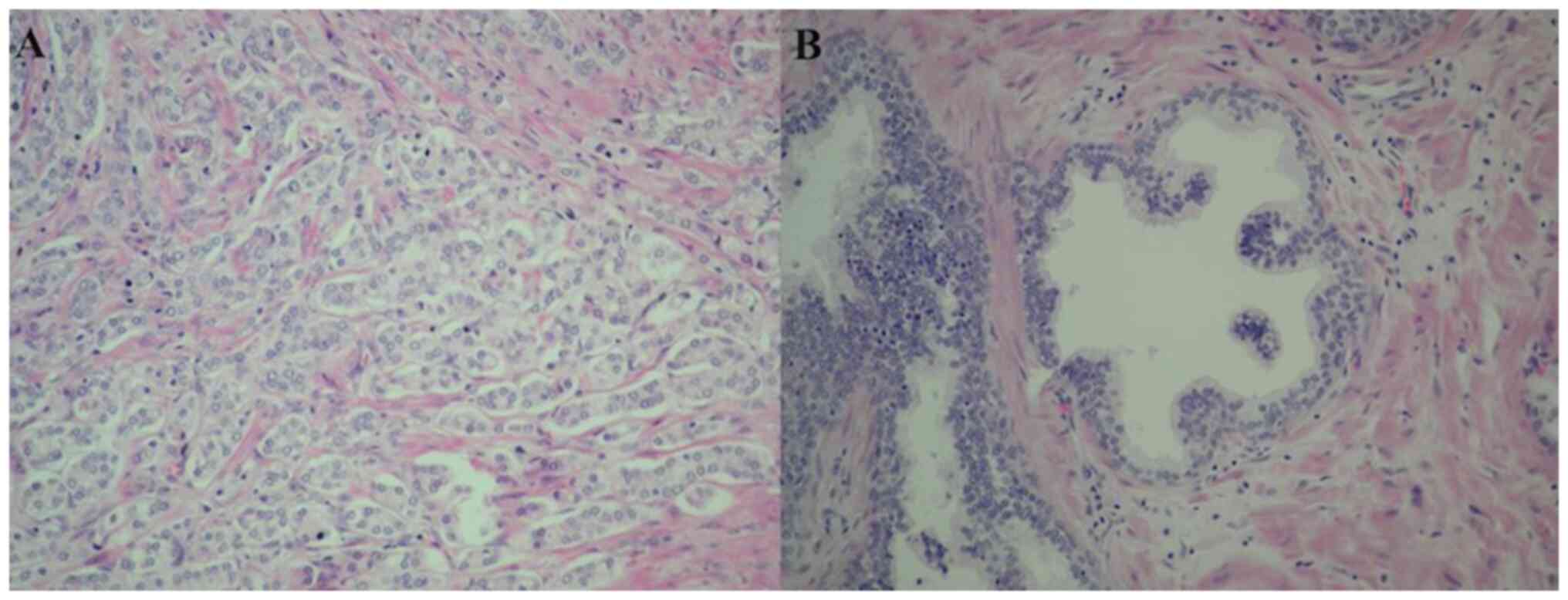
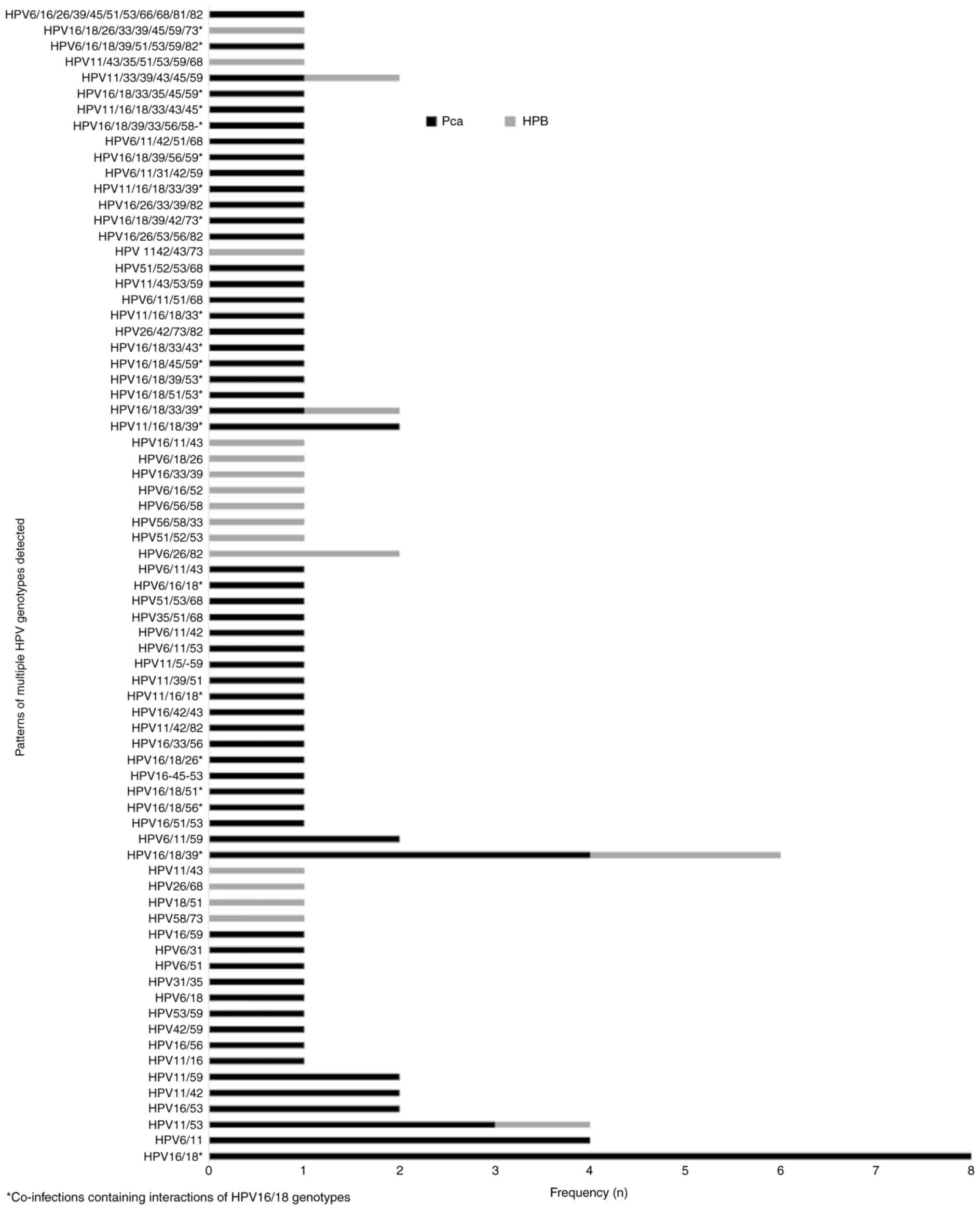
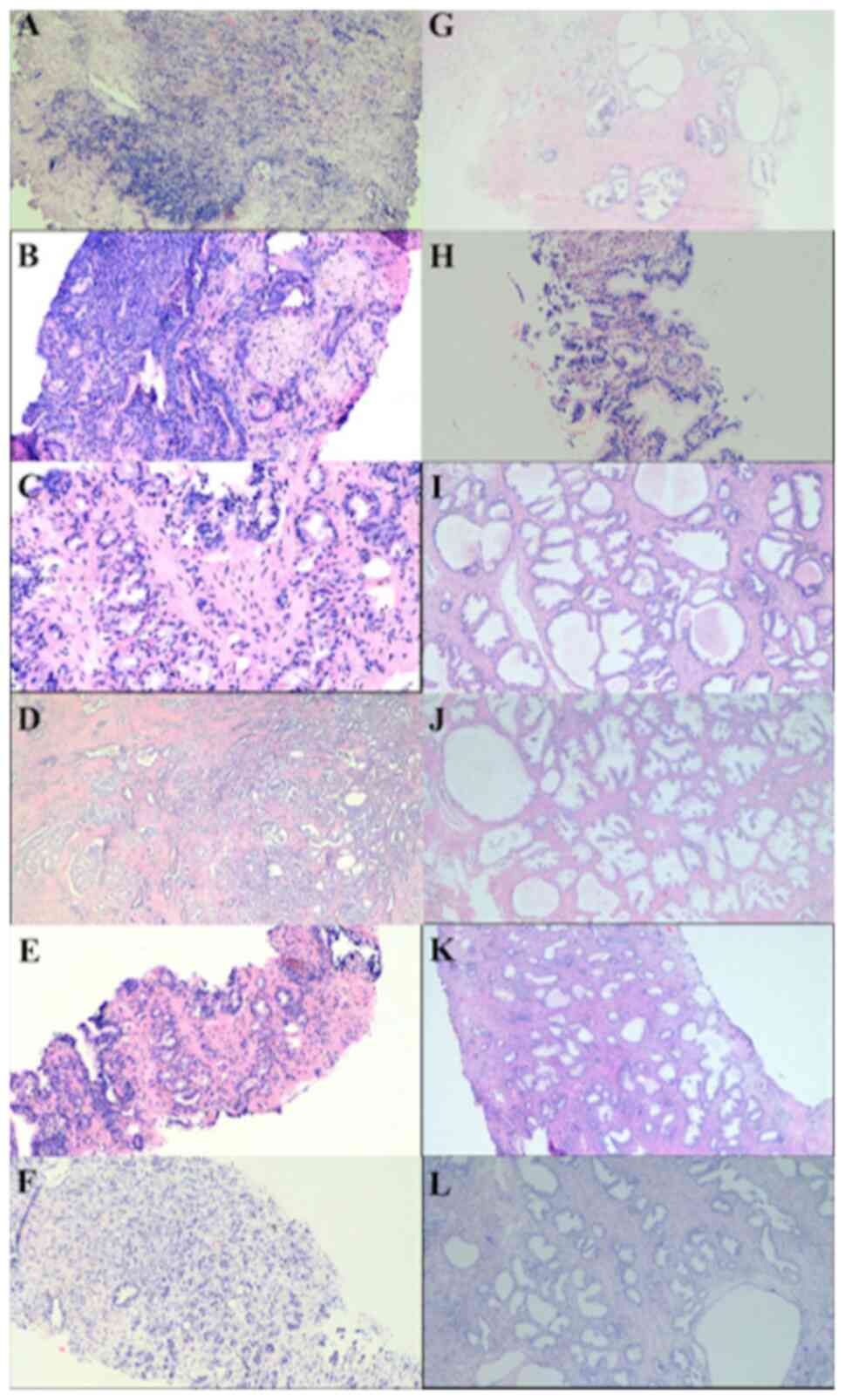
|
1
|
Bergengren O, Pekala KR, Matsoukas K,
Fainberg J, Mungovan SF, Bratt O, Bray F, Brawley O, Luckenbaugh
AN, Mucci L, et al: Update on prostate cancer epidemiology and risk
Factors-A systematic review. Eur Urol. 84:191–206. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Gandaglia G, Leni R, Bray F, Fleshner N,
Freedland SJ, Kibel A, Stattin P, Van Poppel H and La Vecchia C:
Epidemiology and prevention of prostate cancer. Eur Urol Oncol.
4:877–892. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gamboa-Hoil SI: Human papillomavirus in
men. Rev Int Androl. 21(100325)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of
Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Human Immunodeficiency Viruses and
Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Viruses. In: IARC Monographs on the
Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. IARC, Lyon, France,
