Introduction
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a chronic
gastrointestinal disorder affecting 5–20% of the world’s
population. IBS symptoms include abdominal discomfort or pain
associated with altered bowel habits and often bloating and
abdominal distension (1). IBS is
not known to be associated with the development of serious diseases
or with excess mortality (2,3).
However, it considerably reduces the quality of life (1). Apart from the increased morbidity
caused by IBS, it is an economic burden to society in a number of
ways (a rise in sick leave or over-utilization of healthcare
resources) (1).
Chromogranin A (CgA) is a marker for gut endocrine
cells and endocrine tumours (4–6). It
is a 68 kDa protein comprising 439 amino acid residues and was
isolated for the first time from secretory granules of the bovine
adrenal medulla (4,6). CgA is co-stored and co-released with
monoamines and peptide hormones of the adrenal medulla, pituitary
gland, parathyroid, thyroid C-cells, pancreatic islets, endocrine
cells of the gastrointestinal tract and sympathetic nerves
(4,5).
CgA cell density has been found to be reduced in the
colon of IBS patients and it has been suggested that intestinal CgA
cell density may be used as a marker for the diagnosis of IBS
(1,7). The human rectum has the same
endocrine cell types as the colon, namely: serotonin-, peptide YY
(PYY)-, pancreatic polypeptide (PP)-, enteroglucagon- and
somatostatin-producing cells (8,9). The
rectum harbours, however, a larger number of these endocrine cells
(8,9). In addition, the rectum is more
accessible for biopsies than the colon. Therefore, the present
study aimed to determine CgA cell density in the rectum of IBS
patients and to examine whether biopsies would be easier and would
have higher specificity and sensitivity when performed in the
rectum compared to the colon.
Materials and methods
Patients and controls
A total of 47 patients with IBS that fulfilled the
Rome Criteria III (39 females and 8 males; average age, 38 years;
range, 18–65 years) were included in this study (10; http://www.romecriteria.org). A total of 28 patients
had diarrhea (IBS-D) and 19 had constipation (IBS-C) as the
predominant symptom. All patients underwent a complete physical
examination comprising of blood tests (including full blood count,
electrolytes, calcium and inflammatory markers), liver tests and
thyroid function tests.
A total of 27 subjects (19 females and 8 males;
average age, 49 years; range, 18–67 years), who underwent
colonoscopy with rectal biopsies were used as the controls. In 20
of these subjects, colonoscopy was performed due to
gastrointestinal bleeding, the source of which was identified as
haemorrhoids (18 subjects) or angiodysplasia (2 subjects). The
other 7 subjects were examined due to worries resulting from having
relatives diagnosed with colon carcinoma.
The study was performed in accordance with the
Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the local Committee for
Medical Research Ethics. All subjects provided oral and written
informed consent.
Colonoscopy
The patients, as well as the controls underwent
colonoscopy, while biopsies were obtained from the rectum,
approximately 15 cm from the anus. Biopsies were fixed in 4%
buffered paraformaldehyde overnight, embedded in paraffin and cut
into 5 μm-thick sections.
Histopathology and
immunohistochemistry
The sections were stained with haematoxylin and
eosin and immunostained with the avidin-biotin complex (ABC) method
using a Vectastain ABC kit (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA,
USA), as previously described in detail (11). The primary antibody used was
monoclonal mouse anti-N-terminal of purified CgA (DakoCytomation,
Glostrup, Denmark; code no. M869). The second layer biotinylated
mouse anti-IgG was obtained from DakoCytomation.
Computerized image analysis
Computerized image analysis was performed using
Olympus software: Cell ^D. When using ×20 objectives, the frame
(field) on the monitor represents an area of 0.14 mm2 of
the tissue. The number of CgA immunoreactive cells and the area of
the epithelial cells were measured in each field. Measurements were
taken in 10 randomly chosen fields for each individual. Data from
the fields were tabulated, the number of cells/mm2 of
the epithelium was computed and statistically analysed
automatically.
Statistical analysis
Mann-Whitney U test was performed. P-values <0.05
were considered to indicate statistically significant
differences.
