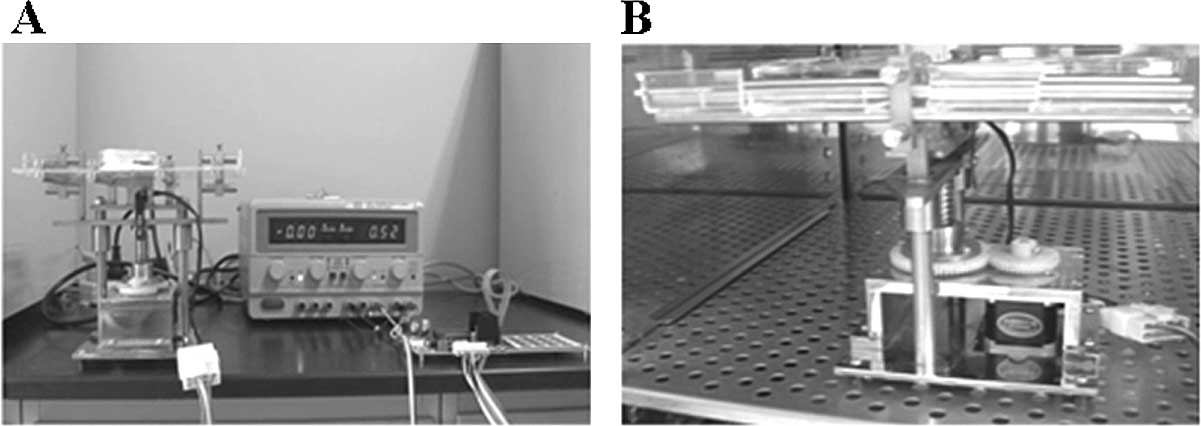
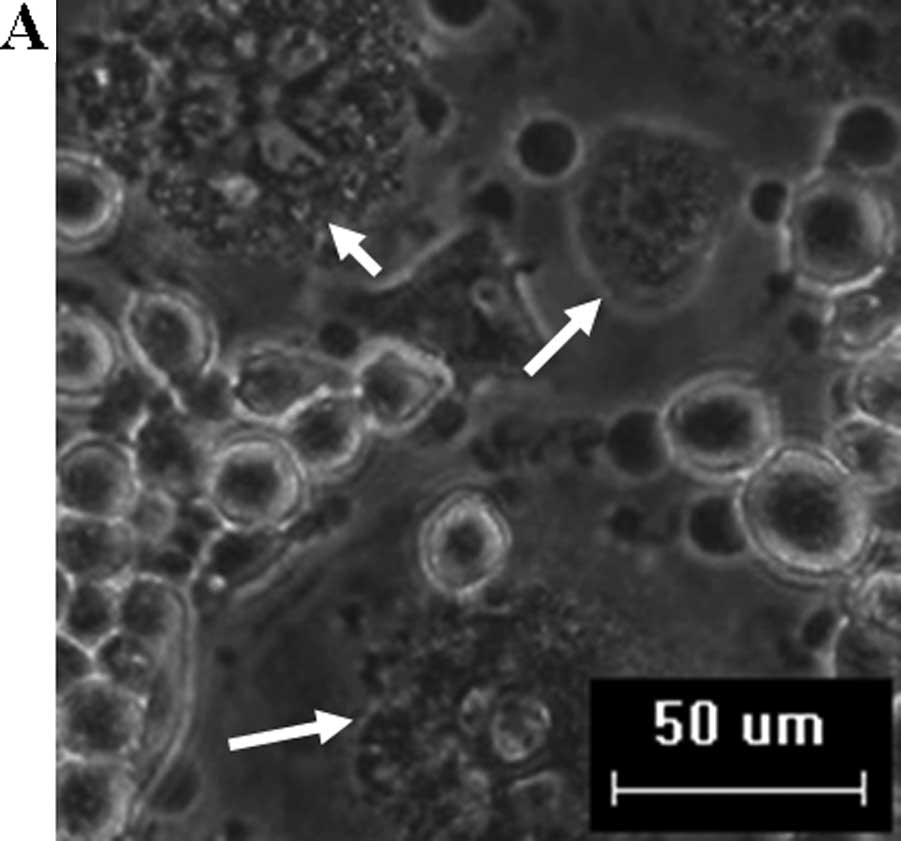
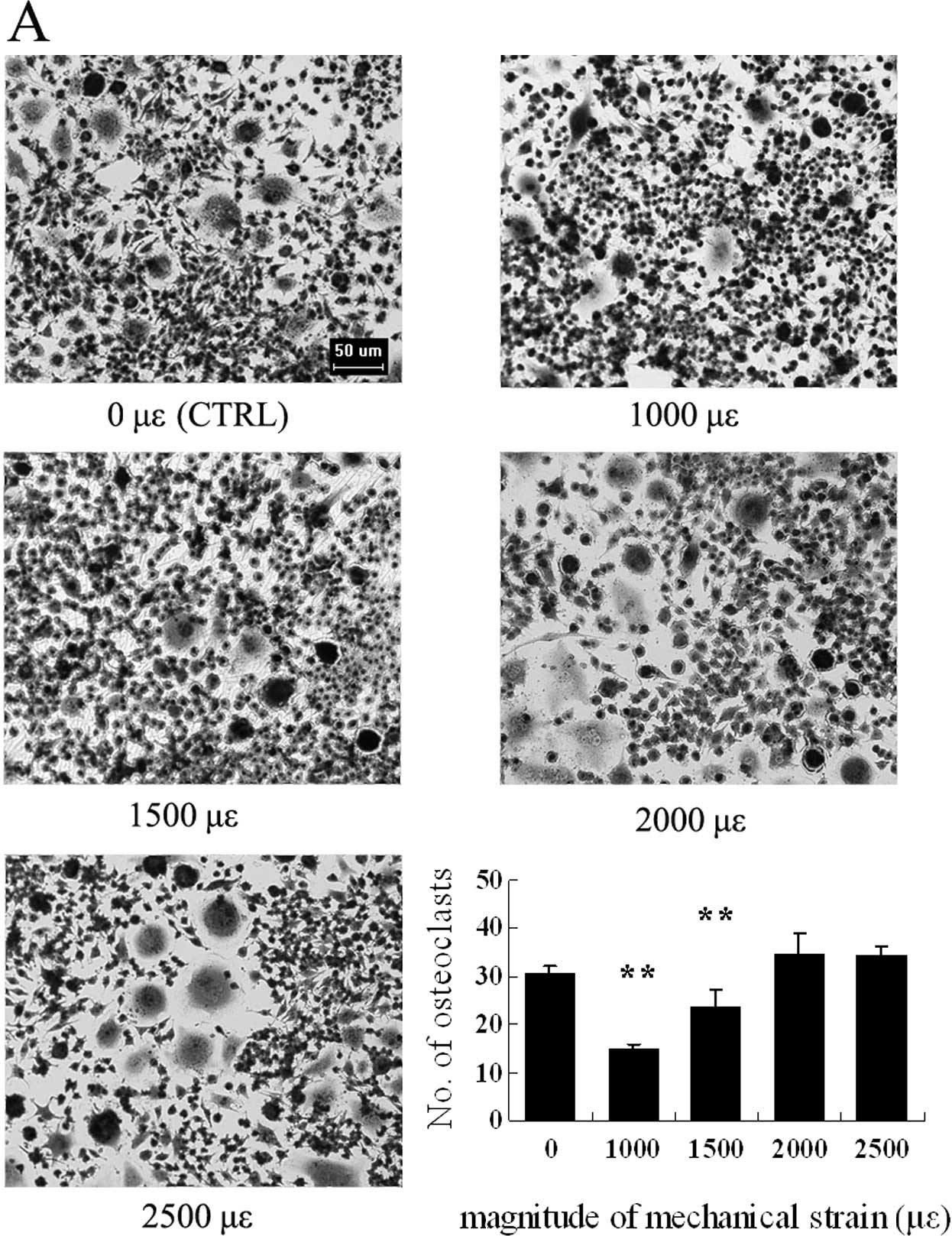
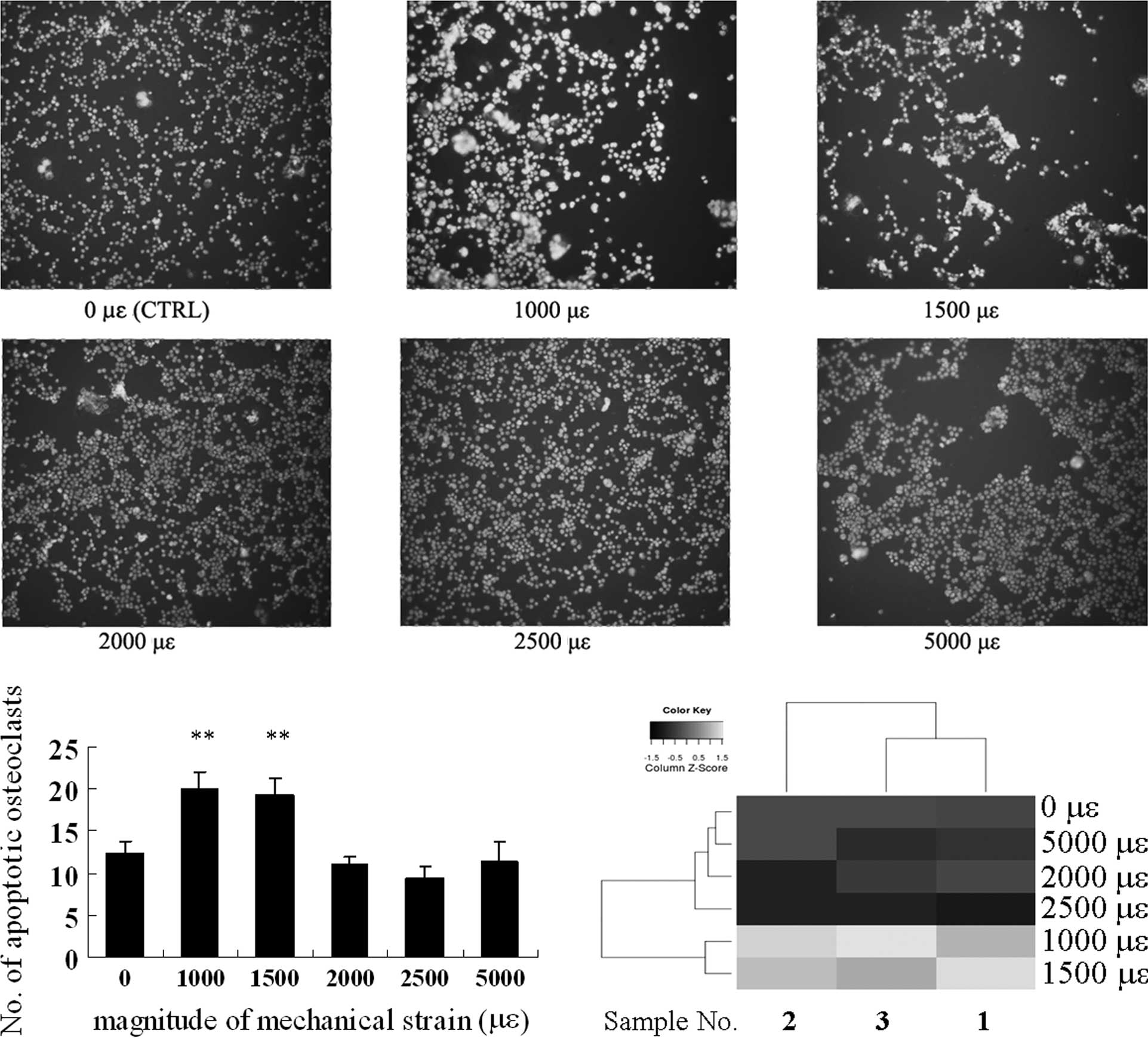
|
1
|
Frost HM: Bone Remodeling Dynamics. Thomas
CC: Springfield, IL: 1963
|
|
2
|
Frost HM: Bone ‘mass’ and the
‘mechanostat’: a proposal. Anat Rec. 219:1–9. 1987.
|
|
3
|
Teitelbaum SL: Osteoclasts: what do they
do and how do they do it? Am J Pathol. 170:427–435. 2007.
|
|
4
|
Kodama H, Nose M, Niida S and Yamasaki A:
Essential role of macrophage colony-stimulating factor in the
osteoclast differentiation supported by stromal cells. J Exp Med.
