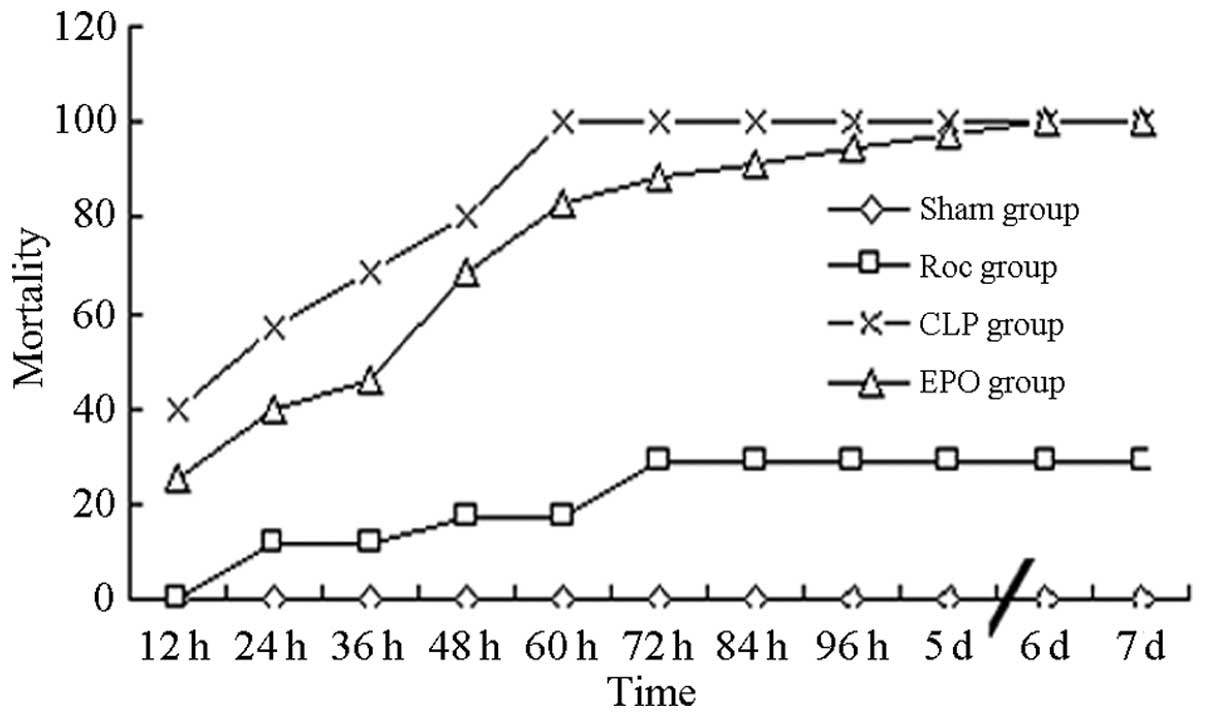
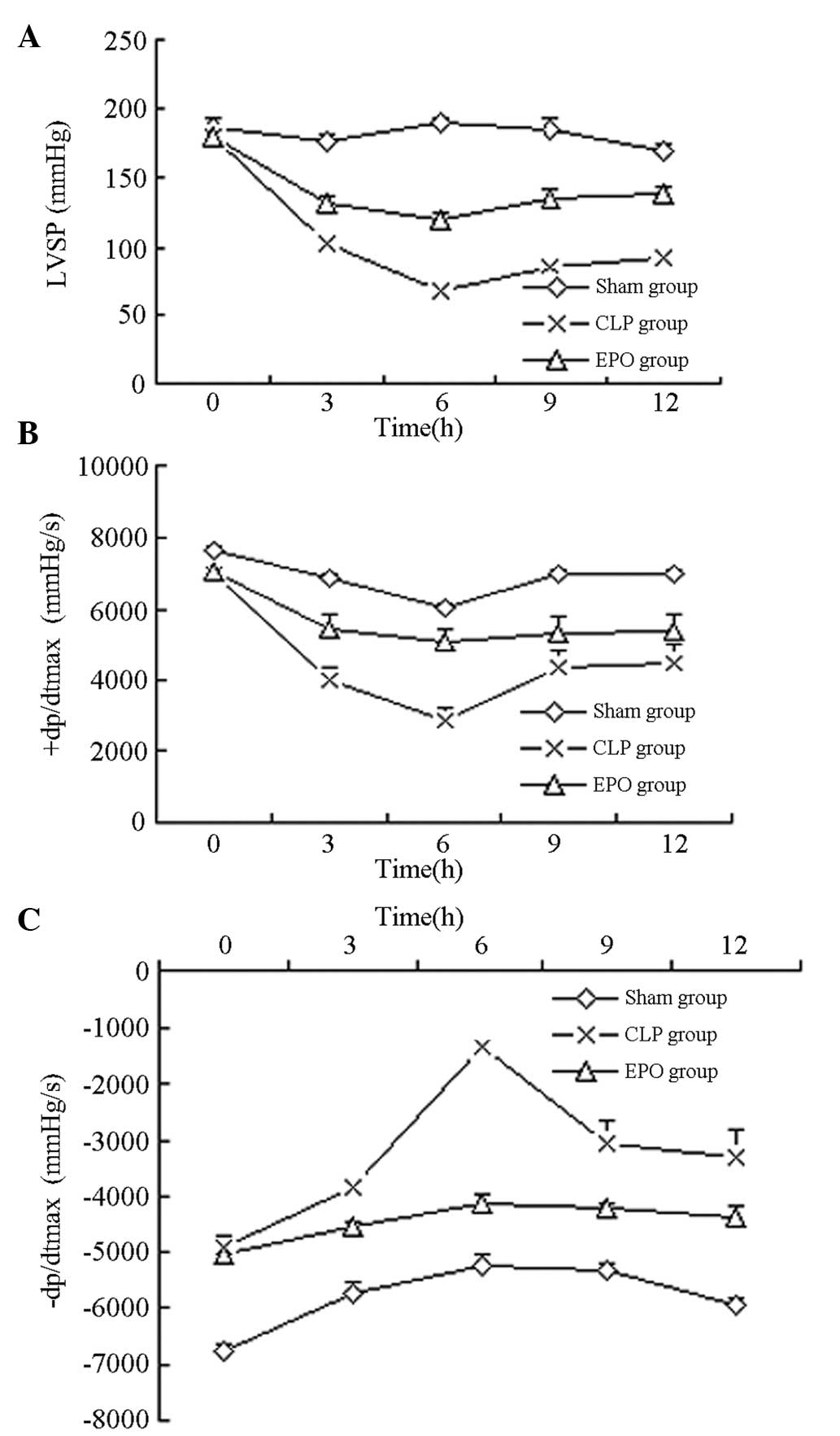
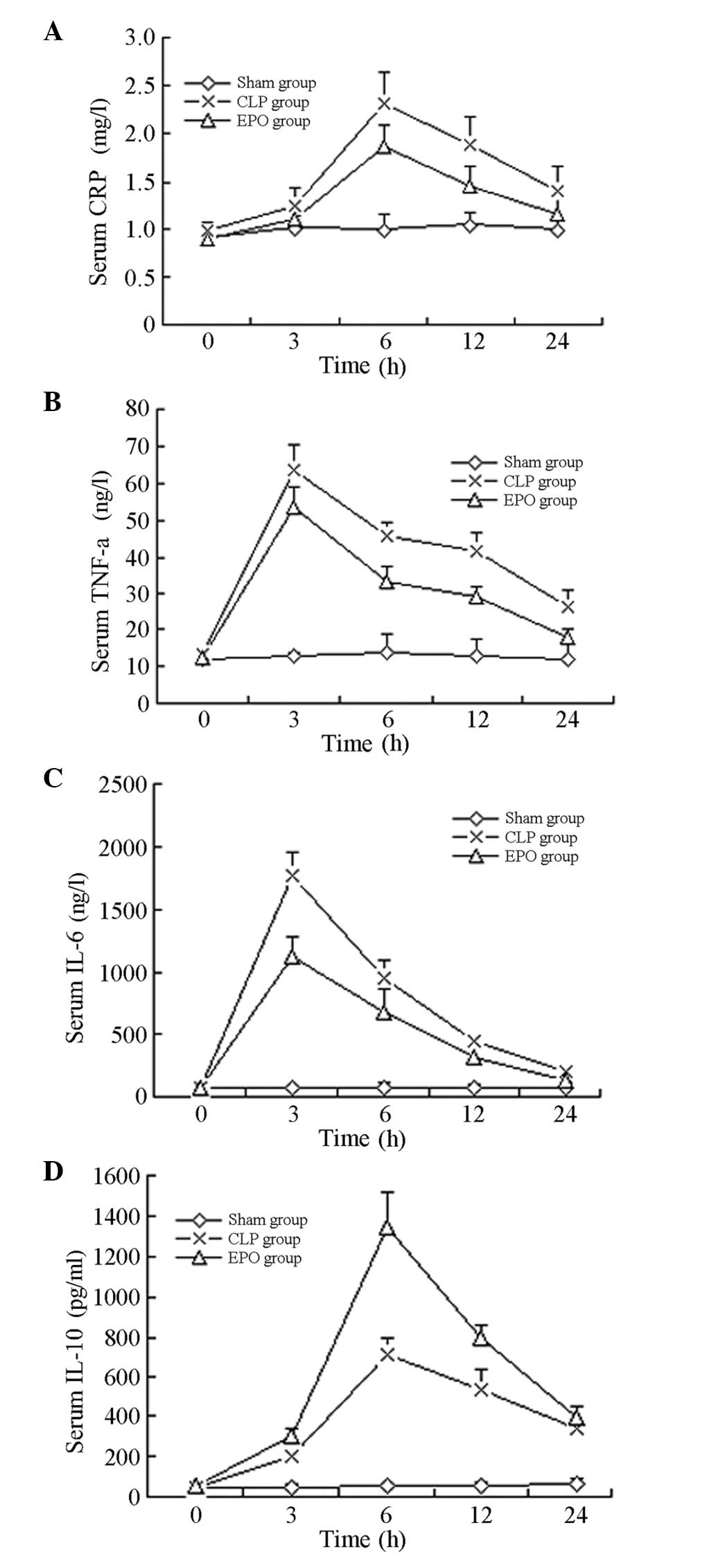
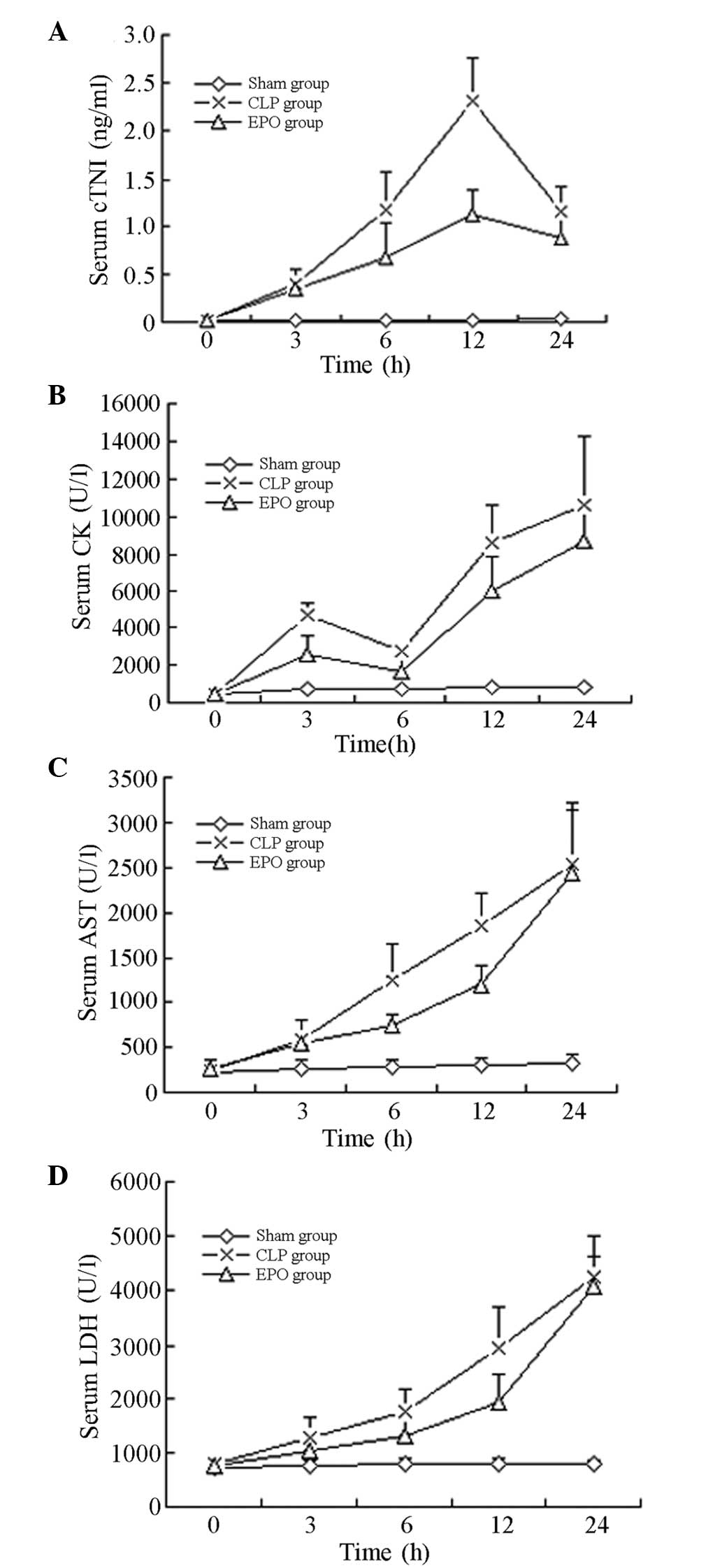
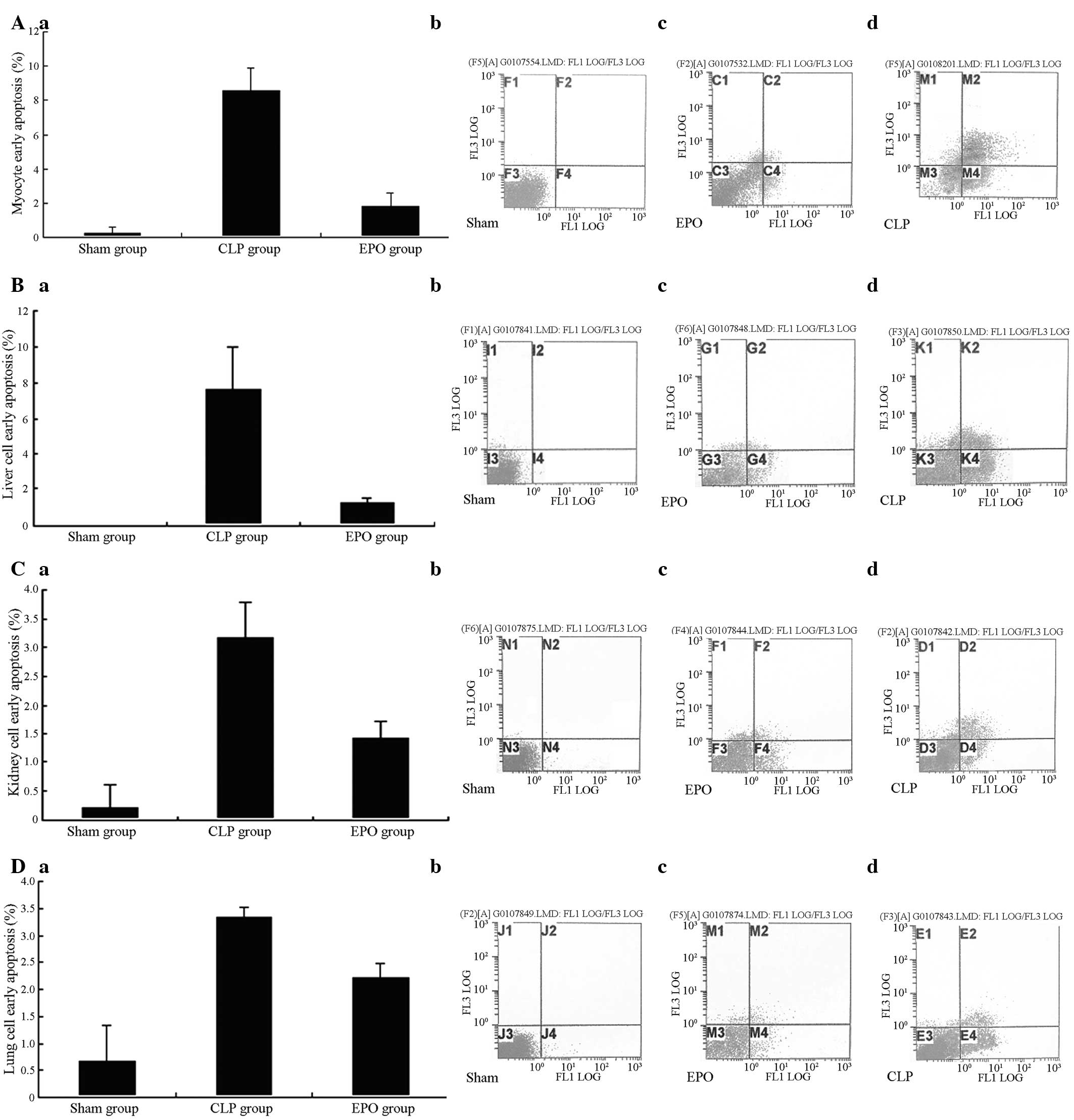
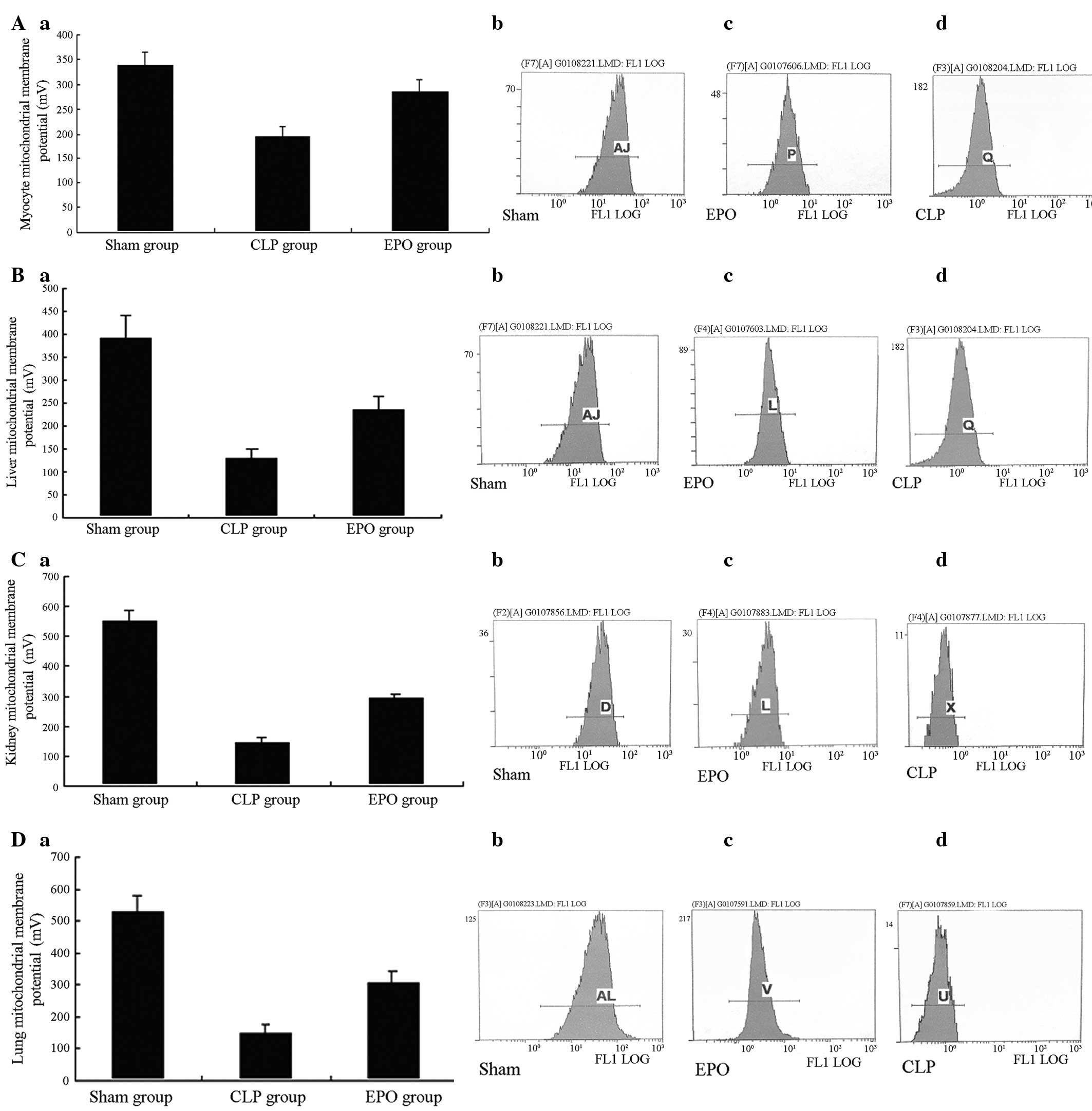
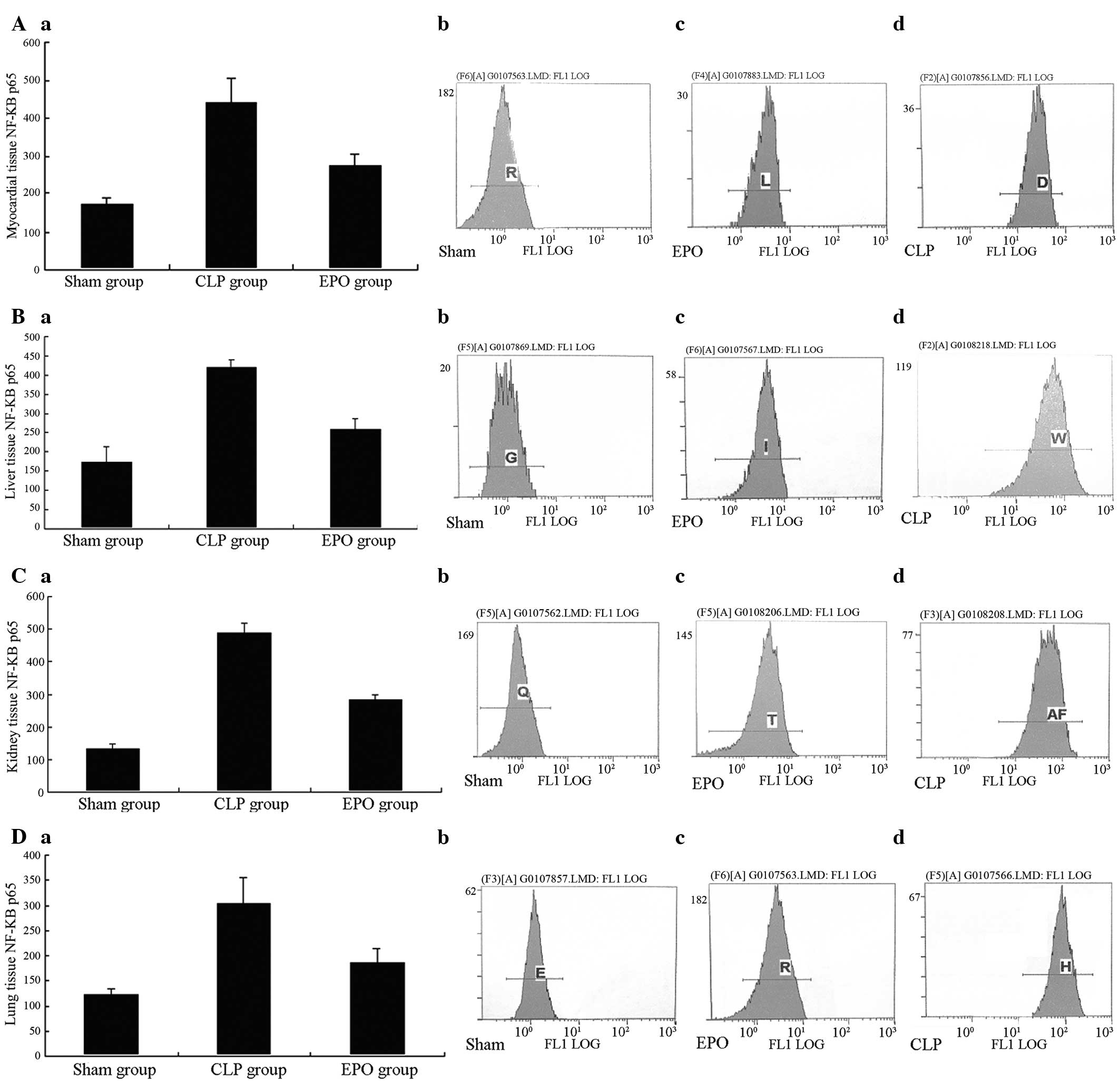
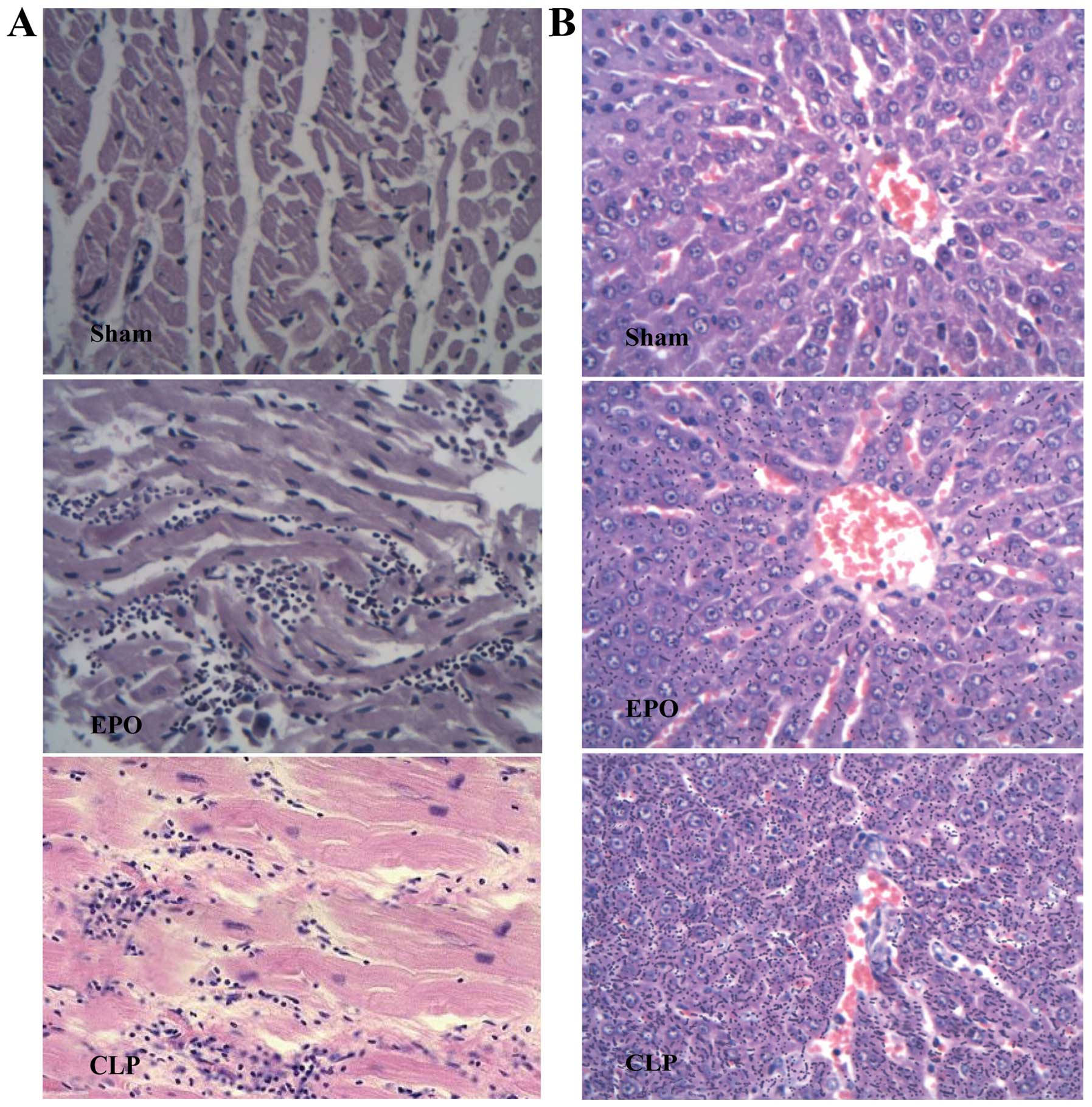
|
1
|
Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, et al:
International Sepsis Definitions Conference: 2001
SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions
