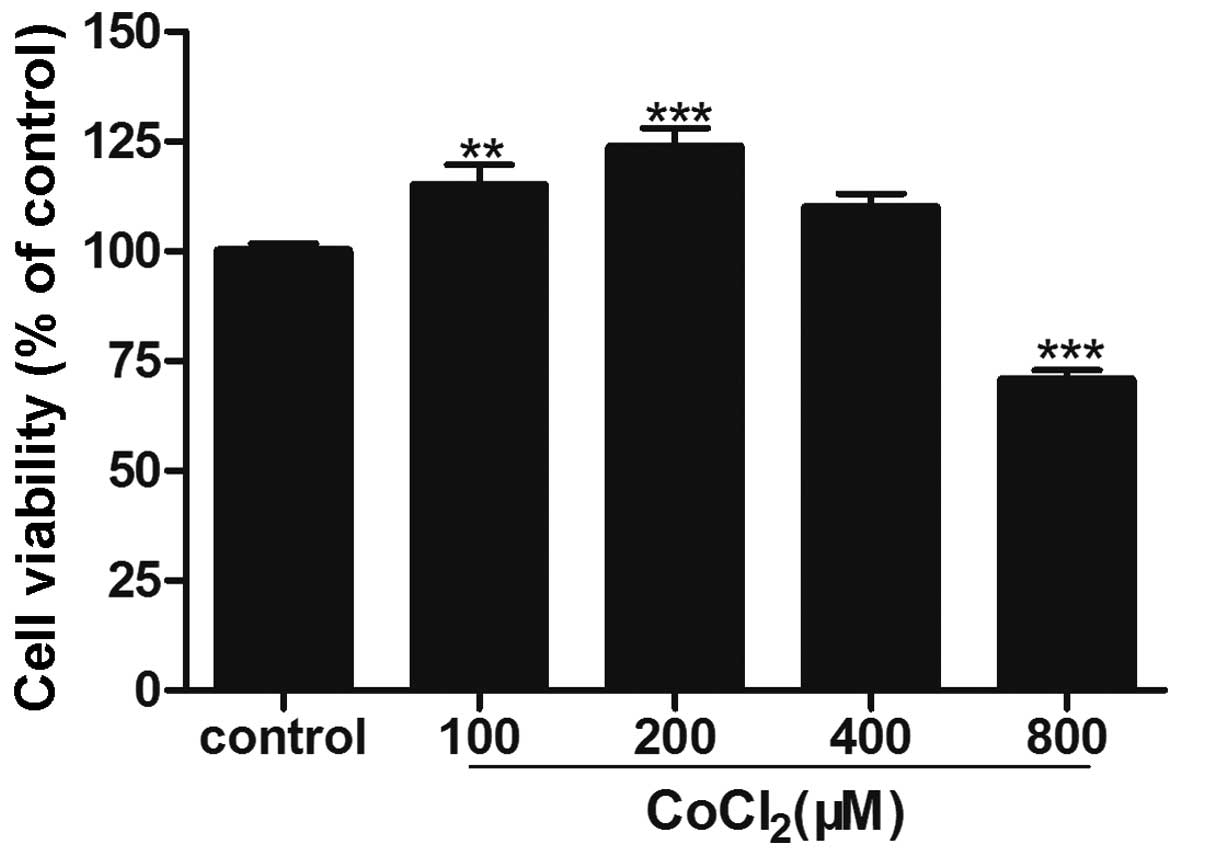
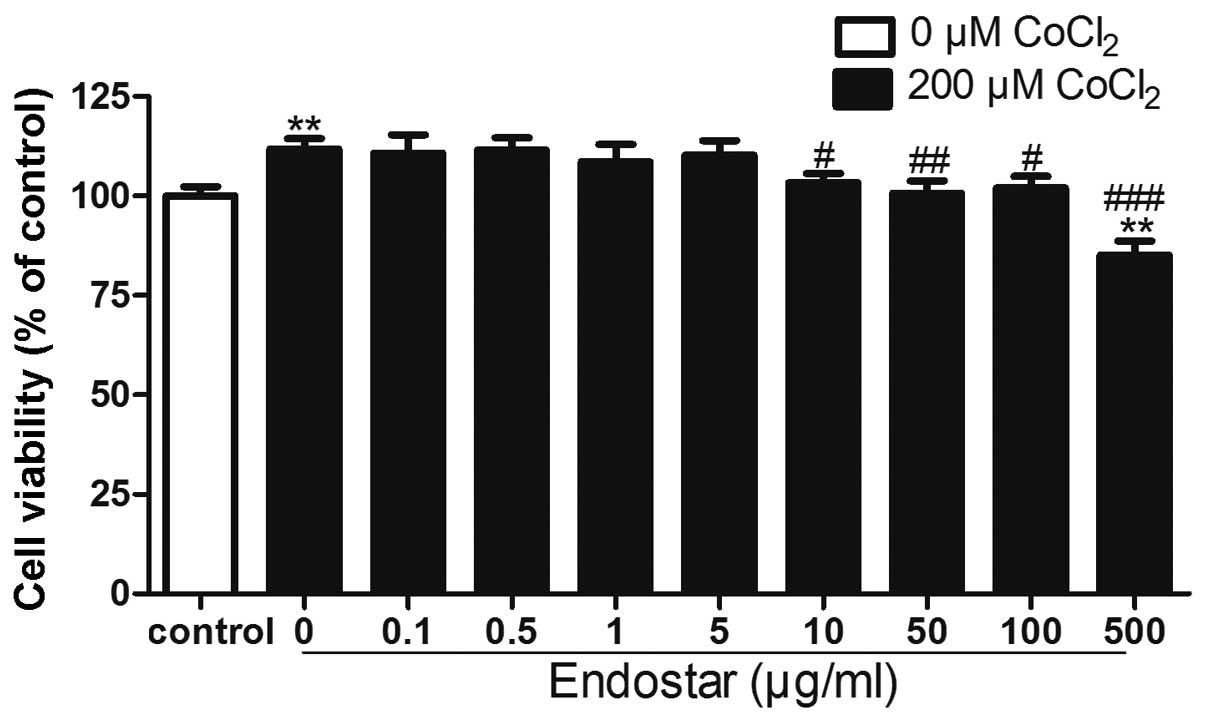
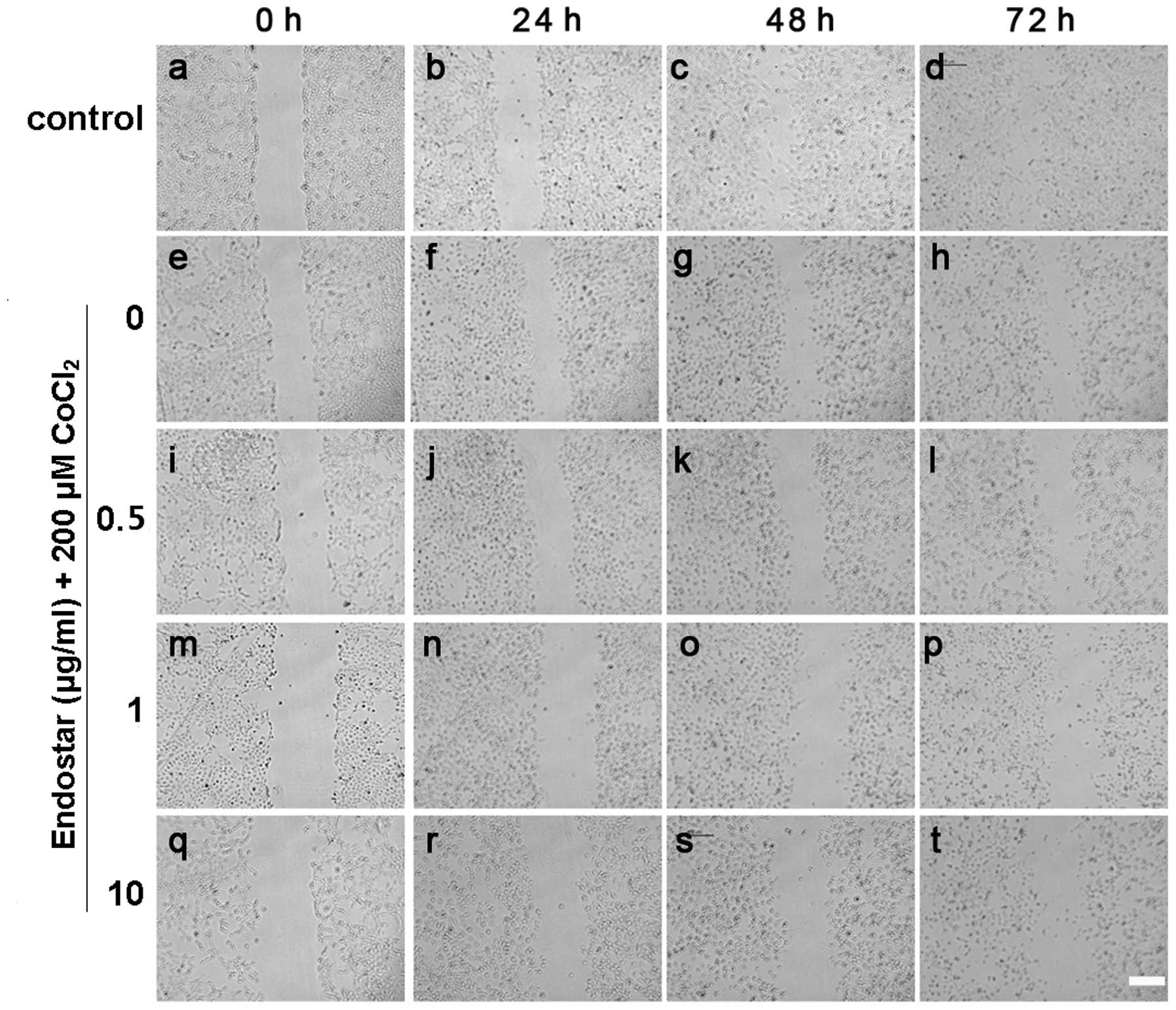
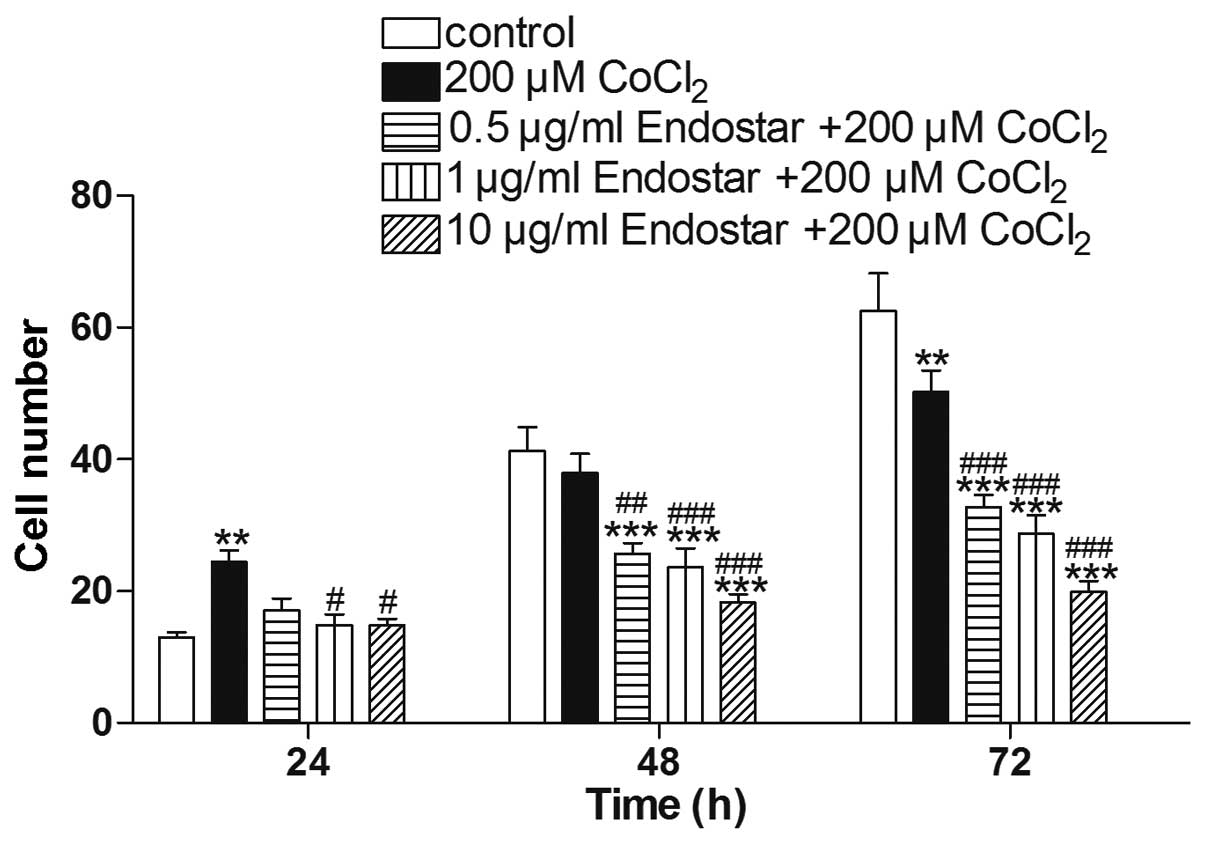
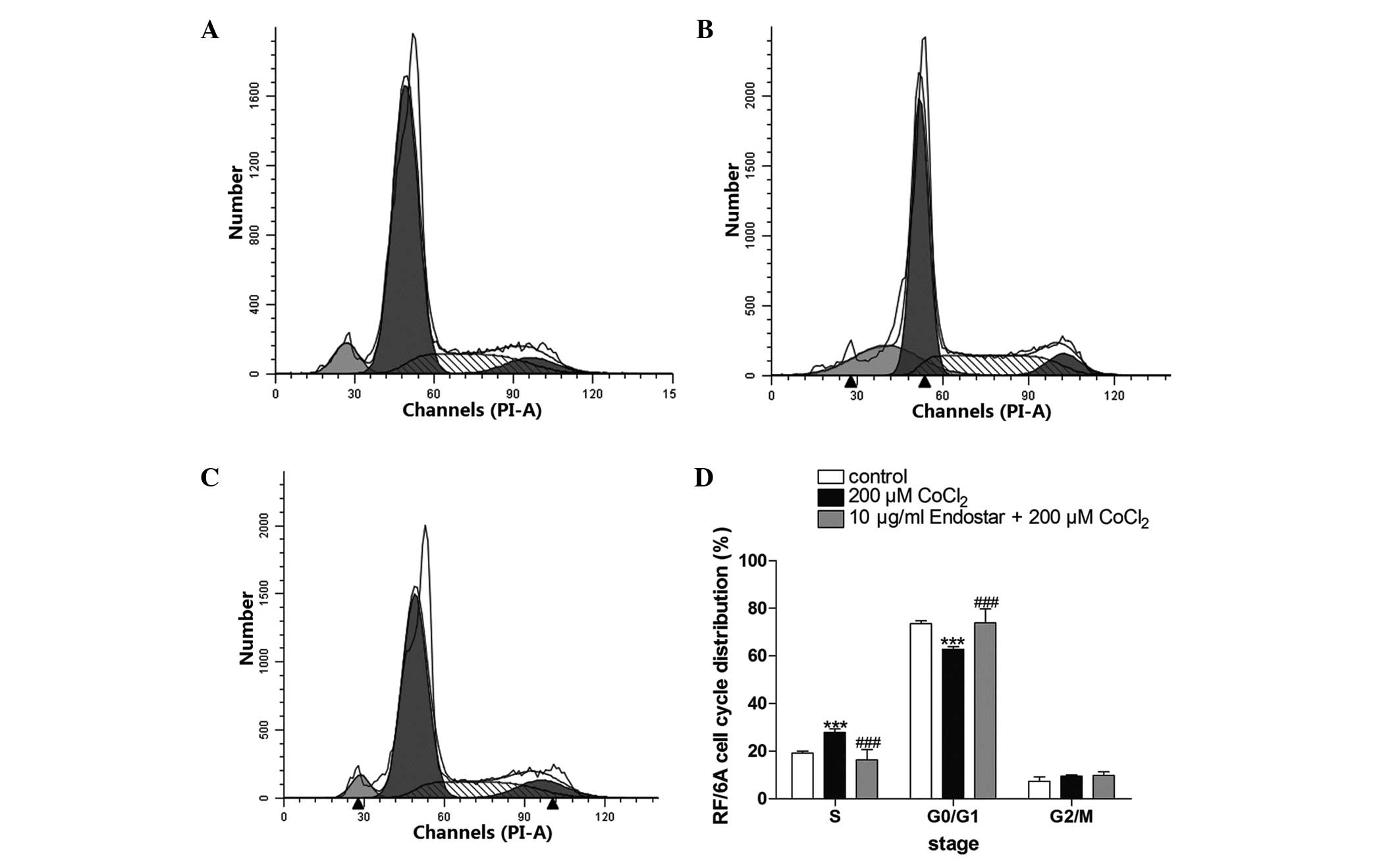
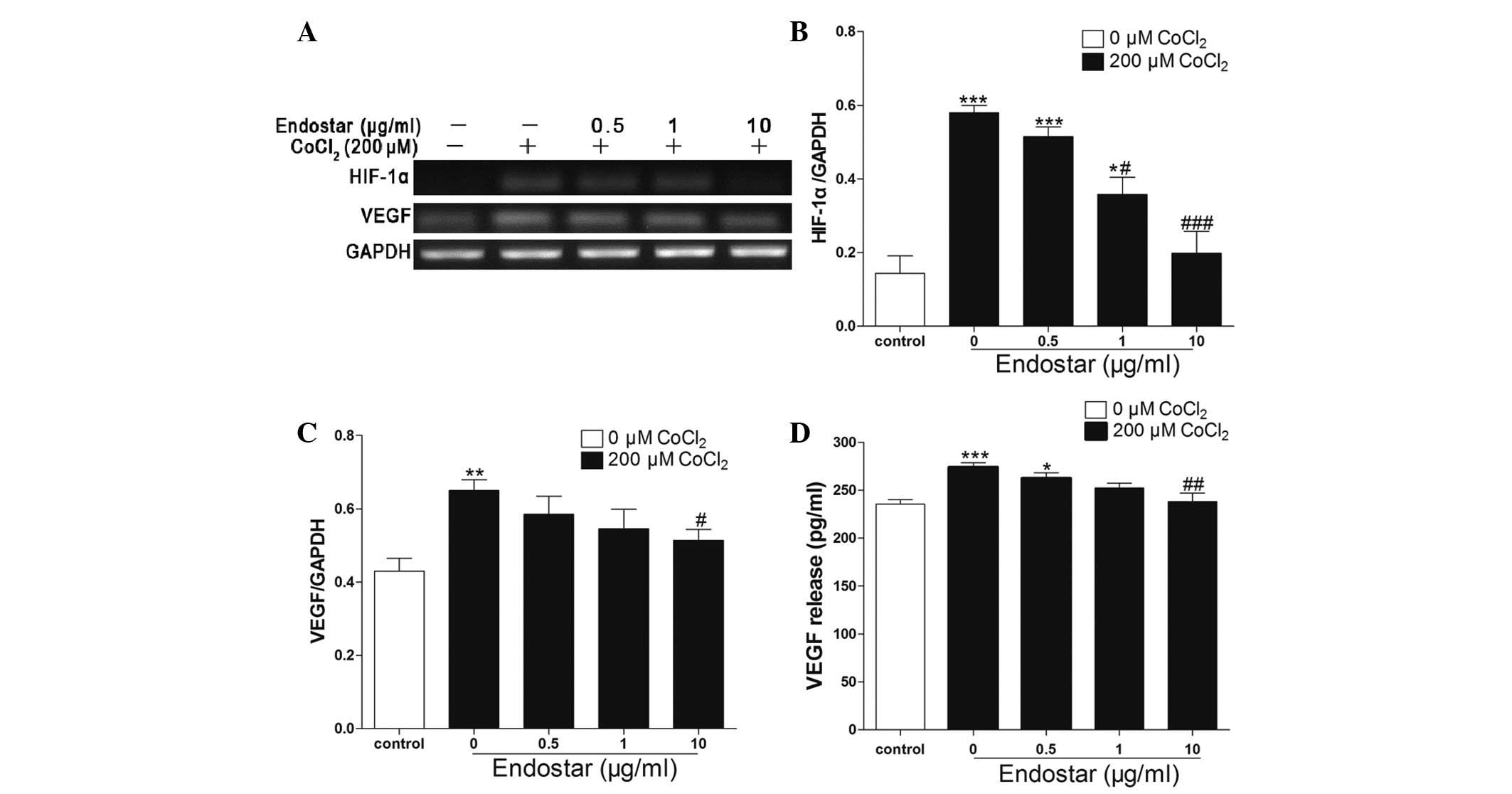
|
1
|
Risau W: Mechanisms of angiogenesis.
Nature. 386:671–674. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ambati J, Ambati BK, Yoo SH, Ianchulev S
and Adamis AP: Age-related macular degeneration: etiology,
pathogenesis, and therapeutic strategies. Surv Ophthalmol.