173:1291–1294. 1991.
|
|
5
|
Yasuda H, Shima N, Nakagawa N, et al:
Identity of osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor (OCIF) and
osteoprotegerin (OPG): a mechanism by which OPG/OCIF inhibits
osteoclastogenesis in vitro. Endocrinology. 139:1329–1337.
1998.
|
|
6
|
Mochizuki A, Takami M, Kawawa T, et al:
Identification and characterization of the precursors committed to
osteoclasts induced by TNF-related activation-induced
cytokine/receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand. J Immunol.
177:4360–4368. 2006.
|
|
7
|
Kong YY, Yoshida H, Sarosi I, et al: OPGL
is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development
and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature. 397:315–323. 1999.
|
|
8
|
Kim N, Odgren PR, Kim DK, Marks SC Jr and
Choi Y: Diverse roles of the tumor necrosis factor family member
TRANCE in skeletal physiology revealed by TRANCE deficiency and
partial rescue by a lymphocyte-expressed TRANCE transgene. Proc Nat
Acad Sci USA. 97:10905–10910. 2000.
|
|
9
|
Dougall WC, Glaccum M, Charrier K, et al:
RANK is essential for osteoclast and lymph node development. Genes
Dev. 13:2412–2424. 1999.
|
|
10
|
Li J, Sarosi I, Yan XQ, et al: RANK is the
intrinsic hematopoietic cell surface receptor that controls
osteoclastogenesis and regulation of bone mass and calcium
metabolism. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA. 97:1566–1571. 2000.
|
|
11
|
Chen XY, Zhang XZ, Guo Y, Li RX, Lin JJ
and Wei Y: The establishment of a mechanobiology model of bone and
functional adaptation in response to mechanical loading. Clin
Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 23(Suppl 1): 88–95. 2008.
|
|
12
|
Suda T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Jimi E,
Gillespie MT and Martin TJ: Modulation of osteoclast
differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor
necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endoc Rev.
20:345–357. 1999.
|
|
13
|
Suzuki N, Yoshimura Y, Deyama Y, Suzuki K
and Kitagawa Y: Mechanical stress directly suppresses osteoclast
differentiation in RAW264.7 cells. Int J Mol Med. 21:291–296.
2008.
|
|
14
|
Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Tanaka S and Suda
T: Generating murine osteoclasts from bone marrow. Methods Mol Med.
80:129–144. 2003.
|
|
15
|
Tang LL, Wang YL, Pan J and Cai SX: The
effect of step-wise increased stretching on rat calvarial
osteoblast collagen production. J Biomech. 37:157–161. 2004.
|
|
16
|
Shibata K, Yoshimura Y, Kikuiri T, et al:
Effect of the release from mechanical stress on osteoclastogenesis
in RAW264.7 cells. Int J Mol Med. 28:73–79. 2011.
|
|
17
|
Kreja L, Liedert A, Hasni S, Claes L and
Ignatius A: Mechanical regulation of osteoclastic genes in human
osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 368:582–587. 2008.
|
|
18
|
Rubin J, Murphy T, Nanes MS and Fan X:
Mechanical strain inhibits expression of osteoclast differentiation
factor by murine stromal cells. Am J Physiol. 278:C1126–1132.
2000.
|
|
19
|
Ichimiya H, Takahashi T, Ariyoshi W,
Takano H, Matayoshi T and Nishihara T: Compressive mechanical
stress promotes osteoclast formation through RANKL expression on
synovial cells. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.
