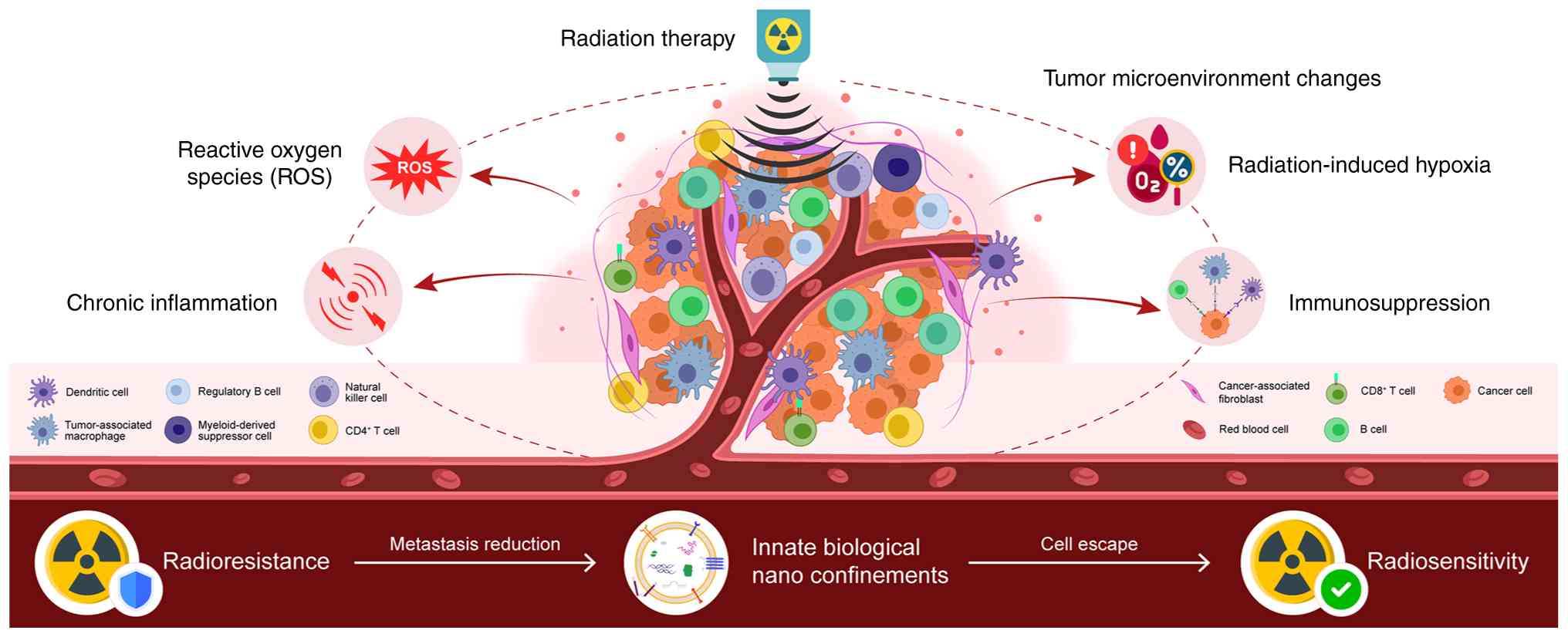
Radiation therapy is a common cancer treatment;
however, radioresistance may result in treatment failure (1). Cancer cells can alter their metabolic
status following radiation therapy to reduce the cytotoxic effects,
thereby diminishing the treatment efficacy (2). The tumor microenvironment (TME) is
defined as the cellular and non-cellular components surrounding
tumor cells. This includes immune cells and stromal material. As
recently reported, altered tumor metabolism influences the TME, and
alterations in the metabolite composition of the TME can support
tumor growth (3,4). Therefore, targeting tumor metabolism in
combination with radiotherapy may enhance the efficacy of cancer
treatment (5). The present review
discusses the metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells following
radiation exposure and summarizes the findings involving the TME to
illustrate the metabolic characteristics of radiotherapy.
Furthermore, the present review introduces novel findings on innate
nanobiological confinements that may influence the TME via novel
mechanisms regulating energy metabolism and signaling pathways
(Fig. 1).
For the present review, ‘Boolean Operators’ such as
AND, OR and NOT were used to search for relevant research
articles/reviews published over the past two decades from the
PubMed database and Clinical Trials website (https://ClinicalTrials.gov) for cancer
microenvironment alterations induced by radiation. Thereafter, only
the articles/reviews containing both ‘cancer microenvironment
alterations’ and ‘radiation/radiotherapy’ were filtered into the
investigational pool.
Radiotherapy is a widely used cancer treatment, with
almost half of cancer patients receiving radiation therapy. It is
usually administered over a period of days or weeks in a targeted,
sub-dose manner, primarily eliminating cancer cells due to DNA
injury through the over expressed reactive oxygen species (ROS)
(6). Radiotherapy can serve as an
adjuvant therapeutic model following radical cancer surgery, or it
can serve as a neoadjuvant therapy for advanced-stage cancer. Its
combination with chemotherapy can enhance the anticancer effect
(7). A number of experimental and
clinical studies have explored its combination with immunotherapy
(8-10);
in addition, investigations are continuing on this matter (Clinical
trial no. NCT02223923). Despite considerable positive progress over
the past decades, radiation resistance remains a key challenge in
the treatment of cancer. The key to overcoming this issue may lie
in targeting the TME, specifically the variety of non-malignant
cells surrounding cancer cells. Radiation therapy alters the TME,
potentially triggering interactions among its components that
contribute to radiotherapy resistance. Therefore, a more in-depth
exploration of TME interaction mechanisms may be critical, as it
may identify mechanisms which can be used to enhance the
therapeutic efficacy of radiotherapy.
