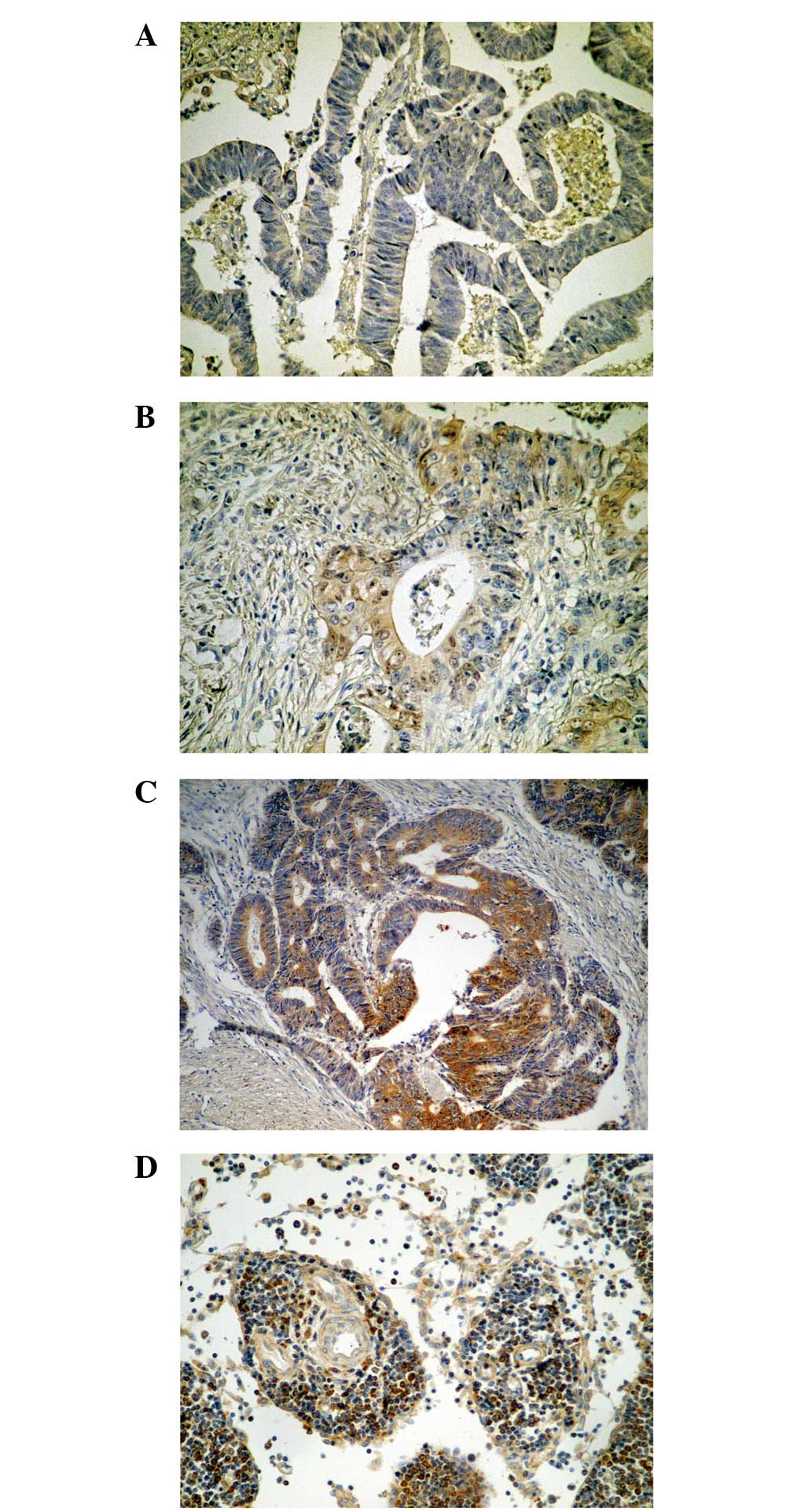
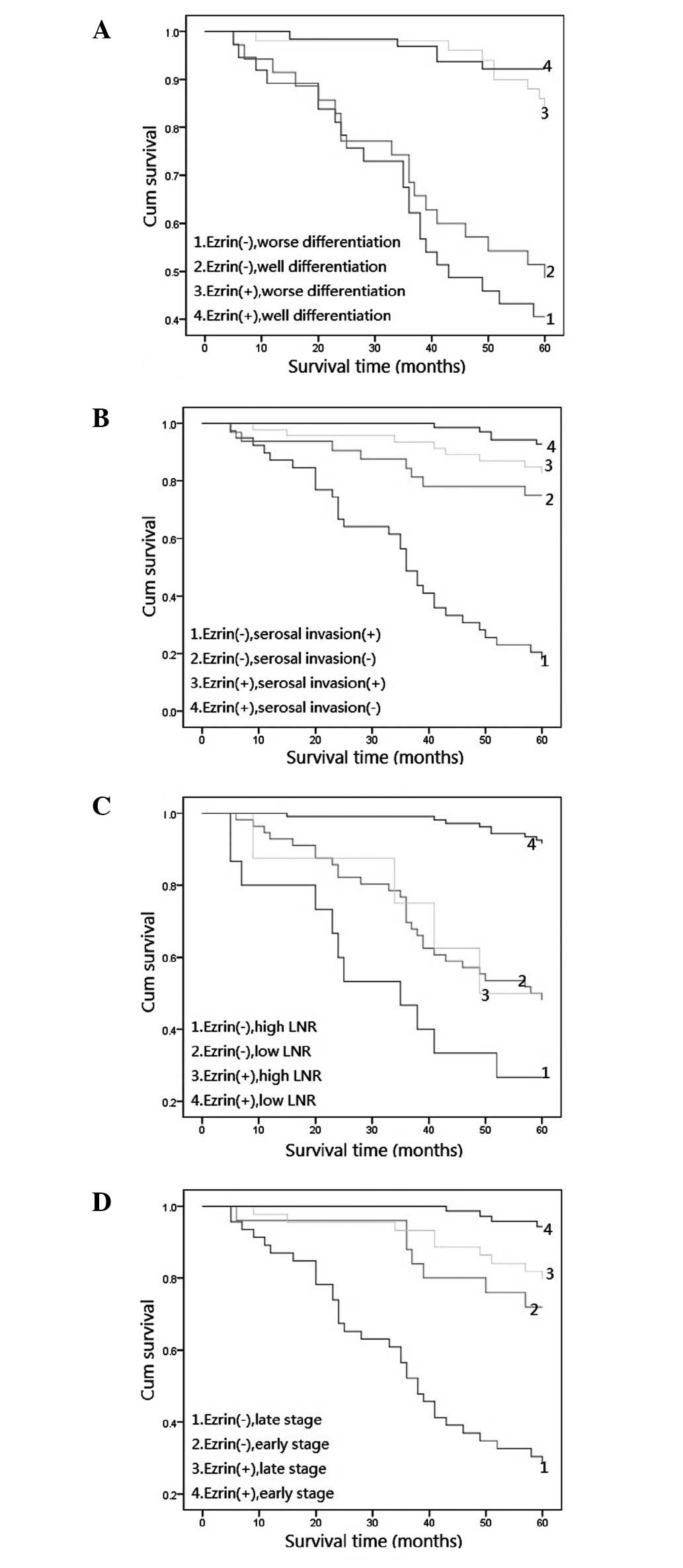
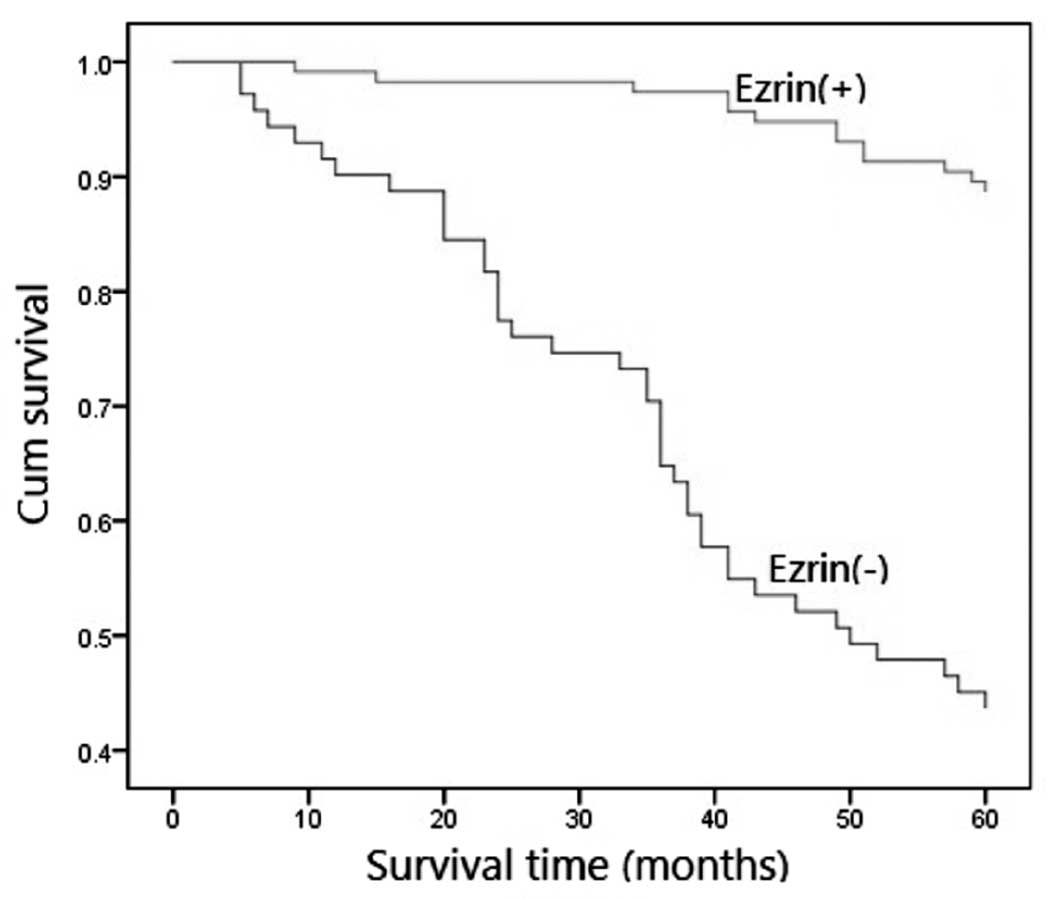
|
1
|
Zlobec I and Lugli A: Prognostic and
predictive factors in colorectal cancer. J Clin Pathol. 61:561–569.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Berman BP, Weisenberger DJ, Aman JF, et
al: Regions of focal DNA hypermethylation and long-range
hypomethylation in colorectal cancer coincide with nuclear
lamina-associated domains. Nat Genet. 44:40–46. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carlisle J, Swart M, Dawe EJ and Chadwick
M: Factors associated with survival after resection of colorectal
adenocarcinoma in 314 patients. Br J Anaesth. 108:430–435. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li D, Yan D, Tang H, Zhou C, et al: IMP3
is a novel prognostic marker that correlates with colon cancer
progression and pathogenesis. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:3499–3506. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fehon RG, McClatchey AI and Bretscher A:
Organizing the cell cortex: the role of ERM proteins. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 11:276–287. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Neisch AL and Fehon RG: Ezrin, radixin and
moesin: key regulators of membrane-cortex interactions and
signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 23:377–382. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xie JJ, Xu LY, Wu ZY, et al: Prognostic
implication of ezrin expression in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 104:538–543. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Korkeila EA, Sundström J, Pyrhönen S and
Syrjänen K: Carbonic anhydrase IX, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α,
ezrin and glucose transporter-1 as predictors of disease outcome in