48:257–293. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Friedman DS, O’Colmain BJ, Munoz B, et al:
Prevalence of age-related macular degeneration in the United
States. Arch Ophthalmol. 122:564–572. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bhutto I and Lutty G: Understanding
age-related macular degeneration (AMD): relationships between the
photoreceptor/retinal pigment epithelium/Bruch’s
membrane/choriocapillaris complex. Mol Aspects Med. 33:295–317.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xie P, Zhang W, Yuan S, et al: Suppression
of experimental choroidal neovascularization by curcumin in mice.
PLoS One. 7:e533292012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yang XM, Wang YS, Zhang J, et al: Role of
PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK in mediating hypoxia-induced expression of
HIF-1alpha and VEGF in laser-induced rat choroidal
neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50:1873–1879. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Dong X, Wang YS, Dou GR, et al: Influence
of DII4 via HIF-1alpha-VEGF signaling on the angiogenesis of
choroidal neovascularization under hypoxic conditions. PLoS One.
6:e184812011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kang HM and Koh HJ: Intravitreal
anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy versus photodynamic
therapy for idiopathic choroidal neovascularization. Am J
Ophthalmol. 155:713–719. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kim YM, Jang JW, Lee OH, et al: Endostatin
inhibits endothelial and tumor cellular invasion by blocking the
activation and catalytic activity of matrix metalloproteinase.
Cancer Res. 60:5410–5413. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Abdollahi A, Hlatky L and Huber PE:
Endostatin: the logic of antiangiogenic therapy. Drug Resist Updat.
8:59–74. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mori K, Ando A, Gehlbach P, et al:
Campochiaro PA. Inhibition of choroidal neovascularization by
intravenous injection of adenoviral vectors expressing secretable
endostatin. Am J Pathol. 159:313–320. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tatar O, Shinoda K, Kaiserling E, et al:
Early effects of triamcinolone on vascular endothelial growth
factor and endostatin in human choroidal neovascularization. Arch
Ophthalmol. 126:193–199. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu W, Ye P, Li Z, Shi J, Wang W and Yao K:
Endostar, a recently introduced recombinant human endostatin,
inhibits proliferation and migration through regulating growth
factors, adhesion factors and inflammatory mediators in
choroid-retinal endothelial cells. Mol Biol. 44:664–670. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Neely KA and Gardner TW: Ocular
neovascularization: clarifying complex interactions. Am J Pathol.
