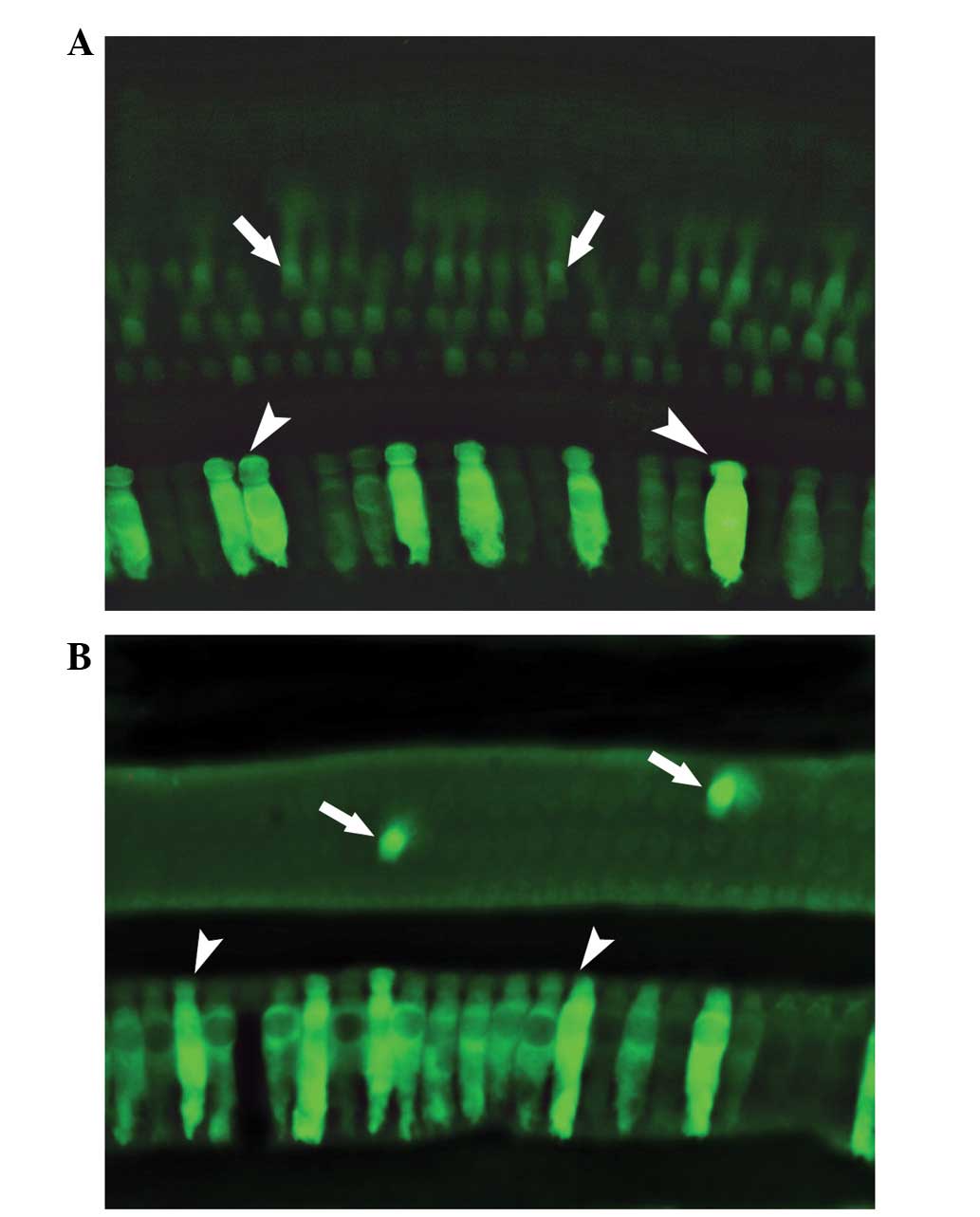
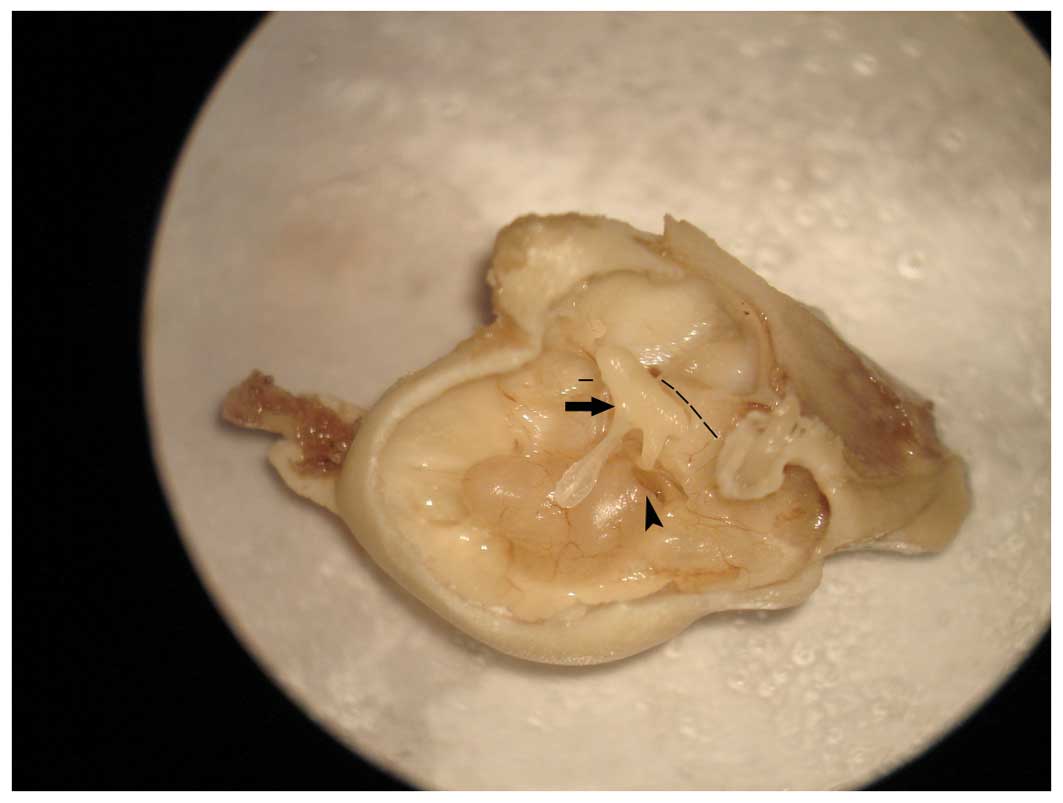
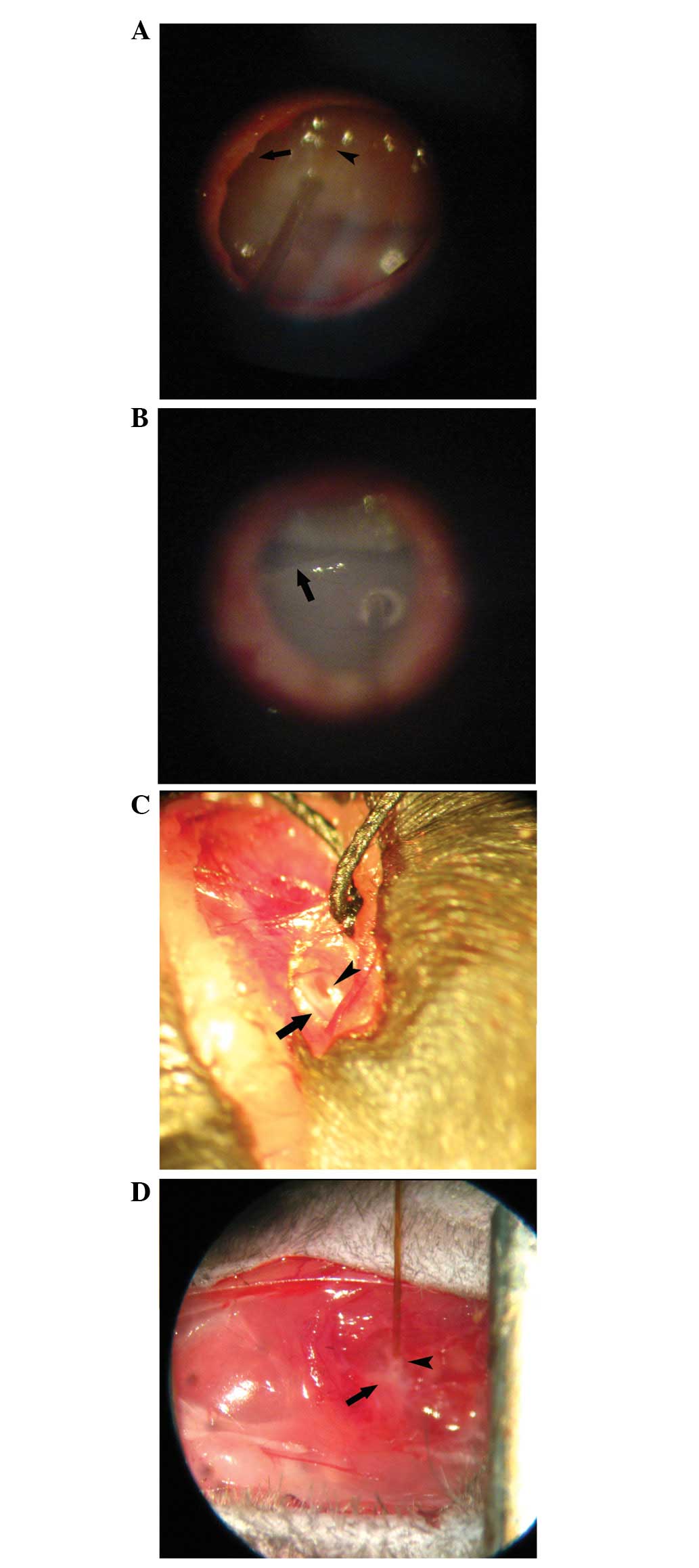
|
1
|
Henry KR, Chole RA, McGinn MD and Frush
DP: Increased ototoxicity in both young and old mice. Arch
Otolaryngol. 107:92–95. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ishiyama G, Ishiyama A, Kerber K and Baloh
RW: Gentamicin ototoxicity: clinical features and the effect on the
human vestibulo-ocular reflex. Acta Otolaryngol. 126:1057–1061.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eshraghi AA, Frachet B, Van De Water TR
and Eter E: Hearing loss in adults. Rev Prat. 59:645–652. 2009.(In
French).
|
|
4
|
Fetoni AR, Mancuso C, Eramo SL, et al: In
vivo protective effect of ferulic acid against noise-induced
hearing loss in the guinea pig. Neuroscience. 169:1575–1588. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Campbell KC, Meech RP, Klemens JJ, et al:
Prevention of noise- and drug-induced hearing loss with
D-methionine. Hear Res. 226:92–103. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee CK, Shin JI and Cho YS: Protective
effect of minocycline against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Clin
Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 4:77–82. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Maniu A, Perde-Schrepler M and Cosgarea M:
Protective effect of L-N-acetylcysteine against gentamycin
ototoxicity in the organ cultures of the rat cochlea. Rom J Morphol
Embryol. 52:159–164. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Agrup C, Gleeson M and Rudge P: The inner
ear and the neurologist. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 78:114–122.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Swan EE, Mescher MJ, Sewell WF, Tao SL and
Borenstein JT: Inner ear drug delivery for auditory applications.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 60:1583–1599. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Staecker H, Gabaizadeh R, Federoff H and
Van De Water TR: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene therapy
prevents spiral ganglion degeneration after hair cell loss.