rectal cancer: multivariate Cox survival models following data
reduction by principal component analysis of the
clinicopathological predictors. Anticancer Res. 31:4529–4535.
2011.
|
|
9
|
Zhang XQ, Chen GP, Wu T, Yan JP and Zhou
JY: Expression and clinical significance of ezrin in non-small-cell
lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 13:196–204. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schlecht NF, Brandwein-Gensler M, Smith
RV, et al: Cytoplasmic ezrin and moesin correlate with poor
survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck
Pathol. 6:232–243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
O’Connell JB, Maggard MA and Ko CY: Colon
cancer survival rates with the new American Joint Committee on
Cancer sixth edition staging. J Natl Cancer Inst. 96:1420–1425.
2004.
|
|
12
|
Wu Q, Li Z, Lin H, et al: DEK
overexpression in uterine cervical cancers. Pathol Int. 58:378–382.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takeuchi K, Kawashima A, Nagafuchi A and
Tsukita S: Structural diversity of band 4.1 superfamily members. J
Cell Sci. 107:1921–1928. 1994.
|
|
14
|
Yonemura S, Hirao M, Doi Y, et al:
Ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM) proteins bind to a positively charged
amino acid cluster in the juxta-membrane cytoplasmic domain of
CD44, CD43, and ICAM-2. J Cell Biol. 140:885–895. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Heiska L, Alfthan K, Grönholm M, et al:
Association of ezrin with intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and -2
(ICAM-1 and ICAM-2). Regulation by phosphatidylinositol 4,
5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 273:21893–21900. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gautreau A, Poullet P, Louvard D and Arpin