Results
Colonoscopy, histopathology and
immunohistochemistry
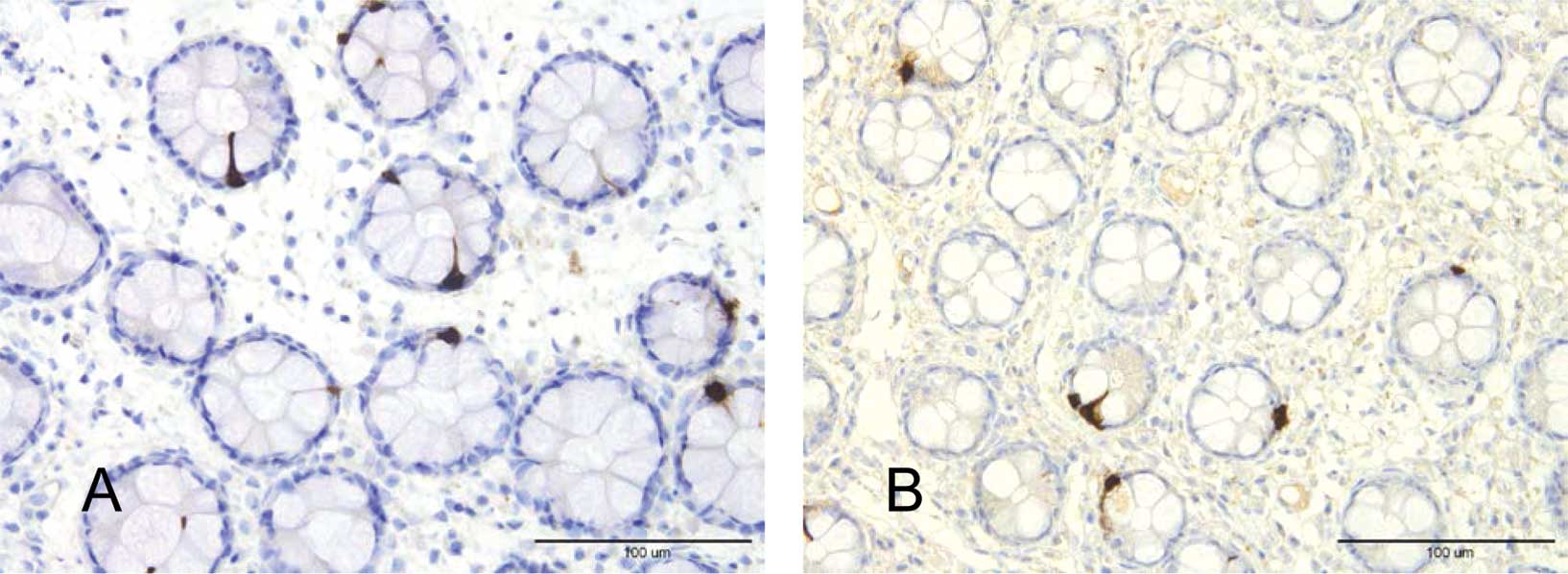
The colons of the patients and the controls were
macroscopically normal. Histopathological examination of the colon
biopsies from patients and controls revealed normal histology. CgA
cells were located mostly in the upper part of the crypts of
Lieberkühn (Fig. 1). These cells
were basket- or flask-shaped.
