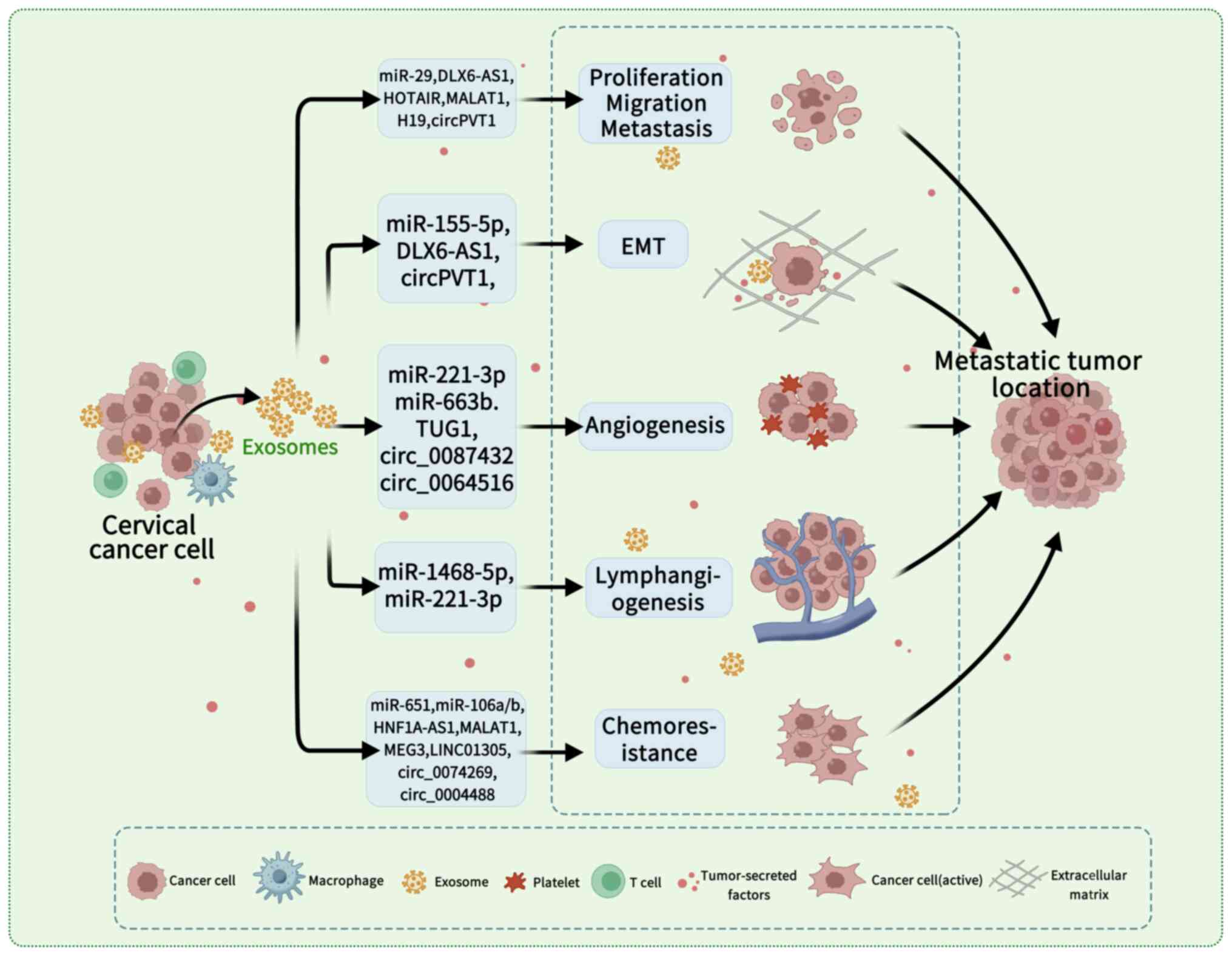
|
1
|
Raghani NR, Chorawala MR, Parekh K, Sharma
A, Alsaidan OA, Alam P, Fareed M and Prajapati B: Exosomal
miRNA-based theranostics in cervical cancer: Bridging diagnostics
and therapy. Med Oncol. 42(193)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Filho AM, Laversanne M, Ferlay J, Colombet
M, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Parkin DM, Soerjomataram I and Bray F: The
GLOBOCAN 2022 cancer estimates: Data sources, methods, and a
snapshot of the cancer burden worldwide. Int J Cancer.
