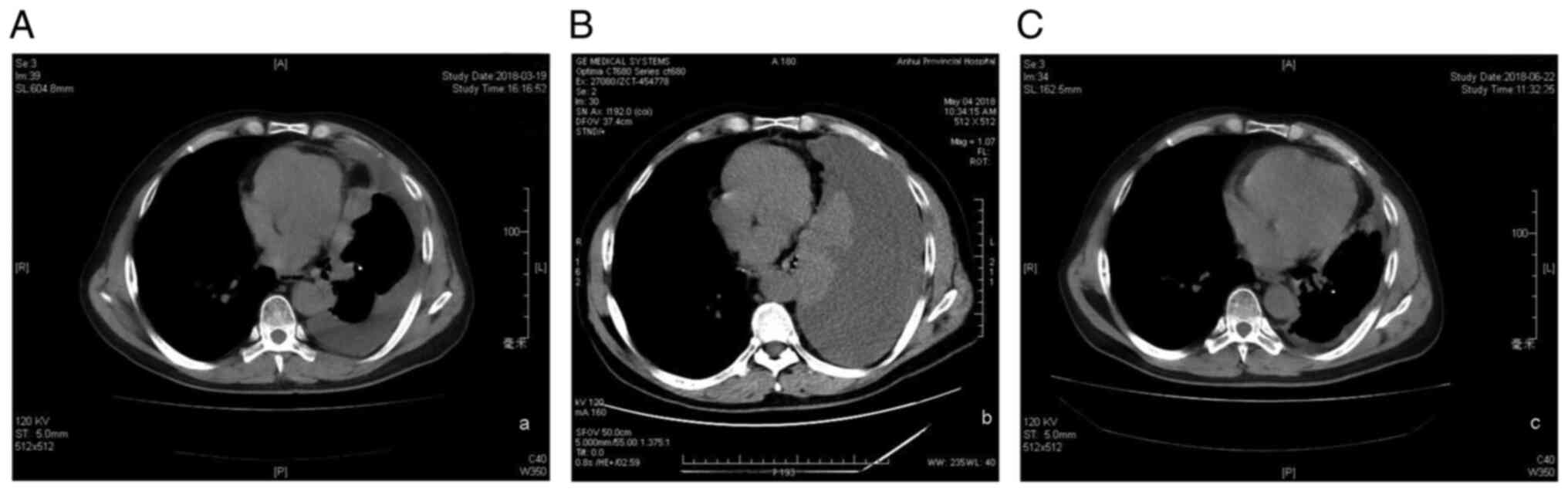
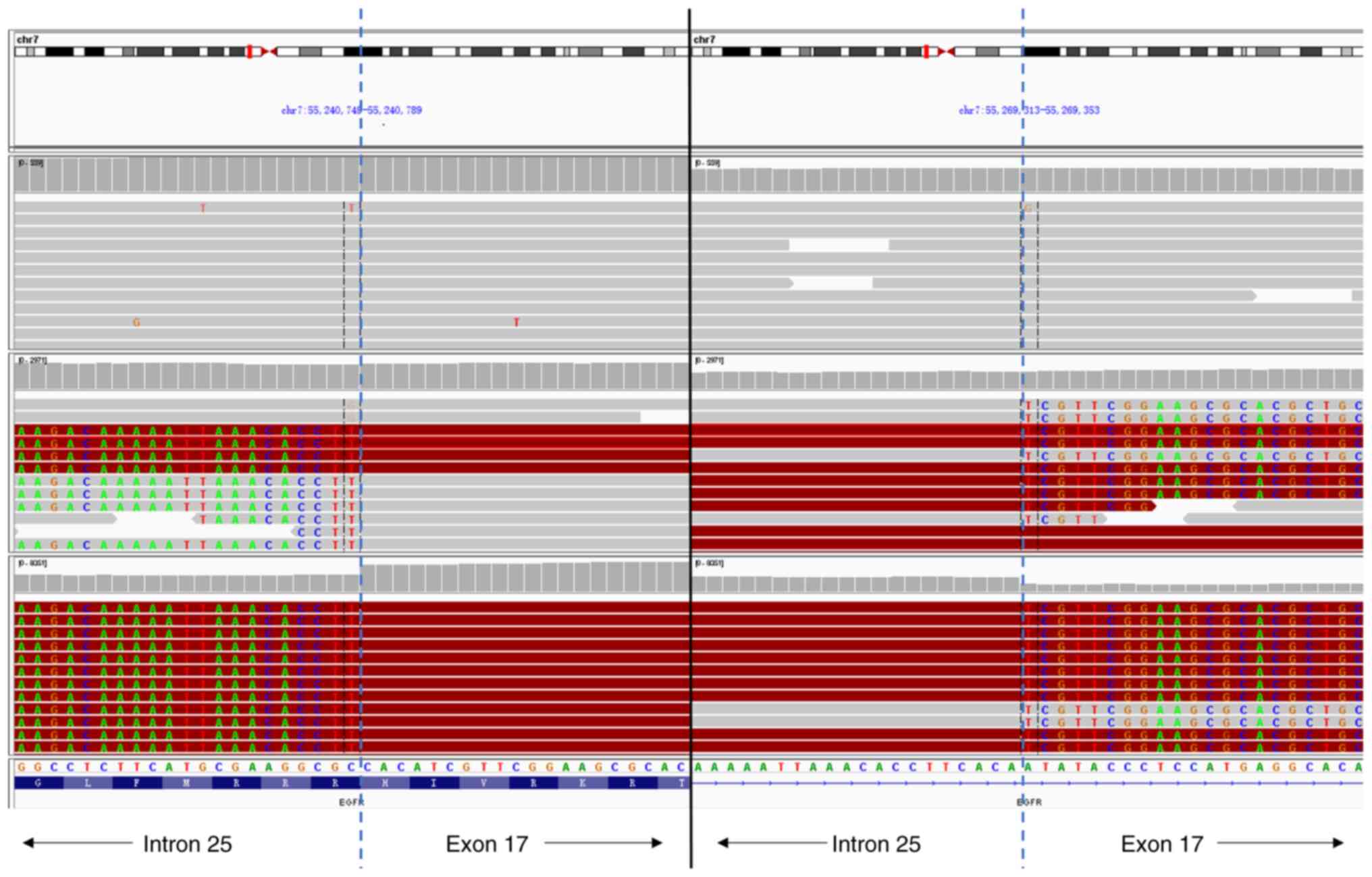
|
1
|
Lim ZF and Ma PC: Emerging insights of
tumor heterogeneity and drug resistance mechanisms in lung cancer
targeted therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 12(134)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH,
Chu DT, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ichinose Y, et
al: Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary
adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 361:947–957. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lee SM, Khan I, Upadhyay S, Lewanski C,
Falk S, Skailes G, Marshall E, Woll PJ, Hatton M, Lal R, et al:
First-line erlotinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung
cancer unsuitable for chemotherapy (TOPICAL): A double-blind,
placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 13:1161–1170.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R,
Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, Palmero R, Garcia-Gomez R,
Pallares C, Sanchez JM, et al: Erlotinib versus standard
chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with
advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer
(EURTAC): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial.
Lancet Oncol. 13:239–246. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ko B, Paucar D and Halmos B: EGFR T790M:
Revealing the secrets of a gatekeeper. Lung Cancer (Auckl).
8:147–159. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Normanno N, Maiello MR, Chicchinelli N,
Iannaccone A, Esposito C, De Cecio R, D'alessio A and De Luca A:
Targeting the EGFR T790M mutation in non-small-cell lung cancer.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 21:159–165. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gallant JN, Sheehan JH, Shaver TM, Bailey
M, Lipson D, Chandramohan R, Red Brewer M, York SJ, Kris MG,
Pietenpol JA, et al: EGFR kinase domain duplication (EGFR-KDD) is a
novel oncogenic driver in lung cancer that is clinically responsive
to afatinib. Cancer Discov. 5:1155–1163. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lababede O and Meziane MA: The eighth
edition of TNM staging of lung cancer: Reference chart and
diagrams. Oncologist. 23:844–848. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nie H, Zhou X, Shuzhang D, Nie C, Zhang X
and Huang J: Palbociclib overcomes afatinib resistance in non-small
cell lung cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 109:1750–1757.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Du Z, Gallant JN, Sheehan J, Meiler J and