pp250-270, 1996. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK321760/.
|
|
5
|
Jensen JE, Becker GL, Jackson JB and
Rysavy MB: Human papillomavirus and associated cancers: A Review.
Viruses. 16(680)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yin SH, Chung SD, Hung SH, Liu TC and Lin
HC: Association of prostate cancer with human papillomavirus
infections: A Case-control study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.
27:743–748. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Arriaga D, Morales F and Canizalez A:
Human papillomavirus and prostate cancer in Mexican men: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control: March
15, 2025 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
8
|
Sosse SA, Laraqui A, Mrabti M, Alami M,
Mzibri ME and Ennaji M: Molecular evaluation of human
papillomavirus as an oncogenic biomarker in prostate cancer. Mol
Biol Rep. 50:5719–5724. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Russo GI, Calogero AE, Condorelli RA,
Scalia G, Morgia G and La Vignera S: Human papillomavirus and risk
of prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging
Male. 23:132–138. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lawson JS and Glenn WK: Evidence for a
causal role by human papillomaviruses in prostate cancer-a
systematic review. Infect Agent Cancer. 15(41)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Moghoofei M, Keshavarz M, Ghorbani S,
Babaei F, Nahand JS, Tavakoli A, Mortazavi HS, Marjani A, Mostafaei
S and Monavari SH: Association between human papillomavirus
infection and prostate cancer: A global systematic review and
meta-analysis. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 15:e59–e67. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tsydenova IA, Ibragimova MK, Tsyganov MM
and Litviakov NV: Human papillomavirus and prostate cancer:
Systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep.
