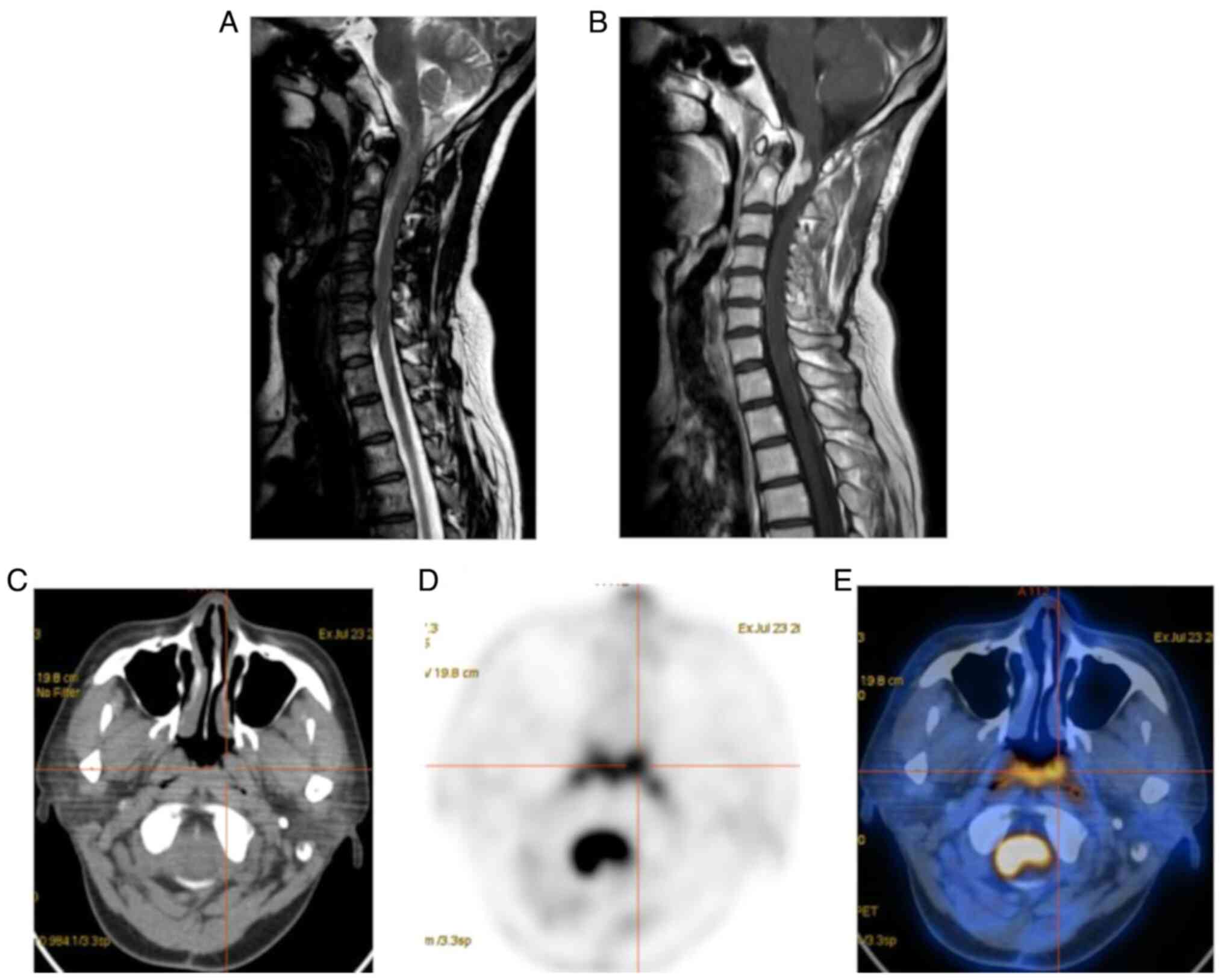
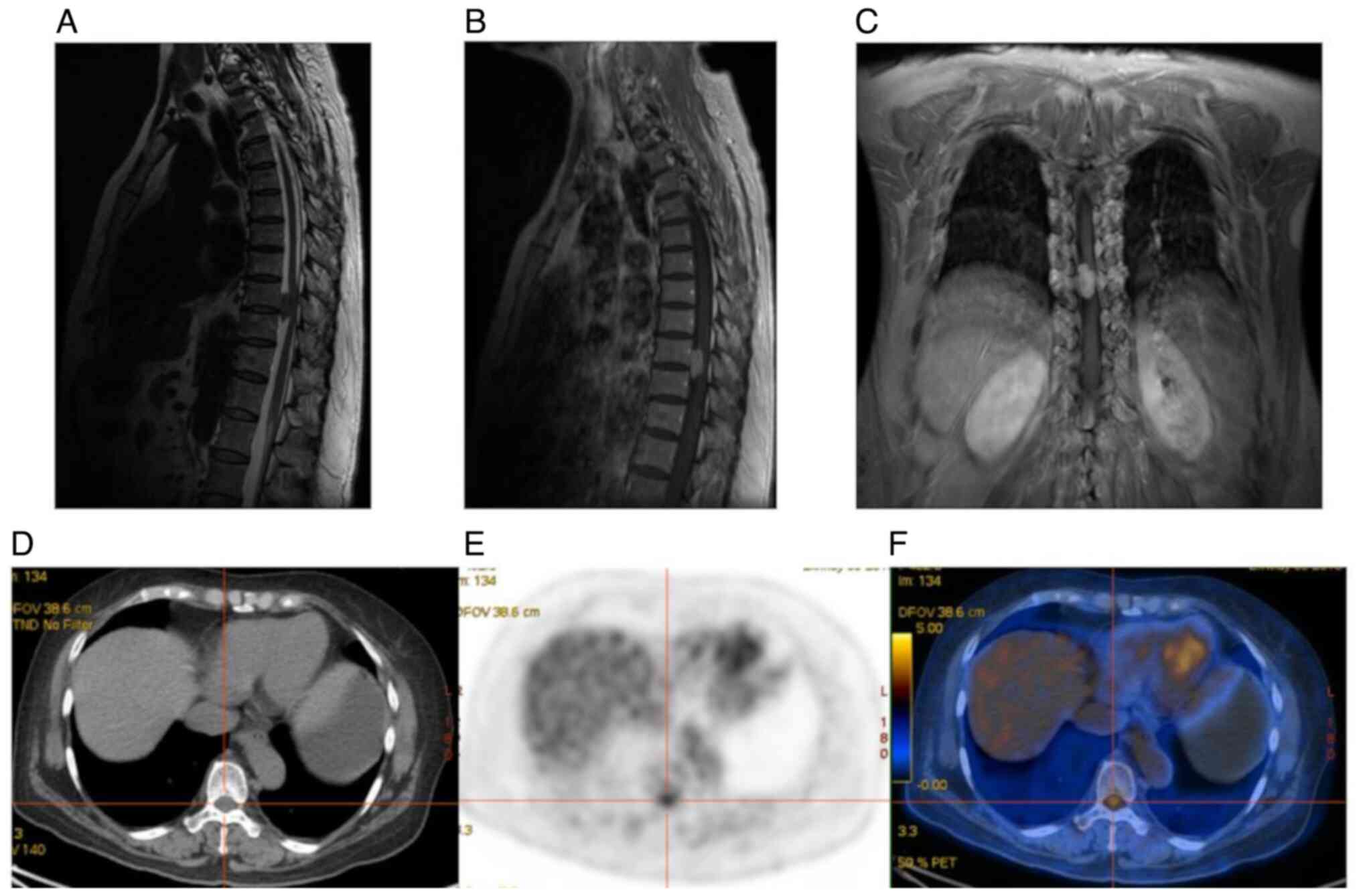
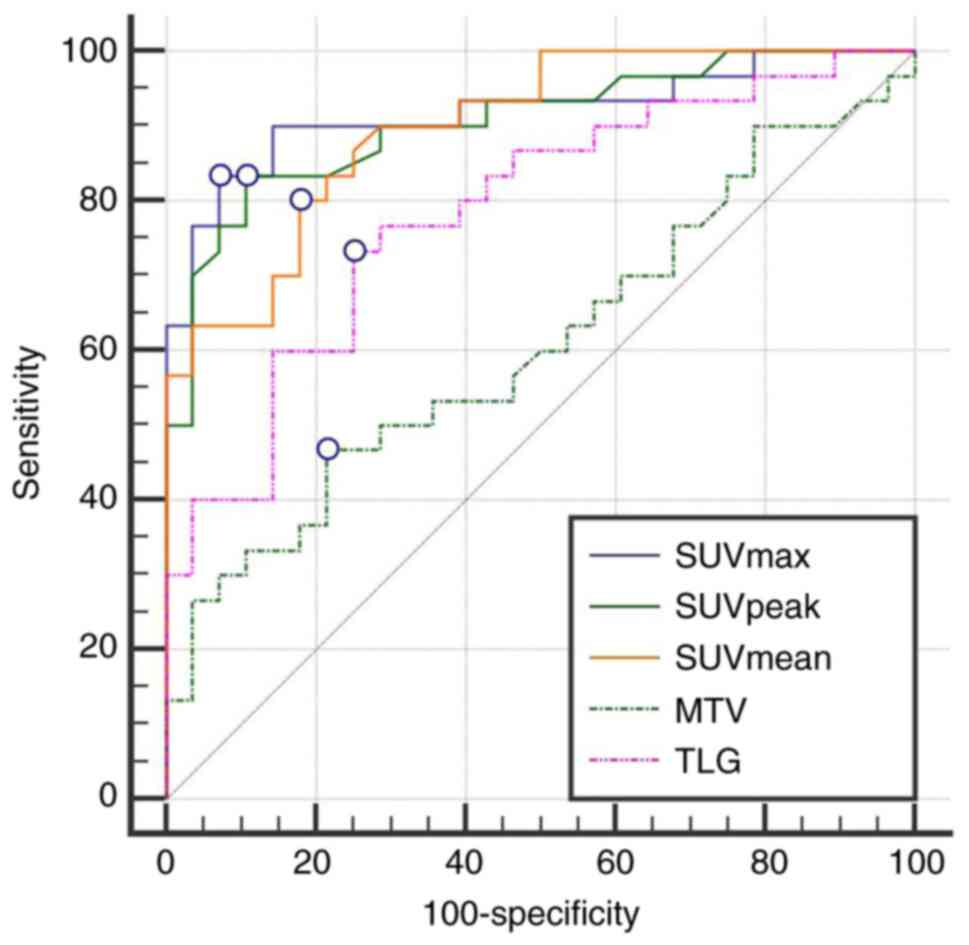
|
1
|
Xia LL, Tang J and Huang SL: Primary
intraspinal benign tumors treated surgically: an analysis from
China. Br J Neurosurg. 1–4. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
2
|
Watts J, Box GA, Galvin A, Van Tonder F,
Trost N and Sutherland T: Magnetic resonance imaging of
intramedullary spinal cord lesions: A pictorial review. J Med
Imaging Radiat Oncol. 58:569–581. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Dammacco F, Rubini G, Ferrari C, Vacca A
and Racanelli V: 18F-FDG PET/CT: A review of diagnostic
and prognostic features in multiple myeloma and related disorders.
Clin Exp Med. 15:1–18. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shen G, Ma H, Pan L, Su M and Kuang A:
Primary spinal poorly differentiated neuroendocrine tumor displayed
on FDG PET/CT. Clin Nucl Med. 44:e586–e587. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Naito K, Yamagata T, Arima H, Abe J,
Tsuyuguchi N, Ohata K and Takami T: Qualitative analysis of spinal
intramedullary lesions using PET/CT. J Neurosurg Spine. 23:613–619.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sher A, Lacoeuille F, Fosse P, Vervueren
L, Cahouet-Vannier A, Dabli D, Bouchet F and Couturier O: For avid
glucose tumors, the SUV peak is the most reliable parameter for
[(18)F]FDG-PET/CT quantification, regardless of acquisition time.