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 119:7–13. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Suzuki M, Yamasoba T, Suzukawa K and Kaga
K: Adenoviral vector gene delivery via the round window membrane in
guinea pigs. Neuroreport. 14:1951–1955. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Duan M, Venail F, Spencer N and Mezzina M:
Treatment of peripheral sensorineural hearing loss: gene therapy.
Gene Ther. 11(Suppl 1): S51–S56. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Praetorius M, Pfannenstiel S, Klingmann C,
Baumann I, Plinkert PK and Staecker H: Expression patterns of
non-viral transfection with GFP in the organ of Corti in vitro and
in vivo. Gene therapy of the inner ear with non-viral vectors. HNO.
56:524–529. 2008.(In German).
|
|
14
|
Cooper LB, Chan DK, Roediger FC, et al:
AAV-mediated delivery of the caspase inhibitor XIAP protects
against cisplatin ototoxicity. Otol Neurotol. 27:484–490. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang M, Zhang YQ, He GX and Sun H:
Protective effect of NT-3 gene mediated by hydroxyapatite
nanoparticle on the cochlea of guinea pigs injured by
excitotoxicity. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 32:563–567.
2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Kawamoto K, Ishimoto S, Minoda R, Brough
DE and Raphael Y: Math1 gene transfer generates new cochlear hair
cells in mature guinea pigs in vivo. J Neurosci. 23:4395–4400.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ylikoski J, Pirvola U, Virkkala J, et al:
Guinea pig auditory neurons are protected by glial cell
line-derived growth factor from degeneration after noise trauma.
Hear Res. 124:17–26. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ghilardi JR, Freeman KT, Jimenez-Andrade
JM, et al: Sustained blockade of neurotrophin receptors TrkA, TrkB
and TrkC reduces non-malignant skeletal pain but not the
maintenance of sensory and sympathetic nerve fibers. Bone.
48:389–398. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Michael AE, Collins TD, Norgate DP,
Gregory L, Wood PJ and Cooke BA: Relationship between ovarian
cortisol:cortisone ratios and the clinical outcome of in vitro
fertilization and embryo transfer (IVF-ET). Clin Endocrinol (Oxf).
51:535–540. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Carnicero E, Garrido JJ, Alonso MT and
Schimmang T: Roles of fibroblast growth factor 2 during innervation
of the avian inner ear. J Neurochem. 77:786–795. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Frolenkov GI, Belyantseva IA, Kurc M,
Mastroianni MA and Kachar B: Cochlear outer hair cell
electromotility can provide force for both low and high intensity
distortion product otoacoustic emissions. Hear Res. 126:67–74.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liberman MC, Zuo J and Guinan JJ Jr:
Otoacoustic emissions without somatic motility: can stereocilia
mechanics drive the mammalian cochlea? J Acoust Soc Am.
116:1649–1655. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ye HB, Shi HB, Wang J, et al: Bilirubin
induces auditory neuropathy in neonatal guinea pigs via auditory
nerve fiber damage. J Neurosci Res. 90:2201–2213. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
El-Badry MM and McFadden SL:
Electrophysiological correlates of progressive sensorineural
pathology in carboplatin-treated chinchillas. Brain Res.
1134:122–130. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xia L, Yin S and Wang J: Inner ear gene
transfection in neonatal mice using adeno-associated viral vector:
a comparison of two approaches. PLoS One. 7:e432182012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Landry TG, Wise AK, Fallon JB and Shepherd
RK: Spiral ganglion neuron survival and function in the deafened
cochlea following chronic neurotrophic treatment. Hear Res.
282:303–313. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Walton JP, Barsz K and Wilson WW:
Sensorineural hearing loss and neural correlates of temporal acuity
in the inferior colliculus of the C57BL/6 mouse. J Assoc Res
Otolaryngol. 9:90–101. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang H, Yin S, Yu Z, Huang Y and Wang J:
Dynamic changes in hair cell stereocilia and cochlear transduction
after noise exposure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 409:616–621.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang SM, Doi T, Asako M, Matsumoto A and
Yamashita T: Optical recording of membrane potential in dissociated
mouse vestibular ganglion cells using a voltage-sensitive dye.
