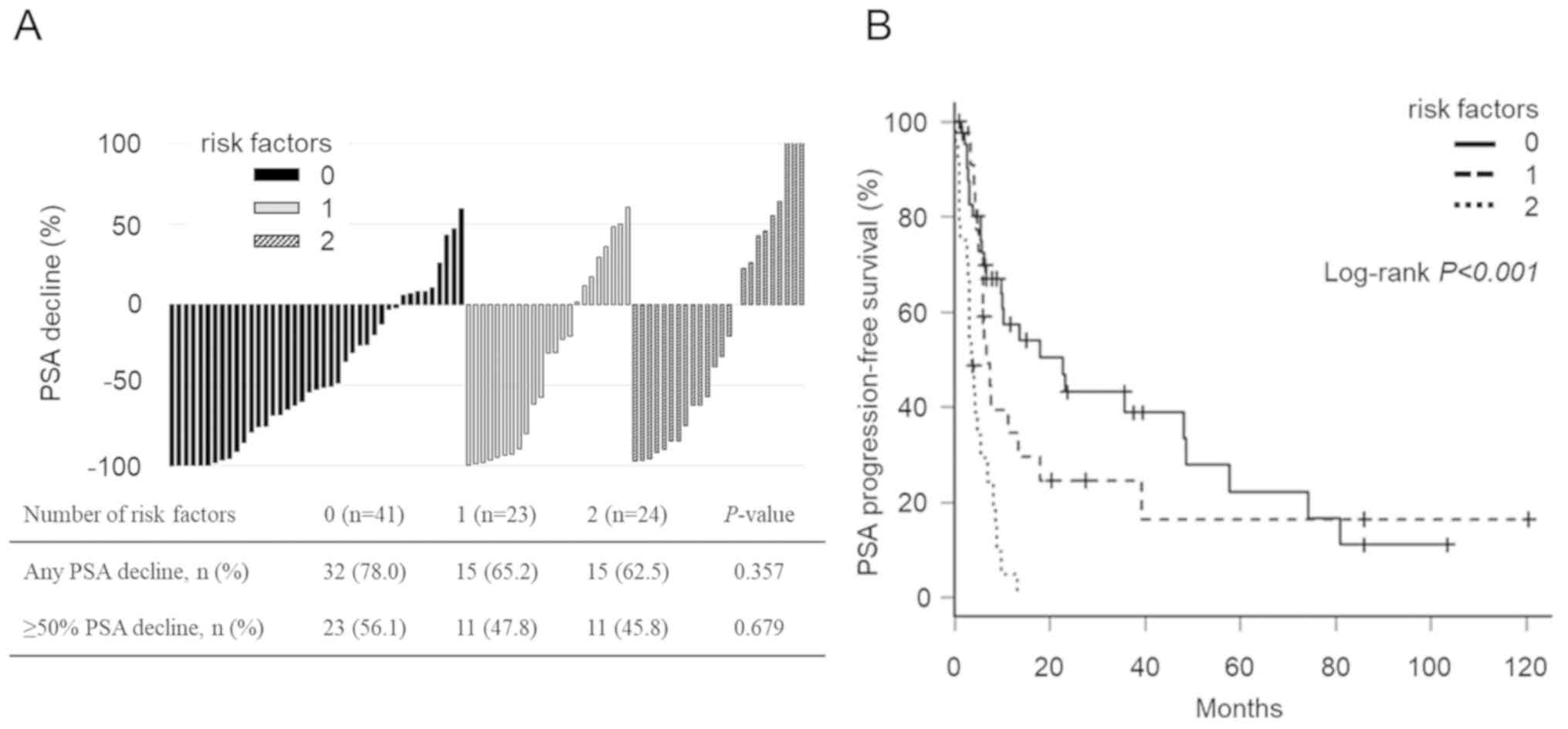
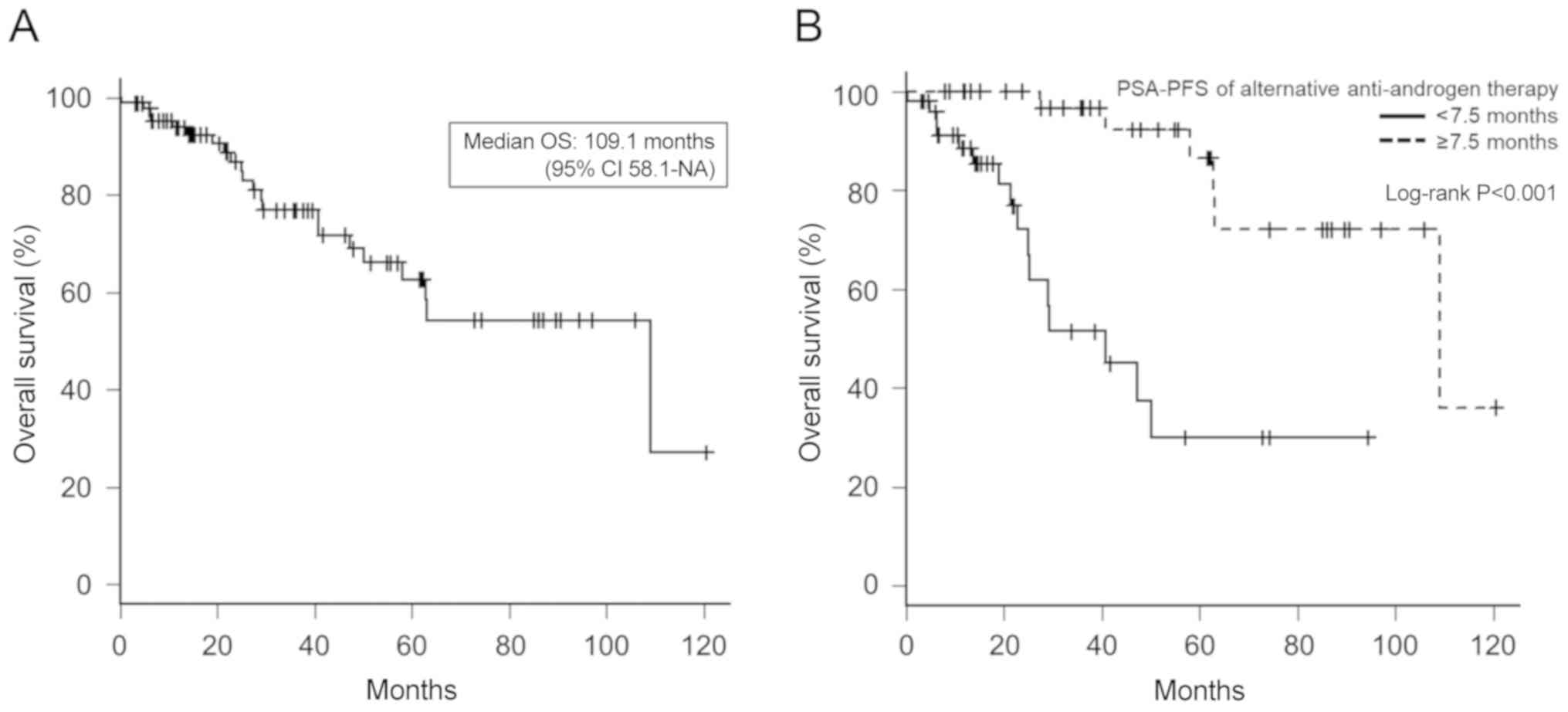
|
1
|
Lorente D, Mateo J, Zafeiriou Z, Smith AD,
Sandhu S, Ferraldeschi R and de Bono JS: Switching and withdrawing
hormonal agents for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nat Rev
Urol. 12:37–47. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Laufer M, Denmeade SR, Sinibaldi VJ,
Carducci MA and Eisenberger MA: Complete androgen blockade for
prostate cancer: What went wrong? J Urol. 164:3–9. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Heidenreich A, Bastian PJ, Bellmunt J,
Bolla M, Joniau S, van der Kwast T, Mason M, Matveev V, Wiegel T,
Zattoni F, et al: EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II:
Treatment of advanced, relapsing, and castration-resistant prostate
cancer. Eur Urol. 65:467–479. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao JG, Liu JD, Shen PF, Tang X, Sun GX,
Zhang XM, Chen JR, Shu KP, Shi M and Zeng H: Prior switching to a
second-line nonsteroidal antiandrogen does not impact the
therapeutic efficacy of abiraterone acetate in patients with
metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A real-world
retrospective study. Asian J Androl. 20:545–550. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
de Bono JS, Oudard S, Ozguroglu M, Hansen
S, Machiels JP, Kocak I, Gravis G, Bodrogi I, Mackenzie MJ, Shen L,
et al: Prednisone plus cabazitaxel or mitoxantrone for metastatic
castration-resistant prostate cancer progressing after docetaxel