3(16597)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Opeyemi Bello R, Willis-Powell L, James O,
Sharma A, Marsh E, Ellis L, Gaston K and Siddiqui Y: Does human
papillomavirus play a causative role in prostate cancer? A
systematic review using bradford Hill's Criteria. Cancers (Basel).
15(3897)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mahmoudi S, Jafari-Sales A, Nasiri R and
Baghi H: Prostate cancer and human papillomavirus infection: A
recent literature review. Rev Res Med Microbiol. 33:100–108.
2022.
|
|
15
|
Ahmed MY, Cakir MO, Salman NA, Sandhu S
and Ashrafi GH: Concurrent high risk HPV35, HPV45, and HPV59
infections in prostate and bladder cancer tissues of a single
patient: A case report. Heliyon. 10(e35074)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Whitaker NJ, Glenn WK, Sahrudin A, Orde
MM, Delprado W and Lawson JS: Human papillomavirus and Epstein Barr
virus in prostate cancer: Koilocytes indicate potential oncogenic
influences of human papillomavirus in prostate cancer. Prostate.
73:236–241. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Medel-Flores O, Valenzuela-Rodríguez VA,
Ocadiz-Delgado R, Castro-Muñoz LJ, Hernández-Leyva S,
Lara-Hernández G, Silva-Escobedo JG, Vidal PG and Sánchez-Monroy V:
Association between HPV infection and prostate cancer in a Mexican
population. Genet Mol Biol. 41:781–789. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Giuliano AR, Nyitray AG, Kreimer AR,
Pierce Campbell CM, Goodman MT, Sudenga SL, Monsonego J and
Franceschi S: EUROGIN 2014 roadmap: Differences in human
papillomavirus infection natural history, transmission and human
papillomavirus-related cancer incidence by gender and anatomic site
of infection. Int J Cancer. 136:2752–2760. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Taylor ML, Mainous AG and Wells BJ:
Prostate cancer and sexually transmitted diseases: A meta-analysis.
Fam Med. 37:506–512. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang WY, Hayes R, Pfeiffer R, Viscidi RP,
Lee FK, Wang YF, Reding D, Whitby D, Papp JR and Rabkin CS:
Sexually transmissible infections and prostate cancer risk. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 17:2374–2381. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liu Z, Nyitray AG, Hwang LY, Swartz MD,
Abrahamsen M, Lazcano-Ponce E, Salmerón J, Quiterio M, Villa LL,
Baggio ML, et al: Human papillomavirus prevalence among 88 male
virgins residing in brazil, mexico, and the united states. J Infect
Dis. 214:1188–1191. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gameiro SF and Flondra KM: Human
Papillomavirus-associated tumor extracellular vesicles in HPV+
tumor microenvironments. J Clin Med. 12(5668)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Luna-Aguirre CM, Reyes-Cortés LM,
Torres-Grimaldo AA, Karr-de-León SF, Cerda-Flores RM, Melo-Nava B,
Aizpuru-Akel VE and Barrera-Saldaña HA: Prevalence of human
papillomavirus types in north and central regions of Mexico.
Epidemiol Infect. 146:1724–1730. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ferreira MT, Mendoza López RV, Gonçalves
MG, Ferreira S, Sirak B, Baggio ML, Lazcano-Ponce E, Nyitray AG,
Giuliano AR, Villa LL, et al: Human papillomavirus 16 lineage a
variants associated with persistent genital infections in men: The
HPV infection in men (HIM) study. J Infect Dis. 228:1748–1757.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Abidi SH, Bilwani F, Ghias K and Abbas F:
Viral etiology of prostate cancer: Genetic alterations and immune
response. A literature review. Int J Surg. 52:136–140.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sfanos KS, Yegnasubramanian S, Nelson WG
and De Marzo AM: The inflammatory microenvironment and microbiome
in prostate cancer development. Nat Rev Urol. 15:11–24.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Silva LLD, Teles AM, Santos JMO, Souza de
Andrade M, Medeiros R, Faustino-Rocha AI, Oliveira PA, Dos Santos
APA, Ferreira Lopes F, Braz G, et al: Malignancy associated with
Low-Risk HPV6 and HPV11: A systematic review and implications for
cancer prevention. Cancers (Basel). 15(4068)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kusters JMA, Brouwer JGM, van Benthem BHB,
Heijne JCM and Schim van der Loeff MF: Global Type-specific genital
human papillomavirus prevalence in men, by sexual orientation: A
systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Infect Dis. 228:1023–1032.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Gallegos-Bolaños J, Rivera-Domínguez JA,
Presno-Bernal JM and Cervantes-Villagrana RD: High prevalence of
co-infection between human papillomavirus (HPV) 51 and 52 in
Mexican population. BMC Cancer. 17(531)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang X, Lu D, Szporn AH, Zakowski MF and
