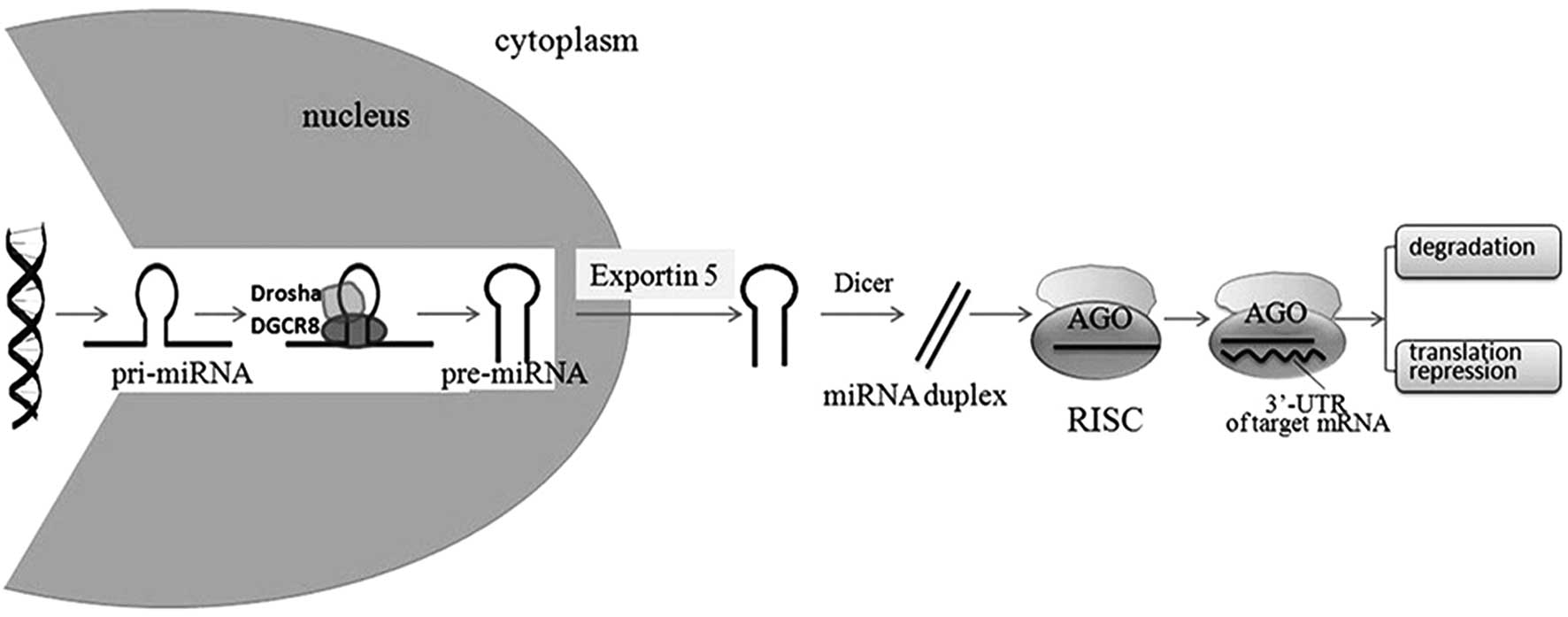
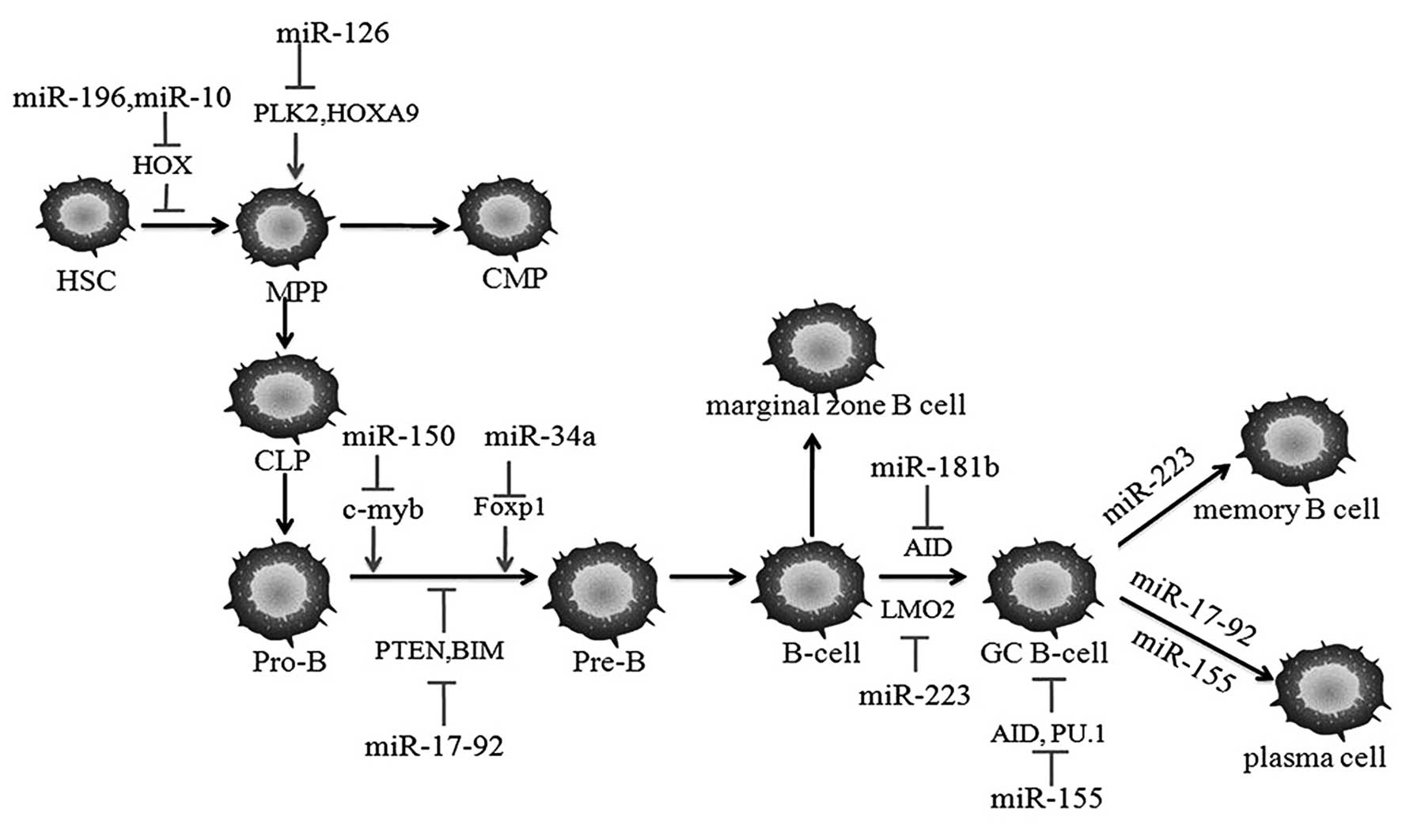
|
1
|
Dores GM, Anderson WF, Curtis RE, et al:
Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and small lymphocytic lymphoma:
overview of the descriptive epidemiology. Br J Haematol.
139:809–819. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tsimberidou AM and Keating MJ: Richter
syndrome: biology, incidence, and therapeutic strategies. Cancer.
103:216–228. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The
C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with
antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993.
|
|
4
|
Carthew RW and Sontheimer EJ: Origins and
mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell. 136:642–655. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim VN, Han J and Siomi MC: Biogenesis of
small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:126–139. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hutvágner G and Zamore PD: A microRNA in a
multiple-turnover RNAi enzyme complex. Science. 297:2056–2060.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bartels CL and Tsongalis GJ: MicroRNAs:
novel biomarkers for human cancer. Clin Chem. 55:623–631. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Joshi D, Gosh K and Vundinti BR: MicroRNAs
in hematological malignancies: a novel approach to targeted
therapy. Hematology. 17:170–175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S, Benner A, et al:
Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N
Engl J Med. 343:1910–1916. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, et al:
Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and
miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:15524–15529. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W
and Tuschl T: Identification of novel genes coding for small
expressed RNAs. Science. 294:853–858. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lia M, Carette A, Tang H, et al:
Functional dissection of the chromosome 13q14 tumor-suppressor
locus using transgenic mouse lines. Blood. 119:2981–2990. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, et al:
miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:13944–13949. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu Q, Fu H, Sun F, et al: miR-16 family
induces cell cycle arrest by regulating multiple cell cycle genes.
Nucleic Acids Res. 36:5391–5404. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Balatti V, Bottoni A, Palamarchuk A, et
al: NOTCH1 mutations in CLL associated with trisomy 12. Blood.
119:329–331. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
López C, Delgado J, Costa D, et al:
Different distribution of NOTCH1 mutations in chronic lymphocytic
leukemia with isolated trisomy 12 or associated with other
chromosomal alterations. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 51:881–889.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fragoso R, Mao T, Wang S, et al:
Modulating the strength and threshold of NOTCH oncogenic signals by
mir-181a-1/b-1. PLoS Genet. 8:e10028552012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gusscott S, Kuchenbauer F, Humphries RK
and Weng AP: Notch-mediated repression of miR-223 contributes to
IGF1R regulation in T-ALL. Leuk Res. 36:905–911. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Austen B, Powell JE, Alvi A, et al:
Mutations in the ATM gene lead to impaired overall and
treatment-free survival that is independent of IGVH mutation status
in patients with B-CLL. Blood. 106:3175–3182. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Skowronska A, Parker A, Ahmed G, et al:
Biallelic ATM inactivation significantly reduces survival in
patients treated on the United Kingdom Leukemia Research Fund
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia 4 trial. J Clin Oncol. 30:4524–4532.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang X, Wan G, Berger FG, He X and Lu X:
The ATM kinase induces microRNA biogenesis in the DNA damage
response. Mol Cell. 41:371–383. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Y, Yu Y, Tsuyada A, et al:
Transforming growth factor-β regulates the sphere-initiating stem
cell-like feature in breast cancer through miRNA-181 and ATM.