Radiation-induced vascular damage, hypoxia and
chronic inflammation in the TME may promote cancer cell survival
and radioresistance (11). Due to
endothelial damage, vascular damage and hypoxia also occur,
possibly owing to the reduced oxygen consumption in irradiated
cells and the survival of certain blood vessels that maintain the
oxygen and nutrients to supply to the tumor continuously (12,13). The
immune clearance of cancer cells following radiotherapy is crucial
for tumor control (14), as the
antitumor immune response can be activated by radiation-induced DNA
damage and in turn, this increases antigen release from cancer
cells (15). However, the
co-existence of hypoxia and high levels of ROS can create a chronic
inflammatory state, in which CD8+ T-cells,
CD4+ T-cells, natural killer and dendritic cells are
suppressed, resulting in the low efficacy of tumor elimination
(16). As an additional
tumor-promoting condition, the higher numbers of regulatory T-cells
(Tregs) and bone marrow-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) ultimately
lead to an immunosuppressive environment.
Cell metabolism is critical for the TME, and
metabolic dysregulation can support cancer cell growth and
therapeutic resistance, both hallmark features of cancer (17). Metabolites and cytokines secreted by
cancer cells can reprogram the metabolism of other TME components,
thereby altering its composition and promoting tumor growth
(18). This metabolic reprogramming
forms a symbiotic association, enabling the exchange of metabolites
to meet the needs of different cell types for metabolic within the
TME. These interactions provide a potential avenue for targeted
cancer treatment without disrupting normal cellular functions.
Therefore, studying metabolic changes in the TME in response to
radiation is essential for developing novel therapeutic
strategies.
Cellular ROS can lead to DNA damage and the
destruction of cellular structures, including cell membranes and
blood vessels, resulting in transient hypoxia and nutrient
deprivation in cancer cells, while simultaneously increasing
antitumor immune cell activity in the TME (19,20).
Cancer cells reprogram their metabolic state to counteract
radiation-induced damage (21). The
metabolic changes that promote cancer survival under radiotherapy
may involve four main features: First, radiation can enhance the
express efficiency of glycolysis pathway (GLP) and the pentose
phosphate pathway (PPP), which are highly associated with
glycolytic adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesis, nucleotide
biosynthesis, membrane phospholipid synthesis, and nicotinamide
adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) regeneration to support
antioxidant responses (22). Second,
elevated ROS can activate novel lethal pathways, for example,
neoplastic iron death (23).
Furthermore, damaged DNA and cell membranes require metabolic
support to facilitate repair processes (24). Finally, cancer-TME metabolic
interactions can lead to the insufficient supply of nutrients to
the tumor by disrupting local blood vessels (25). The nutrients provided by the
surrounding matrix thus become a crucial driving force for cancer
cell metabolism (18).
In the long-term, the efficacy of radiotherapy is
affected by the biological characteristics of the tumor, such as
inherent radioresistance, pathological hypoxia and the consequent
complexity of the TME. Consequently, the more active biological
pathways in cancer cells have been considered potential therapeutic
targets. Antibodies and small-molecule inhibitors targeting
glycolysis and the PPP have further been demonstrated in
preclinical studies with promising results (26-28).
The comprehensive treatment regimen of cetuximab and
radiotherapy has been approved by the FDA (29), whereas therapies such as small
molecular drugs (erlotinib/lapatinib) are still in the stages of
clinical trials (30,31). Cetuximab and panitumumab are
classical anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) antibodies,
which were widely used in the treatment of colorectal cancer.
Through an autocrine and paracrine manner, EGFR is activated by
members from the EGF family. By combining with these EGFs, EGFR
dimers and downstream signaling pathways (KRAS-BRAF-MEK-ERK, PI3K,
AKT and STAT) are activated efficiently. As regards the EGFR, its
tyrosine phosphorylation level has been demonstrated to be
upregulated in growth-restricted squamous cells (32) and breast cancer cells (33). Furthermore, EGFR signaling enhances
the expression of hexokinase II (HKII), while inhibiting the
expression of pyruvate kinase isoenzyme M2(34). Radiation can further activate the
hypoxia-inducing factor 1α subunit, resulting in the increased
transcription of several hypoxia-related genes, such as glucose
transporter 1 (GLUT1) and lactate dehydrogenase A (35). This upregulation increases glycolysis
throughput in glioblastoma (GBM), potentially providing a survival
advantage following radiotherapy. Several preclinical trials have
explored the combination of radiotherapy with 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG)
to counteract this metabolic adaptation (36-38).
The PPP mainly provides NADPH for reducing glutathione (GSH) and
nucleotides for DNA synthesis (39).
This pathway is rapidly upregulated to response to DNA damage,
which is caused by oxidative stress and radiation exposure. The
GLUT1 receptor also regulates the hexokinase-1 (HKI) and pyruvate
kinase (PK) expression level under the stimulation of EGF. HKII has
been observed to be overexpressed in various types of cancer cells
(40). In the cytoplasm, the
voltage-dependent anion channel protein on the mitochondrial
membrane has been observed to be specifically bind with HKII to
resist glucose-6-phosphate (G-6-P) concentration-dependent feedback
inhibition, owing to the high maintenance of G-6-P concentrations
in cancer cells following radiation (41). As a biosynthetic substrate, G-6-P
links glycolysis to the PPP, providing a rationale for the use of
PPP inhibitors in combination with radiotherapy (22). The nicotinamide analog,
6-aminonicotinamide (6-AN), has been shown to inhibit G6PD activity
and enhance sensitivity to radiation (42). The combination of radiotherapy with
2-DG and 6-AN considerably improves the efficacy of radiotherapy.
