|
1
|
Cheung GYC, Bae JS and Otto M:
Pathogenicity and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus.
Virulence. 12:547–569. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Santos M, Santos R, Soeiro P, Silvestre S
and Ferreira S: Resveratrol as an inhibitor of the NorA efflux pump
and resistance modulator in Staphylococcus aureus.
Antibiotics (Basel). 12(1168)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Shoaib M, Aqib AI, Muzammil I, Majeed N,
Bhutta ZA, Kulyar MFEA, Fatima M, Zaheer CF, Muneer A, Murtaza M,
et al: MRSA compendium of epidemiology, transmission,
pathophysiology, treatment, and prevention within one health
framework. Front Microbiol. 13(1067284)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wertheim HFL, Melles DC, Vos MC, van
Leeuwen W, van Belkum A, Verbrugh HA and Nouwen JL: The role of
nasal carriage in Staphylococcus aureus infections. Lancet
Infect Dis. 5:751–762. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
David MZ and Daum RS: Community-associated
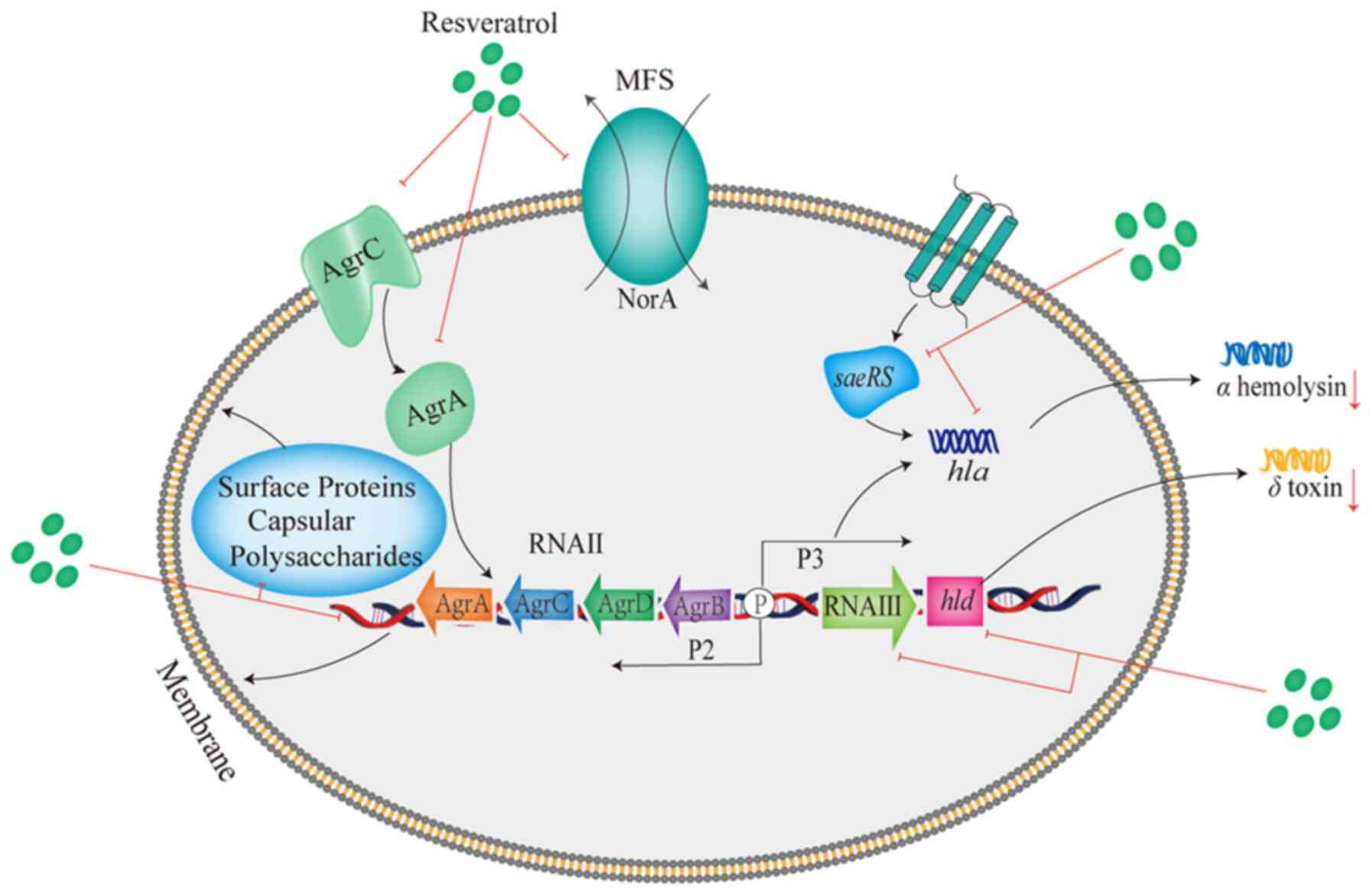
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Epidemiology
and clinical consequences of an emerging epidemic. Clin Microbiol
Rev. 23:616–687. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang Y, Zhang P, Wu J, Chen S, Jin Y, Long
J, Duan G and Yang H: Transmission of livestock-associated
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus between animals,
environment, and humans in the farm. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int.