Oncogene. 30:1470–1480. 2011.
|
|
23
|
Auer RL, Riaz S and Cotter FE: The 13q and
11q B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia-associated regions derive
from a common ancestral region in the zebrafish. Br J Haematol.
137:443–453. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gonzalez D, Martinez P, Wade R, et al:
Mutational status of the TP53 gene as a predictor of response and
survival in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: results
from the LRF CLL4 trial. J Clin Oncol. 29:2223–2229. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mraz M, Pospisilova S, Malinova K, Slapak
I and Mayer J: MicroRNAs in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
pathogenesis and disease subtypes. Leuk Lymphoma. 50:506–509. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Koralov SB, Muljo SA, Galler GR, et al:
Dicer ablation affects antibody diversity and cell survival in the
B lymphocyte lineage. Cell. 132:860–874. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
O’Connell RM, Rao DS, Chaudhuri AA and
Baltimore D: Physiological and pathological roles for microRNAs in
the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:111–122. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou B, Wang S, Mayr C, Bartel DP and
Lodish HF: miR-150, a microRNA expressed in mature B and T cells,
blocks early B cell development when expressed prematurely. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:7080–7085. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xiao C, Calado DP, Galler G, et al:
MiR-150 controls B cell differentiation by targeting the
transcription factor c-Myb. Cell. 131:146–159. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xiao C, Srinivasan L, Calado DP, et al:
Lymphoproliferative disease and autoimmunity in mice with increased
miR-17-92 expression in lymphocytes. Nat Immunol. 9:405–414. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ventura A, Young AG, Winslow MM, et al:
Targeted deletion reveals essential and overlapping functions of
the miR-17 through 92 family of miRNA clusters. Cell. 132:875–886.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
de Yébenes VG, Belver L, Pisano DG, et al:
miR-181b negatively regulates activation-induced cytidine deaminase
in B cells. J Exp Med. 205:2199–2206. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang J, Jima DD, Jacobs C, et al:
Patterns of microRNA expression characterize stages of human B-cell
differentiation. Blood. 113:4586–4594. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fernando TR, Rodriguez-Malave NI and Rao
DS: MicroRNAs in B cell development and malignancy. J Hematol
Oncol. 5:72012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rodriguez A, Vigorito E, Clare S, et al:
Requirement of bic/microRNA-155 for normal immune function.
Science. 316:608–611. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Thai TH, Calado DP, Casola S, et al:
Regulation of the germinal center response by microRNA-155.
Science. 316:604–608. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rao DS, O’Connell RM, Chaudhuri AA,
Garcia-Flores Y, Geiger TL and Baltimore D: MicroRNA-34a perturbs B
lymphocyte development by repressing the forkhead box transcription
factor Foxp1. Immunity. 33:48–59. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ge X and Wang X: Role of Wnt canonical
pathway in hematological malignancies. J Hematol Oncol. 3:332010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Seke Etet PF, Vecchio L and Nwabo Kamdje
AH: Interactions between bone marrow stromal microenvironment and
B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells: any role for Notch, Wnt and
Hh signaling pathways? Cell Signal. 24:1433–1443. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lu D, Zhao Y, Tawatao R, et al: Activation
of the Wnt signaling pathway in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:3118–3123. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gandhirajan RK, Staib PA, Minke K, et al:
Small molecule inhibitors of Wnt/beta-catenin/lef-1 signaling
induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells in vitro
and in vivo. Neoplasia. 12:326–335. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Valastyan S, Reinhardt F, Benaich N, et
al: A pleiotropically acting microRNA, miR-31, inhibits breast
cancer metastasis. Cell. 137:1032–1046. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hashimi ST, Fulcher JA, Chang MH, Gov L,
Wang S and Lee B: MicroRNA profiling identifies miR-34a and miR-21
and their target genes JAG1 and WNT1 in the coordinate regulation
of dendritic cell differentiation. Blood. 114:404–414. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal
K, Jacob ST and Patel T: MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the
PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer.
