Introduction
Inflammation is a fundamental process involved in
protection against infection or injury (1). Macrophages are involved in acute and
chronic inflammation (2,3) and play multidirectional roles in the
integrity of the immune system (4).
Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) is important for macrophage
activation during the innate and acquired immune response (5). Activated macrophages obtain increased
cytokine production and enhanced tumoricidal and microbicidal
function (6,7). In various inflammatory and
granulomatous conditions, IFN-γ is critical in enhancing and
sustaining macrophage activation (8,9).
However, its precise mechanism remains largely unknown and
elucidating its role is essential in order to gain further
understanding of the pathogenesis of inflammation.
THP-1 cells, a human monocytic leukemia cell line,
have been extensively employed as a model for examining the
functional diversity of monocyte/macrophage transition, due to the
similarities in biological behavior of monocytes/macrophages
derived from peripheral blood and the fact that non-adherent cells
can be changed into plastic-adherent macrophages by
αVβ3 integrin expression via ERK activation
in the presence of phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) (10,11).
In the present study, we investigated the effects of
IFN-γ on cell adhesion and the production of tumor necrosis factor
(TNF) using PMA-stimulated THP-1 cells.
Materials and methods
Reagents
PMA was purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA).
IFN-γ was obtained from Peprotech EC, Ltd. (London, UK). U0126 (MEK
inhibitor) and BAY 11-7082 (IκB inhibitor) were obtained from
Calbiochem (La Jolla, CA, USA). Fluorescein isothiocyanate
(FITC)-conjugated primary antibodies for the flow cytometric assay
were as follows: αV integrin, β3 integrin
(BioLegend, San Diego, CA); intercellular adhesion molecule-1
(ICAM-1) (Immunotech, Marseille, France), vascular cell adhesion
molecule-1 (VCAM-1) (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) and
isotype IgG (BD Biosciences Pharmingen, San Diego, CA). Antibodies
for western blot analysis were as follows:
anti-phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2,
phospho-NF-κB p65, anti-ERK1/2 and anti-NF-κB p65 (Cell Signaling
Technology, Beverly, MA, USA). Blocking antibodies were as follows:
αV integrin (Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA), ICAM-1, VCAM-1,
IFN-γR and isotype IgG1 (R&D Systems). Reagents for real-time
PCR were as follows: RNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA),
PrimeScript RT Reagent kit (Takara Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan) and
Thunderbird qPCR mix (Toyobo, Osaka, Japan). Primers were produced
by Takara Bio (Table I), with the
exception of the αV and β3 integrins, which
were produced by Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA).
 | Table IPrimers used for RT-qPCR. |
Table I
Primers used for RT-qPCR.
| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|
| GAPDH |
GCACCGTCAAGGCTGAGAAC |
TGGTGAAGACGCCAGTGGA |
| TNF |
GTGACAAGCCTGTAGCCCATGTT |
TTATCTCTCAGCTCCACGCCATT |
| ICAM-1 |
AACTGACACCTTTGTTAGCCACCTC |
CCCAGTGAAATGCAAACAGGAC |
| VCAM-1 |
CGAAAGGCCCAGTTGAAGGA |
GAGCACGAGAAGCTCAGGAGAAA |
| Integrin
αV |
GGAGCAATTCGACGAGCACT |
TTCATCCCGCAGATACGCTA |
| Integrin
β3 |
TGACGAAAATACCTGCAACCG |
GCATCCTTGCCAGTGTCCTTAA |
Cell culture
Human monocytic THP-1 cells (American Type Culture
Collection, Manassas, VA, USA) were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium
supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum (Gibco, Los Angeles, CA,
USA), 1% penicillin/streptomycin and 1% L-glutamin at 37°C in a
humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere.
