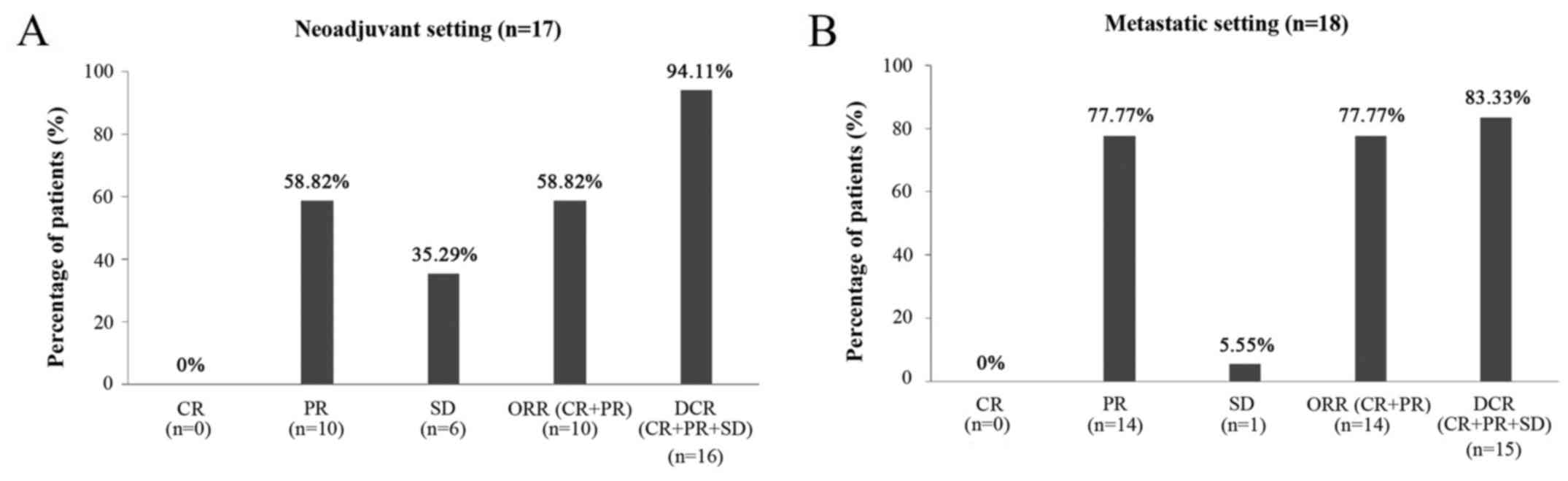
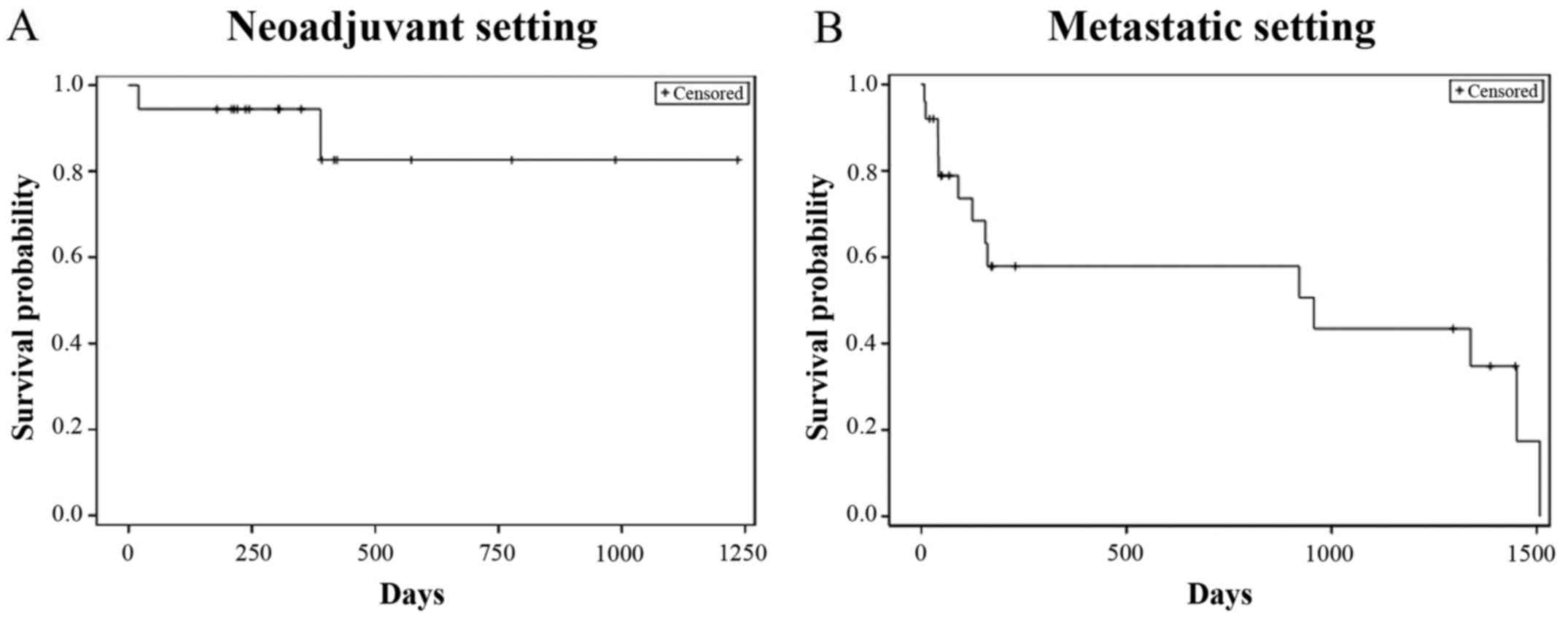
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hunt N and McHale S: The psychological
impact of alopecia. BMJ. 331:951–953. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ajani JA, Lee J, Sano T, Janjigian YY, Fan
D and Song S: Gastric adenocarcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
3(17036)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lerut T: Carcinoma of the esophagus and
gastro-esophageal junction. In: Surgical Treatment: Evidence-Based
and Problem-Oriented. Holzheimer RG, Mannick JA (eds).
Zuckschwerdt, Munich, 2001. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK6982/.
Accessed March 20, 2020.
|
|
5
|
Gee DW and Rattner DW: Management of
gastroesophageal tumors. Oncologist. 12:175–185. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sakamoto J, Matsui T and Kodera Y:
Paclitaxel chemotherapy for the treatment of gastric cancer.
Gastric Cancer. 12:69–78. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bang YJ, Kang WK, Kang YK, Kim HC, Jacques
C, Zuber E, Daglish B, Boudraa Y, Kim WS, Heo DS and Kim NK:
Docetaxel 75mg/m(2) is active and well tolerated in patients with
metastatic or recurrent gastric cancer: A phase II trial. Jpn J
Clin Oncol. 32:248–254. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yahyazadeh-Jabbari SH, Malekpour N,