153:665–670. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hay WW Jr and Bell EF: Oxygen therapy,
oxygen toxicity, and the STOP-ROP trial. Pediatrics. 105:424–425.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Plum SM, Vu HA, Mercer B, Fogler WE and
Fortier AH: Generation of a specific immunological response to
FGF-2 does not affect wound healing or reproduction.
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 26:29–41. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen Y, Li XX, Xing NZ and Cao XG:
Quercetin inhibits choroidal and retinal angiogenesis in vitro.
Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 246:373–378. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ling Y, Yang Y, Lu N, et al: Endostar, a
novel recombinant human endostatin, exerts antiangiogenic effect
via blocking VEGF-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of KDR/Flk-1 of
endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 361:79–84. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang LP, Zou C, Yuan X, Luo W, Wen Y and
Chen Y: N-terminal modification increases the stability of the
recombinant human endostatin in vitro. Biotechnol Appl Biochem.
54:113–120. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu N, Ling Y, Gao Y, et al: Endostar
suppresses invasion through downregulating the expression of matrix
metalloproteinase-2/9 in MDA-MB-435 human breast cancer cells. Exp
Biol Med. 233:1013–1020. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wen QL, Meng MB, Yang B, et al: Endostar,
a recombined humanized endostatin, enhances the radioresponse for
human nasopharyngeal carcinoma and human lung adenocarcinoma
xenografts in mice. Cancer Sci. 100:1510–1519. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bong R, Yang S, Li W, Zhang W and Ming Z:
Systematic review and meta-analysis of Endostar (rh-endostatin)
combined with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treating
advanced non-small cell lung cancer. World J Surg Oncol.
10:1702012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Covello KL, Simon MC and Keith B: Targeted
replacement of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by a
hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha knock-in allele promotes tumor
growth. Cancer Res. 65:2277–2286. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Semenza GL: Angiogenesis in ischemic and
neoplastic disorders. Annu Rev Med. 54:17–28. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Semenza GL: HIF-1: mediator of
physiological and pathophysiological responses to hypoxia. J Appl
Physiol. 88:1474–1480. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kelly BD, Hackett SF, Hirota K, Oshima Y,
Cai Z, Berg-Dixon S, Rowan A, Yan Z, Campochiaro PA and Semenza GL:
Cell type-specific regulation of angiogenic growth factor gene
expression and induction of angiogenesis in nonischemic tissue by a
constitutively active form of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Circ Res.
93:1074–1081. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lukiw WJ, Ottlecz A, Lambrou G, Grueninger
M, Finley J, Thompson HW and Bazan NG: Coordinate activation of
HIF-1 and NF-kappaB DNA binding and COX-2 and VEGF expression in
retinal cells by hypoxia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 44:4163–4170.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Berglin L, Sarman S, van der Ploeg I, et
al: Reduced choroidal neovascular membrane formation in matrix
metalloproteinase-2-deficient mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
44:403–408. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Haas TL: Endothelial cell regulation of
matrix metalloproteinases. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 83:1–7. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Moses MA: The regulation of
neovascularization of matrix metalloproteinases and their
inhibitors. Stem Cells. 15:S180–S189. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jia Y, Liu M, Cao L, et al: Recombinant
human endostatin, Endostar, enhances the effects of
chemo-radiotherapy in a mouse cervical cancer xenograft model. Eur
J Gynaecol Oncol. 32:316–324. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang L, Ge W, Hu K, et al: Endostar
down-regulates HIF-1 and VEGF expression and enhances the
radioresponse to human lung adenocarcinoma cancer cells. Mol Biol
Rep. 39:89–95. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|