Cell attachment assay
The cell attachment assay was performed as described
previously (11). THP-1 cells
(2×105/ml) were incubated in uncoated 96-well plates for
~48 h following PMA stimulation in the presence or absence of
IFN-γ. Total (without washing) and adherent (with washing) cell
numbers were measured by adding the cell count reagent (Nacalai
Tesque, Kyoto, Japan). Following 3 h of incubation, absorbance at
450 nm was calculated using FlexStation 3 (Molecular Devices,
Sunnyvale, CA, USA). Pretreatment with inhibitors (U0126 and BAY
11-7082) or blocking antibodies was performed for 30 min prior to
the addition of PMA with or without IFN-γ, followed by 48 h of
incubation and the obtained data were expressed as the relative
adherent cell number (O.D.).
Western blot analysis
THP-1 cells were incubated in a 100 mm dish for up
to 48 h after PMA stimulation in the presence or absence of IFN-γ.
Cell extracts were obtained for western blot analysis as previously
described (11). Antibodies were
diluted in Hikari (Nacalai) signal enhancer for the detection of
phosphorylated protein. Immunostained blots were stripped with
Restore (Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Jose, CA, USA) and reprobed
with primary antibodies against total protein. LAS-4000 and
MultiGauge software (Fujifilm, Tokyo, Japan) were used for
analysis.
Flow cytometric analysis
THP-1 cells were incubated in a 100 mm dish for 48 h
following stimulation with PMA in the presence or absence of IFN-γ.
Adherent cells were detached by treatment with trypsin/EDTA, washed
with PBS and the non-adherent cells and incubated for 20 min with
primary antibody, followed by fixation with 1% formaldehyde in PBS.