156:1336–1346. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mileshkin LR, Moore KN, Barnes EH, Gebski
V, Narayan K, King MT, Bradshaw N, Lee YC, Diamante K, Fyles AW, et
al: Adjuvant chemotherapy following chemoradiotherapy as primary
treatment for locally advanced cervical cancer versus
chemoradiotherapy alone (OUTBACK): An international, open-label,
randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 24:468–482.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kalluri R and LeBleu VS: The biology,
function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science.
367(eaau6977)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hao Y, Song H, Zhou Z, Chen X, Li H, Zhang
Y, Wang J, Ren X and Wang X: Promotion or inhibition of
extracellular vesicle release: Emerging therapeutic opportunities.
J Control Release. 340:136–148. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Thakur A, Ke X, Chen YW, Motallebnejad P,
Zhang K, Lian Q and Chen HJ: The mini player with diverse
functions: Extracellular vesicles in cell biology, disease, and
therapeutics. Protein Cell. 13:631–654. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Naderi-Meshkin H, Lai X, Amirkhah R, Vera
J, Rasko JEJ and Schmitz U: Exosomal lncRNAs and cancer: Connecting
the missing links. Bioinformatics. 35:352–360. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ran Z, Wu S, Ma Z, Chen X, Liu J and Yang
J: Advances in exosome biomarkers for cervical cancer. Cancer Med.
11:4966–4978. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Diener C, Keller A and Meese E: Emerging
concepts of miRNA therapeutics: From cells to clinic. Trends Genet.
38:613–626. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kang C, Duo Y, Zheng L, Zhao N, Wang J,
Liu Z, Qiu L and Bi F: CAFs-derived exosomes promote the
development of cervical cancer by regulating miR-18a-5p-TMEM170B
signaling axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
694(149403)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nagamitsu Y, Nishi H, Sasaki T, Takaesu Y,
Terauchi F and Isaka K: Profiling analysis of circulating microRNA
expression in cervical cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. 5:189–194.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Pohlers M, Gies S, Taenzer T, Stroeder R,
Theobald L, Ludwig N, Kim YJ, Bohle RM, Solomayer EF, Meese E, et
al: Th17 cells target the metabolic miR-142-5p-succinate
dehydrogenase subunit C/D (SDHC/SDHD) axis, promoting invasiveness
and progression of cervical cancers. Mol Oncol. 18:2157–2178.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Mitra T and Elangovan S: Cervical cancer
development, chemoresistance, and therapy: A snapshot of
involvement of microRNA. Mol Cell Biochem. 476:4363–4385.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Dittmer J and Leyh B: Paracrine effects of
stem cells in wound healing and cancer progression (Review). Int J
Oncol. 44:1789–1798. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jayson GC, Kerbel R, Ellis LM and Harris
AL: Antiangiogenic therapy in oncology: Current status and future
directions. Lancet. 388:518–529. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang L, Li H, Yuan M, Li M and Zhang S:
Cervical cancer cells-secreted exosomal microRNA-221-3p promotes
invasion, migration and angiogenesis of microvascular endothelial
cells in cervical cancer by down-regulating MAPK10 expression.
Cancer Manag Res. 11:10307–10319. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
You X, Sun W, Wang Y, Liu X, Wang A, Liu
L, Han S, Sun Y, Zhang J, Guo L and Zhang Y: Cervical
cancer-derived exosomal miR-663b promotes angiogenesis by
inhibiting vinculin expression in vascular endothelial cells.
Cancer Cell Int. 21(684)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lehuédé C, Dupuy F, Rabinovitch R, Jones
RG and Siegel PM: Metabolic plasticity as a determinant of tumor
growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 76:5201–5208. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhou C, Wei W, Ma J, Yang Y, Liang L,
Zhang Y, Wang Z, Chen X, Huang L, Wang W and Wu S: Cancer-secreted
exosomal miR-1468-5p promotes tumor immune escape via the
immunosuppressive reprogramming of lymphatic vessels. Mol Ther.
29:1512–1528. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhou CF, Ma J, Huang L, Yi HY, Zhang YM,
Wu XG, Yan RM, Liang L, Zhong M, Yu YH, et al: Cervical squamous
cell carcinoma-secreted exosomal miR-221-3p promotes
lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis by targeting VASH1.