Auris Nasus Larynx. 27:15–21. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Poirrier AL, Van den Ackerveken P, Kim TS,
et al: Ototoxic drugs: difference in sensitivity between mice and
guinea pigs. Toxicol Lett. 193:41–49. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ishimoto S, Kawamoto K, Stöver T, Kanzaki
S, Yamasoba T and Raphael Y: A glucocorticoid reduces adverse
effects of adenovirus vectors in the cochlea. Audiol Neurootol.
8:70–79. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang H, Murphy R, Taaffe D, et al:
Efficient cochlear gene transfection in guinea-pigs with
adeno-associated viral vectors by partial digestion of round window
membrane. Gene Ther. 19:255–263. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Maeda Y, Fukushima K, Kawasaki A,
Nishizaki K and Smith RJ: Cochlear expression of a
dominant-negative GJB2R75W construct delivered through the round
window membrane in mice. Neurosci Res. 58:250–254. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sun H, Jiang M and Zhu SH: In vitro and in
vivo studies on hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as a novel vector for
inner ear gene therapy. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za
Zhi. 43:51–57. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
35
|
Lalwani AK and Mhatre AN: Cochlear gene
therapy. Ear Hear. 24:342–348. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Thomas CE, Ehrhardt A and Kay MA: Progress
and problems with the use of viral vectors for gene therapy. Nat
Rev Genet. 4:346–358. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dimitrov EA and Duckert LG: Morphologic
changes in the guinea pig cochlea following cochleostomy - a
preliminary scanning electron microscope study. Otolaryngol Head
Neck Surg. 93:408–413. 1985.
|
|
38
|
Iizuka T, Kanzaki S, Mochizuki H, et al:
Noninvasive in vivo delivery of transgene via adeno-associated
virus into supporting cells of the neonatal mouse cochlea. Hum Gene
Ther. 19:384–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kesser BW and Lalwani AK: Gene therapy and
stem cell transplantation: strategies for hearing restoration. Adv
Otorhinolaryngol. 66:64–86. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Newton VE: Aetiology of bilateral
sensori-neural hearing loss in young children. J Laryngol Otol
Suppl. 10:1–57. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qu C, Gardner P and Schrijver I: The role
of the cytoskeleton in the formation of gap junctions by Connexin
30. Exp Cell Res. 315:1683–1692. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Holt JR: Viral-mediated gene transfer to
study the molecular physiology of the Mammalian inner ear. Audiol
Neurootol. 7:157–160. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yagi M, Magal E, Sheng Z, Ang KA and
Raphael Y: Hair cell protection from aminoglycoside ototoxicity by
adenovirus-mediated overexpression of glial cell line-derived
neurotrophic factor. Hum Gene Ther. 10:813–823. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cheng G, Liu L, Wang P, et al: An in vivo
transfection approach elucidates a role for Aedes aegypti
thioester-containing proteins in flaviviral infection. PLoS One.
6:e227862011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pfannenstiel SC, Praetorius M, Plinkert
PK, Brough DE and Staecker H: Bcl-2 gene therapy prevents
aminoglycoside-induced degeneration of auditory and vestibular hair
cells. Audiol Neurootol. 14:254–266. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shou J, Zheng JL and Gao WQ: Robust
generation of new hair cells in the mature mammalian inner ear by
adenoviral expression of Hath1. Mol Cell Neurosci. 23:169–179.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Jero J, Mhatre AN, Tseng CJ, et al:
Cochlear gene delivery through an intact round window membrane in
mouse. Hum Gene Ther. 12:539–548. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Derby ML, Sena-Esteves M, Breakefield XO
and Corey DP: Gene transfer into the mammalian inner ear using
HSV-1 and vaccinia virus vectors. Hear Res. 134:1–8. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lei L and Han D: Efficient transduction of
spiral ganglion cells using adenovirus type 5 vector in the rat.