30:86521–86539. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zheng P, Liu F, Long J, Jin Y, Chen S,
Duan G and Yang H: Latest advances in the application of humanized
mouse model for Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis.
228:800–809. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Deng J, Zhang BZ, Chu H, Wang XL, Wang Y,
Gong HR, Li R, Yang D, Li C, Dou Y, et al: Adenosine synthase a
contributes to recurrent Staphylococcus aureus infection by
dampening protective immunity. EBioMedicine.
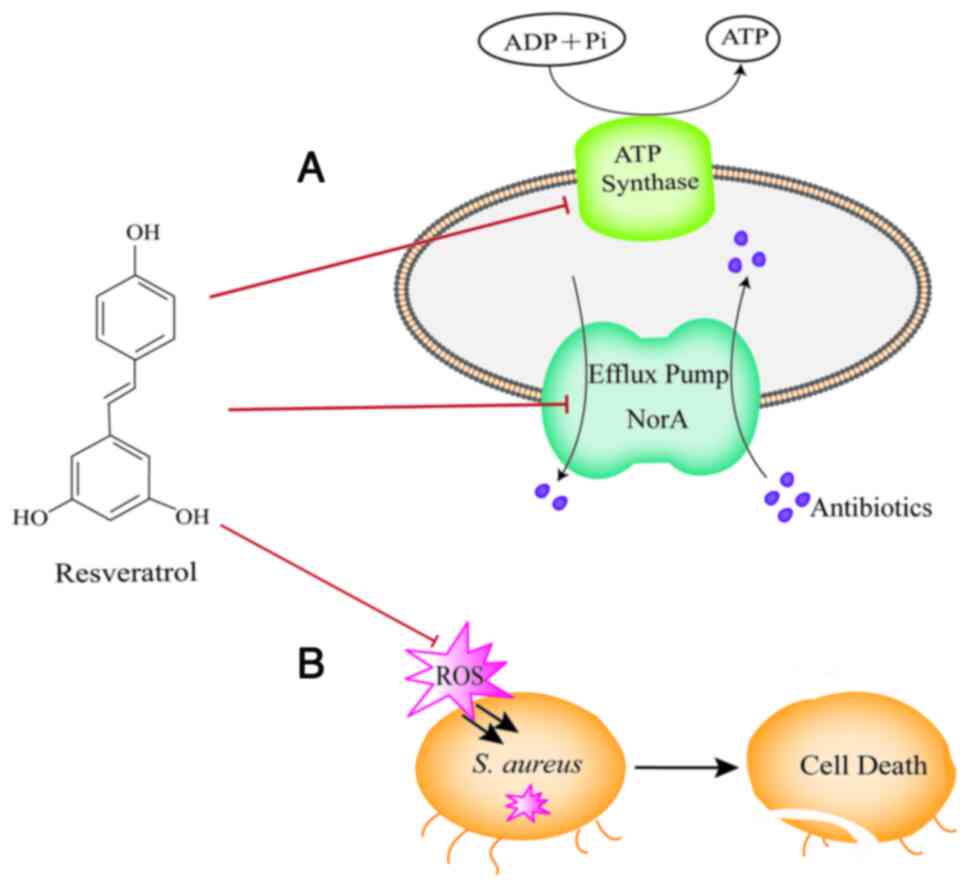
70(103505)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li J, Liu D, Tian X, Koseki S, Chen S, Ye
X and Ding T: Novel antibacterial modalities against methicillin
resistant Staphylococcus aureus derived from plants. Crit
Rev Food Sci Nutr. 59 (Suppl 1):S153–S161. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Malczak I and Gajda A: Interactions of
naturally occurring compounds with antimicrobials. J Pharm Anal.