Oncogene. 38:1256–1268. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bhattacharjee M, Ghosh A, Das S, Sarker S,
Bhattacharya S, Das A, Ghosh S, Chattopadhyay S, Ghosh S and
Adhikary A: systemic codelivery of thymoquinone and doxorubicin by
targeted mesoporous silica nanoparticle sensitizes
doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer by interfering between the
MDR1/P-gp and miR 298 crosstalk. ACS Biomater Sci Eng.
10:6314–6331. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Havryliuk V, Wojtowicz K, Gagat M and
Żuryń A: Exosome-mediated mechanisms of drug resistance in lung
cancer: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 59:358–374. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhu X, Long L, Xiao H and He X:
Cancer-derived exosomal miR-651 as a diagnostic marker restrains
cisplatin resistance and directly targets ATG3 for cervical cancer.
Dis Markers. 2021(1544784)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Raji GR, Sruthi TV, Edatt L, Haritha K,
Sharath Shankar S and Sameer Kumar VB: Horizontal transfer of
miR-106a/b from cisplatin resistant hepatocarcinoma cells can alter
the sensitivity of cervical cancer cells to cisplatin. Cell Signal.
38:146–158. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Li H, Chi X, Li R, Ouyang J and Chen Y:
HIV-1-infected cell-derived exosomes promote the growth and
progression of cervical cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 15:2438–2447.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang J, Jiang M, Qian L, Lin X, Song W,
Gao Y and Zhou Y: The STAT3-miR-223-TGFBR3/HMGCS1 axis modulates
the progression of cervical carcinoma. Mol Oncol. 14:2313–2331.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Cui HJ, Zhang YN and Li HT: Mechanism of
exosome miRNA29 in cervical cancer metastasis. Chin J Cancer Prev
Treat. 25:1365–1370. 2018.
|
|
28
|
Cheng T and Huang S: Roles of non-coding
RNAs in cervical cancer metastasis. Front Oncol.
11(646192)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Eptaminitaki GC, Stellas D, Bonavida B and
Baritaki S: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) signaling in cancer
chemoresistance: From prediction to druggability. Drug Resist
Updat. 65(100866)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
He J, Huang B, Zhang K, Liu M and Xu T:
Long non-coding RNA in cervical cancer: From biology to therapeutic
opportunity. Biomed Pharmacother. 127(110209)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Huang X, Liu X, Du B, Liu X, Xue M, Yan Q,
Wang X and Wang Q: LncRNA LINC01305 promotes cervical cancer
progression through KHSRP and exosome-mediated transfer. Aging
(Albany NY). 13:19230–19242. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ding XZ, Zhang SQ, Deng XL and Qiang JH:
Serum exosomal lncRNA DLX6-AS1 Is a promising biomarker for
prognosis prediction of cervical cancer. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
20(1533033821990060)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Xie F, Xie G and Sun Q: Long noncoding RNA
DLX6-AS1 promotes the progression in cervical cancer by targeting
miR-16-5p/ARPP19 axis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 35:129–136.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhang J, Liu SC, Luo XH, Tao GX, Guan M,
Yuan H and Hu DK: Exosomal long noncoding RNAs are differentially
expressed in the cervicovaginal lavage samples of cervical cancer
patients. J Clin Lab Anal. 30:1116–1121. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhou Y, Wang Y, Lin M, Wu D and Zhao M:
LncRNA HOTAIR promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by
sponging miR-214-3p in HPV16 positive cervical cancer cells. Cancer
Cell Int. 21(400)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tie W and Ge F: MALAT1 inhibits
proliferation of HPV16-positive cervical cancer by sponging
miR-485-5p to promote expression of MAT2A. DNA Cell Biol.
40:1407–1417. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Gao Z, Wang Q, Ji M, Guo X, Li L and Su X:
Exosomal lncRNA UCA1 modulates cervical cancer stem cell
self-renewal and differentiation through microRNA-122-5p/SOX2 axis.