Salmanian B, Foodazi H, Salehi M and Noorizadeh F: The phase 2
study of ‘(TOX) preoperative chemotherapy’ response rate and side
effects in [Locally Advanced Operable Gastric Adenocarcinoma]
patients with docetaxel, oxaliplatin and capcitabine. Iran J Cancer
Prev. 6:133–140. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Spigel DR, Greco FA, Meluch AA, Lane CM,
Farley C, Gray JR, Clark BL, Burris HA III and Hainsworth JD: Phase
I/II trial of preoperative oxaliplatin, docetaxel, and capecitabine
with concurrent radiation therapy in localized carcinoma of the
esophagus or gastroesophageal junction. J Clin Oncol. 28:2213–2219.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhen Y, Xu Z, Sun Y, Guo H, Gong W, Chai J
and Li Z: DOF as neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the treatment of
advanced gastric cancer. Chin J Clin Oncol. 38:564–567. 2011.
|
|
11
|
Van Cutsem E, Moiseyenko VM, Tjulandin S,
Majlis A, Constenla M, Boni C, Rodrigues A, Fodor M, Chao Y, Voznyi
E, et al: Phase III study of docetaxel and cisplatin plus
fluorouracil compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil as first-line
therapy for advanced gastric cancer: A report of the V325 study
group. J Clin Oncol. 24:4991–4997. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nishiyama M and Wada S: Docetaxel: Its
role in current and future treatments for advanced gastric cancer.