treatment: A randomised open-label trial. Lancet. 376:1147–1154.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kantoff PW, Higano CS, Shore ND, Berger
ER, Small EJ, Penson DF, Redfern CH, Ferrari AC, Dreicer R, Sims
RB, et al: Sipuleucel-T immunotherapy for castration-resistant
prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:411–422. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fizazi K, Scher HI, Molina A, Logothetis
CJ, Chi KN, Jones RJ, Staffurth JN, North S, Vogelzang NJ, Saad F,
et al: Abiraterone acetate for treatment of metastatic
castration-resistant prostate cancer: Final overall survival
analysis of the COU-AA-301 randomised, double-blind,
placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 13:983–992. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Scher HI, Fizazi K, Saad F, Taplin ME,
Sternberg CN, Miller K, de Wit R, Mulders P, Chi KN, Shore ND, et
al: Increased survival with enzalutamide in prostate cancer after
chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 367:1187–1197. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Parker C, Nilsson S, Heinrich D, Helle SI,
O'Sullivan JM, Fosså SD, Chodacki A, Wiechno P, Logue J, Seke M, et
al: Alpha emitter radium-223 and survival in metastatic prostate
cancer. N Engl J Med. 369:213–223. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Beer TM, Armstrong AJ, Rathkopf DE, Loriot
Y, Sternberg CN, Higano CS, Iversen P, Bhattacharya S, Carles J,
Chowdhury S, et al: Enzalutamide in metastatic prostate cancer
before chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 371:424–433. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ryan CJ, Smith MR, Fizazi K, Saad F,
Mulders PF, Sternberg CN, Miller K, Logothetis CJ, Shore ND, Small
EJ, et al: Abiraterone acetate plus prednisone versus placebo plus
prednisone in chemotherapy-naive men with metastatic
castration-resistant prostate cancer (COU-AA-302): Final overall
survival analysis of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled
phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 16:152–160. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cornford P, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Briers E,
De Santis M, Gross T, Henry AM, Joniau S, Lam TB, Mason MD, et al:
EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: Treatment of
relapsing, metastatic, and castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Eur Urol. 71:630–642. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Momozono H, Miyake H, Tei H, Harada KI and
Fujisawa M: Clinical outcomes of anti-androgen withdrawal and
subsequent alternative anti-androgen therapy for advanced prostate
cancer following failure of initial maximum androgen blockade. Mol
Clin Oncol. 4:839–844. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yokomizo Y, Kawahara T, Miyoshi Y, Otani
M, Yamanaka S, Teranishi J, Noguchi K, Yao M and Uemura H: Efficacy
of immediate switching from bicalutamide to flutamide as
second-line combined androgen blockade. Biomed Res Int.