13:1452–1470. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang L, Huang Y, Yin G, Wang J, Wang P,
Chen ZY, Wang T and Ren G: Antimicrobial activities of Asian
ginseng, American ginseng, and notoginseng. Phytother Res.
34:1226–1236. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bostanghadiri N, Pormohammad A, Chirani
AS, Pouriran R, Erfanimanesh S and Hashemi A: Comprehensive review
on the antimicrobial potency of the plant polyphenol resveratrol.
Biomed Pharmacother. 95:1588–1595. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Pastor RF, Restani P, Di Lorenzo C, Orgiu
F, Teissedre PL, Stockley C, Ruf JC, Quini CI, Tejedor NG,
Gargantini R, et al: Resveratrol, human health and winemaking
perspectives. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 59:1237–1255. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhang LX, Li CX, Kakar MU, Khan MS, Wu PF,
Amir RM, Dai DF, Naveed M, Li QY, Saeed M, et al: Resveratrol (RV):
A pharmacological review and call for further research. Biomed
Pharmacother. 143(112164)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ignatowicz E and Baer-Dubowska W:
Resveratrol, a natural chemopreventive agent against degenerative
diseases. Pol J Pharmacol. 53:557–569. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Stervbo U, Vang O and Bonnesen C: A review
of the content of the putative chemopreventive phytoalexin
resveratrol in red wine. Food Chem. 101:449–457. 2007.
|
|
17
|
Cottart CH, Nivet-Antoine V,
Laguillier-Morizot C and Beaudeux JL: Resveratrol bioavailability
and toxicity in humans. Mol Nutr Food Res. 54:7–16. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ma DSL, Tan LTH, Chan KG, Yap WH,
Pusparajah P, Chuah LH, Ming LC, Khan TM, Lee LH and Goh BH:
Resveratrol-potential antibacterial agent against foodborne
pathogens. Front Pharmacol. 9(102)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Özyalçın B and Sanlier N: Antiobesity
pathways of pterostilbene and resveratrol: A comprehensive insight.
Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 1–9. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
20
|
Abedini E, Khodadadi E, Zeinalzadeh E,
Moaddab SR, Asgharzadeh M, Mehramouz B, Dao S and Samadi KH: A
comprehensive study on the antimicrobial properties of resveratrol
as an alternative therapy. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2021(8866311)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
El-Mahdy AM, Alqahtani M, Almukainzi M,
Alghoribi MF and Abdel-Rhman SH: Effect of resveratrol and curcumin
on gene expression of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
aureus (MRSA) toxins. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 34:141–148.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Oliveira AR, Domingues FC and Ferreira S:
The influence of resveratrol adaptation on resistance to
antibiotics, benzalkonium chloride, heat and acid stresses of
Staphylococcus aureus and listeria monocytogenes. Food
Control. 73:1420–1425. 2017.
|
|
23
|
Paulo L, Ferreira S, Gallardo E, Queiroz
JA and Domingues F: Antimicrobial activity and effects of
resveratrol on human pathogenic bacteria. World J Microbiol
Biotechnol. 26:1533–1538. 2010.
|
|
24
|
Prevete G, Simonis B, Mazzonna M, Mariani
F, Donati E, Sennato S, Ceccacci F and Bombelli C: Resveratrol and
resveratrol-loaded galactosylated liposomes: Anti-adherence and
cell wall damage effects on Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA.
Biomolecules. 13(1494)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Nøhr-Meldgaard K, Ovsepian A, Ingmer H and
Vestergaard M: Resveratrol enhances the efficacy of aminoglycosides
against Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Antimicrob Agents.
52:390–396. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Singh D, Mendonsa R, Koli M, Subramanian M
and Nayak SK: Antibacterial activity of resveratrol structural
analogues: A mechanistic evaluation of the structure-activity
relationship. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 367:23–32. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu Y, Zhou J, Qu Y, Yang X, Shi G, Wang
X, Hong Y, Drlica K and Zhao X: Resveratrol antagonizes
antimicrobial lethality and stimulates recovery of bacterial
mutants. PLoS One. 11(e0153023)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tegos G, Stermitz FR, Lomovskaya O and
Lewis K: Multidrug pump inhibitors uncover remarkable activity of
plant antimicrobials. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 46:3133–3141.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sun D, Hurdle JG, Lee R, Lee R, Cushman M
and Pezzuto JM: Evaluation of flavonoid and resveratrol chemical
libraries reveals abyssinone II as a promising antibacterial lead.