The expression of cell surface adhesion molecules was determined
using flow cytometric analysis (FACScan, Becton Dickinson, Franklin
Lakes, NJ, USA) and the data were analyzed using FlowJo (Tree Star,
Inc., Ashland, OR, USA). As described previously (11), the mean fluorescence intensity
(MFI) ratio is defined as MFI of the sample (adhesion molecule)/MFI
of isotype IgG. The obtained data were expressed as the relative
MFI ratio, and evaluated by comparing the MFI ratio.
Real-time reverse
transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)
THP-1 cells were cultured in 6 or 12-well plates for
up to 24 h. Following incubation, total RNA extraction, the reverse
transcriptase reaction and real-time PCR were performed as
described previously (11).
Relative gene expression was analyzed using the 2−ΔΔCT
method. In the inhibitor and blocking antibody study, the data were
shown as relative to PMA single treatment.
ELISA
THP-1 cells were cultured with PMA stimulation in
the presence or absence of IFN-γ for up to 48 h without serum
starvation treatment. The concentration of TNF in the supernatant
was measured using an ELISA kit (R&D Systems). The cell number,
measured by hemocytometer, was used as a control for
variability.
Statistical analysis
The data were analyzed by Prism (www.graphpad.com). Comparison between the groups was
performed using one-way ANOVA and the unpaired t-test. Newman-Keuls
post hoc test was used for the ANOVA. P<0.05 was deemed to
indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
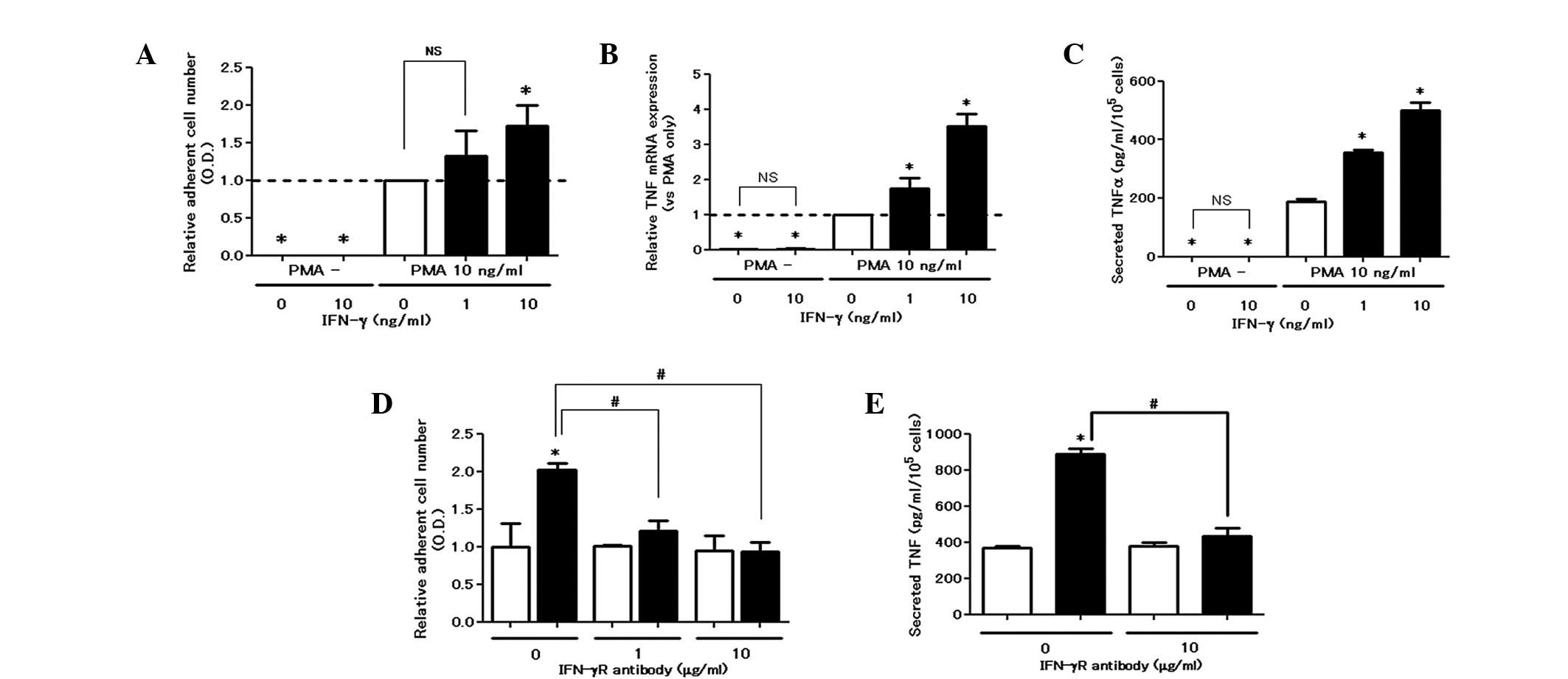
IFN-γ augments PMA-induced cell
attachment and TNF production
In the colorimetric adhesion assay, IFN-γ did not