J Transl Med. 19(229)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Iempridee T: Long non-coding RNA H19
enhances cell proliferation and anchorage-independent growth of
cervical cancer cell lines. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 242:184–193.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang W, Wang Q, Yang Y, Zhou S, Zhang P
and Feng T: The role of exosomal lncRNAs in cancer biology and
clinical management. Exp Mol Med. 53:1669–1673. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Lei L and Mou Q: Exosomal taurine
up-regulated 1 promotes angiogenesis and endothelial cell
proliferation in cervical cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 21:717–725.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Luo X, Wei J, Yang FL, Pang XX, Shi F, Wei
YX, Liao BY and Wang JL: Exosomal lncRNA HNF1A-AS1 affects
cisplatin resistance in cervical cancer cells through regulating
microRNA-34b/TUFT1 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 19(323)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hu Y, Li G, Ma Y, Luo G, Wang Q and Zhang
S: Effect of exosomal lncRNA MALAT1/miR-370-3p/STAT3 positive
feedback loop on PI3K/Akt pathway mediating cisplatin resistance in
cervical cancer cells. J Oncol. 2023(6341011)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Du Y, Geng G, Zhao C, Gao T and Wei B:
LncRNA MEG3 promotes cisplatin sensitivity of cervical cancer cells
by regulating the miR-21/PTEN axis. BMC Cancer.
22(1145)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Verduci L, Strano S, Yarden Y and Blandino
G: The circRNA-microRNA code: Emerging implications for cancer
diagnosis and treatment. Mol Oncol. 13:669–680. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhang S, Chen Z, Sun J, An N and Xi Q:
CircRNA hsa_circRNA_0000069 promotes the proliferation, migration
and invasion of cervical cancer through miR-873-5p/TUSC3 axis.
Cancer Cell Int. 20(287)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ma H, Tian T, Liu X, Xia M, Chen C, Mai L,
Xie S and Yu L: Upregulated circ_0005576 facilitates cervical
cancer progression via the miR-153/KIF20A axis. Biomed
Pharmacother. 118(109311)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Tong Y, Jia L, Li M, Li H and Wang S:
Identification of exosomal circSLC26A4 as a liquid biopsy marker
for cervical cancer. PLoS One. 19(e0305050)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Preußer C, Hung LH, Schneider T, Schreiner
S, Hardt M, Moebus A, Santoso S and Bindereif A: Selective release
of circRNAs in platelet-derived extracellular vesicles. J Extracell
Vesicles. 7(1424473)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Dongre A and Weinberg RA: New insights
into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
implications for cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:69–84.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Wang H, Wei M, Kang Y, Xing J and Zhao Y:
Circular RNA circ_PVT1 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition to
promote metastasis of cervical cancer. Aging (Albany NY).
12:20139–20151. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Zhang XP, Pei JP, Zhang CD, Yusupu M, Han
MH and Dai DQ: Exosomal circRNAs: A key factor of tumor
angiogenesis and therapeutic intervention. Biomed Pharmacother.
156(113921)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Xia H, Yang X, Chen Y, Li H and Chu GF:
Effect of cervical cancer-derived exosomal hsa_circ_0087432 on the
proliferation and migration of HUVECs. Med J Chin People's Liber
Army. 46:327–332. 2021.
|
|
53
|
Wang Y, Xie Y, Wang X, Yang N, Wu Z and
Zhang X: Tumor cells-derived extracellular vesicles carry
circ_0064516 competitively inhibit microRNA-6805-3p and promote
cervical cancer angiogenesis and tumor growth. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 28:97–112. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Wang Y, Liu J, Ma J, Sun T, Zhou Q, Wang
W, Wang G, Wu P, Wang H, Jiang L, et al: Exosomal circRNAs:
Biogenesis, effect and application in human diseases. Mol Cancer.
18(116)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Chen J, Wu S, Wang J, Sha Y and Ji Y:
Hsa_circ_0074269-mediated upregulation of TUFT1 through miR-485-5p
increases cisplatin resistance in cervical cancer. Reprod Sci.
29:2236–2250. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Yi H, Han Y, Li Q, Wang X, Xiong L and Li
S: Circular RNA circ_0004488 increases cervical cancer paclitaxel
resistance via the miR-136/MEX3C signaling pathway. J Oncol.
2022(5435333)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Welsh JA, Goberdhan DCI, O'Driscoll L,
Buzas EI, Blenkiron C, Bussolati B, Cai H, Di Vizio D, Driedonks
TAP, Erdbrügger U, et al: Minimal information for studies of
extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced
approaches. J Extracell Vesicles. 13(e12404)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|