Acta Otolaryngol. 130:810–814. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Duan ML, Ulfendahl M, Laurell G, et al:
Protection and treatment of sensorineural hearing disorders caused
by exogenous factors: experimental findings and potential clinical
application. Hear Res. 169:169–178. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Luebke AE, Foster PK, Muller CD and Peel
AL: Cochlear function and transgene expression in the guinea pig
cochlea, using adenovirus- and adeno-associated virus-directed gene
transfer. Hum Gene Ther. 12:773–781. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Luebke AE, Steiger JD, Hodges BL and
Amalfitano A: A modified adenovirus can transfect cochlear hair
cells in vivo without compromising cochlear function. Gene Ther.
8:789–794. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Holt JR, Johns DC, Wang S, et al:
Functional expression of exogenous proteins in mammalian sensory
hair cells infected with adenoviral vectors. J Neurophysiol.
81:1881–1888. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ishimoto S, Kawamoto K, Stover T, Kanzaki
S, Yamasoba T and Raphael Y: A glucocorticoid reduces adverse
effects of adenovirus vectors in the cochlea. Audiol Neurootol.
8:70–79. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Li Duan M, Bordet T, Mezzina M, Kahn A and
Ulfendahl M: Adenoviral and adeno-associated viral vector mediated
gene transfer in the guinea pig cochlea. Neuroreport. 13:1295–1299.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lalwani A, Walsh B, Reilly P, et al:
Long-term in vivo cochlear transgene expression mediated by
recombinant adeno-associated virus. Gene Ther. 5:277–281. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Stone IM, Lurie DI, Kelley MW and Poulsen
DJ: Adeno-associated virus-mediated gene transfer to hair cells and
support cells of the murine cochlea. Mol Ther. 11:843–848. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lalwani AK, Walsh BJ, Reilly PG, Muzyczka
N and Mhatre AN: Development of in vivo gene therapy for hearing
disorders: introduction of adeno-associated virus into the cochlea
of the guinea pig. Gene Ther. 3:588–592. 1996.
|
|
59
|
Lalwani AK, Walsh BJ, Carvalho GJ,
Muzyczka N and Mhatre AN: Expression of adeno-associated virus
integrated transgene within the mammalian vestibular organs. Am J
Otol. 19:390–395. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kilpatrick LA, Li Q, Yang J, Goddard JC,
Fekete DM and Lang H: Adeno-associated virus-mediated gene delivery
into the scala media of the normal and deafened adult mouse ear.
Gene Ther. 18:569–578. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu Y, Okada T, Sheykholeslami K, et al:
Specific and efficient transduction of Cochlear inner hair cells
with recombinant adeno-associated virus type 3 vector. Mol Ther.
12:725–733. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Walters RW, Yi SM, Keshavjee S, et al:
Binding of adeno-associated virus type 5 to 2,3-linked sialic acid
is required for gene transfer. J Biol Chem. 276:20610–20616. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Xiao W, Chirmule N, Berta SC, McCullough
B, Gao G and Wilson JM: Gene therapy vectors based on
adeno-associated virus type 1. J Virol. 73:3994–4003.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhong L, Li B, Jayandharan G, et al:
Tyrosine-phosphorylation of AAV2 vectors and its consequences on
viral intracellular trafficking and transgene expression. Virology.
381:194–202. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chen X, Frisina RD, Bowers WJ, Frisina DR
and Federoff HJ: HSV amplicon-mediated neurotrophin-3 expression
protects murine spiral ganglion neurons from cisplatin-induced
damage. Mol Ther. 3:958–963. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Keithley EM, Woolf NK and Harris JP:
Development of morphological and physiological changes in the
cochlea induced by cytomegalovirus. Laryngoscope. 99:409–414. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Stearns GS, Keithley EM and Harris JP:
Development of high endothelial venule-like characteristics in the
spiral modiolar vein induced by viral labyrinthitis. Laryngoscope.