2016:40831832016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yasui M, Uemura K, Yoneyama S, Kawahara T,
Hattori Y, Teranishi JI, Inoue M, Ohta JI, Yokomizo Y, Yao M, et
al: Predictors of poor response to secondary alternative
antiandrogen therapy with flutamide in metastatic
castration-resistant prostate cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2016.(Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Choi JI, Kim YB, Yang SO, Lee JK and Jung
TY: Efficacy of alternative antiandrogen therapy for prostate
cancer that relapsed after initial maximum androgen blockade.
Korean J Urol. 52:461–465. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Okegawa T, Nutahara K and Higashihara E:
Alternative antiandrogen therapy in patients with
castration-resistant prostate cancer: A single-center experience.
Int J Urol. 17:950–955. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Suzuki H, Okihara K, Miyake H, Fujisawa M,
Miyoshi S, Matsumoto T, Fujii M, Takihana Y, Usui T, Matsuda T, et
al: Alternative nonsteroidal antiandrogen therapy for advanced
prostate cancer that relapsed after initial maximum androgen
blockade. J Urol. 180:921–927. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Epstein JI, Allsbrook WC Jr, Amin MB and
Egevad LL; ISUP Grading Committee, : The 2005 international society
of urological pathology (ISUP) consensus conference on gleason
grading of prostatic carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 29:1228–1242.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Scher HI, Halabi S, Tannock I, Morris M,
Sternberg CN, Carducci MA, Eisenberger MA, Higano C, Bubley GJ,
Dreicer R, et al: Design and end points of clinical trials for
patients with progressive prostate cancer and castrate levels of
testosterone: Recommendations of the prostate cancer clinical
trials working group. J Clin Oncol. 26:1148–1159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chi K, Hotte SJ, Joshua AM, North S, Wyatt
AW, Collins LL and Saad F: Treatment of mCRPC in the
AR-axis-targeted therapy-resistant state. Ann Oncol. 26:2044–2056.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kanda Y: Investigation of the freely
available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone
Marrow Tranfsplant. 48:452–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fukagai T, Namiki TS, Carlile RG, Yoshida
H and Namiki M: Comparison of the clinical outcome after hormonal
therapy for prostate cancer between Japanese and Caucasian men. BJU
Int. 97:1190–1193. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Namiki M, Ueno S, Kitagawa Y, Fukagai T
and Akaza H: Effectiveness and adverse effects of hormonal therapy
for prostate cancer: Japanese experience and perspective. Asian J
Androl. 14:451–457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Okihara K, Ukimura O, Kanemitsu N,
Mizutani Y, Kawauchi A and Miki T; Kyoto Prefectural University of
Medicine Prostate Cancer Research Group, : Clinical efficacy of
alternative antiandrogen therapy in Japanese men with relapsed
prostate cancer after first-line hormonal therapy. Int J Urol.
14:128–132. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ryan CJ, Smith MR, de Bono JS, Molina A,
Logothetis CJ, de Souza P, Fizazi K, Mainwaring P, Piulats JM, Ng
S, et al: Abiraterone in metastatic prostate cancer without
previous chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 368:138–148. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fitzpatrick JM, Bellmunt J, Fizazi K,
Heidenreich A, Sternberg CN, Tombal B, Alcaraz A, Bahl A, Bracarda
S, Di Lorenzo G, et al: Optimal management of metastatic
castration-resistant prostate cancer: Highlights from a European
expert consensus panel. Eur J Cancer. 50:1617–1627. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nakai Y, Tanaka N, Miyake M, Inoue T, Anai
S and Fujimoto K: Response to flutamide, as second-line therapy
after bicalutamide, predicts efficacy of abiraterone, not that of
enzalutamide. BMC Res Notes. 11:3422018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Prekovic S, van Royen ME, Voet AR, Geverts
B, Houtman R, Melchers D, Zhang KY, Van den Broeck T, Smeets E,
Spans L, et al: The effect of F877L and T878A mutations on androgen
receptor response to enzalutamide. Mol Cancer Ther. 15:1702–1712.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|