Gastric Cancer. 12:132–141. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Einzig AI, Neuberg D, Remick SC, Karp DD,
O'Dwyer PJ, Stewart JA and Benson AB III: Phase II trial of
docetaxel (Taxotere) in patients with adenocarcinoma of the upper
gastrointestinal tract previously untreated with cytotoxic
chemotherapy: The eastern cooperative oncology group (ECOG) results
of protocol E1293. Med Oncol. 13:87–93. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ridwelski K, Gebauer T, Fahlke J, Kroning
H, Kettner E, Meyer F, Eichelmann K and Lippert H: Combination
chemotherapy with docetaxel and cisplatin for locally advanced and
metastatic gastric cancer. Ann Oncol. 12:47–51. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Constenla M, Garcia-Arroyo R, Lorenzo I,
Carrete N, Campos B and Palacios P: Docetaxel, 5-fluorouracil, and
leucovorin as treatment for advanced gastric cancer: Results of a
phase II study. Gastric Cancer. 5:142–147. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Roy A, Cunningham D, Hawkins R, Sörbye H,
Adenis A, Barcelo JR, Lopez-Vivanco G, Adler G, Canon JL, Lofts F,
et al: Docetaxel combined with irinotecan or 5-fluorouracil in
patients with advanced oesophago-gastric cancer: A randomised phase
II study. Br J Cancer. 107:435–441. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kurt E, Cubukcu E, Karabulut B, Olmez OF,
Kurt M, Avci N, Ozdemir F, Tunali D, Evrensel T and Manavoglu O: A
multi-institutional evaluation of carboplatin plus docetaxel
regimen in elderly patients with advanced gastric cancer. J BUON.
18:147–153. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thuss-Patience PC, Kretzschmar A, Dogan Y,
Rothmann F, Blau I, Schwaner I, Breithaupt K, Bichev D, Grothoff M,
Grieser C and Reichardt P: Docetaxel and capecitabine for advanced
gastric cancer: Investigating dose-dependent efficacy in two
patient cohorts. Br J Cancer. 105:505–512. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
ten Tije AJ, Verweij J, Loos WJ and
Sparreboom A: Pharmacological effects of formulation vehicles:
Implications for cancer chemotherapy. Clin Pharmacokinet.
42:665–685. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Coors EA, Seybold H, Merk HF and Mahler V:
Polysorbate 80 in medical products and nonimmunologic anaphylactoid
reactions. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 95:593–599. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Schwartzberg LS and Navari RM: Safety of
polysorbate 80 in the oncology setting. Adv Ther. 35:754–767.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
FDA Drug Safety Communication (2014, June
20). FDA warns that cancer drug docetaxel may cause symptoms of
alcohol intoxication after treatment. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm401752.htm.
Accessed March 20, 2020.
|
|
23
|
Mirza A and Mithal N: Alcohol intoxication
with the new formulation of docetaxel. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol).
23:560–561. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ho MY and Mackey JR: Presentation and
management of docetaxel-related adverse effects in patients with
breast cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 6:253–259. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ahmad A, Sheikh S, Ali SM, Ahmad MU,
Paithankar M, Saptarishi D, Maheshwari K, Kumar K, Singh J and
Patel G: Development of aqueous based formulation of docetaxel:
Safety and pharmacokinetics in patients with advanced solid tumors.
J Nanomed Nanotechnol. 6(1)2015.
|
|
26
|
Lewis LD, Miller AA, Rosner GL, Dowell JE,
Valdivieso M, Relling MV, Egorin MJ, Bies RR, Hollis DR, Levine EG,
et al: A comparison of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of
docetaxel between African-American and Caucasian cancer patients:
CALGB 9871. Clin Cancer Res. 13:3302–3311. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ahmad A, Sheikh S, Taran R, Srivastav SP,
Prasad K, Rajappa SJ, Kumar V, Gopichand M, Paithankar M, Sharma M,
et al: Therapeutic efficacy of a novel nanosomal docetaxel lipid
suspension compared with taxotere in locally advanced or metastatic
breast cancer patients. Clin Breast Cancer. 14:177–181.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ashraf M, Sajjad R, Khan M, Shah M, Bhat Y
and Wani Z: 156P Efficacy and safety of a novel nanosomal docetaxel
lipid suspension (NDLS) as an anti cancer agent-a retrospective
study. Ann Oncol. 27:ix46–ix51. 2016.
|
|
29
|
Naik R and Khan MA: Doceaqualip in a
patient with prostate cancer who had an allergic reaction to
conventional docetaxel: A case report. Mol Clin Oncol. 6:341–343.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Prasanna R, Bunger D and Khan MA: Efficacy
and safety of DoceAqualip in a patient with locally advanced
cervical cancer: A case report. Mol Clin Oncol. 8:296–299.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Vyas V, Joshi N and Khan M: Novel
docetaxel formulation (NDLS) in low cardiac reserve ovarian cancer.