induce cell attachment, whereas it dose-dependently upregulated
adhesion in the presence of PMA (Fig.
1A). Similarly, IFN-γ elevated the production of TNF at the
mRNA and protein levels in the presence of PMA (Fig. 1B and C). The enhancing effect of
IFN-γ on cell attachment and TNF production was eliminated by the
blocking antibody for the IFN-γ receptor, confirming its
receptor-mediated action (Fig. 1E and
F).
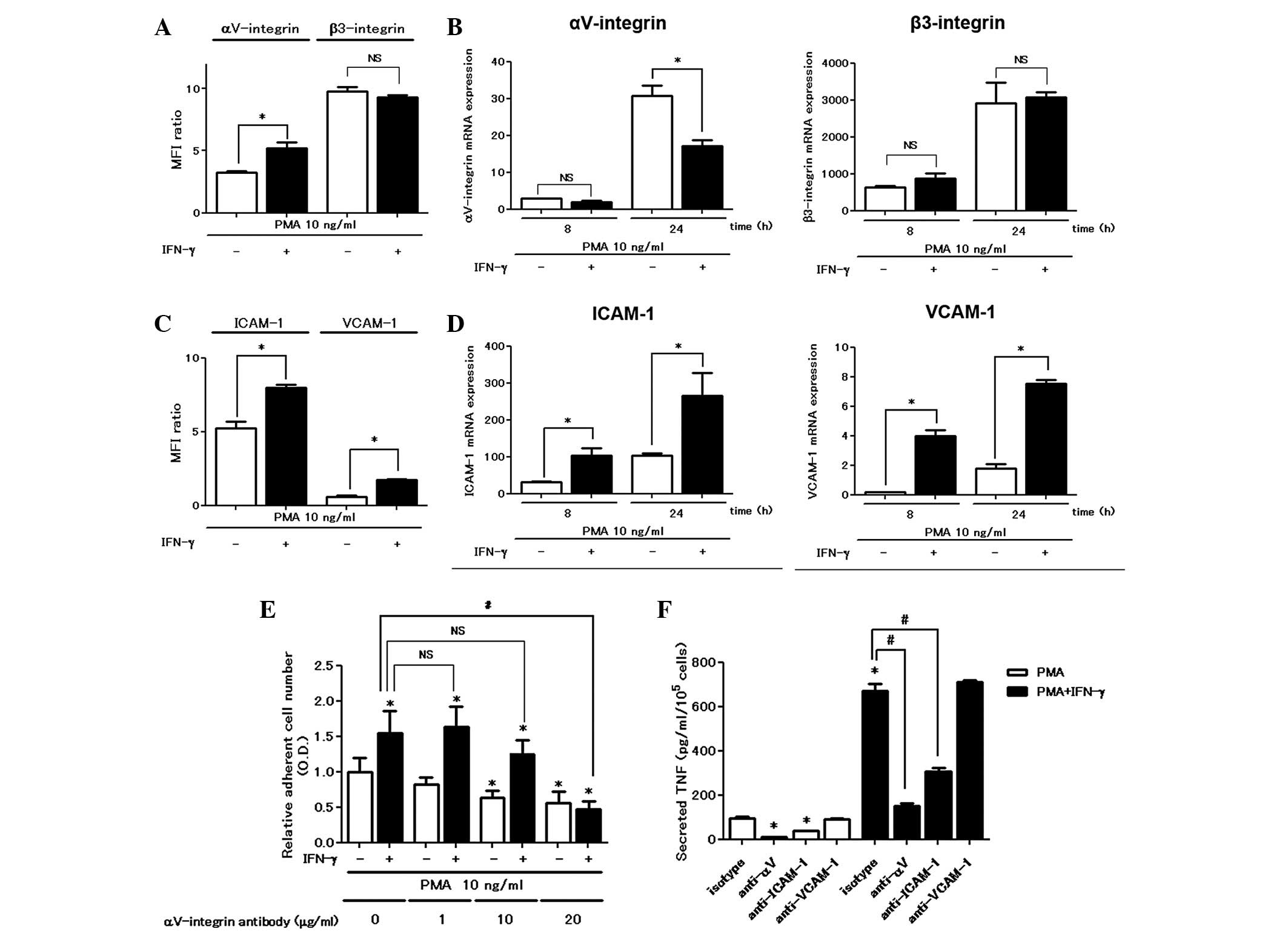
The αV integrin is involved in
the enhancing effects of IFN-γ on cell attachment and TNF
production
We examined the expression of cell surface adhesion
molecules using a flow cytometric assay. IFN-γ enhanced
cell-surface αV integrin expression in the flow
cytometric assay; however, it did not increase either αV
integrin mRNA or β3 integrin expression levels (Fig. 2A and B). IFN-γ was active in
upregulating the expression of other adhesion molecules such as
ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 at the mRNA and protein levels (Fig. 2C and D). Pretreatment with the
αV integrin blocking antibody (10 μg/ml) significantly
inhibited PMA-stimulated cell attachment, confirming the
involvement of the αV integrin in PMA-induced plastic
adhesion and a higher concentration (20 μg/ml) of the blocking
antibody was required in order to inhibit the cell attachment
enhanced by treatment with IFN-γ (Fig.
2E). However, the blocking antibodies for ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 did
not inhibit PMA with or without IFN-γ-induced cell attachment even
at higher concentrations (data not shown). Furthermore, treatment
with the blocking antibody for ICAM-1 suppressed PMA with or
without IFN-γ-induced TNF secretion (Fig. 2F).