Genes involved in the regulation of glycolysis are contributors to
cancer cell survival. Radiation exposure can activate HIF1, and
increase glycolysis and the level of antioxidants (5). The upregulation of EGF signaling
induced by radiation may lead to the accumulation of glycolytic
intermediates in cancer cells (43).
During glycolysis, G-6-P can be shunted into the PPP, where the
ribonucleotides produced are essential for post-radiation DNA
repair (44).
High energy generated by ionizing radiation drives
the formation of ROS through the chemical and physical interaction
between ions and cellular components, which mainly includes
bioactive hydrogen peroxide (H2O2),
superoxide anion (O2-) and hydroxyl radical
(OH-). Persistent high levels of ROS lead to oxidative
stress, which may influence the structural and functional state of
DNA, cell or intra-cell membranes, proteins, and so on, ultimately
triggering cell death. Although increase levels of ROS may promote
cancer growth and progress, excessively high levels of ROS can have
anticancer effects (6).
An adaptive change in redox metabolism can be
induced by radiation-induced oxidative stress in cancer cells
(45,46), and the potential association between
radiation and consequently enhanced antioxidant metabolism has been
confirmed in previous studies (47,48). The
NRF2-mediated antioxidant responses activated by ionizing radiation
has been well demonstrated in breast cancer cells (49). Additionally, the analysis of the
blood of patients with cancer receiving radiation therapy has
revealed reduced levels of the antioxidant, GSH (50), whereas genome-wide metabolic models
from The Cancer Genome Atlas have indicated the antioxidant NADPH
with an increased synthesis rate in radioresistant cancer cells
(51).
Radiotherapy, by its ion beams, directly attacks and
injures the structures of cellular macromolecular and organelles,
which in turn stimulates cancer cells to activate its adaptive
repair pathways through macromolecular response, many of which
depend on cellular metabolism (5,52,53). The
primary anticancer mechanism of radiotherapy is that radiation can
induce different types of lethal damage on DNA. However, the high
genomic instability of cancer cells reduces radiation-induced DNA
damage before it reaches toxic levels (44). Therefore, an effective DNA damage
response is partially determined by the innate radioresistance of
cancer cells; further studies are required to focus on how to
effectively increase the radiosensitivity of cancer cells when
facing different types of radiation by targeting DNA repair
pathways (54-56).
DNA repair relies on the rich nucleotide pool supported by the
active metabolism. These pools afford the essential demands for
chromatin modifications and protein activation (57-59).
For single- and double-strand DNA breaks, purine and
pyrimidine nucleotide pools are necessary and essential. In fact,
experimental studies have demonstrated that an increased nucleotide
synthesis rate and more active pathways related to these processes
are closely associated with the radioresistance of cancer cells
(60,61). Notably, nucleotide metabolism
presents context-dependent characteristics in different types of
cancer following radiotherapy. The inhibition of GMP resynthesis
with mycophenolate mofetil has also been shown to radiosensitize
GBMs (62). Glutamine is a precursor
for de novo nucleotide synthesis; a previous in vitro
and in vivo study demonstrated delayed DNA repair and
enhanced radiosensitivity in cancer models followign the knockdown
of glutamine synthesis (63). Other
pathways involved in nucleotide synthesis in cancer cells include
the PPP ribo5-phosphate (R5P) and serine-glycine metabolism during
the post-radiation. The involvement of these pathways in promoting
radioresistance through DNA repair warrants further investigation
(64). Histone methylation and
acetylation patterns can regulate DNA repair conditionally
(65), although the mechanisms
involved remain unclear (66). ATP
is associated with protein phosphorylation and the activation of
proteins involved in DNA repair (67). Notably, in hepatoma cells,
combination therapy with metformin and radiation has been shown to
reduce ATP levels in cancer cells and decreases DNA repair
capacity, thereby enhancing radiosensitivity (68).
Fatty acids constitute the cornerstone of cell
membranes. They are the base of repair on damage induced by
radiation. Cells meet their metabolic lipid requirements through
de novo biosynthesis and uptake from the microenvironment
(69). Fatty acid synthase (FASN), a
key enzyme among de novo palmitate synthase, is associated
with cancer radioresistance (70).
FASN overexpression is associated with the cancer cell
radioresistance, whereas the inhibition of FASN enhances the
anticancer effects of radiation (71); however, the precise mechanisms
involved remain to be elucidated. FASN may increase intracellular
palmitate levels and regulate the expression of PARP1 through the
NF-κB pathway (72), thereby
supporting radiation resistance through NF-κB-mediated signaling
(73).
The dysregulation of cholesterol synthesis is also
linked to cellular radioresistance. Cholesterol plays a crucial
role in organizing the cell membrane and forming the vascular
system, both of them benefit cancer cells following radiation
exposure (74). Zoledronic acid, an
inhibitor of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase, sensitizes
radiation-resistant pancreatic cancer lines. Conversely, the
inhibition of cholesterol synthesis is reportedly associated with
the increased survival of patients with lung cancer undergoing
radiotherapy (75). These converse
results emphasize the functional and environmental specific changes
in lipid metabolism that mediate radiation resistance. Apart from
the inherent metabolic heterogeneity of cancer cells, the role of
lipid metabolism may be determined by the availability of different
lipids in the TME following radiotherapy.
The complexity of the metabolism of TME components
can influence cell-cell interactions, and can even alter the
outcomes of diseases. Therefore, understanding the metabolic status
of the TME following radiotherapy is essential.
