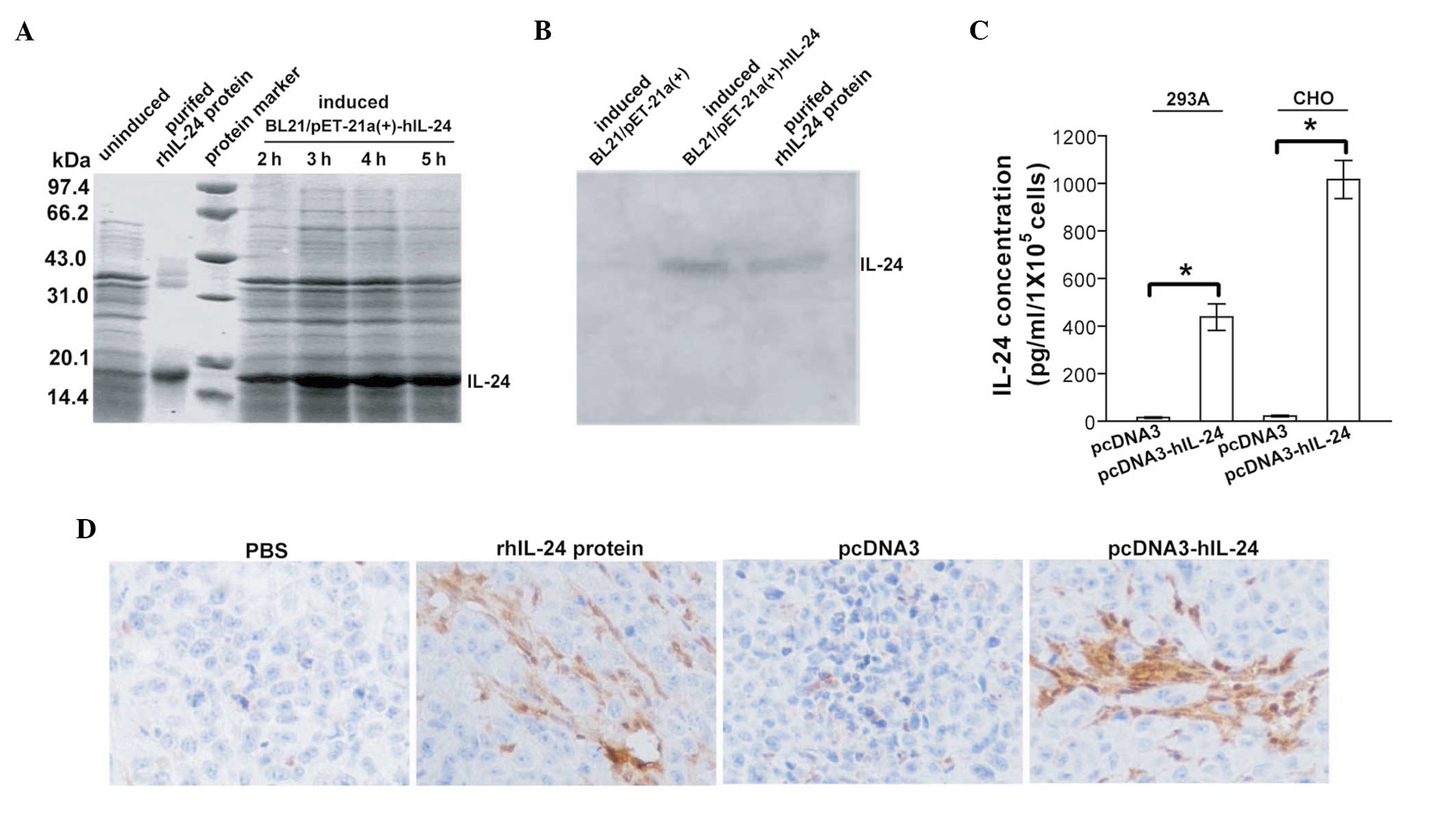
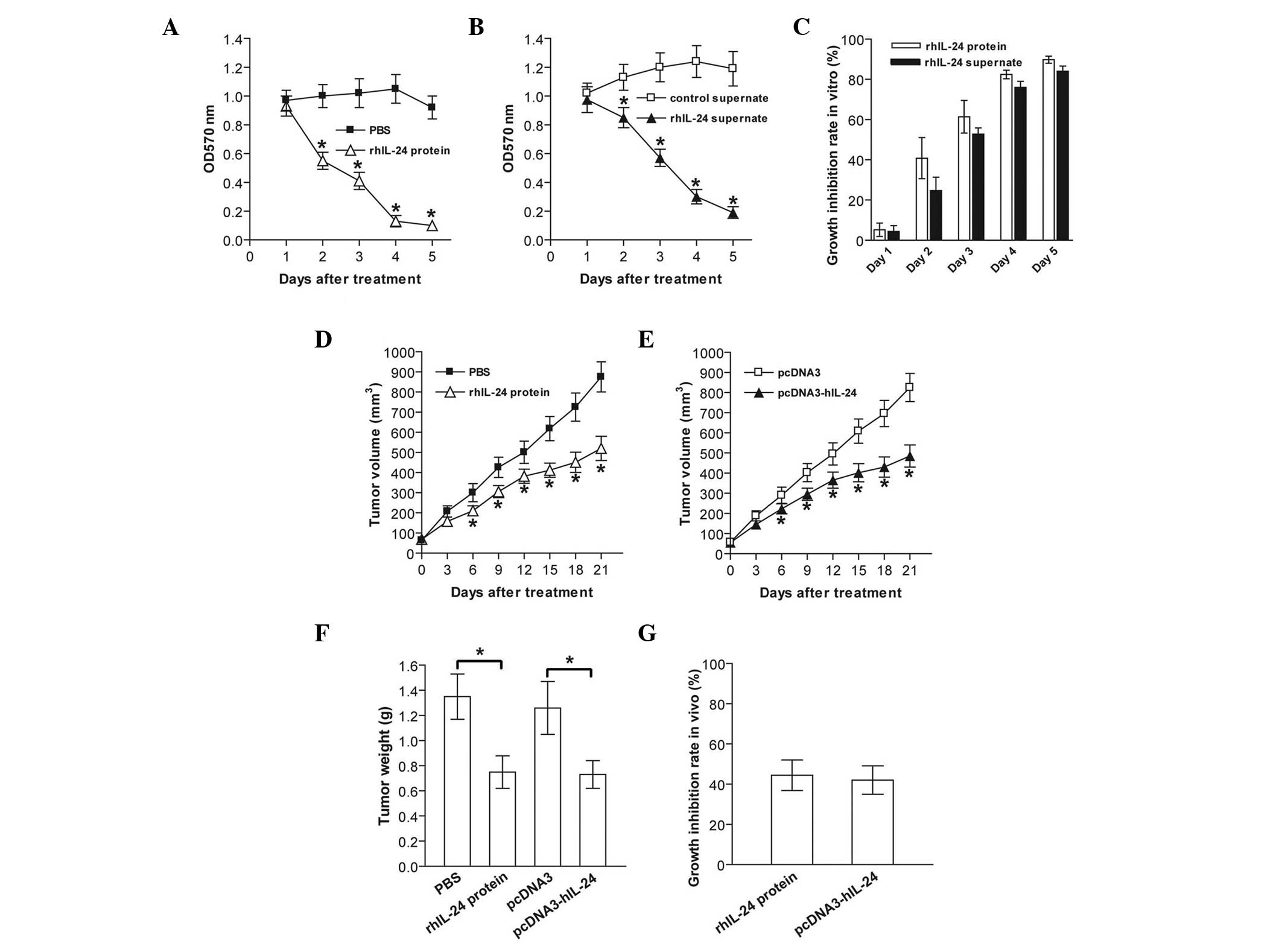
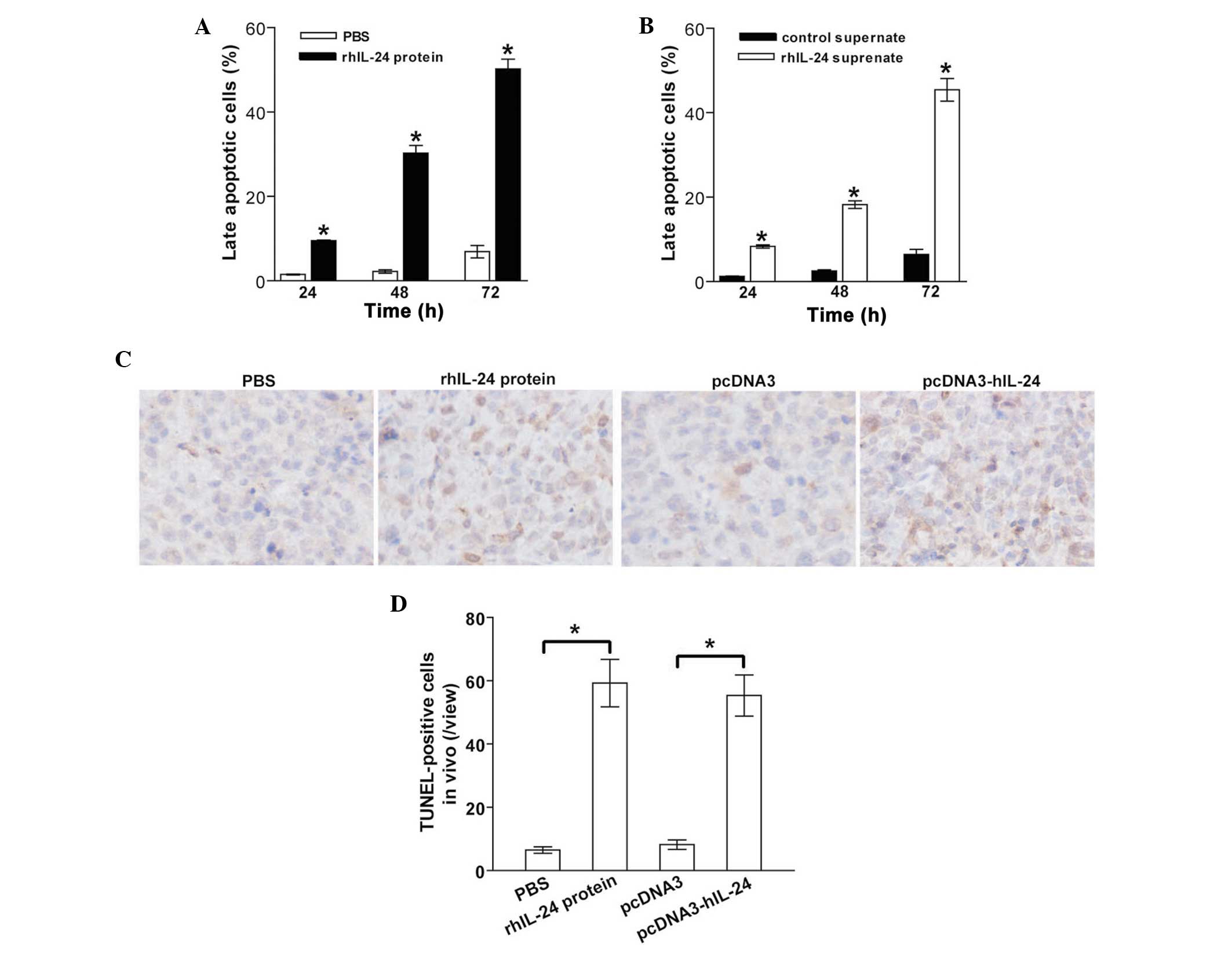
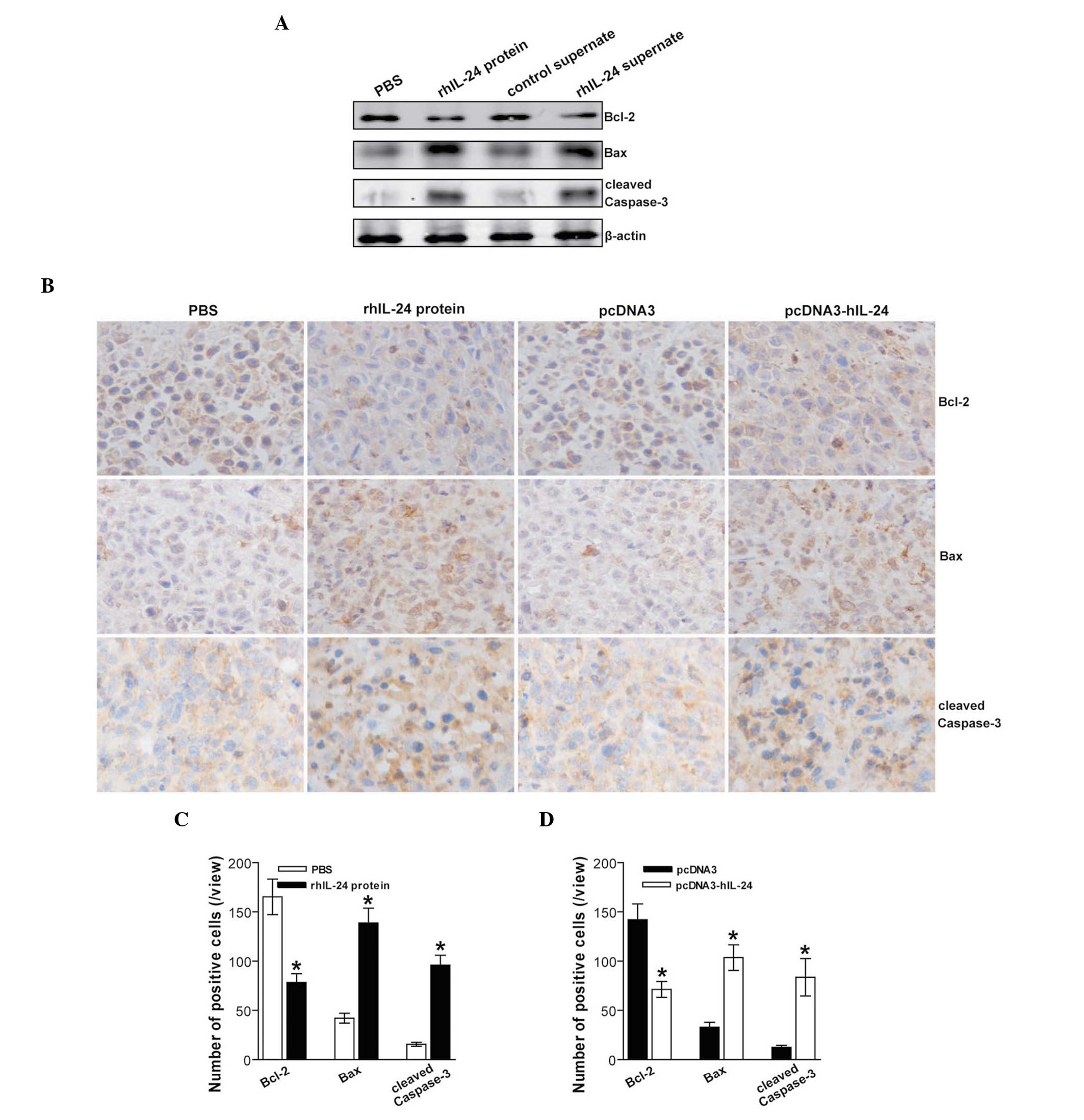
|
1
|
Sauane M, Gopalkrishnan RV, Sarkar D, Su
ZZ, Lebedeva IV, Dent P, et al: MDA-7/IL-24: novel cancer growth
suppressing and apoptosis inducing cytokine. Cytokine Growth Factor
Rev. 14:35–51. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fisher PB: Is mda-7/IL-24 a ‘magic bullet’
for cancer? Cancer Res. 65:10128–10138. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Whitaker EL, Filippov VA and
Duerksen-Hughes PJ: Interleukin 24: Mechanisms and therapeutic
potential of an anti-cancer gene. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
23:323–331. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ramesh R, Mhashilkar AM, Tanaka F, Saito
Y, Branch CD, Sieger K, et al: Melanoma differentiation-associated
gene 7/interleukin (IL)-24 is a novel ligand that regulates
angiogenesis via the IL-22 receptor. Cancer Res. 63:5105–5113.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Saeki T, Mhashilkar A, Swanson X, Zou-Yang
XH, Sieger K, Kawabe S, et al: Inhibition of human lung cancer
growth following adenovirus-mediated mda-7 gene expression in vivo.