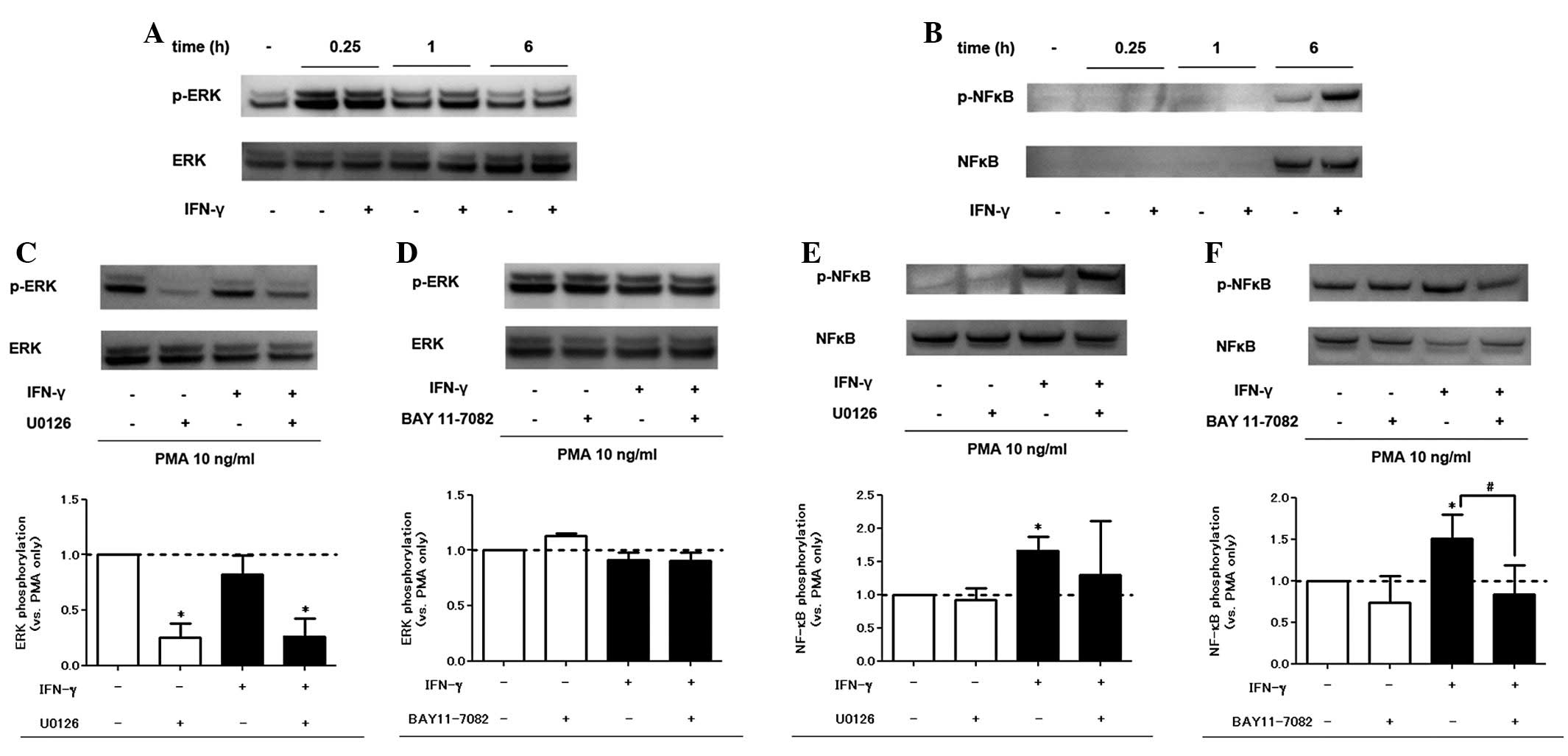
IFN-γ treatment augments NF-κB
phosphorylation but not ERK phosphorylation
We analyzed the PMA and IFN-γ-induced phosphorylated
proteins in the signaling pathways of inflammation. In western blot
analysis, PMA alone induced ERK and NF-κB phosphorylation. Addition
of IFN-γ also enhanced NF-κB phosphorylation, but not ERK
phosphorylation (Fig. 3A and B).