Computerized image analysis
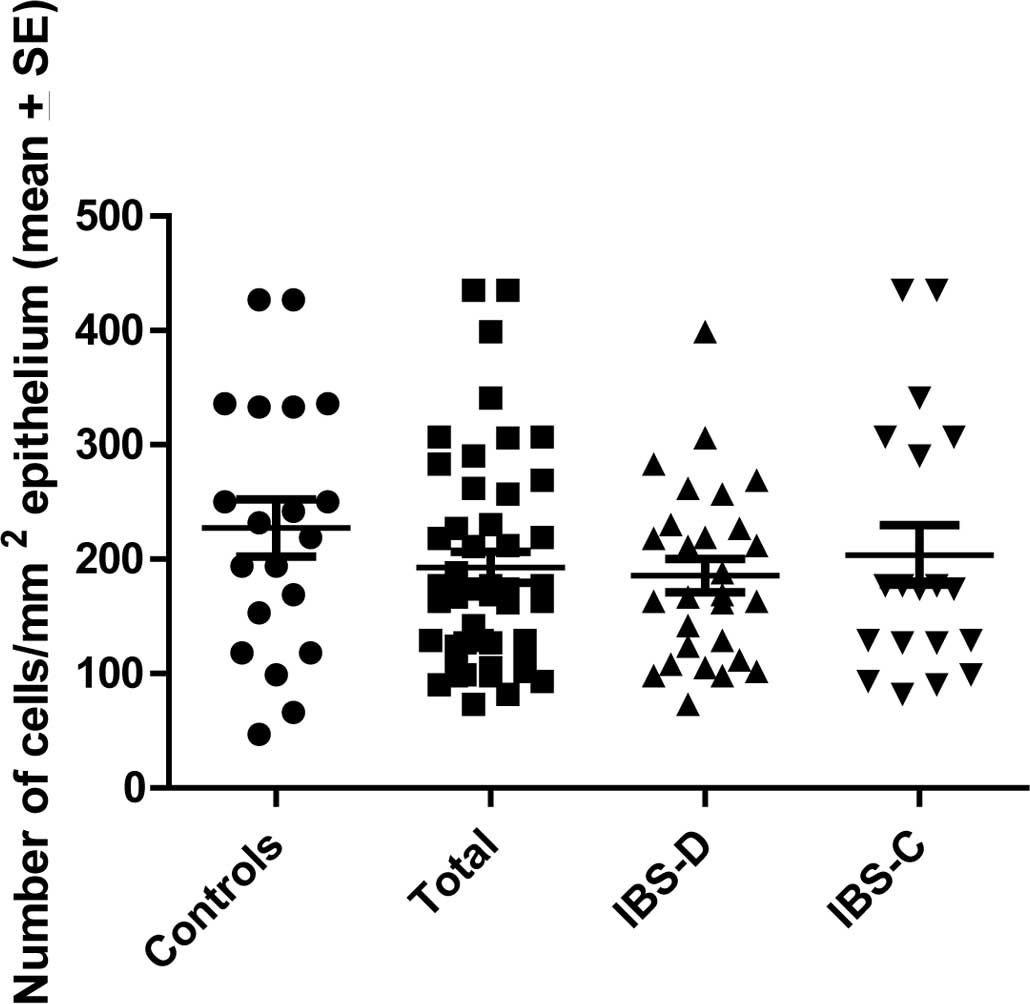
The CgA density in the controls was 206.3±22.2 (mean
± SEM), in all IBS patients 190.2±14.3, in IBS-D patients
188.8±14.7 and in IBS-C patients 195.3±34.1 (Fig. 2). There was no statistically
significant difference between the controls, IBS, IBS-D or IBS-C
patients (P=0.5, 0.5 and 0.7, respectively).
Discussion
The age and gender of the patients and healthy
controls used in this study did not match completely. The control
subjects were slightly older and the proportion of males to females
was higher. In previous studies, however, age and gender have been
found to have no effect on the density of intestinal endocrine
cells in adults (8,12). The present findings demonstrating
that rectal CgA cell density in patients with IBS does not differ
from that of the controls was unexpected. However, taking into
consideration that the colon and the rectum have different
physiological functions, this observation becomes less surprising.
Thus, the main function of the colon is absorbing water, sodium and
some fat soluble vitamins, whereas the rectum acts as a reservoir
for faeces and plays a principal role in defection (13). As mentioned previously, the rectum,
besides containing the same endocrine cells as the colon, harbours
a larger number of these cells as well as a larger supply of
autonomic innervation compared to the colon (13).
The rectum is accessible for biopsies subsequent to
a simple rigid rectoscope without any rigorous intestinal
cleansing. On the other hand, biopsies from the colon require
intestinal preparation, availability of a flexible colonoscope and
a specialist with the knowledge of performing a colonoscopy. That
is why the rectum has been chosen as a representative of the large
intestine in several studies investigating endocrine cells in IBS
patients (14–17). The present findings raise a warning
against using the rectum as a representative of the large
intestine, particularly in investigations concerning endocrine
cells in a pathological condition.
