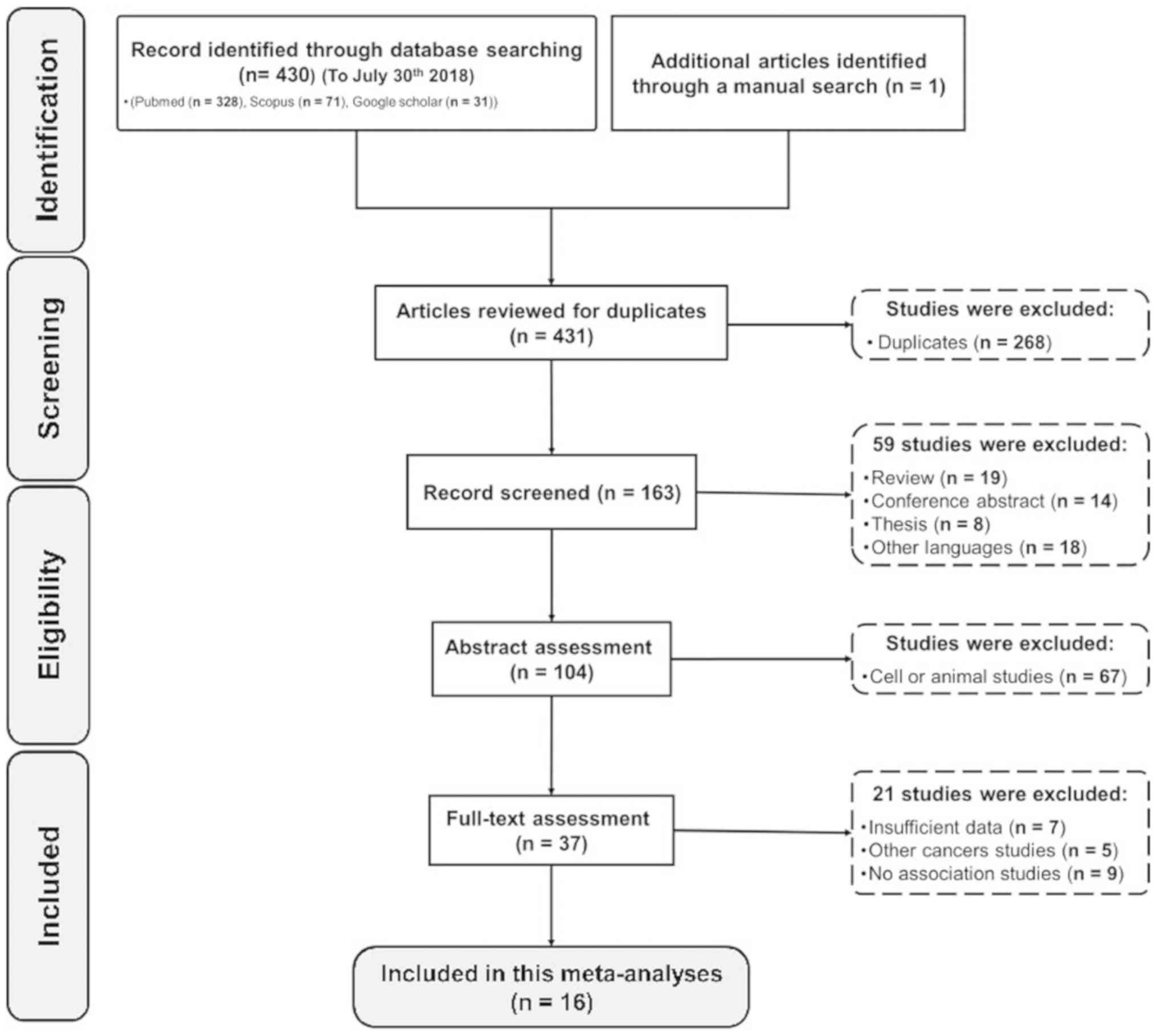
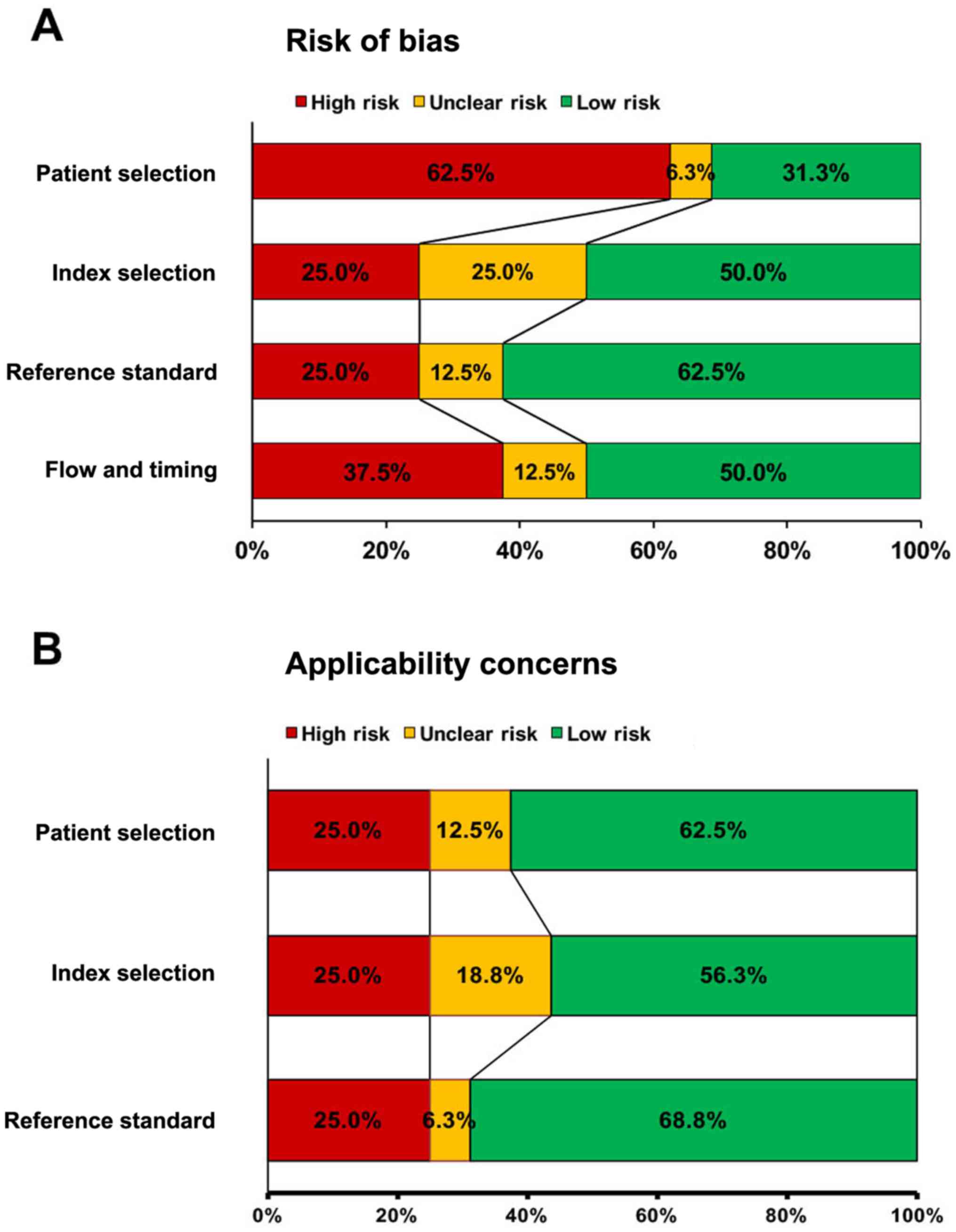
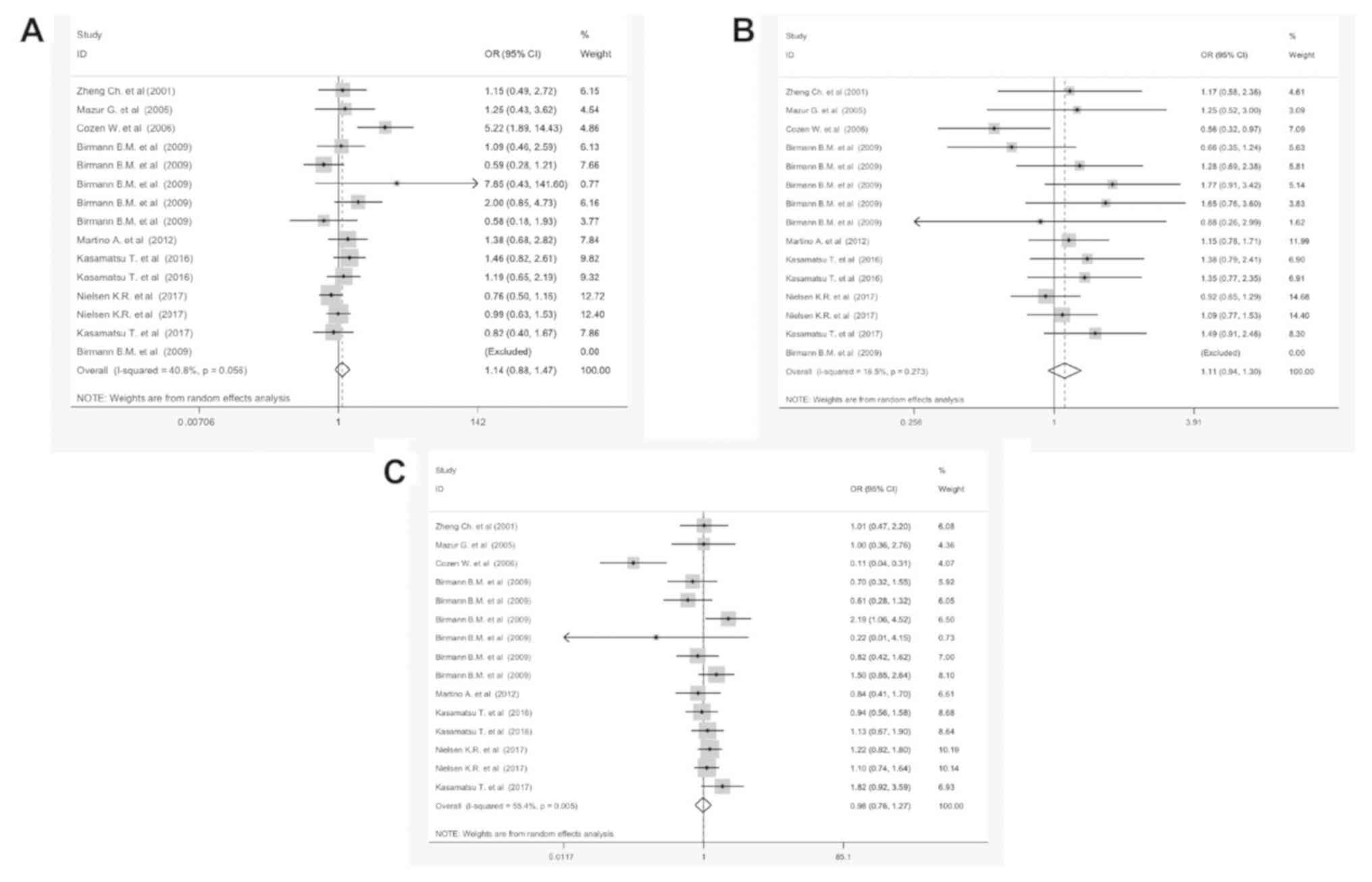
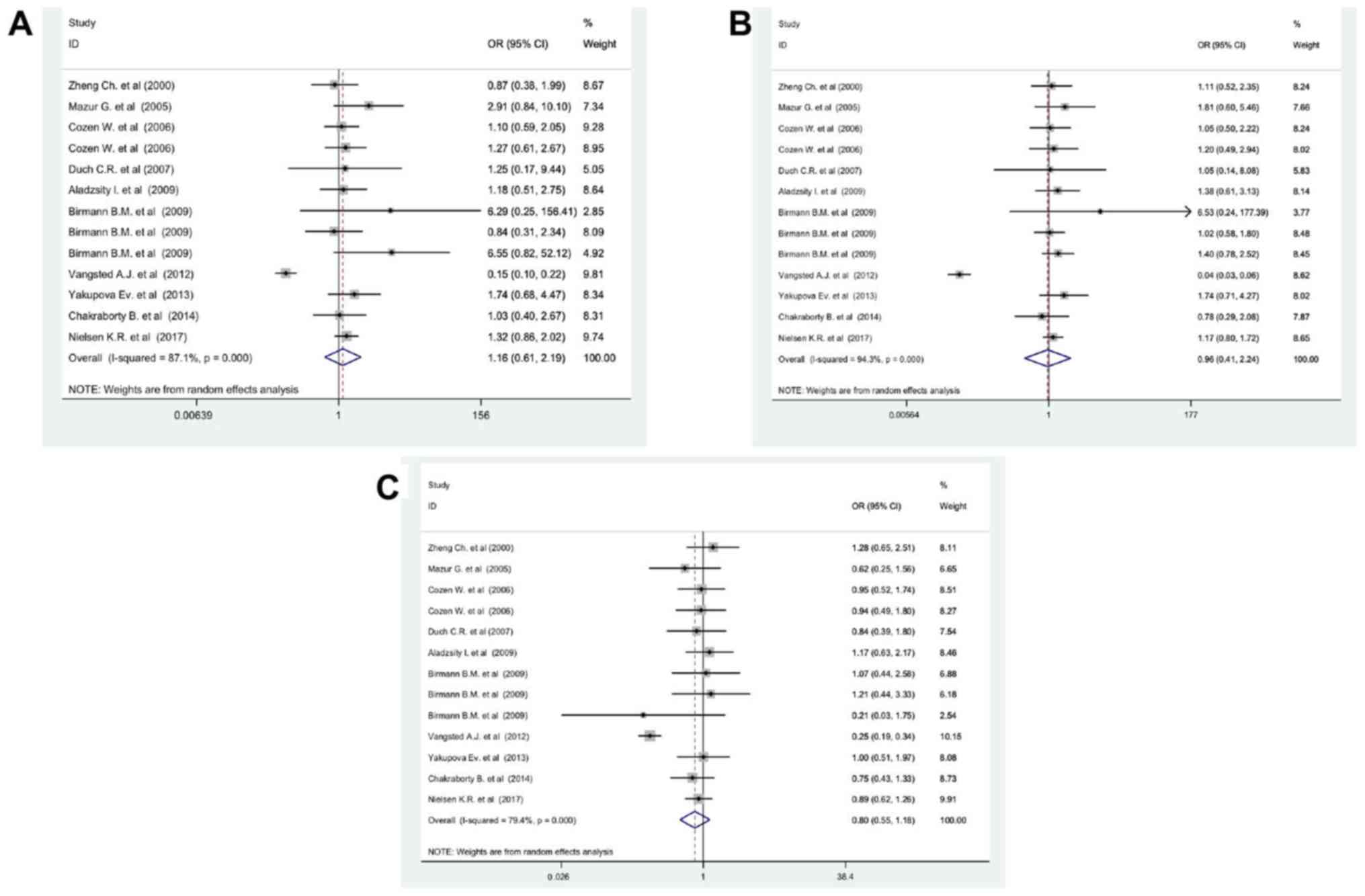
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Shi H, Chen Z, Xie J and Chen N: The
prevalence and management of multiple myeloma-induced kidney
disease in China. Kidney Dis (Basel). 1:235–40. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Holstein SA and McCarthy PL:
Immunomodulatory drugs in multiple myeloma: Mechanisms of action
and clinical experience. Drugs. 77:505–520. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Huang QC and Ding JY: Research advance in
light Chain escape of multiple myeloma-Review. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue
Ye Xue Za Zhi. 25:1833–1836. 2017.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
T V, V G and A ND: Multiple myeloma index
for risk of infection. J Cancer. 9:2211–2214. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chen YF and Lu YL: Survival and prognosis
analysis of 57 patients with multiple myeloma. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue
Ye Xue Za Zhi. 25:1436–1443. 2017.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Curado MP, Oliveira MM, Silva DRM and
Souza DLB: Epidemiology of multiple myeloma in 17 Latin American
countries: An update. Cancer Med. 7:2101–2108. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tang CH, Liu HY, Hou HA, Qiu H, Huang KC,
Siggins S, Rothwell LA and Liu Y: Epidemiology of multiple myeloma
in Taiwan, a population based study. Cancer Epidemiol. 55:136–141.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Soekojo CY, de Mel S, Ooi M, Yan B and
Chng WJ: Potential clinical application of genomics in multiple
myeloma. Int J Mol Sci. 9(pii: E1721)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Willenbacher W, Seeber A, Steiner N,
Willenbacher E, Gatalica Z, Swensen J, Kimbrough J and Vranic S:
Towards Molecular profiling in multiple myeloma: A literature
review and early indications of its efficacy for informing
treatment strategies. Int J Mol Sci. 19(pii: E2087)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jupe S, Ray K, Roca CD, Varusai T,
Shamovsky V, Stein L, D'Eustachio P and Hermjakob H: Interleukins
and their signaling pathways in the Reactome biological pathway
database. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 141:1411–1416. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yasui H, Hideshima T, Richardson PG and
Anderson KC: Novel therapeutic strategies targeting growth factor
signalling cascades in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol.
132:385–397. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Naka T, Nishimoto N and Kishimoto T: The
paradigm of IL-6: From basic science to medicine. Arthritis Res. 4
(Suppl 3):S233–S242. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ishikawa H, Tsuyama N and Kawano MM:
Interleukin-6-induced proliferation of human myeloma cells
associated with CD45 molecules. Int J Hematol. 78:95–105.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Liu FT, Zhu PQ, Ou YX, Liu WW, Xia GF and
Luo HL: Positive association between IL-16 rs1131445 polymorphism
and cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Minerva Med. 107:84–91.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hong JB, Zuo W, Wang AJ and Lu NH:
Helicobacter pylori infection synergistic with IL-1β gene
polymorphisms potentially contributes to the carcinogenesis of
gastric cancer. Int J Med Sci. 13:298–303. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kasamatsu T, Kimoto M, Takahashi N, Minato
Y, Gotoh N, Takizawa M, Matsumoto M, Sawamura M, Yokohama A, Handa
H, et al: IL17A and IL23R gene polymorphisms affect the clinical
features and prognosis of patients with multiple myeloma. Hematol
Oncol. 36:196–201. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li Y, Du Z, Wang X, Wang G and Li W:
Association of IL-6 promoter and receptor polymorphisms with
multiple myeloma risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Genet
Test Mol Biomarkers. 20:587–596. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Banu C, Moise A, Arion CV, Coriu D, Tănase
A and Constantinescu I: Cytokine gene polymorphisms support
diagnostic monitoring of Romanian multiple myeloma patients. J Med
Life. 4:264–268. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Birmann BM, Tamimi RM, Giovannucci E,
Rosner B, Hunter DJ, Kraft P, Mitsiades C, Anderson KC and Colditz
GA: Insulin-like growth factor-1- and interleukin-6-related gene
variation and risk of multiple myeloma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 18:282–288. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Vangsted AJ, Klausen TW, Ruminski W,
Gimsing P, Andersen NF, Gang AO, Abildgaard N, Knudsen LM, Nielsen
JL, Gregersen H and Vogel U: The polymorphism IL-1beta T-31C is
associated with a longer overall survival in patients with multiple
myeloma undergoing auto-SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 43:539–545.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Abazis-Stamboulieh D, Oikonomou P,
Papadoulis N, Panayiotidis P, Vrakidou E and Tsezou A: Association
of interleukin-1A, interleukin-1B and interleukin-1 receptor
antagonist gene polymorphisms with multiple myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma.
