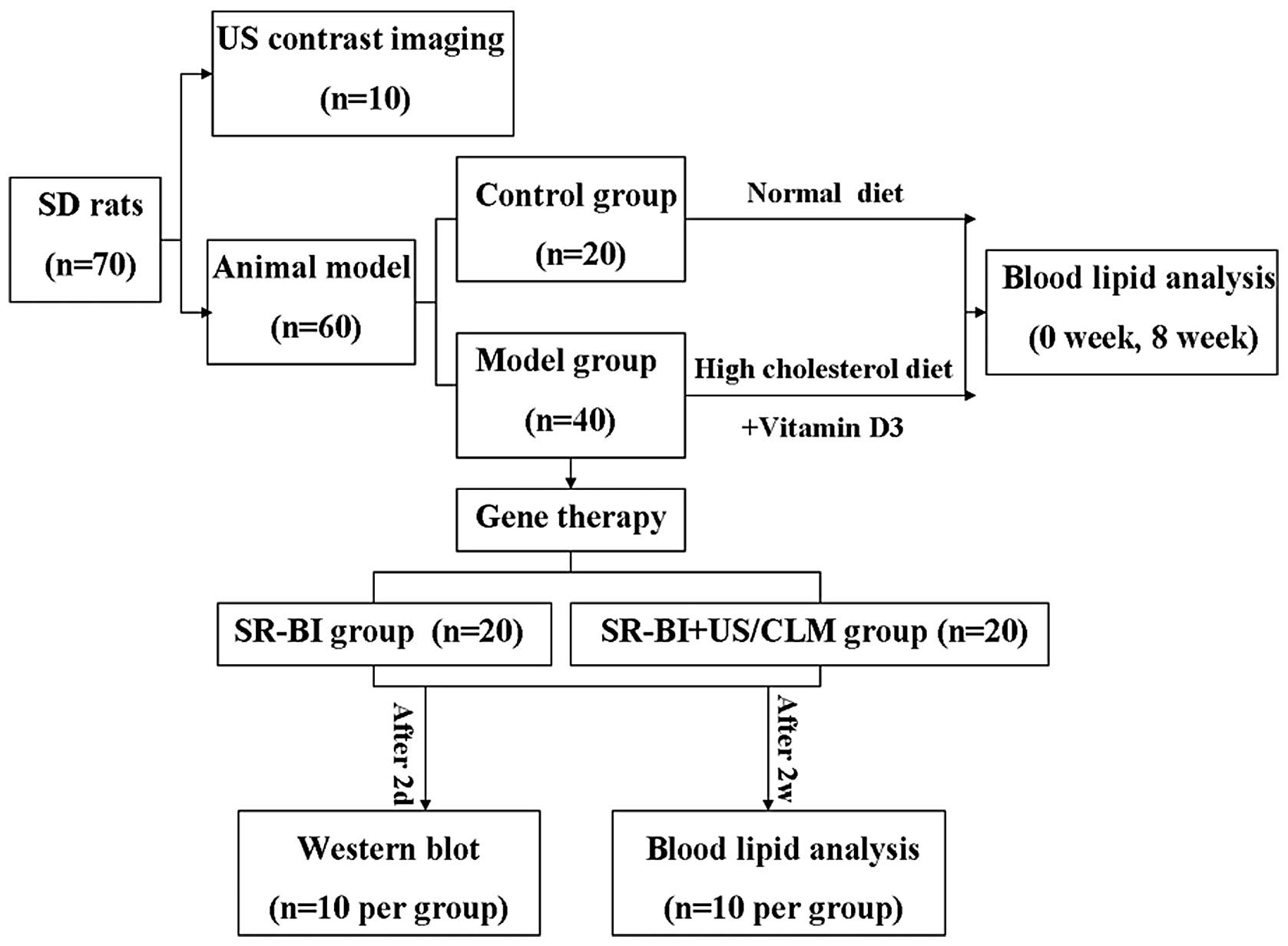
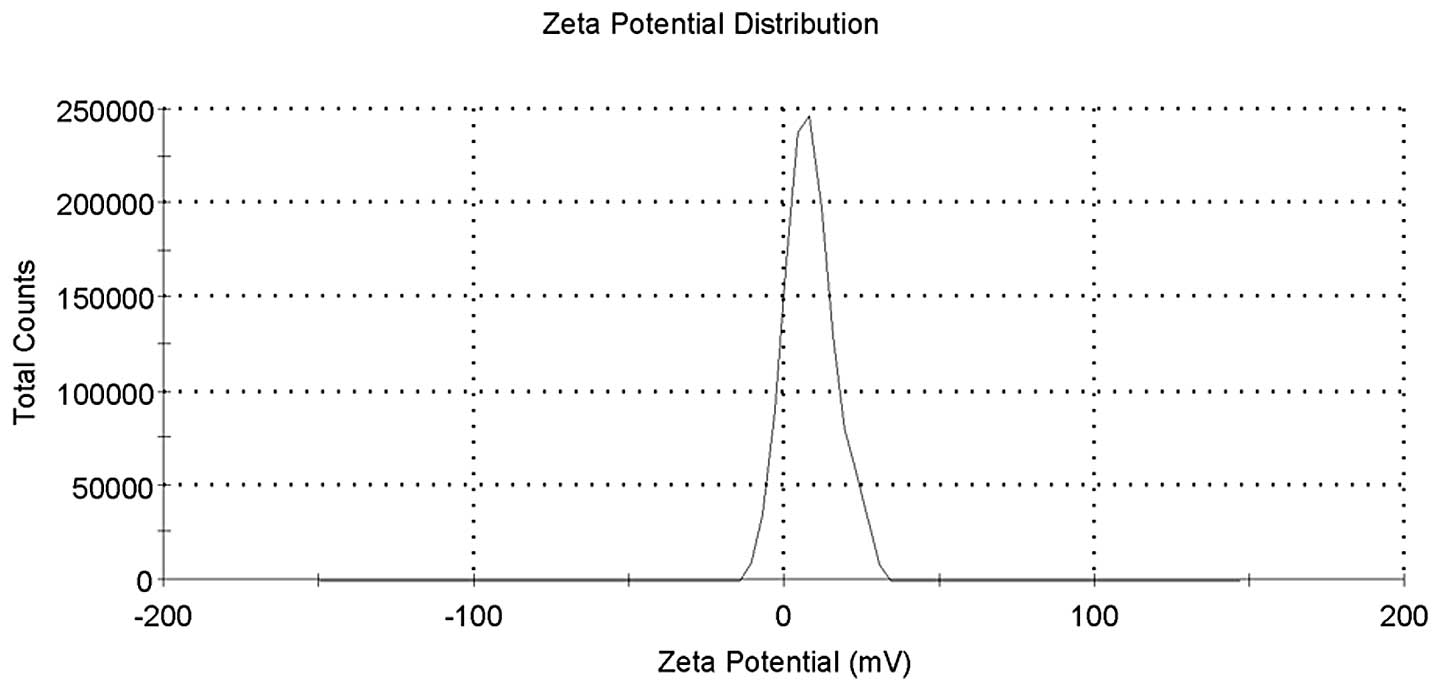
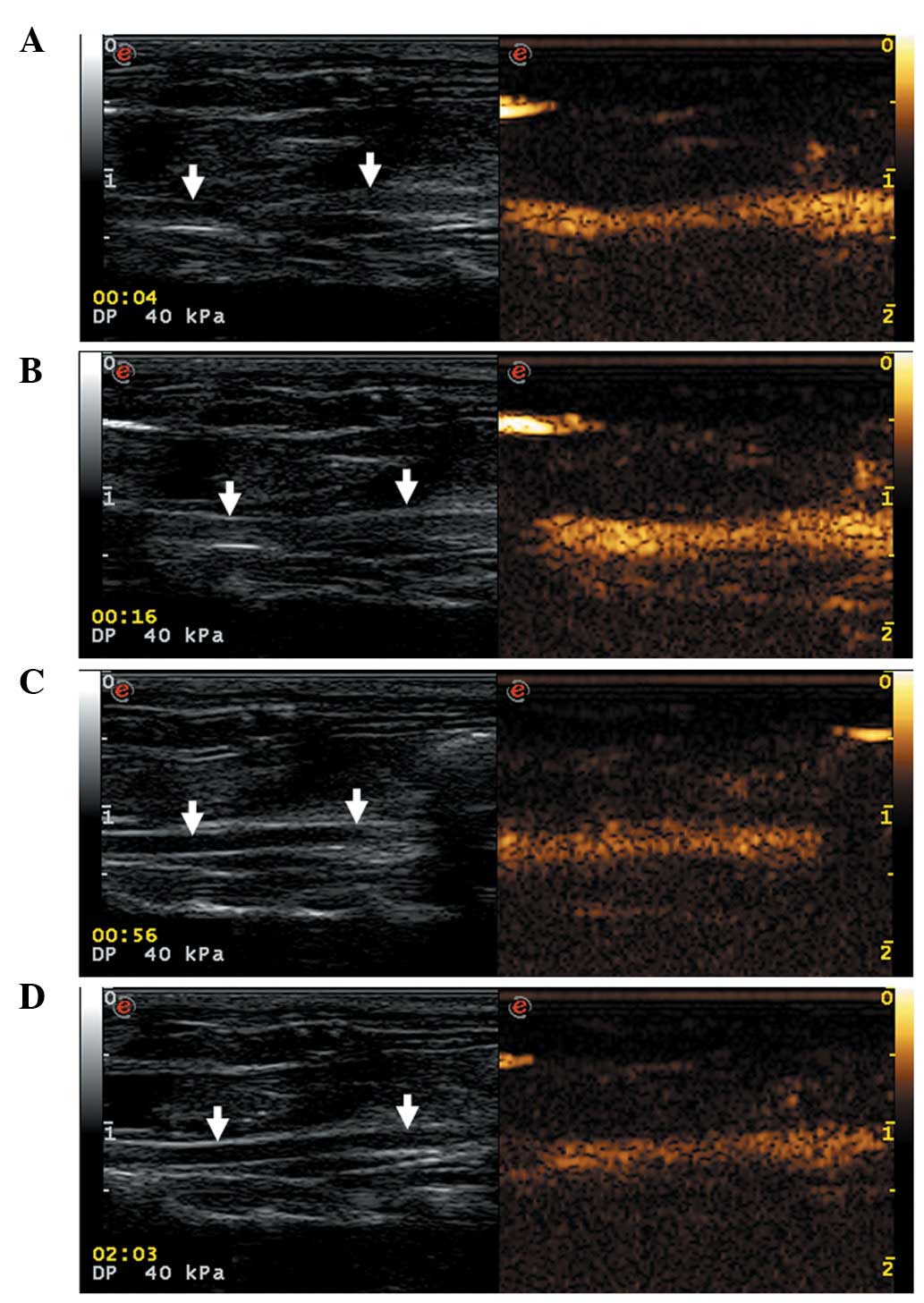
|
1
|
Suanarunsawat T, Devakul Na Ayutthaya W,
Songsak T, Thirawarapan S and Poungshompoo S: Antioxidant activity
and lipid-lowering effect of essential oils extracted from
Ocimum sanctum L. leaves in rats fed with a high cholesterol
diet. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 46:52–59. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parthasarathy S, Barnett J and Fong LG:
High-density lipoprotein inhibits the oxidative modification of
low-density lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1044:275–283. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fielding CJ and Fielding PE: Molecular
physiology of reverse cholesterol transport. J Lipid Res.
36:211–228. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Oram JF and Yokoyama S:
Apolipoprotein-mediated removal of cellular cholesterol and
phospholipids. J Lipid Res. 37:2473–2491. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Han J, Parsons M, Zhou X, Nicholson AC,
Gotto AM Jr and Hajjar DP: Functional interplay between the
macrophage scavenger receptor class B type I and pitavastatin
(NK-104). Circulation. 110:3472–3479. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hakkarainen T, Hemminki A, Curiel DT and
Wahlfors J: A conditionally replicative adenovirus that codes for a
TK-GFP fusion protein (Ad5Delta24TK-GFP) for evaluation of the
potency of oncolytic virotherapy combined with molecular
chemotherapy. Int J Mol Med. 18:751–759. 2006.