ChemMedChem. 7:1541–1545. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chan MMY: Antimicrobial effect of
resveratrol on dermatophytes and bacterial pathogens of the skin.
Biochem Pharmacol. 63:99–104. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jung CM, Heinze TM, Schnackenberg LK,
Mullis LB, Elkins SA, Elkins CA, Steele RS and Sutherland JB:
Interaction of dietary resveratrol with animal-associated bacteria.
FEMS Microbiol Lett. 297:266–273. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zakova T, Rondevaldova J, Bernardos A,
Landa P and Kokoska L: The relationship between structure and in
vitro antistaphylococcal effect of plant-derived stilbenes. Acta
Microbiol Immunol Hung. 65:467–476. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Skroza D, Šimat V, Smole Možina S,
Katalinić V, Boban N and Generalić Mekinić I: Interactions of
resveratrol with other phenolics and activity against food-borne
pathogens. Food Sci Nutr. 7:2312–2318. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Qin N, Tan X, Jiao Y, Liu L, Zhao W, Yang
S and Jia A: RNA-Seq-based transcriptome analysis of
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilm
inhibition by ursolic acid and resveratrol. Sci Rep.
4(5467)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Su Y, Ma L, Wen Y, Wang H and Zhang S:
Studies of the in vitro antibacterial activities of several
polyphenols against clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules. 19:12630–12639.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Duan J, Li M, Hao Z, Shen X, Liu L, Jin Y,
Wang S, Guo Y, Yang L, Wang L and Yu F: Subinhibitory
concentrations of resveratrol reduce alpha-hemolysin production in
Staphylococcus aureus isolates by downregulating saeRS.
Emerg Microbes Infect. 7(136)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Morán A, Gutierrez S, Martinez-Blanco H,
Ferrero MA, Monteagudo-Mera A and Rodriguez-Aparicio LB: Non-toxic
plant metabolites regulate staphylococcus viability and biofilm
formation: A natural therapeutic strategy useful in the treatment
and prevention of skin infections. Biofouling. 30:1175–1182.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Tang F, Li L, Meng XM, Li B, Wang CQ, Wang
SQ, Wang TL and Tian YM: Inhibition of alpha-hemolysin expression
by resveratrol attenuates Staphylococcus aureus virulence.
Microb Pathog. 127:85–90. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Rasko DA and Sperandio V: Anti-virulence
strategies to combat bacteria-mediated disease. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 9:117–128. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Cheung GYC and Otto M: Virulence
mechanisms of staphylococcal animal pathogens. Int J Mol Sci.
24(14587)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Vestergaard M and Ingmer H: Antibacterial
and antifungal properties of resveratrol. Int J Antimicrob Agents.
53:716–723. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Gordon RJ and Lowy FD: Pathogenesis of
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Clin
Infect Dis. 46 (Suppl 5):S350–S359. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Karygianni L, Ren Z, Koo H and Thurnheer
T: Biofilm matrixome: Extracellular components in structured
microbial communities. Trends Microbiol. 28:668–681.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Singh S, Singh SK, Chowdhury I and Singh
R: Understanding the mechanism of bacterial biofilms resistance to
antimicrobial agents. Open Microbiol J. 11:53–62. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Vivero-Lopez M, Pereira-Da-Mota AF,
Carracedo G, Huete-Toral F, Parga A, Otero A, Concheiro A and
Alvarez-Lorenzo C: Phosphorylcholine-based contact lenses for
sustained release of resveratrol: Design, antioxidant and
antimicrobial performances, and in vivo behavior. ACS Appl Mater
Interfaces. 14:55431–55446. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Vivero-Lopez M, Muras A, Silva D, Serro
AP, Otero A, Concheiro A and Alvarez-Lorenzo C: Resveratrol-loaded
hydrogel contact lenses with antioxidant and antibiofilm
performance. Pharmaceutics. 13(532)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Cho HS, Lee JH, Cho MH and Lee J: Red
wines and flavonoids diminish Staphylococcus aureus
virulence with anti-biofilm and anti-hemolytic activities.