Metabolites provided by the extracellular matrix can
promote cancer recovery following radiotherapy (76). In the TME, metabolic productions of
larger amounts of non-malignant cells can also promote cancer cell
growth in environments that lack nutrients (77). Glutamine from cancer-associated
fibroblasts (CAFs) and serine from neurons in the TME can enhance
cancer metabolism by supplying ribose-1-phosphate, thereby
improving the DNA repair capacity after radiation exposure
(78). The TME can also provide
lipids to cancer cells, supporting their survival following
radiotherapy (79). CAFs have been
demonstrated to promote pancreatic and colorectal cancers
progression via lipid and branched-chain ketoacid supply (80). Cancer cells can also induce adipocyte
fat breakdown, resulting in releasing the fatty acids into the TME.
The hypoxic state following radiation therapy reduces lipid
synthesis pathways, increasing cancer cell dependence on exogenous
lipid uptake (81). Hypoxia induces
the expression of HIF, which can facilitate the cancer cells
enriching fatty acids, thereby protecting them from
radiation-induced ROS (82). Hypoxia
also promotes cancer cells to adsorb unsaturated fatty acids by
activating serum/glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 (SGK1), whereas
the inhibition of SGK1 can enhance the effects of radiotherapy
(83). Radiation exposure increases
intercellular ROS levels in cancers, and substantial ROS levels in
the TME are associated with precancerous lesions (45). Through the stabilization of HIF-1α by
ROS and the promotion of angiogenesis, the survival of cancer cells
is enhanced under radiotherapy. ROS can also promote the activation
of CAFs (84,85).
During the post-radiation time, changes in metabolic
factors may reprogram the immune activity in the TME, such as the
increased production of ROS which can inhibit immune cells
(5,52). ROS can affect the phenotype of
tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), promoting a change into a
protumor state; ROS can also lead to the recruitment of more Tregs
and MDSCs at tumor sites, suppress T-cell activity, and reduce the
number of natural killer cells in the TME (86). With elevated levels of lipids in the
TME, immune cell function may be altered. For example, excess free
fatty acids can lead to lipid accumulation in natural killer cells,
thereby reducing their immune capacity. In addition, metabolic
interactions between effector T-cells, cancer cells and Tregs can
increase lipid accumulation, inducing cellular senescence (69). Effector T-cells and, tumor-promoting
Tregs/TAMs have very different energy demands, namely aerobic
glycolysis and fatty acid oxidation, respectively. Systemic
radiation can lead to lipid accumulation and dysfunction in
dendritic cells, thereby inducing a dysfunction in the immune
response, which is linked to carcinogenesis (87). As previously mentioned, the
extracellular matrix may secrete lipids, and obesity may contribute
to elevated lipid levels in the TME (79,80).
Increased glycolytic activity following radiation leads to lactate
accumulation and TME acidification. High lactate levels inhibit
effector T-cell function, promote macrophage differentiation into
the immunosuppressed M2 phenotype, and alter monocyte secretion of
pro-inflammatory cytokines. Therefore, even though radiation can
promote immune cell with higher capacity, metabolic reorganization
in cancer cells may contribute to an immunosuppressive
environment.
Tumors are commonly considered as dependent
pseudo-organs. In these pseudo-organs, there is a complex
interaction between cancer cells and various non-tumor cells,
forming a complex network. In this network, cancer cells strive to
maintain their malignant proliferation by altering their metabolic
properties continuously (88). As is
commonly known, cancer cells exhibit an upregulated glycolysis and
downregulated oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). However, in a
previous study, OXPHOS was reported to be upregulated, even
occurring concurrently with a high level of glycolysis (89).
Cancer cells have a high heterogeneity as regards
the metabolic phenotype. In cancer cells, some substances, such as
glucose, lactate, pyruvate and hydroxybutyrate have a higher
metabolic rate than in normal cells, contributing to the complex
tumor metabolic ecology. This metabolic heterogeneity and
complexity help cancer cells to maintain a dominant position in
energy acquisition, whether they utilize ATP, maintain redox
balance, or establish metabolic coupling with any other cells
(90). Regardless, acquiring energy
and essential substances for anabolism determine the fate of any
type of cells. Within the same biological system, different cell
types compete for energy demands through specific mechanisms. Only
those cells that prioritize energy utilization can develop
preferentially. The following paragraph discusses innate biological
nano-confinements (iBNCs). iBNCs are a proposed concept referring
to any naturally occurring structural and functional nanodomains
within biological systems.
Nano-confinement refers to the restriction of
materials within nanoscale regions. When certain materials, such as
some bioactive molecules (such as protein, DNA and RNA) are
confined at the nanoscale, they may exhibit a unique behavior
distinct from that observed at the macroscale (91). Furthermore, the nano-confinement
approach provides a basis for the development of novel cancer
therapeutic strategies related to energy and substance utilization
(92,93). It is considered that biological
nano-confinements widely exist within biological systems, referred
to as iBNCs, which play critical roles in tumorigenesis,
progression and metastasis via novel mechansisms (94). For instance, CAR-T therapy has
exhibited promising outcomes in hematological malignancies.
However, in the majority of solid tumors, such as liver, gastric
and lung cancer, its effects are limited (95). The higher fluidity of hematological
malignancies does not provide a stable environment of the formation
and maintenance of iBNCs; therefore, these malignancies often
develop resistance to therapeutic interventions, such as
chemotherapies and radiotherapies. However, as solid tumors have a
relatively stable physical environment, iBNCs can easily be formed.
They have the additional capacity to resist drugs/radiation, and
ultimately survive from intervention strategies (94).
Cancer cells can alter and reprogram their metabolic
profile in response to the cellular damage induced by radiation.
