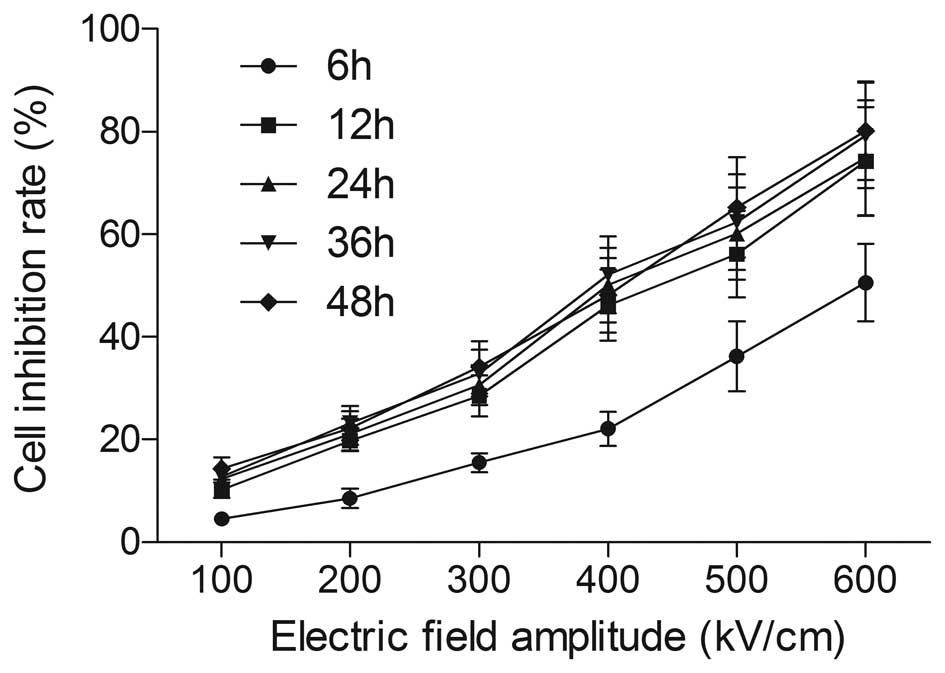
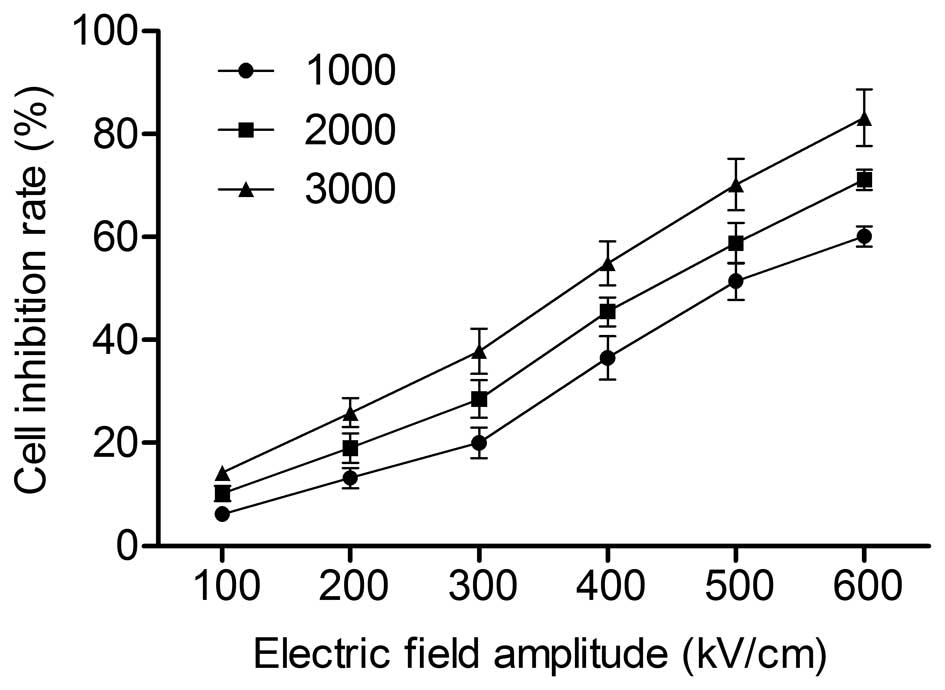
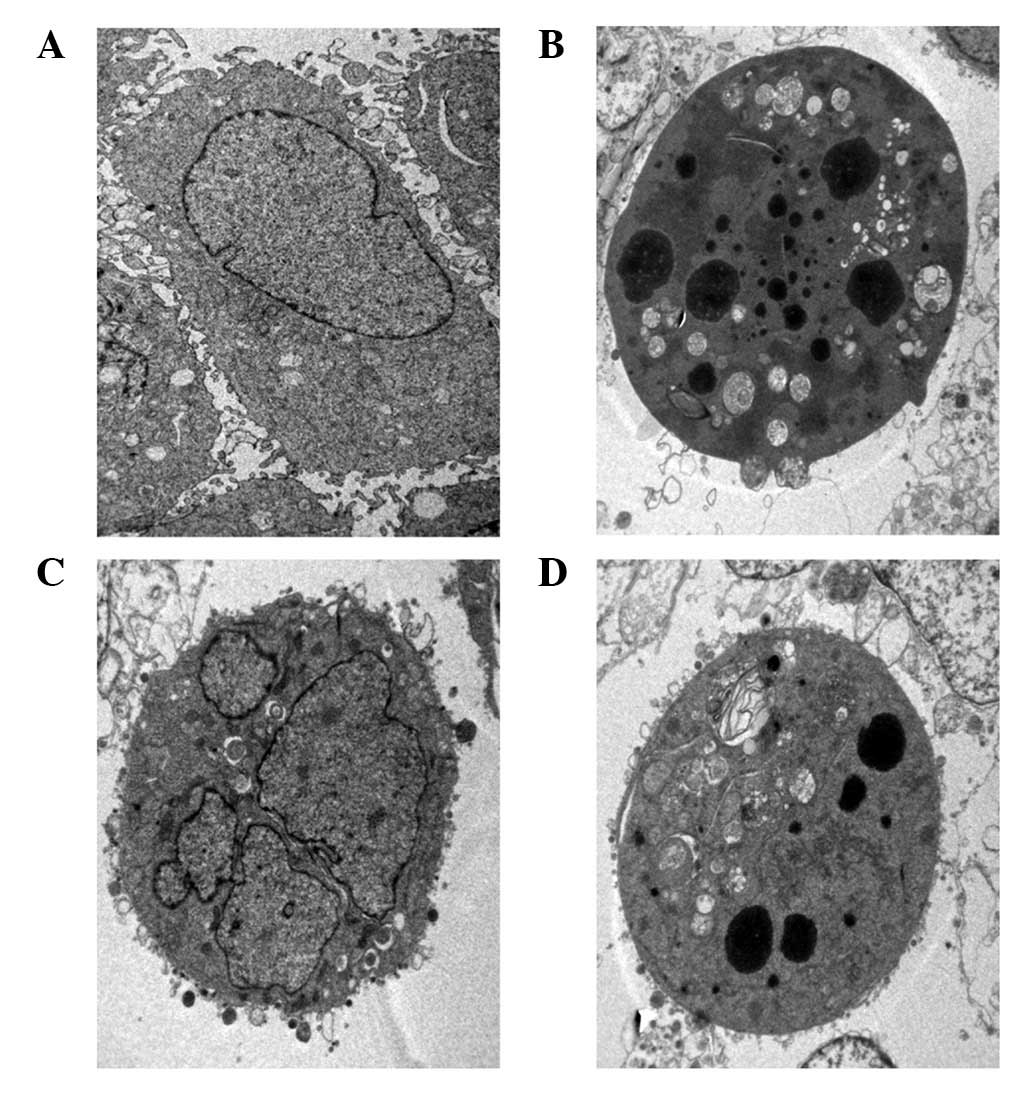
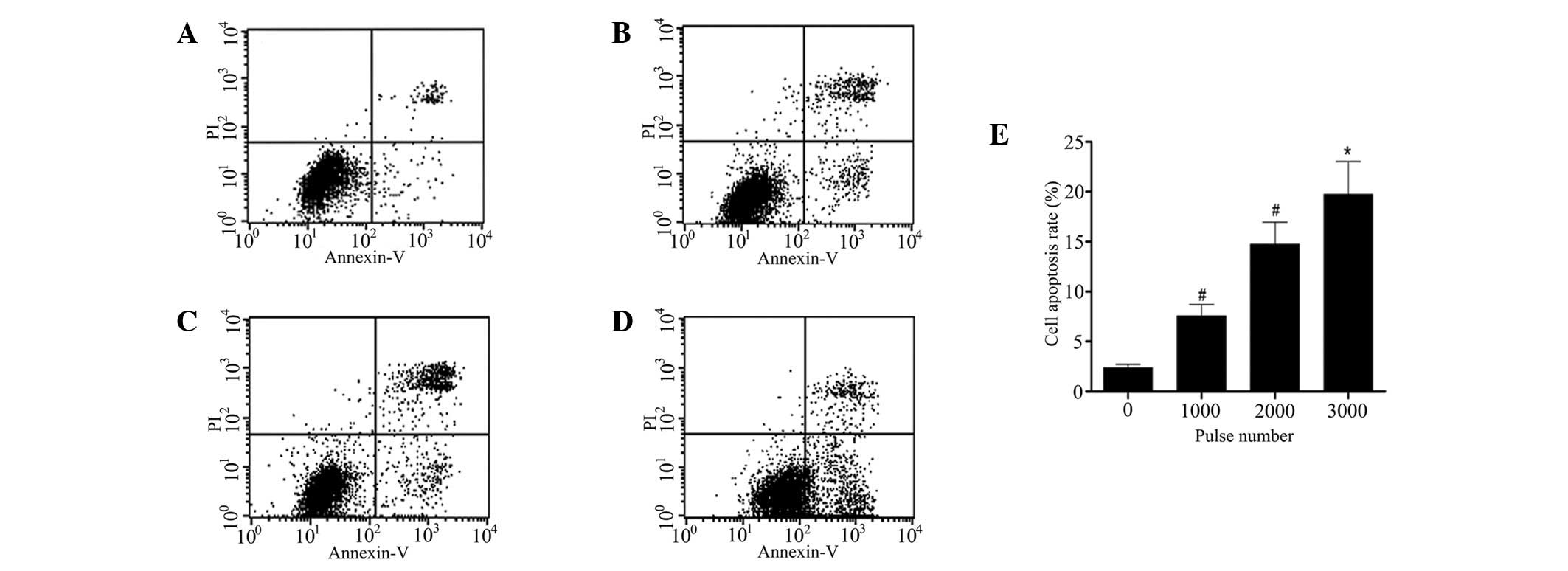
|
1
|
Bray F, Loos AH, McCarron P, et al: Trends
in cervical squamous cell carcinoma incidence in 13 European
countries: changing risk and the effects of screening. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 14:677–686. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pecorelli S, Pasinetti B, Angioli R,
Favalli G and Odicino F: Systemic therapy for gynecological
neoplasms: ovary, cervix, and endometrium. Cancer Chemother Biol
Response Modif. 22:515–544. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Green J, Kirwan J, Tierney J, et al:
Concomitant chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer of the
uterine cervix. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 3:CD0022252005.
|
|
4
|
Barnes FS and Greenebaum B: Biological and
medical aspects of electromagnetic fields. Handbook of Biological
Effects of Electromagnetic Fields. 3rd edition. CRC Press; Florida:
2006
|
|
5
|
Joshi RP and Schoenbach KH: Bioelectric
effects of intense ultrashort pulses. Crit Rev Biomed Eng.
38:255–304. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Weaver JC: Electroporation: a general
phenomenon for manipulating cells and tissues. J Cell Biochem.