Biofouling. 31:1–11. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Lee K, Lee JH, Ryu SY, Cho MH and Lee J:
Stilbenes reduce Staphylococcus aureus hemolysis, biofilm
formation, and virulence. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 11:710–717.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Miller MB and Bassler BL: Quorum sensing
in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 55:165–199. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Santos CA, Lima EMF, Franco BDGM and Pinto
UM: Exploring phenolic compounds as quorum sensing inhibitors in
foodborne bacteria. Front Microbiol. 12(735931)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Fatima M, Amin A, Alharbi M, Ishtiaq S,
Sajjad W, Ahmad F, Ahmad S, Hanif F, Faheem M and Khalil AAH:
Quorum quenchers from reynoutria japonica in the battle against
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Molecules. 28(2635)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Ji G, Beavis R and Novick RP: Bacterial
interference caused by autoinducing peptide variants. Science.
276:2027–2030. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Wang B and Muir TW: Regulation of
virulence in Staphylococcus aureus: Molecular mechanisms and
remaining puzzles. Cell Chem Biol. 23:214–224. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Zhang Y, Ma N, Tan P and Ma X: Quorum
sensing mediates gut bacterial communication and host-microbiota
interaction. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 64:3751–3763. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Paulander W, Varming AN, Bojer MS, Friberg
C, Bæk K and Ingmer H: The agr quorum sensing system in
Staphylococcus aureus cells mediates death of
sub-population. BMC Res Notes. 11(503)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Kong C, Neoh HM and Nathan S: Targeting
Staphylococcus aureus toxins: A potential form of
anti-virulence therapy. Toxins (Basel). 8(72)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Berube BJ and Bubeck Wardenburg J:
Staphylococcus aureus α-toxin: Nearly a century of intrigue.
Toxins (Basel). 5:1140–1166. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Singh V and Phukan UJ: Interaction of host
and Staphylococcus aureus protease-system regulates
virulence and pathogenicity. Med Microbiol Immunol. 208:585–607.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Alqahtani M, Almukainzi M, Alghoribi MF
and El-Mahdy AM: Antivirulence effects of trans-resveratrol and
curcumin on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
(MRSA) from Saudi Arabia. Life (Basel). 14(491)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Ika IM, Vincken JP, van Dinteren S, Ter
Beest E, Pos KM and Araya-Cloutier C: Prenylated isoflavonoids from
Fabaceae against the NorA efflux pump in Staphylococcus
aureus. Sci Rep. 13(22548)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Jang S: Multidrug efflux pumps in
Staphylococcus aureus and their clinical implications. J
Microbiol. 54:1–8. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Schindler BD, Jacinto P and Kaatz GW:
Inhibition of drug efflux pumps in Staphylococcus aureus:
Current status of potentiating existing antibiotics. Future
Microbiol. 8:491–507. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Liu L, Ingmer H and Vestergaard M:
Genome-wide identification of resveratrol intrinsic resistance
determinants in Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics (Basel).
10(82)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Liu L, Beck C, Nøhr-Meldgaard K, Peschel
A, Kretschmer D, Ingmer H and Vestergaard M: Inhibition of the atp
synthase sensitizes Staphylococcus aureus towards human
antimicrobial peptides. Sci Rep. 10(11391)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Vestergaard M, Nøhr-Meldgaard K, Bojer MS,
Krogsgård Nielsen C, Meyer RL, Slavetinsky C, Peschel A and Ingmer
H: Inhibition of the ATP synthase eliminates the intrinsic
resistance of Staphylococcus aureus towards polymyxins.
mBio. 8:e01114–17. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Vestergaard M, Roshanak S and Ingmer H:
Targeting the ATP synthase in Staphylococcus aureus small
colony variants, streptococcus pyogenes and pathogenic fungi.
Antibiotics (Basel). 10(376)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Alshehri FS: Resveratrol ameliorates
vancomycin-induced testicular dysfunction in male rats. Medicina
(Kaunas). 59(486)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Tosato MG, Schilardi PL, de Mele MFL,
Thomas AH, Miñán A and Lorente C: Resveratrol enhancement
Staphylococcus aureus survival under levofloxacin and
photodynamic treatments. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 51:255–259.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Dwyer DJ, Collins JJ and Walker GC:
Unraveling the physiological complexities of antibiotic lethality.
Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 55:313–332. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Dos Santos DP, Galantini MPL, Ribeiro IS,
Muniz IPR, Pereira IS and da Silva RAA: Photoactivated resveratrol
controls intradermal infection by Staphylococcus aureus in
mice: A pilot study. Lasers Med Sci. 35:1341–1347. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Dos Santos DP, Soares Lopes DP, de Moraes
RC Jr, Vieira Gonçalves C, Pereira Rosa L, da Silva Rosa FC and da
Silva RAA: Photoactivated resveratrol against Staphylococcus
aureus infection in mice. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther.
25:227–236. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Lee IT, Lin CC, Yang CC, Hsiao LD, Wu MY
and Yang CM: Resveratrol attenuates Staphylococcus
aureus-induced monocyte adhesion through downregulating
PDGFR/AP-1 activation in human lung epithelial cells. Int J Mol
Sci. 19(3058)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Shevelev AB, La Porta N, Isakova EP,
Martens S, Biryukova YK, Belous AS, Sivokhin DA, Trubnikova EV,
Zylkova MV, Belyakova AV, et al: In vivo antimicrobial and
wound-healing activity of resveratrol, dihydroquercetin, and
dihydromyricetin against Staphylococcus aureus, pseudomonas
aeruginosa, and candida albicans. Pathogens. 9(296)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Wu S and Huang J: Resveratrol alleviates
Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia by inhibition of the NLRP3
inflammasome. Exp Ther Med. 14:6099–6104. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Joseph A, Balakrishnan A, Shanmughan P,
Maliakel B and Illathu Madhavamenon K: Micelle/hydrogel composite
as a ‘natural self-emulsifying reversible hybrid hydrogel (N'SERH)’
enhances the oral bioavailability of free (unconjugated)
resveratrol. ACS Omega. 7:12835–12845. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Walle T: Bioavailability of resveratrol.
Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1215:9–15. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Boocock DJ, Faust GES, Patel KR, Schinas
AM, Brown VA, Ducharme MP, Booth TD, Crowell JA, Perloff M, Gescher
AJ, et al: Phase I dose escalation pharmacokinetic study in healthy
volunteers of resveratrol, a potential cancer chemopreventive
agent. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 16:1246–1252.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Brown VA, Patel KR, Viskaduraki M, Crowell
JA, Perloff M, Booth TD, Vasilinin G, Sen A, Schinas AM, Piccirilli
G, et al: Repeat dose study of the cancer chemopreventive agent
resveratrol in healthy volunteers: Safety, pharmacokinetics, and
effect on the insulin-like growth factor axis. Cancer Res.
70:9003–9011. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Wang LX, Heredia A, Song H, Zhang Z, Yu B,
Davis C and Redfield R: Resveratrol glucuronides as the metabolites
of resveratrol in humans: Characterization, synthesis, and anti-HIV
activity. J Pharm Sci. 93:2448–2457. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Walle T, Hsieh F, DeLegge MH, Oatis JE Jr
and Walle UK: High absorption but very low bioavailability of oral
resveratrol in humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 32:1377–1382.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Tsugami Y, Nii T and Isobe N: Effects of
topical application of resveratrol on tight junction barrier and
antimicrobial compound production in lactating goat mammary glands.
Vet Res. 55(20)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Cottart CH, Nivet-Antoine V and Beaudeux
JL: Review of recent data on the metabolism, biological effects,
and toxicity of resveratrol in humans. Mol Nutr Food Res. 58:7–21.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Turner RS, Thomas RG, Craft S, van Dyck
CH, Mintzer J, Reynolds BA, Brewer JB, Rissman RA, Raman R and
Aisen PS: Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study. A randomized,
double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of resveratrol for Alzheimer
disease. Neurology. 85:1383–1391. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Shaito A, Posadino AM, Younes N, Hasan H,
Halabi S, Alhababi D, Al-Mohannadi A, Abdel-Rahman WM, Eid AH,
Nasrallah GK and Pintus G: Potential adverse effects of
resveratrol: A literature review. Int J Mol Sci.
21(2084)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Brown K, Theofanous D, Britton RG, Aburido
G, Pepper C, Sri Undru S and Howells L: Resveratrol for the
management of human health: How far have we come? A systematic
review of resveratrol clinical trials to highlight gaps and
opportunities. Int J Mol Sci. 25(747)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Yadegar S, Mohammadi F, Yadegar A,
Mohammadi Naeini A, Ayati A, Milan N, Tayebi A, Seyedi SA,
Nabipoorashrafi SA, Rabizadeh S, et al: Effects and safety of
resveratrol supplementation in older adults: A comprehensive
systematic review. Phytother Res. 38:2448–2461. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|