The specific inhibitory effect of U0126 and BAY 11-7082 on the
signaling pathways was confirmed (Fig.
3C–F). As for viability, pretreatment with signaling pathway
inhibitors did not affect cell viability in the trypan blue
exclusion assay within the range of concentrations used in the
experiment (data not shown).
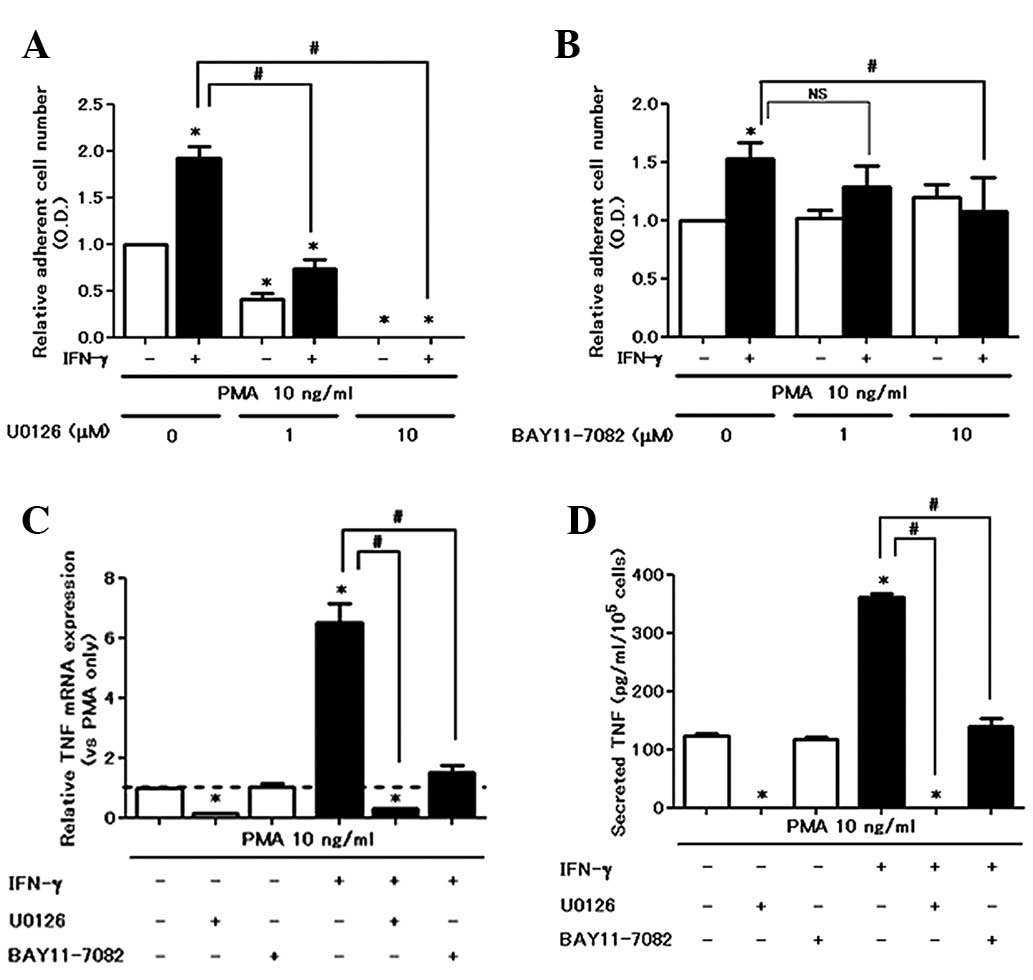
IFN-γ amplifies PMA-induced cell
attachment and TNF production via the NF-κB pathway
We examined the effect of inhibitors on cell
attachment and TNF production from PMA with or without
IFN-γ-treated cells. With regard to cell attachment, U0126 (MEK
inhibitor) completely inhibited PMA ± IFN-γ-induced cell attachment
in a dose-dependent manner (Fig.