Conference. Intensive Care Med. 29:530–538. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shimaoka M and Park EJ: Advances in
understanding sepsis. Eur J Anaesthesiol Suppl. 42:146–153. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J,
Clermont G, Carcillo J and Pinsky MR: Epidemiology of severe sepsis
in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and
associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 29:1303–1310. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dellinger RP, Carlet JM, Masur H, et al:
Surviving Sepsis Campaign Management Guidelines Committee:
Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines for management of severe
sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med. 32:858–873. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Meziani F, Tesse A and Andriantsitohaina
R: Microparticles are vectors of paradoxical information in
vascular cells including the endothelium: role in health and
diseases. Pharmacol Rep. 60:75–84. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tetta C, Fonsato V, Ronco C and Camussi G:
Recent insights into the pathogenesis of severe sepsis. Crit Care
Resusc. 7:32–39. 2005.
|
|
7
|
Silva E, da Passos RH, Ferri MB and de
Figueiredo LF: Sepsis: from bench to bedside. Clinics (Sao Paulo).
63:109–120. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cinel I and Dellinger RP: Advances in
pathogenesis and management of sepsis. Curr Opin Infect Dis.
20:345–352. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tramontano AF, Muniyappa R, Black AD, et
al: Erythropoietin protects cardiac myocytes from hypoxia-induced