Oncogene. 21:4558–4566. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nishikawa T, Ramesh R, Munshi A, Chada S
and Meyn RE: Adenovirus-mediated mda-7 (IL24) gene therapy
suppresses angiogenesis and sensitizes NSCLC xenograft tumors to
radiation. Mol Ther. 9:818–828. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Caudell EG, Mumm JB, Poindexter N,
Ekmekcioglu S, Mhashilkar AM, Yang XH, et al: The protein product
of the tumor suppressor gene, melanoma differentiation-associated
gene 7, exhibits immunostimulatory activity and is designated
IL-24. J Immunol. 168:6041–6046. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ramesh R, Ito I, Gopalan B, Saito Y,
Mhashilkar AM and Chada S: Ectopic production of MDA-7/IL-24
inhibits invasion and migration of human lung cancer cells. Mol
Ther. 9:510–518. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sauane M, Su ZZ, Gupta P, Lebedeva IV,
Dent P, Sarkar D and Fisher PB: Autocrine regulation of mda-7/IL-24
mediates cancer-specific apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:9763–9768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hamed HA, Das SK, Sokhi UK, Park MA,
Cruickshanks N, Archer K, et al: Combining histone deacetylase
inhibitors with MDA-7/IL-24 enhances killing of renal carcinoma
cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 14:1039–1049. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tinoco G, Warsch S, Glück S, Avancha K and
Montero AJ: Treating breast cancer in the 21st century: Emerging
biological therapies. J Cancer. 4:117–132. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Patani N, Douglas-Jones A, Mansel R, Jiang
W and Mokbel K: Tumour suppressor function of MDA-7/IL-24 in human
breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 10:292010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Frewer NC, Ye L, Sun PH, Owen S, Ji K,
Frewer KA, et al: Potential implication of IL-24 in
lymphangiogenesis of human breast cancer. Int J Mol Med.
31:1097–1104. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sarkar D, Su ZZ, Vozhilla N, Park ES,
Gupta P and Fisher PB: Dual cancer-specific targeting strategy
cures primary and distant breast carcinomas in nude mice. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:14034–14039. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sauane M, Gopalkrishnan RV, Choo HT, Gupta
P, Lebedeva IV, Yacoub A, et al: Mechanistic aspects of mda-7/IL-24
cancer cell selectivity analysed via a bacterial fusion protein.
Oncogene. 23:7679–7690. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pei DS, Yang ZX, Zhang BF, Yin XX, Li LT,
Li HZ and Zheng JN: Enhanced apoptosis-inducing function of
MDA-7/IL-24 RGD mutant via the increased adhesion to tumor cells. J
Interferon Cytokine Res. 32:66–73. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Weidner N: Current pathologic methods for
measuring intratumoral microvessel density within breast carcinoma
and other solid tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 36:169–180. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lebedeva IV, Emdad L, Su ZZ, Gupta P,
Sauane M, Sarkar D, et al: mda-7/IL-24, novel anticancer cytokine:
Focus on bystander antitumor, radiosensitization and antiangiogenic
properties and overview of the phase I clinical experience
(Review). Int J Oncol. 31:985–1007. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cunningham CC, Chada S, Merritt JA, Tong
A, Senzer N, Zhang Y, et al: Clinical and local biological effects
of an intratumoral injection of mda-7 (IL24; INGN 241) in patients
with advanced carcinoma: a phase I study. Mol Ther. 11:149–159.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Xie Y, Sheng W, Xiang J, Ye Z, Zhu Y, Chen
X and Yang J: Recombinant human IL-24 suppresses lung carcinoma
cell growth via induction of cell apoptosis and inhibition of tumor
angiogenesis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 23:310–320. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yan S, Zhang H, Xie Y, Sheng W, Xiang J,
Ye Z, et al: Recombinant human interleukin-24 suppresses gastric
carcinoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Invest.
28:85–93. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sauane M, Gupta P, Lebedeva IV, Su ZZ,
Sarkar D, Randolph A, et al: N-glycosylation of MDA-7/IL-24 is
dispensable for tumor cell-specific apoptosis and ‘bystander’
antitumor activity. Cancer Res. 66:11869–11877. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Danial NN and Korsmeyer SJ: Cell death:
Critical control points. Cell. 116:205–219. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Welti J, Loges S, Dimmeler S and Carmeliet
P: Recent molecular discoveries in angiogenesis and antiangiogenic
therapies in cancer. J Clin Invest. 123:3190–3200. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|