4A). However, BAY 11-7082 counteracted the IFN-γ-induced cell
attachment increase (Fig. 4B), but
did not inhibit PMA-induced cell attachment. U0126 almost
completely eliminated the production of TNF in PMA with or without
IFN-γ-stimulated cells at mRNA and protein levels (Fig. 4C and 4D). By contrast, BAY 11-7082
enhanced the production of TNF in PMA with a single treatment.
However, BAY 11-7082 significantly suppressed IFN-γ-enhanced TNF
production (Fig. 4C and D). These
data indicate that the ERK pathway is critical for mediating
PMA-induced baseline cell activation and that an increase by IFN-γ
is dependent on the NF-κB pathway.
Discussion
IFN-γ induces adhesion molecule expression,
amplifies inflammatory cytokine production and promotes
monocyte/macrophage antimicrobial and antitumor activity (12). The enhancement of
lipopolysaccharide (LPS) responses by IFN-γ is known as a priming
effect (13). However, the
mechanism involved in macrophage adhesion and cytokine production
amplification remains unclear. In this study, we revealed the
pivotal role of the NF-κB pathway in mediating the upregulation of
IFN-γ using PMA-induced THP-1 cell adhesion and a TNF secretion
assay.
The presence of a non-absorbable foreign body
induces persistent inflammation, known as a foreign body reaction,
in vivo, although biomaterial surface properties are
important in modulating its reaction (14,15).
The importance of IFN-γ in the foreign body reaction is indicated
in an animal study (16) and IFN-γ
appears to be a crucial cytokine in granuloma formation as it
accelerates their various functions, including their adhesive
properties.
After treatment with PMA, the non-adherent THP-1
monocytic cells became adherent to plastic, which was blocked by
αV integrin function-blocking antibody as described in a
previous study (11). In the
present study, IFN-γ upregulated cell adhesion and cell surface
αV integrin expression in the presence of PMA.
Accordingly, sufficient concentration of αV integrin
blocking antibody was acquired for the inhibition of IFN-γ-enhanced
adhesion. Blocking antibodies for other adhesion molecules with the
immunoglobulin superfamily, such as ICAM-1 and VCAM-1, which were
also upregulated by IFN-γ treatment, failed to inhibit the
amplification of cell adherence. Qualitative alteration of adhesion
molecules, including increased avidity, may also be involved in the
enhancement of adhesive properties, since the upregulation of the
αV integrin protein was not accompanied by mRNA
expression. In contrast to cell adhesion, the ICAM-1 blocking
antibody inhibited the production of TNF. The difference in
effectiveness between the αV integrin blocking antibody
and the ICAM-1 blocking antibody against cell adhesion is due to
the different mechanisms involved in cell adhesion; the former is
mainly involved in cell-matrix adhesion and the latter is involved
in cell-cell adhesion.
The ERK signaling pathway is critical for
PMA-induced cell adherence and TNF secretion. PMA treatment induced
ERK phosphorylation and subsequent cell adhesion and TNF
expression. U0126 (MEK inhibitor) almost completely eliminated
PMA-induced adhesion and TNF production, a result that is in
agreement with previous observations (11). Even in co-stimulation with PMA and
IFN-γ, U0126 delivered a profound inhibition of adhesion and TNF
production, emphasizing the fundamental role of the ERK pathway in
macrophage function.
NF-κB appears to be important in mediating IFN-γ
bioactivity. IFN-γ enhanced the phosphorylation of NF-κB without
any effect on ERK phosphorylation. In addition, BAY 11-7082 was an
effective inhibitor of the IFN-γ-induced enhancing action on
adhesion and TNF production. BAY 11-7082 has been widely used as an
anti-inflammatory agent in previous studies (17,18)
and our results support its inhibitory effects on IFN-γ-enhancing
action in adhesion and TNF production by macrophages.
In conclusion, we revealed a close correlation
between IFN-γ action and the NF-κB pathway with regards to
PMA-induced THP-1 cell adhesion and TNF production, which explains,
in part, the process by which IFN-γ accelerates the inflammatory
process.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the technical support we
received from the Research Support Center at Kyushu University’s
Graduate School of Medical Sciences. This study was in part
supported by grants from the Ministry of Health, Labour and
Welfare, and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science
and Technology, Japan.