48:2196–2203. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mazur G, Bogunia-Kubik K, Wróbel T,
Karabon L, Polak M, Kuliczkowski K and Lange A: IL-6 and IL-10
promoter gene polymorphisms do not associate with the
susceptibility for multiple myeloma. Immunol Lett. 96:241–246.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Cozen W, Gebregziabher M, Conti DV, Van
Den Berg DJ, Coetzee GA, Wang SS, Rothman N, Bernstein L, Hartge P,
Morhbacher A, et al: Interleukin-6-related genotypes, body mass
index, and risk of multiple myeloma and plasmacytoma. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 15:2285–2291. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Iakupova EV, Grinchuk OV, Kalimullina DKh,
Bakirov BA, Galimova RR, Makarova OV, Khusnutdinova EK and
Viktorova TV: Molecular genetic analysis of the interleukin 6 and
tumor necrosis factor alpha gene polymorphisms in multiple myeloma.
Mol Biol (Mosk). 37:420–424. 2003.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D,
Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P and Stewart LA: PRISMA-P Group:
Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis
protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: Elaboration and explanation. BMJ.
350(g7647)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Richardson WS, Wilson MC, Nishikawa J and
Hayward RS: The well-built clinical question: A key to
evidence-based decisions. ACP J Club. 123:A12–A13. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stang A: Critical evaluation of the
Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of
nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol.
25:603–605. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME,
Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, Leeflang MM, Sterne JA and Bossuyt
PM: QUADAS-2 Group: QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality
assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med.
155:529–536. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ.
327:557–560. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Heavener T and Vassar M: A review of
publication bias in the gastroenterology literature. Indian J
Gastroenterol. 37:58–62. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zheng C, Huang DR, Bergenbrant S, Sundblad
A, Osterborg A, Björkholm M, Holm G and Yi Q: Interleukin 6, tumour
necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1beta and interleukin 1 receptor
antagonist promoter or coding gene polymorphisms in multiple
myeloma. Br J Haematol. 109:39–45. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zheng C, Huang D, Liu L, Wu R, Bergenbrant
Glas S, Osterborg A, Bjorkholm M, Holm G, Yi Q and Sundblad A:
Interleukin-10 gene promoter polymorphisms in multiple myeloma. Int
J Cancer. 95:184–188. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Aladzsity I, Kovács M, Semsei A, Falus A,
Szilágyi A, Karádi I, Varga G, Füst G and Várkonyi J: Comparative
analysis of IL6 promoter and receptor polymorphisms in
myelodysplasia and multiple myeloma. Leuk Res. 33:1570–1573.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Vangsted AJ, Nielsen KR, Klausen TW,
Haukaas E, Tjønneland A and Vogel U: A functional polymorphism in
the promoter region of the IL1B gene is associated with risk of
multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 158:515–518. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Nielsen KR, Rodrigo-Domingo M, Steffensen
R, Baech J, Bergkvist KS, Oosterhof L, Schmitz A, Bødker JS,
Johansen P, Vogel U, et al: Interactions between SNPs affecting
inflammatory response genes are associated with multiple myeloma
disease risk and survival. Leuk Lymphoma. 58:2695–2704.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Martino A, Buda G, Maggini V, Lapi F,
