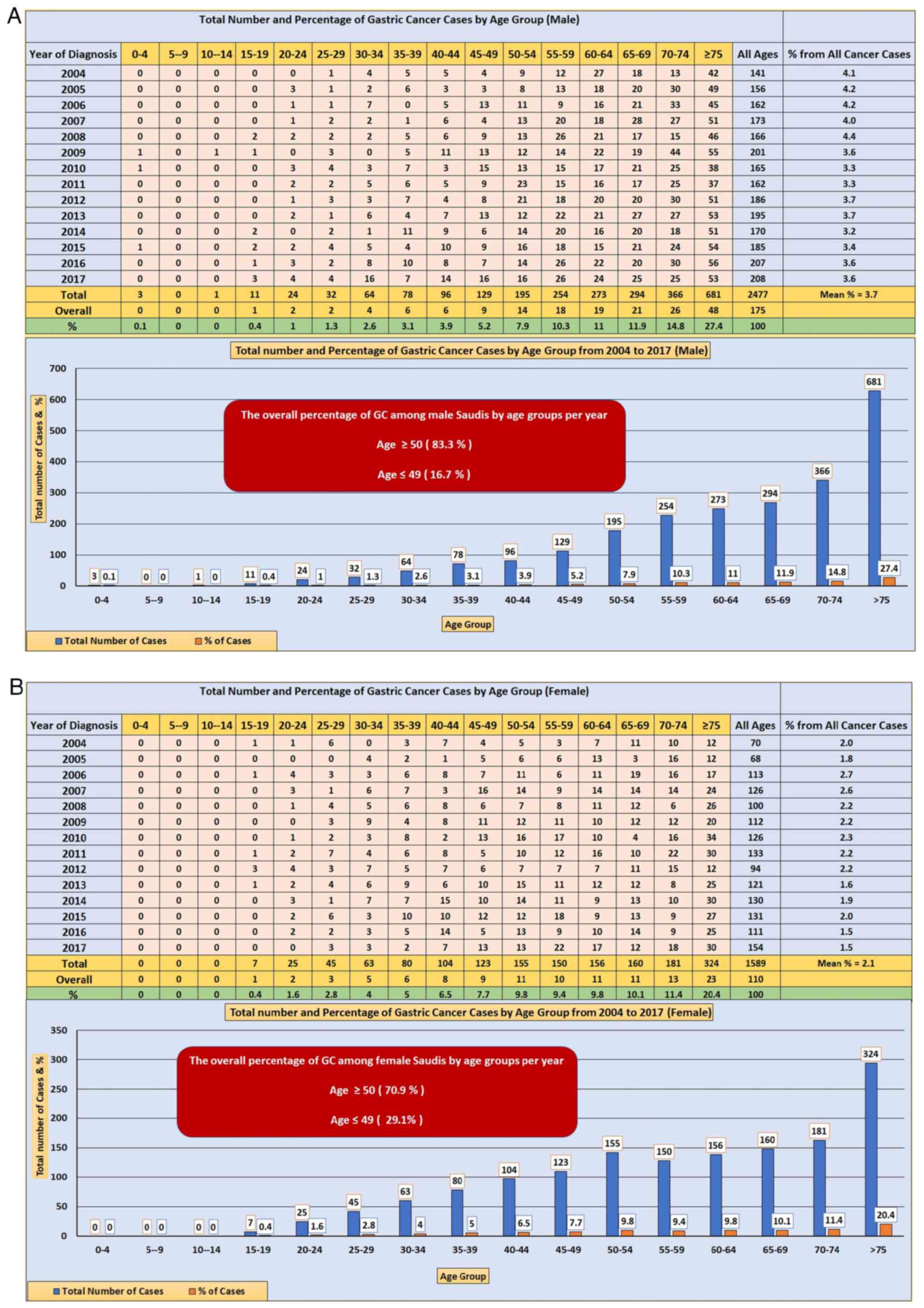
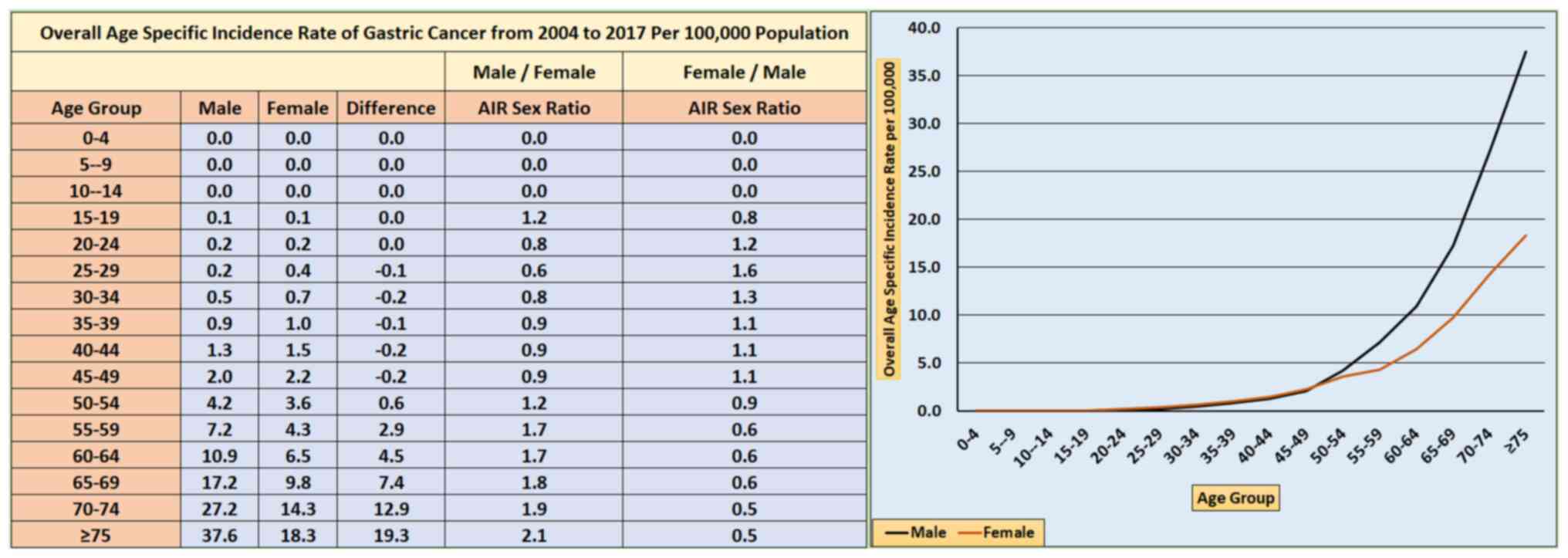
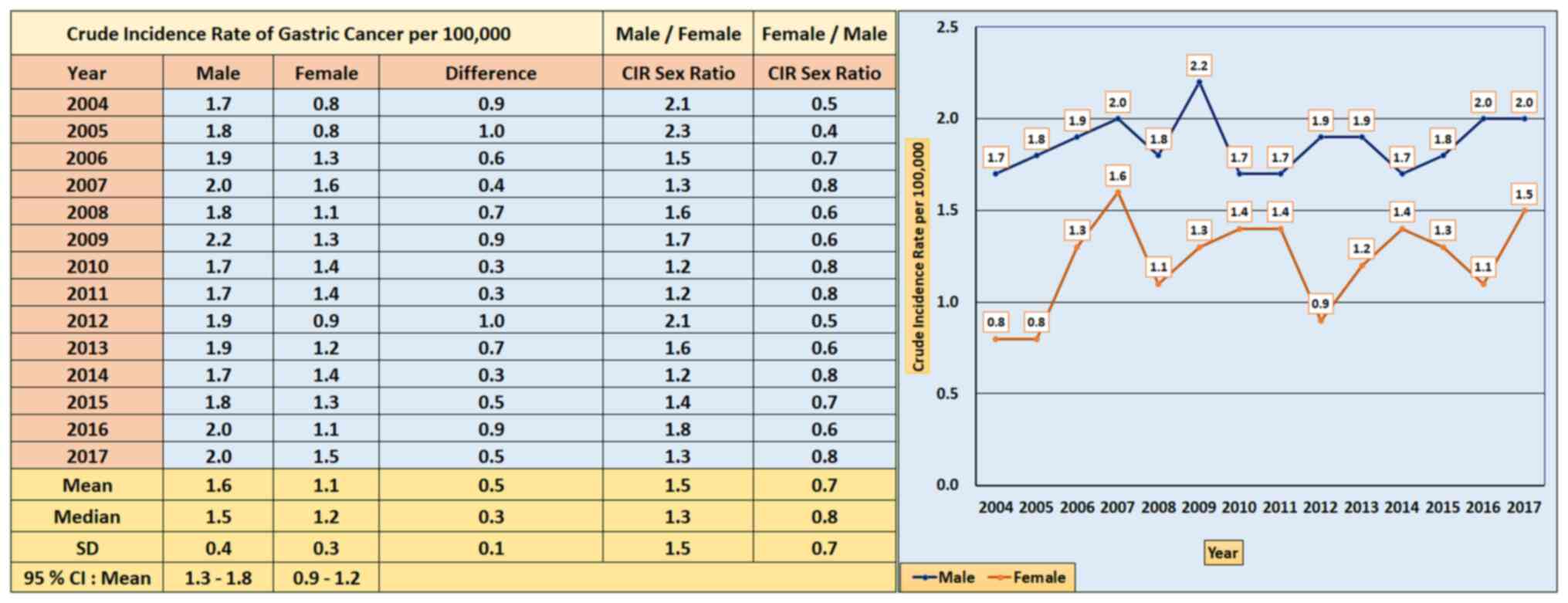
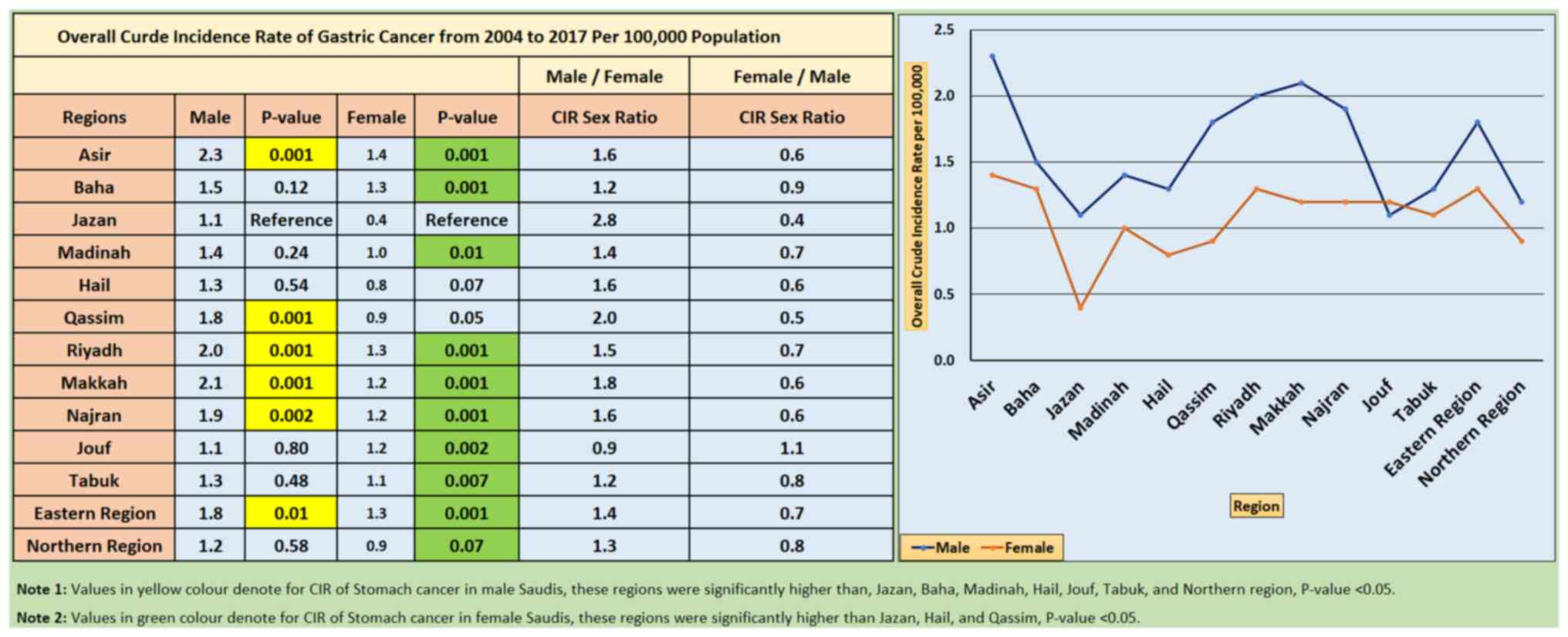