Si Q: A comparative study of the genotype profiles of high-risk
human papillomavirus infection in male and female HIV-positive
patients and their correlation with anal cytology and biopsy. J Am
Soc Cytopathol. 11:21–30. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gaisa MM, Liu Y, Deshmukh AA, Stone KL and
Sigel KM: Electrocautery ablation of anal high-grade squamous
intraepithelial lesions: Effectiveness and key factors associated
with outcomes. Cancer. 126:1470–1479. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Torres-Ibarra L, Conde-Glez CJ, Salmerón
J, Palefsky J, Hernández-Nevares P, Sánchez-Alemán MA,
Magis-Rodríguez C and Lazcano-Ponce E: Risk factors for anal
HPV-16/18 infection in Mexican HIV-infected men who have sex with
men. Prev Med. 69:157–64. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang Z, Yang Y, Zhang L, Wu Y, Jia P, Ma
Q and Wang D: Relationship between cervicovaginal microecological
changes and HPV16/18 infection and cervical cancer in women of
childbearing age. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 53:825–834. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ao M, Yao X, Zheng D, Gu X and Xi M: Risk
of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 3 or more diagnoses for
human papillomavirus16/18-positive women by cytology and
co-infection status. Infect Agent Cancer. 18(57)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Nelson C and Mirabello L: Human
papillomavirus genomics: Understanding carcinogenicity. Tumour
Virus Res. 15(20025)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network.
Integrated genomic and molecular characterization of cervical
cancer. Nature. 543:378–384. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Mirabello L, Yeager M, Cullen M, Cullen M,
Boland JF, Chen Z, Wentzensen N, Zhang X, Yu K, Yang Q, et al:
HPV16 sublineage associations with Histology-specific cancer risk
using HPV Whole-genome sequences in 3200 women. J Natl Cancer Inst.
108(djw100)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xi LF, Kiviat NB, Hildesheim A, Galloway
DA, Wheeler CM, Ho J and Koutsky LA: Human papillomavirus type 16
and 18 variants: Race-related distribution and persistence. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 98:1045–1052. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Iwasaka T, Hayashi Y, Yokoyama M, Hara K,
Matsuo N and Sugimori H: ‘Hit and run’ oncogenesis by human
papillomavirus type 18 DNA. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 7:219–223.
1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Glenn WK, Ngan CC, Amos TG, Edwards RJ,
Swift J, Lutze-Mann L, Shang F, Whitaker NJ and Lawson JS: High
risk human papilloma viruses (HPVs) are present in benign prostate
tissues before development of HPV associated prostate cancer.
Infect Agent Cancer. 12(46)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Sun J, Xiang J, An Y, Xu J, Xiong Y, Wang
S and Xia Q: Unveiling the Association between HPV and Pan-Cancers:
A Bidirectional Two-sample mendelian randomization study. Cancers
(Basel). 15(5147)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Sarkar P, Malik S, Banerjee A, Datta C,
Pal DK, Ghosh A and Saha A: Differential microbial signature
associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer.
Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 12(894777)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sehn JK: Prostate cancer pathology: Recent
updates and controversies. Mo Med. 115:151–155. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Humphrey PA: Histopathology of prostate
cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 7(a030411)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hesterberg AB, Gordetsky JB and Hurley PJ:
Cribriform prostate cancer: Clinical pathologic and molecular
considerations. Urology. 155:47–54. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Sayan M, Tuac Y, Akgul M, Pratt GK, Rowan
MD, Akbulut D, Kucukcolak S, Tjio E, Moningi S, Leeman JE, et al:
Prognostic significance of the cribriform pattern in prostate
cancer: Clinical outcomes and genomic alterations. Cancers (Basel).
16(1248)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Russo GI, Soeterik T, Puche-Sanz I, Broggi
G, Lo Giudice A, De Nunzio C, Lombardo R, Marra G and Gandaglia G:
European Association of Urology Young Academic Urologists.
Oncological outcomes of cribriform histology pattern in prostate
cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prostate
Cancer Prostatic Dis. 26:646–654. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Woenckhaus J and Fenic I: Proliferative
inflammatory atrophy: A background lesion of prostate cancer?