References
|
1
|
Takeda K, Ichiki T, Narabayashi E, et al:
Inhibition of prolyl hydroxylase domain-containing protein
suppressed lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-α expression.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:2132–2137. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Allison AC, Ferluga H and Schorlemmer HU:
The role of macrophage activation in chronic inflammation. Agents
Actions. 8:27–35. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sorg C: Macrophages in acute and chronic
inflammation. Chest. 100:173S–175S. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Todd RF III, Alvarez PA, Brott DA and Liu
DY: Bacterial lipopolysaccharide, phorbol myristate acetate, and
muramyl dipeptide stimulate the expression of a human monocyte
surface antigen, Mo3e. J Immunol. 135:3869–3877. 1985.
|
|
5
|
Schroder K, Hertzog PJ, Ravasi T and Hume
DA: Interferon-γ: an overview of signals, mechanisms and functions.
J Leukoc Biol. 75:163–189. 2004.
|
|
6
|
Scheibenbogen C and Andreesen R:
Development regulation of the cytokine repertoire in human
macrophages: IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, and M-CSF. J Leukoc Biol. 50:35–42.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cassatella MA, Bazzoni F, Flynn RM, Dusi
S, Trinchieri G and Rossi F: Molecular basis of interferon-γ and
lipopolysaccharide enhancement of phagocyte respiratory burst
capability. Studies on the gene expression of several NADPH oxidase
components. J Biol Chem. 265:20241–20246. 1990.
|
|
8
|
Moller DR: Cells and cytokines involved in
the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis.
16:24–31. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sasaki M, Namioka Y, Ito T, et al: Role of
ICAM-1 in the aggregation and adhesion of human alveolar
macrophages in response to TNF-α and IFN-γ. Mediators Inflamm.
10:309–313. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chanput W, Mes J, Vreeburg RA, Savelkoul
HF and Wichers HJ: Trascription profiles of LPS-stimulated THP-1
monocytes and macrophages: a tool to study inflammation modulating
effects of food-derived compounds. Food Funct. 1:254–261. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kurihara Y, Nakahara T and Furue M:
αVβ3-integrin expression through ERK
activation mediates cell attachment and is necessary for production
of tumor necrosis factor alpha in monocytic THP-1 cells stimulated
by phorbol myristate acetate. Cell Immunol. 270:25–31. 2011.
|
|
12
|
Kimball ES, Kovacs E, Clark MC and
Schneider CR: Activation of cytokine production and adhesion
molecule on THP-1 myelomonocytic cells by macrophage
colony-stimulating factor in combination with interferon-γ. J
Leukoc Biol. 58:585–594. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hayes MP, Freeman SL and Donnelly RP:
IFN-γ priming of monocytes enhances LPS-induced TNF production by
augmenting both transcription and mRNA stability. Cytokine.
7:427–435. 1995.
|
|
14
|
Klinge U, Theuer S, Krott E and Fiebeler
A: Absence of circulating aldosterone attenuates foreign body
reaction around surgical sutures. Lagenbecks Arch Surg.
395:429–435. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Anderson JM, Rodriguez A and Chang DT:
Foreign body reaction to biomaterials. Semin Immunol. 20:86–100.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Khouw IM, van Wachem PB, van der Worp RJ,
van den Berg TK, de Leij LF and van Luyn MJ: Systemic anti-IFN-γ
treatment and role of macrophage subsets in the foreign body
reaction to dermal sheep collagen in rats. J Biomed Mater Res.
49:297–304. 2000.
|
|
17
|
Juliana C, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Wu J, et
al: Anti-inflammatory compounds parthenolide and Bay 11-7082 are
direct inhibitors of the inflammasome. J Biol Chem. 285:9792–9802.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu B, Liu Z, Wang P, Wu C and Xu H: A
nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor BAY11-7082 inhibits interaction
between human endothelial cells, T cells and monocytes. Transplant
Proc. 40:2724–2728. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|