The TME plays a crucial role by supplying precursor substances that
support cancer metabolism alterations, presenting potential targets
for therapeutic intervention. A key consideration is that iBNCs may
help to elucidate the prioritization of energy and substance
utilization by cancer cells in solid tumors in hypoxic and
nutrition-deprived environments. This may provide further insight
into the reason why CAR-T therapies are more effective for
hematological cancers than solid tumors, and could explain the
synergetic enhancement observed when CAR-T therapy is used in
combination with chemotherapy. Further studies are required to
focus on validating the therapeutic potential of targeting
radiation-induced metabolic reprogramming through preclinical and
clinical research, with an emphasis on tumor-type-specific
metabolic responses.
Not applicable.
Funding: No funding was received.
Not applicable.
All authors (HL, XZ, ZH and JY) were involved the
collection and interpretation of data from the literature, and in
the writing and preparation of the draft of the manuscript. JY
conceived and designed the study, and provided the critical
revision of the article content. All authors have read and approved
the final version of the manuscript. Data authentication is not
applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Otsuki Y, Yamasaki J, Suina K, Okazaki S,
Koike N, Saya H and Nagano O: Vasodilator oxyfedrine inhibits
aldehyde metabolism and thereby sensitizes cancer cells to
xCT-targeted therapy. Cancer Sci. 111:127–136. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Dandachi D and Morón F: Effects of HIV on
the tumor microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1263:45–54.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lin J, Liu Y, Liu P, Qi W, Liu J, He X,
Liu Q, Liu Z, Yin J, Lin J, et al: SNHG17 alters anaerobic
glycolysis by resetting phosphorylation modification of PGK1 to
foster pro-tumor macrophage formation in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 42(339)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mittal A, Nenwani M, Sarangi I, Achreja A,
Lawrence TS and Nagrath D: Radiotherapy-induced metabolic hallmarks
in the tumor microenvironment. Trends Cancer. 8:855–869.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jia C, Wang Q, Yao X and Yang J: The role
of DNA damage induced by low/high dose ionizing radiation in cell
carcinogenesis. Explor Res Hypothesis Med. 6:177–184. 2021.
|
|
7
|
Tang B, Zhu J, Shi Y, Wang Y, Zhang X,
Chen B, Fang S, Yang Y, Zheng L, Qiu R, et al: Tumor cell-intrinsic
MELK enhanced CCL2-dependent immunosuppression to exacerbate
hepatocarcinogenesis and confer resistance of HCC to radiotherapy.
Mol Cancer. 23(137)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lin X, Liu Z, Dong X, Wang K, Sun Y, Zhang
H, Wang F, Chen Y, Ling J, Guo Y, et al: Radiotherapy enhances the
anti-tumor effect of CAR-NK cells for hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Transl Med. 22(929)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Dillon MT, Boylan Z, Smith D, Guevara J,
Mohammed K, Peckitt C, Saunders M, Banerji U, Clack G, Smith SA, et
al: PATRIOT: A phase I study to assess the tolerability, safety and
biological effects of a specific ataxia telangiectasia and
Rad3-related (ATR) inhibitor (AZD6738) as a single agent and in
combination with palliative radiation therapy in patients with
solid tumours. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 12:16–20. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Dillon MT, Guevara J, Mohammed K, Patin
EC, Smith SA, Dean E, Jones GN, Willis SE, Petrone M, Silva C, et
al: Durable responses to ATR inhibition with ceralasertib in tumors
with genomic defects and high inflammation. J Clin Invest.
134(e175369)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kameni LE, Januszyk M, Berry CE, Downer MA
Jr, Parker JB, Morgan AG, Valencia C, Griffin M, Li DJ, Liang NE,
et al: A review of radiation-induced vascular injury and clinical
impact. Ann Plast Surg. 92:181–185. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Choi SH, Hong ZY, Nam JK, Lee HJ, Jang J,
Yoo RJ, Lee YJ, Lee CY, Kim KH, Park S, et al: A hypoxia-induced
vascular endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in development of
radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Clin Cancer Res.
21:3716–3726. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wijerathne H, Langston JC, Yang Q, Sun S,
Miyamoto C, Kilpatrick LE and Kiani MF: Mechanisms of
radiation-induced endothelium damage: Emerging models and
technologies. Radiother Oncol. 158:21–32. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Guilbaud E, Naulin F, Meziani L, Deutsch E
and Galluzzi L: Impact of radiation therapy on the immunological
tumor microenvironment. Cell Chem Biol. 32:678–693. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lee AK, Pan D, Bao X, Hu M, Li F and Li
CY: Endogenous retrovirus activation as a key mechanism of
anti-tumor immune response in radiotherapy. Radiat Res.
193:305–317. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chen Z, Han F, Du Y, Shi H and Zhou W:
Hypoxic microenvironment in cancer: Molecular mechanisms and
therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
8(70)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jiang W, Jin WL and Xu AM: Cholesterol
metabolism in tumor microenvironment: Cancer hallmarks and
therapeutic opportunities. Int J Biol Sci. 20:2044–2071.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li YJ, Zhang C, Martincuks A, Herrmann A
and Yu H: STAT proteins in cancer: Orchestration of metabolism. Nat
Rev Cancer. 23:115–134. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Renaudin X: Reactive oxygen species and
DNA damage response in cancer. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 364:139–161.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
An X, Yu W, Liu J, Tang D, Yang L and Chen
X: Oxidative cell death in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic
opportunities. Cell Death Dis. 15(556)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Punnasseril JMJ, Auwal A, Gopalan V, Lam
AK and Islam F: Metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells and
therapeutics targeting cancer metabolism. Cancer Med.