Andrologia. 40:134–137. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
De Marzo AM, Marchi VL, Epstein JI and
Nelson WG: Proliferative inflammatory atrophy of the prostate:
Implications for prostatic carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol.
155:1985–1992. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Sfanos KS and De Marzo AM: Prostate cancer
and inflammation: The evidence. Histopathology. 60:199–215.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Mani RS, Amin MA, Li X, Kalyana-Sundaram
S, Veeneman BA, Wang L, Ghosh A, Aslam A, Ramanand SG, Rabquer BJ,
et al: Inflammation-induced oxidative stress mediates gene fusion
formation in prostate cancer. Cell Rep. 17:2620–2631.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Kwon OJ, Zhang L, Ittmann MM and Xin L:
Prostatic inflammation enhances basal-to-luminal differentiation
and accelerates initiation of prostate cancer with a basal cell
origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:E592–E600. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
de Bono JS, Guo C, Gurel B, De Marzo AM,
Sfanos KS, Mani RS, Gil J, Drake CG and Alimonti A: Prostate
carcinogenesis: Inflammatory storms. Nat Rev Cancer. 20:455–469.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sadri Nahand J, Esghaei M, Hamidreza
Monavari S, Moghoofei M, Jalal Kiani S, Mostafaei S, Mirzaei H and
Bokharaei-Salim F: The assessment of a possible link between
HPV-mediated inflammation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis in Prostate
cancer. Int Immunopharmacol. 88(106913)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Fatemipour M, Nahand JS, Fard Azar ME,
Baghi HB, Taghizadieh M, Sorayyayi S, Hussen BM, Mirzaei H,
Moghoofei M and Bokharaei-Salim F: Human papillomavirus and
prostate cancer: The role of viral expressed proteins in the
inhibition of anoikis and induction of metastasis. Microb Pathog.
152(104576)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Li S, Hong X, Wei Z, Xie M, Li W, Liu G,
Guo H, Yang J, Wei W and Zhang S: Ubiquitination of the HPV
Oncoprotein E6 Is Critical for E6/E6AP-Mediated p53 degradation.
Front Microbiol. 10(2483)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
El-Deiry WS: p21(WAF1) mediates Cell-cycle
inhibition, relevant to cancer suppression and therapy. Cancer Res.
76:5189–5191. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Barr AR, Cooper S, Heldt FS, Butera F,
Stoy H, Mansfeld J, Novák B and Bakal C: DNA damage during S-phase
mediates the proliferation-quiescence decision in the subsequent G1
via p21 expression. Nat Commun. 8(14728)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Szymonowicz KA and Chen J: Biological and
clinical aspects of HPV-related cancers. Cancer Biol Med.
17:864–878. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Wang G, Zhao D, Spring DJ and DePinho RA:
Genetics and biology of prostate cancer. Genes Dev. 32:1105–1140.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Sullivan GF, Yang JM, Vassil A, Yang J,
Bash-Babula J and Hait WN: Regulation of expression of the
multidrug resistance protein MRP1 by p53 in human prostate cancer
cells. J Clin Invest. 105:1261–1267. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Rigalli JP, Reichel M and Tocchetti GN:
Human papilloma virus (HPV) 18 proteins E6 and E7 up-regulate ABC
transporters in oropharyngeal carcinoma. Involvement of the
nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) pathway. Cancer Lett. 428:69–76.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Khooshemehri P, Jamaldini S, Ziaee S,
Afshari M, Sattari M, Narouie B, Sotoudeh M, Montazeri V, Sarhangi
N and Hasanzad M: Genetic polymorphism of mismatch repair genes and
susceptibility to prostate cancer. Urol J. 17:271–275.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Poku VO and Iram SH: A critical review on
modulators of Multidrug Resistance Protein 1 in cancer cells.
PeerJ. 10(e12594)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Boccardo E, Lepique AP and Villa LL: The
role of inflammation in HPV carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis.
31:1905–1912. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Sundström K, Ploner A, Arnheim-Dahlström
L, Eloranta S, Palmgren J, Adami HO, Ylitalo Helm N, Sparén P and
Dillner J: Interactions between high- and low-risk HPV types reduce
the risk of squamous cervical cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
107(djv185)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Wu Z, Li TY, Jiang M, Yu L, Zhao J, Wang
H, Zhang X, Chen W and Qiao Y: Human papillomavirus (HPV) 16/18 E6
oncoprotein expression in infections with single and multiple
genotypes. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 12:95–102. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|