103:334–341. 2007.
|
|
20
|
Rubin J, Fan X, Biskobing DM, Taylor WR
and Rubin CT: Osteoclastogenesis is repressed by mechanical strain
in an in vitro model. J Orthop Res. 17:639–645. 1999.
|
|
21
|
Burger EH, Klein-Nulend J and Smit TH:
Strain-derived canalicular fluid flow regulates osteoclast activity
in a remodelling osteon – a proposal. J Biomech. 36:1453–1459.
2003.
|
|
22
|
McAllister TN, Du T and Frangos JA: Fluid
shear stress stimulates prostaglandin and nitric oxide release in
bone marrow-derived preosteoclast-like cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 270:643–648. 2000.
|
|
23
|
Kurata K, Uemura T, Nemoto A, et al:
Mechanical strain effect on bone-resorbing activity and messenger
RNA expressions of marker enzymes in isolated osteoclast culture. J
Bone Miner Res. 16:722–730. 2001.
|
|
24
|
Zhang Q, Liang X, Zhu B, et al: Effects of
fluid shear stress on mRNA expression of carbonic anhydrase II in
polarized rat osteoclasts. Cell Biol Int. 30:714–720. 2006.
|
|
25
|
Childs LM, Paschalis EP, Xing L, et al: In
vivo RANK signaling blockade using the receptor activator of
NF-κB:Fc effectively prevents and ameliorates wear debris-induced
osteolysis via osteoclast depletion without inhibiting
osteogenesis. J Bone Miner Res. 17:192–199. 2002.
|
|
26
|
Feeley BT, Liu NQ, Conduah AH, et al:
Mixed metastatic lung cancer lesions in bone are inhibited by
noggin overexpression and Rank:Fc administration. J Bone Miner Res.
21:1571–1580. 2006.
|
|
27
|
Kim H, Choi HK, Shin JH, et al: Selective
inhibition of RANK blocks osteoclast maturation and function and
prevents bone loss in mice. J Clin Invest. 119:813–825. 2009.
|
|
28
|
Blavier L and Delaisse JM: Matrix
metalloproteinases are obligatory for the migration of
preosteoclasts to the developing marrow cavity of primitive long
bones. J Cell Sci. 108:3649–3659. 1995.
|
|
29
|
Sato T, Foged NT and Delaissé JM: The
migration of purified osteoclasts through collagen is inhibited by
matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. J Bone Miner Res. 13:59–66.
1998.
|
|
30
|
Ishibashi O, Niwa S, Kadoyama K and Inui
T: MMP-9 antisense oligodeoxynucleotide exerts an inhibitory effect
on osteoclastic bone resorption by suppressing cell migration. Life
Sci. 79:1657–1660. 2006.
|
|
31
|
Hill PA, Murphy G, Docherty AJ, et al: The
effects of selective inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)
on bone resorption and the identification of MMPs and TIMP-1 in
isolated osteoclasts. J Cell Sci. 107(Pt 11): 3055–3064. 1994.
|
|
32
|
Spessotto P, Rossi FM, Degan M, et al:
Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction hampers migration of osteoclast-like
cells by down-regulating MMP-9. J Cell Biol. 158:1133–1144.
2002.
|
|
33
|
Alatalo SL, Halleen JM, Hentunen TA,
Monkkonen J and Vaananen HK: Rapid screening method for osteoclast
differentiation in vitro that measures tartrate-resistant acid
phosphatase 5b activity secreted into the culture medium. Clin
Chem. 46:1751–1754. 2000.
|
|
34
|
Rissanen JP, Suominen MI, Peng Z and
Halleen JM: Secreted tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5b is a
Marker of osteoclast number in human osteoclast cultures and the
rat ovariectomy model. Calcif Tissue Int. 82:108–115. 2008.
|
|
35
|
Fujisaki K, Tanabe N, Suzuki N, et al:
Receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand induces the expression of
carbonic anhydrase II, cathepsin K, and matrix metalloproteinase-9
in osteoclast precursor RAW264.7 cells. Life Sci. 80:1311–1318.
2007.
|