14(e71244)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Shimoni-Sebag A, Abramovich I, Agranovich
B, Massri R, Stossel C, Atias D, Raites-Gurevich M, Yizhak K, Golan
T, Gottlieb E and Lawrence YR: A metabolic switch to the
pentose-phosphate pathway induces radiation resistance in
pancreatic cancer. Radiother Oncol. 202(110606)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhang H, Ma J, Hou C, Luo X, Zhu S, Peng
Y, Peng C, Li P, Meng H, Xia Y, et al: A ROS-mediated
oxidation-O-GlcNAcylation cascade governs ferroptosis. Nat Cell
Biol. 27:1288–1300. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen H, Zhang C, Fu Y, Li L, Qiao X, Zhang
S, Luo H, Chen S, Liu X and Zhong Q: Repair of damaged lysosomes by
TECPR1-mediated membrane tubulation during energy crisis. Cell Res.
36:51–71. 2026.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cognet G and Muir A: Identifying metabolic
limitations in the tumor microenvironment. Sci Adv.
10(eadq7305)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cutshaw G, Joshi N, Wen X, Quam E,
Bogatcheva G, Hassan N, Uthaman S, Waite J, Sarkar S, Singh B and
Bardhan R: Metabolic response to small molecule therapy in
colorectal cancer tracked with Raman spectroscopy and metabolomics.
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 63(e202410919)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sørensen DM, Büll C, Madsen TD,
Lira-Navarrete E, Clausen TM, Clark AE, Garretson AF, Karlsson R,
Pijnenborg JFA, Yin X, et al: Identification of global inhibitors
of cellular glycosylation. Nat Commun. 14(948)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li S, McCraw AJ, Gardner RA, Spencer DIR,
Karagiannis SN and Wagner GK: Glycoengineering of therapeutic
antibodies with small molecule inhibitors. Antibodies (Basel).
10(44)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yamamoto VN, Thylur DS, Bauschard M,
Schmale I and Sinha UK: Overcoming radioresistance in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 63:44–51. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Stone HB, Bernhard EJ, Coleman CN, Deye J,
Capala J, Mitchell JB and Brown JM: Preclinical data on efficacy of
10 drug-radiation combinations: Evaluations, concerns, and
recommendations. Transl Oncol. 9:46–56. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lubet RA, Kumar A, Fox JT, You M, Mohammed
A, Juliana MM and Grubbs CJ: Efficacy of EGFR inhibitors and NSAIDs
against basal bladder cancers in a rat model: Daily vs weekly
dosing, combining EGFR inhibitors with naproxen, and effects on RNA
expression. Bladder Cancer. 7:335–345. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Beizaei K, Gleißner L, Hoffer K, Bußmann
L, Vu AT, Steinmeister L, Laban S, Möckelmann N, Münscher A,
Petersen C, et al: Receptor tyrosine kinase MET as potential target
of multi-kinase inhibitor and radiosensitizer sorafenib in HNSCC.
Head Neck. 41:208–215. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yan Y, Hein AL, Greer PM, Wang Z, Kolb RH,
Batra SK and Cowan KH: A novel function of HER2/Neu in the
activation of G2/M checkpoint in response to γ-irradiation.
Oncogene. 34:2215–2226. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Liu Z, Ning F, Cai Y, Sheng H, Zheng R,
Yin X, Lu Z, Su L, Chen X, Zeng C, et al: The EGFR-P38 MAPK axis
up-regulates PD-L1 through miR-675-5p and down-regulates HLA-ABC
via hexokinase-2 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Commun
(Lond). 41:62–78. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang Y, Wang J and Li Z: Association of
HIF1-α gene polymorphisms with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
prognosis in patients receiving radiation therapy. Aging (Albany
NY). 13:6849–6865. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Shah SS, Rodriguez GA, Musick A, Walters
WM, de Cordoba N, Barbarite E, Marlow MM, Marples B, Prince JS,
Komotar RJ, et al: Targeting glioblastoma stem cells with
2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) potentiates radiation-induced unfolded
protein response (UPR). Cancers (Basel). 11(159)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Nile DL, Rae C, Walker DJ, Waddington JC,
Vincent I, Burgess K, Gaze MN, Mairs RJ and Chalmers AJ: Inhibition
of glycolysis and mitochondrial respiration promotes
radiosensitisation of neuroblastoma and glioma cells. Cancer Metab.
9(24)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Singh D, Banerji AK, Dwarakanath BS,
Tripathi RP, Gupta JP, Mathew TL, Ravindranath T and Jain V:
Optimizing cancer radiotherapy with 2-deoxy-d-glucose dose
escalation studies in patients with glioblastoma multiforme.
Strahlenther Onkol. 181:507–514. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
TeSlaa T, Ralser M, Fan J and Rabinowitz
JD: The pentose phosphate pathway in health and disease. Nat Metab.
5:1275–1289. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yadav D, Yadav A, Bhattacharya S, Dagar A,
Kumar V and Rani R: GLUT and HK: Two primary and essential key
players in tumor glycolysis. Semin Cancer Biol. 100:17–27.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Xie Y, Liu X, Xie D, Zhang W, Zhao H, Guan
H and Zhou PK: Voltage-dependent anion channel 1 mediates
mitochondrial fission and glucose metabolic reprogramming in
response to ionizing radiation. Sci Total Environ.
946(174246)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Li M, Dong Y, Wang Z, Zhao Y, Dai Y and
Zhang B: Engineering hypoxia-responsive 6-aminonicotinamide
prodrugs for on-demand NADPH depletion and redox manipulation. J
Mater Chem B. 12:8067–8075. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Yang L, Lu P, Yang X, Li K, Chen X, Zhou Y
and Qu S: Downregulation of annexin A3 promotes ionizing
radiation-induced EGFR activation and nuclear translocation and
confers radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Exp Cell Res.
418(113292)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Huang R and Zhou PK: DNA damage repair:
Historical perspectives, mechanistic pathways and clinical
translation for targeted cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target
Ther. 6(254)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Farhood B, Ashrafizadeh M, Khodamoradi E,
Hoseini-Ghahfarokhi M, Afrashi S, Musa AE and Najafi M: Targeting
of cellular redox metabolism for mitigation of radiation injury.