Gastroenterology. 133:647–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lou Y, Yang X, Wang F, Cui Z and Huang Y:
MicroRNA-21 promotes the cell proliferation, invasion and migration
abilities in ovarian epithelial carcinomas through inhibiting the
expression of PTEN protein. Int J Mol Med. 26:819–827.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Rossi S, Shimizu M, Barbarotto E, et al:
microRNA fingerprinting of CLL patients with chromosome 17p
deletion identify a miR-21 score that stratifies early survival.
Blood. 116:945–952. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kapinas K, Kessler C, Ricks T, Gronowicz G
and Delany AM: miR-29 modulates Wnt signaling in human osteoblasts
through a positive feedback loop. J Biol Chem. 285:25221–25231.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Huang K, Zhang JX, Han L, You YP, Jiang T,
Pu PY and Kang CS: MicroRNA roles in beta-catenin pathway. Mol
Cancer. 9:2522010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Rassenti LZ, Huynh L, Toy TL, et al:
ZAP-70 compared with immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene mutation
status as a predictor of disease progression in chronic lymphocytic
leukemia. N Engl J Med. 351:893–901. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Calin GA, Ferracin M, Cimmino A, et al: A
MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in
chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 353:1793–1801. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Moussay E, Wang K, Cho JH, et al: MicroRNA
as biomarkers and regulators in B-cell chronic lymphocytic
leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:6573–6578. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bomben R, Gobessi S, Dal Bo M, et al: The
miR-17~92 family regulates the response to Toll-like receptor 9
triggering of CLL cells with unmutated IGHV genes. Leukemia.
26:1584–1593. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zenz T, Eichhorst B, Busch R, et al: TP53
mutation and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin
Oncol. 28:4473–4479. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Fabbri M, Bottoni A, Shimizu M, et al:
Association of a microRNA/TP53 feedback circuitry with pathogenesis
and outcome of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. JAMA.
305:59–67. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Mraz M, Malinova K, Kotaskova J, et al:
miR-34a, miR-29c and miR-17-5p are downregulated in CLL patients
with TP53 abnormalities. Leukemia. 23:1159–1163. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Leong KG and Karsan A: Recent insights
into the role of Notch signaling in tumorigenesis. Blood.
107:2223–2233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Fabbri G, Rasi S, Rossi D, et al: Analysis
of the chronic lymphocytic leukemia coding genome: role of NOTCH1
mutational activation. J Exp Med. 208:1389–1401. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Puente XS, Pinyol M, Quesada V, et al:
Whole-genome sequencing identifies recurrent mutations in chronic
lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature. 475:101–105. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Rossi D, Rasi S, Fabbri G, et al:
Mutations of NOTCH1 are an independent predictor of survival in
chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 119:521–529. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Cichocki F, Felices M, McCullar V,
Presnell SR, Al-Attar A, Lutz CT and Miller JS: Cutting edge:
microRNA-181 promotes human NK cell development by regulating Notch
signaling. J Immunol. 187:6171–6175. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Li X, Sanda T, Look AT, Novina CD and von
Boehmer H: Repression of tumor suppressor miR-451 is essential for
NOTCH1-induced oncogenesis in T-ALL. J Exp Med. 208:663–675. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Mansouri L, Cahill N, Gunnarsson R, et al:
NOTCH1 and SF3B1 mutations can be added to the hierarchical
prognostic classification in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Leukemia. 27:512–514. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D, et al:
Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic lymphocytic
leukemia: a report from the International Workshop on Chronic
Lymphocytic Leukemia updating the National Cancer Institute-Working
Group 1996 guidelines. Blood. 111:5446–5456. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Zenz T, Mohr J, Edelmann J, et al:
Treatment resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: the role of
the p53 pathway. Leuk Lymphoma. 50:510–513. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zenz T, Mohr J, Eldering E, et al: miR-34a
as part of the resistance network in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Blood. 113:3801–3808. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Asslaber D, Piñón JD, Seyfried I, et al:
microRNA-34a expression correlates with MDM2 SNP309 polymorphism
and treatment-free survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood.
115:4191–4197. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Bond GL, Hu W, Bond EE, et al: A single
nucleotide polymorphism in the MDM2 promoter attenuates the p53
tumor suppressor pathway and accelerates tumor formation in humans.
Cell. 119:591–602. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Moussay E, Palissot V, Vallar L, et al:
Determination of genes and microRNAs involved in the resistance to
fludarabine in vivo in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Mol Cancer.
9:1152010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhu DX, Zhu W, Fang C, et al: miR-181a/b
significantly enhances drug sensitivity in chronic lymphocytic
leukemia cells via targeting multiple anti-apoptosis genes.
Carcinogenesis. 33:1294–1301. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ferracin M, Zagatti B, Rizzotto L, et al:
MicroRNAs involvement in fludarabine refractory chronic lymphocytic
leukemia. Mol Cancer. 9:1232010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|