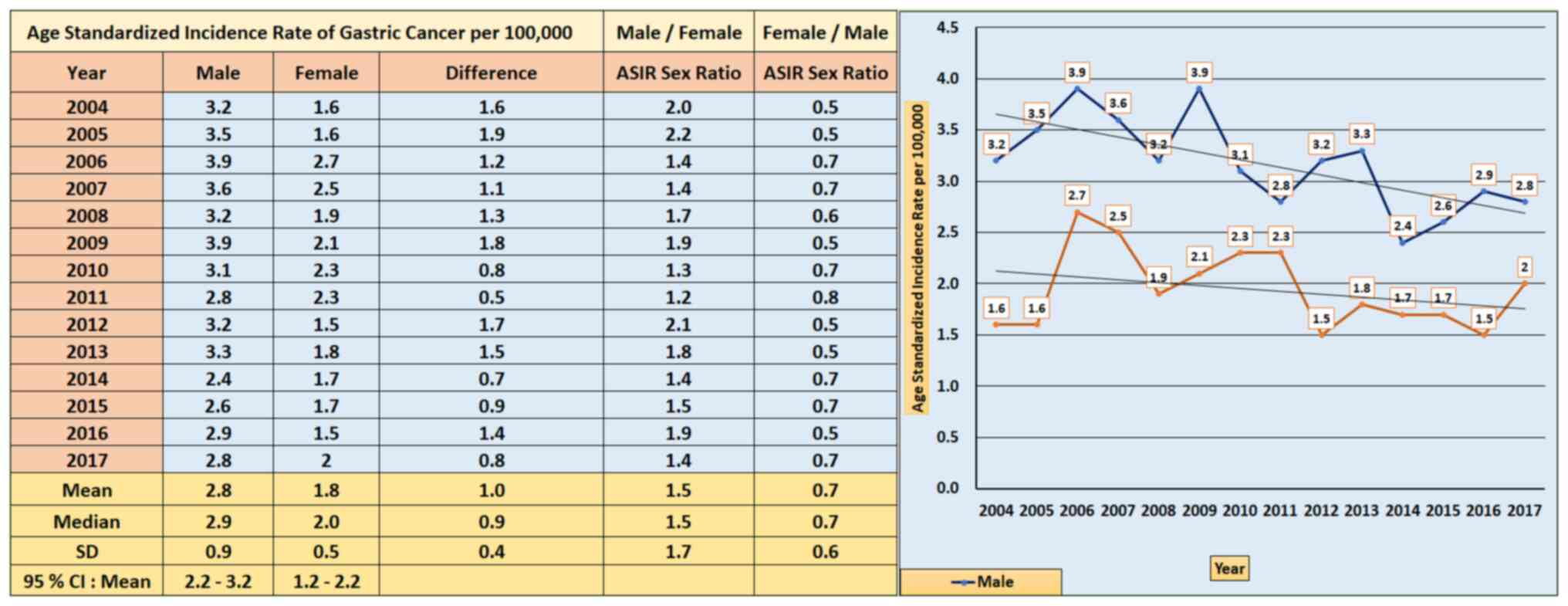
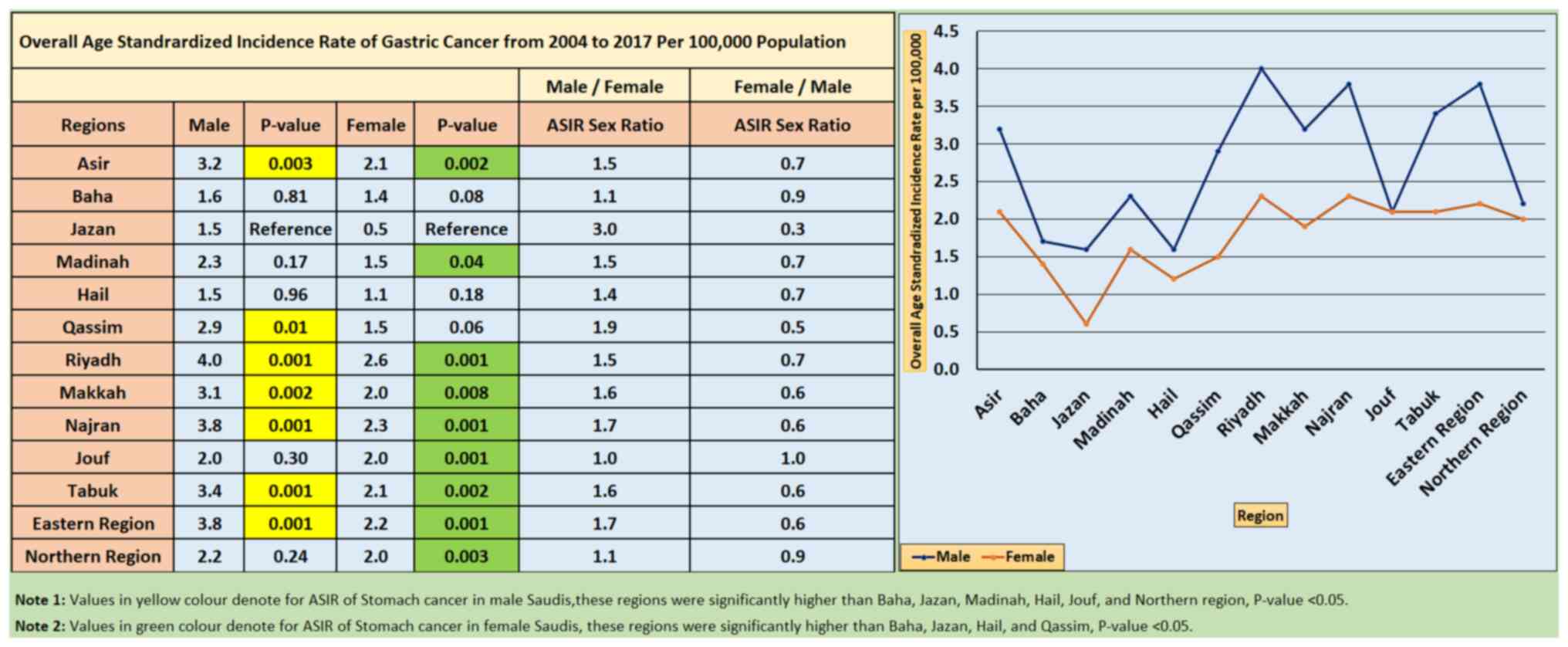
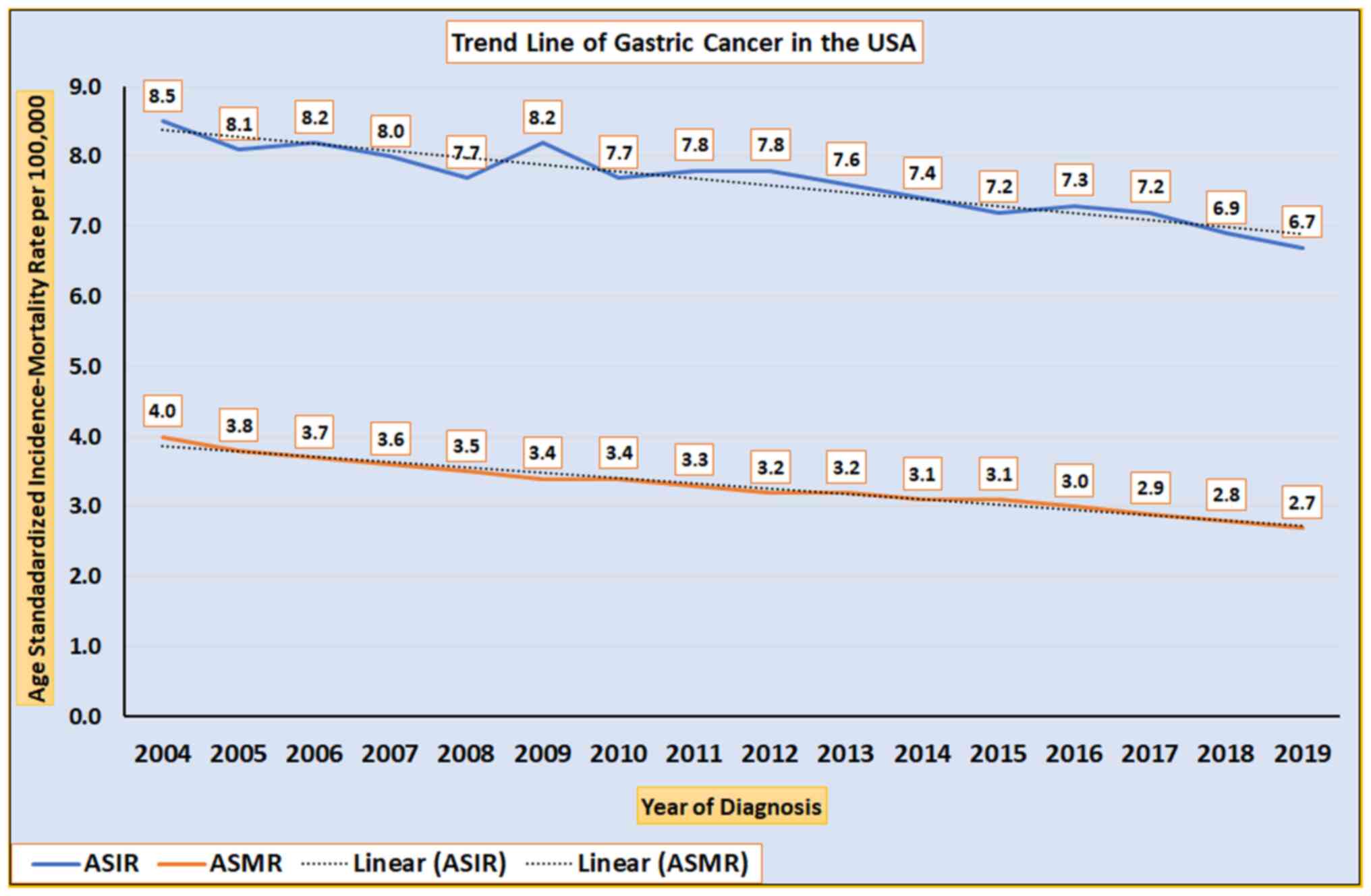
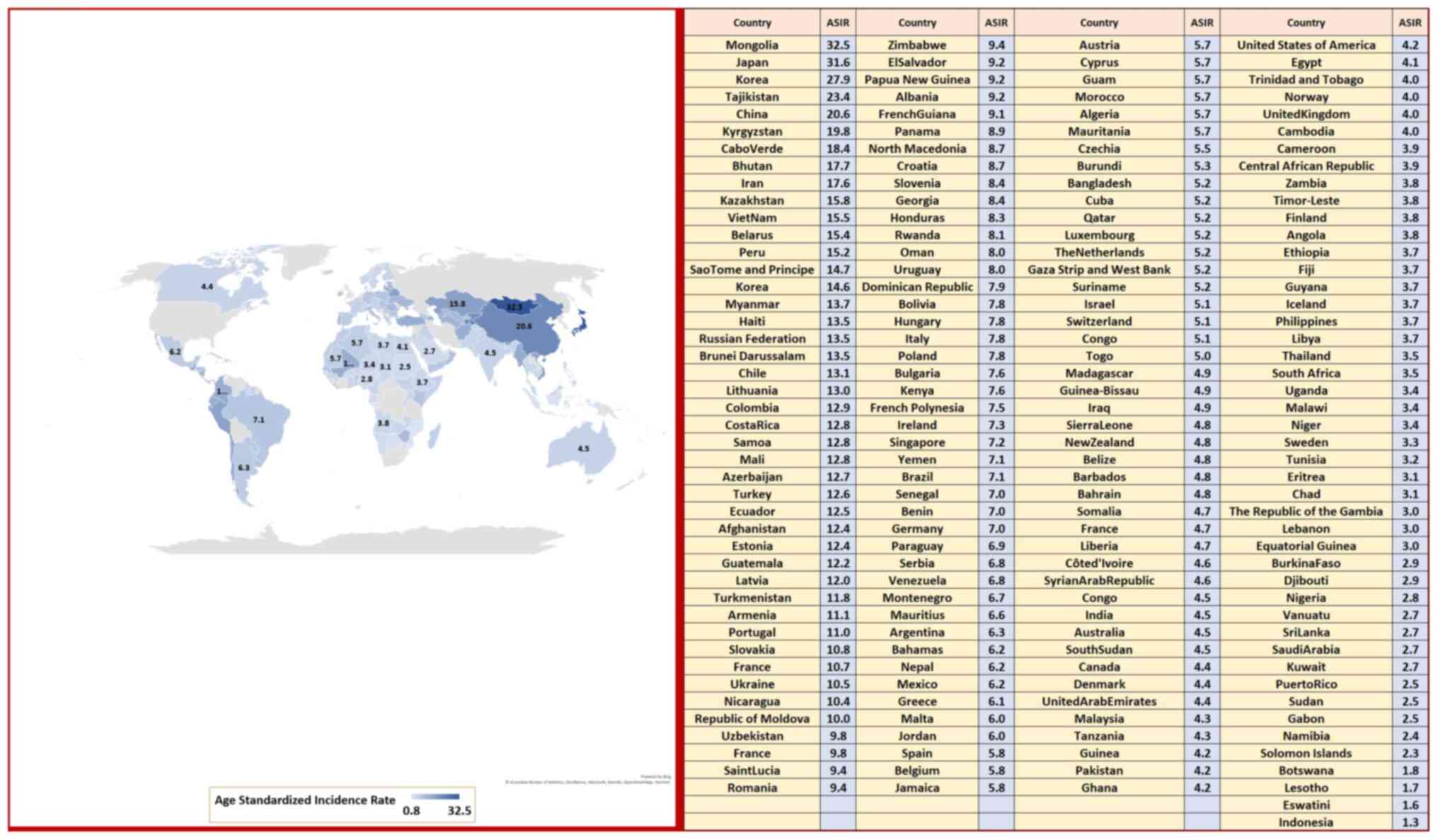
|
1
|
Machlowska J, Baj J, Sitarz M, Maciejewski
R and Sitarz R: Gastric cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors,
classification, genomic characteristics and treatment strategies.
Int J Mol Ici. 21(4012)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mukkamalla SKR, Recio-Boiles A and Babiker
HM: Gastric cancer. In: StatPearls (Internet). StatPearls
Publishing, Treasure Island, FL, 2022.
|
|
4
|
Ang T and Fock KM: Clinical epidemiology
of gastric cancer. Singapore Med J. 55:621–628. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ferro A, Peleteiro B, Malvezzi M, Bosetti
C, Bertuccio P, Levi F, Negri E, La Vecchia C and Lunet N:
Worldwide trends in gastric cancer mortality (1980-2011), with
predictions to. 2015, and incidence by subtype. Eur J Cancer.