Life Sci. 250(117570)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Zheng Z, Su J, Bao X, Wang H, Bian C, Zhao
Q and Jiang X: Mechanisms and applications of radiation-induced
oxidative stress in regulating cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol.
14(1247268)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Alonso-González C, González A,
Martínez-Campa C, Menéndez-Menéndez J, Gómez-Arozamena J,
García-Vidal A and Cos S: Melatonin enhancement of the
radiosensitivity of human breast cancer cells is associated with
the modulation of proteins involved in estrogen biosynthesis.
Cancer Lett. 370:145–152. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Giallourou NS, Rowland IR, Rothwell SD,
Packham G, Commane DM and Swann JR: Metabolic targets of watercress
and PEITC in MCF-7 and MCF-10A cells explain differential
sensitisation responses to ionising radiation. Eur J Nutr.
58:2377–2391. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Qin S, He X, Lin H, Schulte BA, Zhao M,
Tew KD and Wang GY: Nrf2 inhibition sensitizes breast cancer stem
cells to ionizing radiation via suppressing DNA repair. Free Radic
Biol Med. 169:238–247. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Derindağ G, Akgül HM, Kızıltunç A, Özkan
Hİ, Kızıltunç Özmen H and Akgül N: Evaluation of saliva
glutathione, glutathione peroxidase, and malondialdehyde levels in
head-neck radiotherapy patients. Turk J Med Sci. 51:644–649.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Lewis JE, Forshaw TE, Boothman DA, Furdui
CM and Kemp ML: Personalized genome-scale metabolic models identify
targets of redox metabolism in radiation-resistant tumors. Cell
Syst. 12:68–81.e11. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Guo S, Yao Y, Tang Y, Xin Z, Wu D, Ni C,
Huang J, Wei Q and Zhang T: Radiation-induced tumor immune
microenvironments and potential targets for combination therapy.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8(205)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Read GH, Bailleul J, Vlashi E and
Kesarwala AH: Metabolic response to radiation therapy in cancer.
Mol Carcinog. 61:200–224. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Wang M, Chen S and Ao D: Targeting DNA
repair pathway in cancer: Mechanisms and clinical application.
MedComm (2020). 2:654–691. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Wu Y, Song Y, Wang R and Wang T: Molecular
mechanisms of tumor resistance to radiotherapy. Mol Cancer.
22(96)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Lin J, Song T, Li C and Mao W: GSK-3β in
DNA repair, apoptosis, and resistance of chemotherapy, radiotherapy
of cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res.
1867(118659)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Sobanski T, Rose M, Suraweera A, O'Byrne
K, Richard DJ and Bolderson E: Cell metabolism and DNA repair
pathways: implications for cancer therapy. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9(633305)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Zheng Y, Li H, Bo X and Chen H: Ionizing
radiation damage and repair from 3D-genomic perspective. Trends
Genet. 39:1–4. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Bamodu OA, Chang HL, Ong JR, Lee WH, Yeh
CT and Tsai JT: Elevated PDK1 expression drives PI3K/AKT/MTOR
signaling promotes radiation-resistant and dedifferentiated
phenotype of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cells. 9(746)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Morillo-Huesca M, G López-Cepero I,
Conesa-Bakkali R, Tomé M, Watts C, Huertas P, Moreno-Bueno G, Durán
RV and Martínez-Fábregas J: Radiotherapy resistance driven by
asparagine endopeptidase through ATR pathway modulation in breast
cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 44(74)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Meng W, Palmer JD, Siedow M, Haque SJ and
Chakravarti A: Overcoming radiation resistance in gliomas by
targeting metabolism and DNA repair pathways. Int J Mol Sci.
23(2246)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Benjanuwattra J, Chaiyawat P, Pruksakorn D
and Koonrungsesomboon N: Therapeutic potential and molecular
mechanisms of mycophenolic acid as an anticancer agent. Eur J
Pharmacol. 887(173580)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Fu S, Li Z, Xiao L, Hu W, Zhang L, Xie B,
Zhou Q, He J, Qiu Y, Wen M, et al: Glutamine synthetase promotes
radiation resistance via facilitating nucleotide metabolism and
subsequent DNA damage repair. Cell Rep. 28:1136–1143.e4.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Madsen HB, Peeters MJ, Straten PT and
Desler C: Nucleotide metabolism in the regulation of tumor
microenvironment and immune cell function. Curr Opin Biotechnol.
84(103008)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
López-Hernández L, Toolan-Kerr P,
Bannister AJ and Millán-Zambrano G: Dynamic histone modification
patterns coordinating DNA processes. Mol Cell. 85:225–237.
2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Charidemou E and Kirmizis A: A two-way
relationship between histone acetylation and metabolism. Trends
Biochem Sci. 49:1046–1062. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Kitabatake K, Kaji T and Tsukimoto M: ATP
and ADP enhance DNA damage repair in γ-irradiated BEAS-2B human
bronchial epithelial cells through activation of P2X7 and P2Y12
receptors. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 407(115240)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Koritzinsky M: Metformin: A novel
biological modifier of tumor response to radiation therapy. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 93:454–464. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Scott JS, Nassar ZD, Swinnen JV and Butler
LM: Monounsaturated fatty acids: Key regulators of cell viability
and intracellular signaling in cancer. Mol Cancer Res.