103:890–898. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ailles LE and Naldini L: HIV-1-derived
lentiviral vectors. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 261:31–52.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Blomer U, Naldini L, Kafri T, Trono D,
Verma IM and Gage FH: Highly efficient and sustained gene transfer
in adult neurons with a lentivirus vector. J Virol. 71:6641–6649.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Han JJ, Mhatre AN, Wareing M, et al:
Transgene expression in the guinea pig cochlea mediated by a
lentivirus-derived gene transfer vector. Hum Gene Ther.
10:1867–1873. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Felgner PL, Gadek TR, Holm M, et al:
Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection
procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 84:7413–7417. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wareing M, Mhatre AN, Pettis R, et al:
Cationic liposome mediated transgene expression in the guinea pig
cochlea. Hear Res. 128:61–69. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Jero J, Tseng CJ, Mhatre AN and Lalwani
AK: A surgical approach appropriate for targeted cochlear gene
therapy in the mouse. Hear Res. 151:106–114. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Beavis AD: On the inhibition of the
mitochondrial inner membrane anion uniporter by cationic
amphiphiles and other drugs. J Biol Chem. 264:1508–1515.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Bottega R and Epand RM: Inhibition of
protein kinase C by cationic amphiphiles. Biochemistry.
31:9025–9030. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Datiles MJ, Johnson EA and McCarty RE:
Inhibition of the ATPase activity of the catalytic portion of ATP
synthases by cationic amphiphiles. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1777:362–368. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Tamura T, Kita T, Nakagawa T, et al: Drug
delivery to the cochlea using PLGA nanoparticles. Laryngoscope.
115:2000–2005. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Shimamura M, Morishita R, Endoh M, et al:
HVJ-envelope vector for gene transfer into central nervous system.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 300:464–471. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Oshima K, Shimamura M, Mizuno S, et al:
Intrathecal injection of HVJ-E containing HGF gene to cerebrospinal
fluid can prevent and ameliorate hearing impairment in rats. FASEB
J. 18:212–214. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Ishimoto S, Kawamoto K, Kanzaki S and
Raphael Y: Gene transfer into supporting cells of the organ of
Corti. Hear Res. 173:187–197. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Yamasoba T, Yagi M, Roessler BJ, Miller JM
and Raphael Y: Inner ear transgene expression after adenoviral
vector inoculation in the endolymphatic sac. Hum Gene Ther.
10:769–774. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Shibata SB, Di Pasquale G, Cortez SR,
Chiorini JA and Raphael Y: Gene transfer using bovine
adeno-associated virus in the guinea pig cochlea. Gene Ther.
16:990–997. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Stover T, Yagi M and Raphael Y: Cochlear
gene transfer: round window versus cochleostomy inoculation. Hear
Res. 136:124–130. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Konishi M, Kawamoto K, Izumikawa M,
Kuriyama H and Yamashita T: Gene transfer into guinea pig cochlea
using adeno-associated virus vectors. J Gene Med. 10:610–618. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Nomura Y, Hara M and Kurata T:
Experimental herpes simplex virus and cytomegalovirus
labyrinthitis. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 457:57–66. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Weiss MA, Frisancho JC, Roessler BJ and
Raphael Y: Viral-mediated gene transfer in the cochlea. Int J Dev
Neurosci. 15:577–583. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Nadol JB Jr: Intercellular junctions in
the organ of Corti. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 87:70–80. 1978.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Kimura RS: The ultrastructure of the organ
of Corti. Int Rev Cytol. 42:173–222. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Fritzsch B, Farinas I and Reichardt LF:
Lack of neurotrophin 3 causes losses of both classes of spiral
ganglion neurons in the cochlea in a region-specific fashion. J
Neurosci. 17:6213–6225. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Griffith AJ, Ji W, Prince ME, Altschuler
RA and Meisler MH: Optic, olfactory, and vestibular
dysmorphogenesis in the homozygous mouse insertional mutant Tg9257.
J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol. 19:157–163. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Kawamoto K, Oh SH, Kanzaki S, Brown N and
Raphael Y: The functional and structural outcome of inner ear gene
transfer via the vestibular and cochlear fluids in mice. Mol Ther.
4:575–585. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|