Open Access J Cancer Oncol. 2(000122)2018.
|
|
32
|
Gupta S, Pawar SS and Bunger D: Successful
downstaging of locally recurrent penile squamous cell carcinoma
with neoadjuvant nanosomal docetaxel lipid suspension (NDLS) based
regimen followed by curative surgery. BMJ Case Rep.
2017(bcr2017220686)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Tetzlaff ED, Cheng JD and Ajani JA: Review
of docetaxel in the treatment of gastric cancer. Ther Clin Risk
Manag. 4:999–1007. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in
Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®). Gastric Cancer. Version 1.2019-March
14, 2019. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/gastric.pdf.
July 1, 2020.
|
|
36
|
Menges M and Hoehler T: Neoadjuvant
therapy of gastric cancer: A decisive step forward. Gastrointest
Tumors. 1:99–104. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Inno A, Basso M, Cassano A and Barone C: A
review of docetaxel: Its use in the treatment of gastric cancer.
Clin Med Insights 2: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.4137/CMT.S5191.
|
|
38
|
Pauligk C, Tannapfel A, Meiler J, Luley
KB, Kopp HG, Homann N, Hofheinz RD, Schmalenberg H, Probst S, Haag
GM, et al: Pathological response to neoadjuvant 5-FU, oxaliplatin,
and docetaxel (FLOT) versus epirubicin, cisplatin, and 5-FU (ECF)
in patients with locally advanced, resectable
gastric/esophagogastric junction (EGJ) cancer: Data from the phase
II part of the FLOT4 phase III study of the AIO. J Clin Oncol.
33:4016. 2015.
|
|
39
|
Hu SB, Liu CH, Wang X, Dong YW, Zhao L,
Liu HF, Cao Y, Zhong DR, Liu W, Li YL, et al: Pathological
evaluation of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer.
World J Surg Oncol. 17(3)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Roth AD, Fazio N, Stupp R, Falk S,
Bernhard J, Saletti P, Koberle D, Borner MM, Rufibach K, Maibach R,
et al: Docetaxel, cisplatin, and fluorouracil; docetaxel and
cisplatin; and epirubicin, cisplatin, and fluorouracil as systemic
treatment for advanced gastric carcinoma: A randomized phase II
trial of the Swiss group for clinical cancer research. J Clin
Oncol. 25:3217–3223. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Rosenberg AJ, Rademaker A, Hochster HS,
Ryan T, Hensing T, Shankaran V, Baddi L, Mahalingam D, Mulcahy MF
and Benson AB III: Docetaxel, oxaliplatin, and 5-fluorouracil (DOF)
in metastatic and unresectable gastric/gastroesophageal junction
adenocarcinoma: A phase II study with long-term follow-up.
Oncologist. 24:1039–e642. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Di Cosimo S, Ferretti G, Fazio N,
Silvestris N, Carlini P, Alimonti A, Gelibter A, Felici A, Papaldo
P and Cognetti F: Docetaxel in advanced gastric cancer-review of
the main clinical trials. Acta Oncol. 42:693–700. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Weiss RB, Donehower RC, Wiernik PH, Ohnuma
T, Gralla RJ, Trump DL, Baker JR Jr, Van Echo DA, Von Hoff DD and
Leyland-Jones B: Hypersensitivity reactions from taxol. J Clin
Oncol. 8:1263–1268. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Obradović MMS, Hamelin B, Manevski N,
Couto JP, Sethi A, Coissieux MM, Münst S, Okamoto R, Kohler H,
Schmidt A and Bentires-Alj M: Glucocorticoids promote breast cancer
metastasis. Nature. 567:540–544. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|