Although CgA cell density, representing the total
endocrine cell content of the rectum, remained unchanged in IBS
patients, changes in specific endocrine cells should not be
excluded. The findings asserting that changes in the serotonin
cells do occur in the rectum of patients with IBS support this
assumption (14–17). However, additional studies are
required to clarify this hypothesis.
In conclusion, the present study demonstrates that
although the rectum comprises the same endocrine cell types as the
colon, attention should be paid when drawing conclusions regarding
the whole large intestine from studies conducted on the rectum.
This particularly applies when investigating endocrine cells.
Acknowledgements
The present study was supported by a grant from
Helse-Fonna.
References
|
1
|
El-Salhy M, Gundersen D, Hatlebakk JG and
Hausken T: Irritable bowel syndrome. Nova Scientific Publisher; New
York, NY: 2012
|
|
2
|
Drossman DA, Morris CB, Schneck S, Hu YJ,
Norton NJ, Norton WF, Weinland SR, et al: International survey of
patients with IBS: symptom features and their severity, health
status, treatments, and risk taking to achieve clinical benefit. J
Clin Gastroenterol. 43:541–550. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sloth H and Jorgensen LS: Chronic
non-organic upper abdominal pain: diagnostic safety and prognosis
of gastrointestinal and non-intestinal symptoms. A 5-to 7-year
follow-up study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 23:1275–1280.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Taupenot L, Harper KL and O’Connor DT: The
chromogranin-secretogranin family. N Engl J Med. 348:1134–1149.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wicdenmann B and Huttner WB: Synaptophysin
and chromogranin/secretogranins - widespread constituents of
distinct types of neuroendocrine vesicales and new tools in tumor
diagnosis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 58:95–121.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Deftos LJ: Chromogranin A: its role in
endocrine function and as an endocrine and neuroendocrine tumor
marker. Endocr Rev. 12:181–187. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
El-Salhy M, Lomholt-Beck B and Hausken T:
Chromogranin as a tool in the diagnosis of irritable bowel
syndrome. Scan J Gastroenterol. 45:1435–1439. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sandström O and El-Salhy M: Human rectal
endocrine cells and aging. Mech Ageing Dev. 108:219–226.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sjölund K, Sandèn G, Håkanson R and
Sundler F: Endocrine cells in human intestine: an
immunocytochemical study. Gastroenterology. 85:1120–1130.
1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Longstreth GF, Thompson WG, Chey WD,
Houghton LA, Mearin F and Spiller RC: Functional bowel disorder.
Gastroenterology. 130:1480–91. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
El-Salhy M, Stenling R and Grimelius L:
Peptidergic innervation and endocrine cells in the human liver.
Scand J Gastroenterol. 28:809–815. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sandström O and El-Salhy M: Aging and
endocrine cells of human duodenum. Mech Ageing Dev. 108:39–48.
1999.
|
|
13
|
Nordgren S: Kolon. Hellerstöm P:
Janssen-Cilag AB; Stockholm: pp. 63–78. 1993
|
|
14
|
Spiller RC, Jenkins D, Thornely, Hebden
JM, Wright T, Skinner M and Neal KR: Increased rectal mucosal
enteroendocrine cells, T lymphocytes, and increased gut
permeability following acute Campylobacter enteritis and in
post-dysenteric irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 47:804–811. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Dunlop SP, Jenkins D, Neal KR and Spiller
RC: Relative importance of enterochromaffin cells hyperplasia,
anxiety, and depression in postinfectious IBS. Gastroenterology.
125:1651–1659. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee KJ, Kim YB, Kwon HC, Kim DK and Cho
SW: The alteration of enterochromaffin cell, mast cell and lamina
propria T lymphocyte numbers in irritable bowel syndrome and its
relationship with psychological factors. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
23:1689–1694. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim HS, Lim JH, Park H and Lee SI:
Increased immunoendocrine cells in intestinal mucosa of
postinfectious irritable bowel syndrome patients 3 years after
acute Shigella infection- an observation in small case
control study. Yonsei Med J. 51:45–51. 2010.
|