Lupia A, Di Bello D, Orciuolo E, Galimberti S, Barale R, Petrini M
and Rossi AM: Could age modify the effect of genetic variants in
IL6 and TNF-α genes in multiple myeloma? Leuk Res. 36:594–597.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chakraborty B, Vishnoi G, Gowda SH and
Goswami B: Interleukin-6 gene-174 G/C promoter polymorphism and its
association with clinical profile of patients with multiple
myeloma. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 13:e402–e407. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kasamatsu T, Saitoh T, Ino R, Gotoh N,
Mitsui T, Shimizu H, Matsumoto M, Sawamura M, Yokohama A, Handa H,
et al: Polymorphism of IL-10 receptor β affects the prognosis of
multiple myeloma patients treated with thalidomide and/or
bortezomib. Hematol Oncol. 35:711–718. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Duch CR, Figueiredo MS, Ribas C, Almeida
MS, Colleoni GW and Bordin JO: Analysis of polymorphism at site-174
G/C of interleukin-6 promoter region in multiple myeloma. Braz J
Med Biol Res. 40:265–267. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Stephens OW, Zhang Q, Qu P, Zhou Y, Chavan
S, Tian E, Williams DR, Epstein J, Barlogie B and Shaughnessy JD
Jr: An intermediate-risk multiple myeloma subgroup is defined by
sIL-6r: Levels synergistically increase with incidence of SNP
rs2228145 and 1q21 amplification. Blood. 119:503–512.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Tobias A: Assessing the influence of a
single study in the meta-analysis estimate. Stata Techn Bull.
47:15–17. 1999.
|
|
44
|
Dukat-Mazurek A, Bieniaszewska M, Hellmann
A, Moszkowska G and Trzonkowski P: Association of cytokine gene
polymorphisms with the complications of allogeneic haematopoietic
stem cell transplantation. Hum Immunol. 78:672–683. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lu Y, Gu J, Lu H, Zhu Q, Zhang F, Wang X,
Lu L and Zhang C: Association between IL-17A +197 G/A polymorphism
and cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers.
20:24–30. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Galicia JC, Tai H, Komatsu Y, Shimada Y,
Akazawa K and Yoshie H: Polymorphisms in the IL-6 receptor (IL-6R)
gene: Strong evidence that serum levels of soluble IL-6R are
genetically influenced. Genes Immun. 5:513–516. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Fishman D, Faulds G, Jeffery R,
Mohamed-Ali V, Yudkin JS, Humphries S and Woo P: The effect of
novel polymorphisms in the interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene on IL-6
transcription and plasma IL-6 levels, and an association with
systemic-onset juvenile chronic arthritis. J Clin Invest.
102:1369–1376. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Sultana Z, Bankura B, Pattanayak AK,
Sengupta D, Sengupta M, Saha ML, Panda CK and Das M: Association of
Interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha genetic
polymorphisms with gastric cancer in India. Environ Mol Mutagen.
59:653–667. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Demeter J, Messer G, Ramisch S, Mee JB, di
Giovine FS, Schmid M, Herrmann F and Porzsolt F: Polymorphism
within the second intron of the IL-1 receptor antagonist gene in
patients with hematopoietic malignancies. Cytokines Mol Ther.
2:239–242. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ziakas PD, Karsaliakos P, Prodromou ML and
Mylonakis E: Interleukin-6 polymorphisms and hematologic
malignancy: A re-appraisal of evidence from genetic association
studies. Biomarkers. 18:625–631. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Singh PK, Chandra G, Bogra J, Gupta R,
Kumar V, Jain A, Hussain SR, Mahdi AA and Ahmad MK: Association of
interleukin-6 genetic polymorphisms with risk of OSCC in Indian
population. Meta Gene. 4:142–51. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|