51:426–435. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mir LM: Nucleic acids
electrotransfer-based gene therapy (electrogenetherapy): past,
current and future. Mol Biotechnol. 43:167–176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Okino M, Tomie H, Kanesada H, Marumoto M,
Esato K and Suzuki H: Optimal electric conditions in electrical
impulse chemotherapy. Jpn J Cancer Res. 83:1095–1101. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hofmann GA, Dev SB, Dimmer S and Nanda GS:
Electroporation therapy: a new approach for the treatment of head
and neck cancer. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 46:752–759. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dev SB, Rabussay DP, Widera G and Hofmann
GA: Medical applications of electroporation. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci.
28:206–223. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tien HT and Ottova A: The bilayer lipid
membrane (BLM) under electrical fields. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr
Insul. 10:717–727. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lee EW, Chen C, Prieto VE, Dry SM, Loh CT
and Kee ST: Advanced hepatic ablation technique for creating
complete cell death: irreversible electroporation. Radiology.
255:426–433. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou W, Xiong Z, Liu Y, Yao C and Li C:
Low voltage irreversible electroporation induced apoptosis in HeLa
cells. J Cancer Res Ther. 8:80–85. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stacey M, Stickley J, Fox P, Statler V,
Schoenbach K, Beebe SJ and Buescher S: Differential effects in
cells exposed to ultra-short, high intensity electric fields: cell
survival, DNA damage, and cell cycle analysis. Mutat Res.
542:65–75. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Katsuki S, Nomura N, Koga H, et al:
Biological effects of narrow band pulsed electric fields. IEEE
Trans Dielectr Electr Insul. 14:663–668. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chen N, Garner AL, Chen G, et al:
Nanosecond electric pulses penetrate the nucleus and enhance
speckle formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 364:220–225. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Craviso GL, Chatterjee P, Maalouf G, et
al: Nanosecond electric pulse-induced increase in intracellular
calcium in adrenal chromaffin cells triggers calcium-dependent
catecholamine release. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul.
16:1294–1301. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Baum CE, Stone AP and Tyo JS:
Ultra-Wideband, Short-Pulse Electromagnetics. 8. Springer Press;
New York: 2007
|
|
19
|
Bajracharya C, Shu X, Baum CE and
Schoenbach KH: Target detection with impulse radiating antenna.
IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag Lett. 10:496–499. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Long Z, Yao C, Li C, Mi Y and Sun C:
Focusing properties of picosecond electric pulses in non-invasive
cancer treatment. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi.
27:1128–1132. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
21
|
Evan GI and Vousden KH: Proliferation,
cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature. 411:342–348. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249. 2009.
|
|
23
|
Beebe SJ and Schoenbach KH: Nanosecond
pulsed electric fields: a new stimulus to activate intracellular
signaling. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2005:297–300. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schoenbach KH, Joshi RP, Kolb JF, et al:
Ultrashort electrical pulses open a new gateway into biological
cells. Proc IEEE. 92:1122–1137. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yao C, Mo D, Li C, Sun C and Mi Y: Study
of transmembrane potentials of inner and outer membranes induced by
pulsed-electric-field model and simulation. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci.
35:1541–1549. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yao C, Mi Y, Li C, et al: Study of
transmembrane potentials on cellular inner and outer membrane -
frequency response model and its filter characteristic simulation.
IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 55:1792–1799. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Camp JT, Shu X, Beebe SJ, Blackmore PF and
Schoenbach KH: Bioelectric studies with subnanosecond pulsed
electric fields. In: 2009 IEEE Pulsed Power Conference; June
28-July 2; pp. 876–879. 2009
|
|
28
|
Schoenbach KH, Shu X, Joshi RP, Camp JT,
Heeren T, Kolb JF and Beebe SJ: The effect of intense subnanosecond
electrical pulses on biological cells. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci.
36:414–422. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Schoenbach KH, Katsuki S, Akiyama H, et
al: Biological effects of intense subnanosecond electrical pulses.
In: Proceedings of the Power Modulator Symposium, 2006. Conference
Record of the 2006 Twenty-Seventh International; May 14–18; pp.
573–576. 2006
|
|
30
|
Hua YY, Wang XS, Zhang Y, Yao CG, Zhang XM
and Xiong ZA: Intense picosecond pulsed electric fields induce
apoptosis through a mitochondrial-mediated pathway in HeLa cells.
Mol Med Rep. 5:981–987. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|