M: Ezrin, a plasma membrane-microfilament linker, signals cell
survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:7300–7305. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou B, Leng J, Hu M, et al: Ezrin is a
key molecule in the metastasis of MOLT4 cells induced by
CCL25/CCR9. Leuk Res. 34:769–776. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu Y, Khan J, Khanna C, et al: Expression
profiling identifies the cytoskeletal organizer ezrin and the
developmental homeoprotein Six-1 as key metastatic regulators. Nat
Med. 2:175–181. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Khanna C, Wan X, Bose S, et al: The
membrane-cytoskeleton linker ezrin is necessary for osteosarcoma
metastasis. Nat Med. 10:182–186. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Karmakar S and Das C: Modulation of ezrin
and E-cadherin expression by IL-1beta and TGF-beta1 in human
trophoblasts. J Reprod Immunol. 64:9–29. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hiscox S and Jiang WG: Ezrin regulates
cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion, a possible role with
E-cadherin/beta-catenin. J Cell Sci. 112:3081–3090. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gao P, Song YX, Wang ZN, et al: Integrated
ratio of metastatic to examined lymph nodes and number of
metastatic lymph nodes into the AJCC staging system for colon
cancer. PLoS One. 7:e350212012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Telian SH and Bilchik AJ: Significance of
the lymph node ratio in stage III colon cancer. Ann Surg Oncol.
15:1557–1578. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang J, Kulaylat M, Rockette H, et al:
Should total number of lymph nodes be used as a quality of care
measure for stage III colon cancer? Ann Surg. 249:559–563. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|