Lovly CM: Intramolecular dimerization of EGFR kinase domain
duplication as a novel activation mechanism. J Thoracic Oncol. 12
(Suppl)(S1536)2017.
|
|
11
|
Baik CS, Wu D, Smith C, Martins RG and
Pritchard CC: Durable response to tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy
in a lung cancer patient harboring epidermal growth factor receptor
tandem kinase domain duplication. J Thoracic Oncol. 10:e97–e99.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhu YC, Wang WX, Xu CW, Tan QH, Li JY,
Zhuang W, Song ZB, Du KQ, Chen G, Lv TF and Song Y: Lung
adenocarcinoma patient with an EGFR kinase domain duplication (KDD)
and the response to icotinib. J Thorac Dis. 10:E359–E363.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang J, Li X, Xue X, Ou Q, Wu X, Liang Y,
Wang X, You M, Shao YW, Zhang Z and Zhang S: Clinical outcomes of
EGFR kinase domain duplication to targeted therapies in NSCLC. Int
J Cancer. 144:2677–2682. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Russo A, Franchina T, Ricciardi G,
Battaglia A, Picciotto M and Adamo V: Heterogeneous responses to
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors
(TKIs) in patients with uncommon EGFR mutations: New insights and
future perspectives in this complex clinical scenario. Int J Mol
Sci. 20(1431)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Schoenfeld AJ, Bandlamudi C, Lavery JA,
Montecalvo J, Namakydoust A, Rizvi H, Egger J, Concepcion CP, Paul
S, Arcila ME, et al: The genomic landscape of SMARCA4 alterations
and associations with outcomes in patients with lung cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 26:5701–5708. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Westover D, Zugazagoitia J, Cho BC, Lovly
CM and Paz-Ares L: Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first- and
second-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ann Oncol. 29
(Suppl 1):i10–i19. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Rolfo C, Mack PC, Scagliotti GV, Baas P,
Barlesi F, Bivona TG, Herbst RS, Mok TS, Peled N, Pirker R, et al:
Liquid biopsy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A
statement paper from the IASLC. J Thorac Oncol. 13:1248–1268.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Shi Y, Au JS, Thongprasert S, Srinivasan
S, Tsai CM, Khoa MT, Heeroma K, Itoh Y, Cornelio G and Yang PC: A
prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in
Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of
adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER). J Thorac Oncol. 9:154–162.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|