20:1354–1364. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Chen J, Zhang F, Ren X, Wang Y, Huang W,
Zhang J and Cui Y: Targeting fatty acid synthase sensitizes human
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to radiation via downregulating
frizzled class receptor 10. Cancer Biol Med. 17:740–752.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Zhan N, Li B, Xu X, Xu J and Hu S:
Inhibition of FASN expression enhances radiosensitivity in human
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 15:4578–4584.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Wu X, Dong Z, Wang CJ, Barlow LJ, Fako V,
Serrano MA, Zou Y, Liu JY and Zhang JT: FASN regulates cellular
response to genotoxic treatments by increasing PARP-1 expression
and DNA repair activity via NF-κB and SP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:E6965–E6973. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Chuang HY, Lee YP, Lin WC, Lin YH and
Hwang JJ: Fatty acid inhibition sensitizes androgen-dependent and
-independent prostate cancer to radiotherapy via FASN/NF-κB
pathway. Sci Rep. 9(13284)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Werner E, Alter A, Deng Q, Dammer EB, Wang
Y, Yu DS, Duong DM, Seyfried NT and Doetsch PW: Ionizing radiation
induction of cholesterol biosynthesis in lung tissue. Sci Rep.
9(12546)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
You Y, Wang Q, Li H, Ma Y, Deng Y, Ye Z
and Bai F: Zoledronic acid exhibits radio-sensitizing activity in
human pancreatic cancer cells via inactivation of STAT3/NF-κB
signaling. Onco Targets Ther. 12:4323–4330. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Peng J, Yin X, Yun W, Meng X and Huang Z:
Radiotherapy-induced tumor physical microenvironment remodeling to
overcome immunotherapy resistance. Cancer Lett.
559(216108)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Vitale I, Manic G, Coussens LM, Kroemer G
and Galluzzi L: Macrophages and metabolism in the tumor
microenvironment. Cell Metab. 30:36–50. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Nan D, Yao W, Huang L, Liu R, Chen X, Xia
W, Sheng H, Zhang H, Liang X and Lu Y: Glutamine and cancer:
Metabolism, immune microenvironment, and therapeutic targets. Cell
Commun Signal. 23(45)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
An D, Zhai D, Wan C and Yang K: The role
of lipid metabolism in cancer radioresistance. Clin Transl Oncol.
25:2332–2349. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Cao Z, Quazi S, Arora S, Osellame LD,
Burvenich IJ, Janes PW and Scott AM: Cancer-associated fibroblasts
as therapeutic targets for cancer: Advances, challenges, and future
prospects. J Biomed Sci. 32(7)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Mukherjee A, Bezwada D, Greco F,
Zandbergen M, Shen T, Chiang CY, Tasdemir M, Fahrmann J, Grapov D,
La Frano MR, et al: Adipocytes reprogram cancer cell metabolism by
diverting glucose towards glycerol-3-phosphate thereby promoting
metastasis. Nat Metab. 5:1563–1577. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Lee PWT, Suwa T, Kobayashi M, Yang H,
Koseki LR, Takeuchi S, Chow CCT, Yasuhara T and Harada H: Hypoxia-
and Postirradiation reoxygenation-induced HMHA1/ARHGAP45 expression
contributes to cancer cell invasion in a HIF-dependent manner. Br J
Cancer. 131:37–48. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Matschke J, Wiebeck E, Hurst S, Rudner J
and Jendrossek V: Role of SGK1 for fatty acid uptake, cell survival
and radioresistance of NCI-H460 lung cancer cells exposed to acute
or chronic cycling severe hypoxia. Radiat Oncol.
11(75)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Bai M, Xu P, Cheng R, Li N, Cao S, Guo Q,
Wang X, Li C, Bai N, Jiang B, et al: ROS-ATM-CHK2 axis stabilizes
HIF-1α and promotes tumor angiogenesis in hypoxic microenvironment.
Oncogene. 44:1609–1619. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Basheeruddin M and Qausain S:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α) and cancer: Mechanisms of
tumor hypoxia and therapeutic targeting. Cureus.
16(e70700)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Shah R, Ibis B, Kashyap M and Boussiotis
VA: The role of ROS in tumor infiltrating immune cells and cancer
immunotherapy. Metabolism. 151(155747)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Gao F, Liu C, Guo J, Sun W, Xian L, Bai D,
Liu H, Cheng Y, Li B, Cui J, et al: Radiation-driven lipid
accumulation and dendritic cell dysfunction in cancer. Sci Rep.
5(9613)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Lyssiotis CA and Kimmelman AC: Metabolic
interactions in the tumor microenvironment. Trends Cell Biol.
27:863–875. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Ashton TM, McKenna WG, Kunz-Schughart LA
and Higgins GS: Oxidative phosphorylation as an emerging target in
cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 24:2482–2490. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Peiris-Pagés M,
Pestell RG, Sotgia F and Lisanti MP: Cancer metabolism: A
therapeutic perspective. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:11–31.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Ko J, Berger R, Lee H, Yoon H, Cho J and
Char K: Electronic effects of nano-confinement in functional
organic and inorganic materials for optoelectronics. Chem Soc Rev.
50:3585–3628. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Liu G, Müller AJ and Wang D: Confined
crystallization of polymers within nanopores. Acc Chem Res.
54:3028–3038. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Napolitano S, Glynos E and Tito NB: Glass
transition of polymers in bulk, confined geometries, and near
interfaces. Rep Prog Phys. 80(036602)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Lu S, Zhao ZQ, Wang Q, Lv ZW and Yang JS:
Biological nano confinement: A promising target for inhibiting
cancer cell progress and metastasis. Oncologie. 24:591–597.
2022.
|
|
95
|
Kuttiappan A, Chenchula S, Vardhan KV,
Padmavathi R, Varshini TS, Amerneni LS, Amerneni KC and Chavan MR:
CAR T-cell therapy in hematologic and solid malignancies:
Mechanisms, clinical applications, and future directions. Med
Oncol. 42(376)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|