EJNMMI Res. 6(21)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Duarte PS, Zhuang H, Castellucci P and
Alavi A: The receiver operating characteristic curve for the
standard uptake value in a group of patients with bone marrow
metastasis. Mol Imaging Biol. 4:157–160. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Fawzy MF, Almassry HN and Ismail AM: What
can be achieved by using MR-DWI and ADC value in cases of
intramedullary spinal cord lesions of non-traumatic causes? Egyp J
Radio Nucl Med. 49:711–718. 2018.
|
|
9
|
Kessler J, Pawha P, Shpilberg K and
Tanenbaum L: Diffusion-weighted Imaging Facilitates Detection of
Spinal Multiple Myeloma and Assists in Diagnosing Equivocal
Lesions. Radiological Society of North America 2011 Scientific
Assembly and Annual Meeting, November 26 - December 2, 2011,
Chicago, IL. http://archive.rsna.org/2011/11001777.html. Accessed
April 15, 2021.
|
|
10
|
Piroth MD, Pinkawa M, Holy R, Klotz J,
Nussen S, Stoffels G, Coenen HH, Kaiser HJ, Langen KJ and Eble MJ:
Prognostic value of early [18F]fluoroethyltyrosine positron
emission tomography after radiochemotherapy in glioblastoma
multiforme. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 80:176–184.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tomura N, Ito Y, Matsuoka H, Saginoya T,
Numazawa SI, Mizuno Y and Watanabe K: PET findings of
intramedullary tumors of the spinal cord using [18F] FDG and [11C]
methionine. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 34:1278–1283. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Laufer I, Lis E, Pisinski L, Akhurst T and
Bilsky MH: The accuracy of [(18)F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron
emission tomography as confirmed by biopsy in the diagnosis of
spine metastases in a cancer population. Neurosurgery. 64:107–113;
discussion 113-4. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Schmidt GP, Schoenberg SO, Schmid R, Stahl
R, Tiling R, Becker CR, Reiser MF and Baur-Melnyk A: Screening for
bone metastases: Whole-body MRI using a 32-channel system versus
dual-modality PET-CT. Eur Radiol. 17:939–949. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Martins ES, Duque C, Rebelo O and Batista
S: Primary intramedullary spinal-cord lymphoma (PISCL): A rare
entity with a challenging diagnosis. BMJ Case Rep.
14(e242548)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sahel OA, Bazine A, Nabih SO, Benameur Y,
Biyi A and Doudouh A: Unsuspected intramedullary spinal cord
metastasis detected by FDG PET/CT. Indian J Nucl Med. 35:353–354.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liu M, Lu L, Liu Q, Bai Y and Dong A: FDG
PET/CT in disseminated intracranial and intramedullary spinal cord
tuberculomas. Clin Nucl Med. 46:266–269. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Liu Q, Liu M, Bai Y and Dong A: Solitary
acute inflammatory demyelinating lesion of the cervical spinal cord
mimicking malignancy on FDG PET/CT. Clin Nucl Med. 45:1023–1025.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mostardi PM, Diehn FE, Rykken JB, Eckel
LJ, Schwartz KM, Kaufmann TJ, Wood CP, Wald JT and Hunt CH:
Intramedullary spinal cord metastases: Visibility on PET and
correlation with MRI features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 35:196–201.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Viel T, Talasila KM, Monfared P, Wang J,
Jikeli JF, Waerzeggers Y, Neumaier B, Backes H, Brekka N, Thorsen
F, et al: Analysis of the growth dynamics of angiogenesis-dependent
and -independent experimental glioblastomas by multimodal
small-animal PET and MRI. J Nucl Med. 53:1135–1145. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|