50:1330–1344. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Edwards BK, Noone AM, Mariotto AB, Simard
EP, Boscoe FP, Henley SJ, Jemal A, Cho H, Anderson RN, Kohler BA,
et al: Annual Report to the Nation on the status of cancer,
1975-2010, featuring prevalence of comorbidity and impact on
survival among persons with lung, colorectal, breast, or prostate
cancer. Cancer. 120:1290–1314. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kaneko S and Yoshimura T: Time trend
analysis of gastric cancer incidence in Japan by histological
types, 1975-1989. Br J Cancer. 84:400–405. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
American Cancer Society. Key statistics
about stomach cancer. American Cancer Society, Atlanta, GA, 2022.
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/stomach-cancer/about/key-statistics.html.
Accessed September 20, 2022.
|
|
9
|
International Agency for Research on
Cancer (IARC): GLOBOCAN. Maps: Section for Cancer Incidence and
Mortality. IARC, Lyon, 2020. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home. Accessed September 20,
2020.
|
|
10
|
Saudi Cancer Registry. Cancer Incidence
Report Saudi Arabia 2017. Saudi Cancer Registry, Riyadh, 2017.
|
|
11
|
Kong X, Wang JL, Chen HM and Fang JY:
Comparison of the clinicopathological characteristics of young and
Elderly patients with gastric carcinoma: A meta analysis. J Surg
Oncol. 106:346–352. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Takatsu Y, Hiki N, Nunobe S, Ohashi M,
Honda M, Yamaguchi T, Nakajima T and Sano T: Clinicopathological
features of gastric cancer in young patients. Gastric Cancer.
19:472–478. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Milne AN, Sitarz R, Carvalho R, Carneiro F
and Offerhaus GJ: Early onset gastric cancer: On the road to
unraveling gastric carcinogenesis. Curr Mol Med. 7:15–28.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Forman D and Burley V: Gastric cancer:
Global pattern of the disease and an overview of environmental risk
factors. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 20:633–649.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Suryawala K, Soliman D, Mutyala M, Nageeb
S, Boktor M, Seth A, Aravantagi A, Sheth A, Morris J, Jordan P, et
al: Gastric cancer in women: A regional health-center seven year
retrospective study. World J Gastroenterol. 21:7805–7813.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Rawla P and Barsouk A: Epidemiology of
gastric cancer: Global trends, risk factors and prevention. Prz
Gastroenterol. 14:26–38. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yang D, Hendifar A, Lenz C, Togawa K, Lenz
F, Lurje G, Pohl A, Winder T, Ning Y, Groshen S and Lenz HJ:
Survival of metastatic gastric cancer: Significance of age, sex and
race/ethnicity. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2:77–84. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chen C, Gong X, Yang X, Shang X, Du Q,
Liao Q, Xie R, Chen Y and Xu J: The roles of estrogen and estrogen
receptors in gastrointestinal disease (review). Oncol Lett.
18:5673–5680. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
National Cancer Institute (NCI): Cancer of
the stomach-cancer stat facts. NCI, Bethesda, MD, 2022. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/stomach.html.
Retrieved September 26, 2022.
|
|
20
|
Sitarz R, Skierucha M, Mielko J, Offerhaus
GJA, Maciejewski R and Polkowski WP: Gastric cancer: Epidemiology,
prevention, classification, and treatment. Cancer Manag Res.
10:239–248. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lombe DC, Mwaba CK, Msadabwe SC, Banda L,
Mwale M, Pupwe G, Kamfwa P, Kanduza M, Munkupa H, Maliti B, et al:
Zambia's national cancer centre response to the COVID-19
pandemic-an opportunity for improved care. Ecancermedicalscience.
14(1051)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kartik A, Garg D and Singh RB:
Implications of reduced health care services for cancer patients in
India and similar resource-limited health care systems during
COVID-19 pandemic. Asia Pac J Public Health. 32:287–288.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Pulumati A, Pulumati A, Dwarakanath BS,
Verma A and Papineni RVL: Technological advancements in cancer
diagnostics: Improvements and limitations. Cancer Rep (Hoboken).
6(e1764)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|