|
|
7
|
Iwamoto HS, Trapnell BC, McConnell CJ,
Daugherty C and Whitsett JA: Pulmonary inflammation associated with
repeated, prenatal exposure to an E1, E3-deleted adenoviral vector
in sheep. Gene Ther. 6:98–106. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Taniyama Y, Tachibana K, Hiraoka K, et al:
Development of safe and efficient novel nonviral gene transfer
using ultrasound: enhancement of transfection efficiency of naked
plasmid DNA in skeletal muscle. Gene Ther. 9:372–380. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Taniyama Y, Tachibana K, Hiraoka K, et al:
Local delivery of plasmid DNA into rat carotid artery using
ultrasound. Circulation. 105:1233–1239. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Christiansen JP, French BA, Klibanov AL,
Kaul S and Lindner JR: Targeted tissue transfection with ultrasound
destruction of plasmid-bearing cationic microbubbles. Ultrasound
Med Biol. 29:1759–1767. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang SL: Liposomes in ultrasonic drug and
gene delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 60:1167–1176. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Suzuki R, Takizawa T, Negishi Y, et al:
Gene delivery by combination of novel liposomal bubbles with
perfluoropropane and ultrasound. J Control Release. 117:130–136.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lindner JR: Microbubbles in medical
imaging: current applications and future directions. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 3:527–532. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li T, Tachibana K and Kuroki M and Kuroki
M: Gene transfer with echo-enhanced contrast agents: comparison
between Albunex, Optison and Levovist in mice - initial results.
Radiology. 229:423–428. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ilies MA, Seitz WA and Balaban AT:
Cationic lipids in gene delivery: principles, vector design and
therapeutical applications. Curr Pharm Des. 8:2441–2473. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hirko A, Tang F and Hughes JA: Cationic
lipid vectors for plasmid DNA delivery. Curr Med Chem.
10:1185–1193. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ritsch A, Tancevski I, Schgoer W, et al:
Molecular characterization of rabbit scavenger receptor class B
types I and II: portal to central vein gradient of expression in
the liver. J Lipid Res. 45:214–222. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang W: Lyophilization and development of
solid protein pharmaceuticals. Int J Pharm. 203:1–60. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Franks F: Freeze-drying of bioproducts:
putting principles into practice. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 45:221–229.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Molina MD, Armstrong TK, Zhang Y, Patel
MM, Lentz YK and Anchordoquy TJ: The stability of lyophilized
lipid/DNA complexes during prolonged storage. J Pharm Sci.
93:2259–2273. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
del Pozo-Rodríguez A, Solinís MA, Gascón
AR and Pedraz JL: Short- and long-term stability study of
lyophilized solid lipid nanoparticles for gene therapy. Eur J Pharm
Biopharm. 71:181–189. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kasper JC, Schaffert D, Ogris M, Wagner E
and Friess W: Development of a lyophilized plasmid/LPEI polyplex
formulation with long-term stability - A step closer from promising
technology to application. J Control Release. 151:246–255. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hsu JJ, Tintut Y and Demer LL: Vitamin D
and osteogenic differentiation in the artery wall. Clin J Am Soc
Nephrol. 3:1542–1547. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hung CR, Chen WH and Wang PS: Protective
effect of lysozyme chloride on gastric oxidative stress and
hemorrhagic ulcers in severe atherosclerotic rats. Med Sci Monit.
13:BR271–BR279. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu Y, Li J, Wang J, Si Q, Zhang J, Jiang Y
and Chu L: Anti-atherogenic effects of centipede acidic protein in
rats fed an atherogenic diet. J Ethnopharmacol. 122:509–516. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wan CW, Wong CN, Pin WK, et al:
Chlorogenic acid exhibits cholesterol lowering and fatty liver
attenuating properties by up-regulating the gene expression of
PPAR-α in hypercholesterolemic rats induced with a high-cholesterol
diet. Phytother Res. 2012:Jun 6–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
27
|
Hong SC, Zhao SP and Wu ZH: Effect of
probucol on HDL metabolism and class B type I scavenger receptor
(SR-BI) expression in the liver of hypercholesterolemic rabbits.
Int J Cardiol. 115:29–35. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Acton S, Rigotti A, Landschulz KT, Xu S,
Hobbs HH and Krieger M: Identification of scavenger receptor SR-BI
as a high density lipoprotein receptor. Science. 271:518–520. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hirano K, Yamashita S, Nakagawa Y, et al:
Expression of human scavenger receptor class B type I in cultured
human monocyte-derived macrophages and atherosclerotic lesions.
Circ Res. 85:108–116. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Trigatti BL, Krieger M and Rigotti A:
Influence of the HDL receptor SR-BI on lipoprotein metabolism and
atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:1732–1738. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chinetti G, Gbaguidi FG, Griglio S, et al:
CLA-1/SR-BI is expressed in atherosclerotic lesion macrophages and
regulated by activators of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptors. Circulation. 101:2411–2417. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|