apoptosis through an Akt-dependent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 308:990–994. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Maiese K, Li F and Chong ZZ:
Erythropoietin in the brain: can the promise protect be fulfilled?
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 25:577–583. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Juul SE, Yachnis AT and Chistensen RD:
Tissue distribution of erythropoietin and erythropoietin receptor
in the developing human fetus. Early Hum Dev. 52:235–249. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cai Z, Manalo DJ, Wei G, et al: Hearts
from rodents exposed to intermittent hypoxia orerythropoietin are
protected against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Circulatio.
108:79–85. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Aoshiba K, Onizawa S, Tsuji T and Nagai A:
Therapeutic effects of erythropoietin in murine models ofendotoxin
shock. Crit Care Med. 37:889–898. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bemardi P, Scorrano L, Colonna R,
Petronilli V and Di Lisa F: Mitochondria and cell death.
Mechanistic aspects and methodological issues. Eur J Biochem.
264:687–701. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tan C, Dlugosz PJ, Peng J, et al:
Auto-activation of the apoptosis protein Bax increases
mitochondrial membrane permeability and is inhibited by BCL-2. J
Biol Chem. 281:14764–14775. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Germ DR and Reed JC: Mitochondria and
apoptosis. Science. 281:1309–1312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Nechushtan A, Smith CL, Lamensdorf I, Yoon
SH and Youle RJ: Bax and Bak coalesce into novel
mitochondria-associated clusters during apoptosis. J Cell Biol.
153:1265–1276. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dschietzig T, Richter C, Pfannenschmidt G,
et al: Dexamethasone inhibits stimulation of pulmonary endothelins
by proinflammatory cytokines: possible involvement of a nuclear
factor kappa B dependent mechanism. Intensive Care Med. 27:751–756.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yinjun L, Jie J and Yungui W: Triptolide
inhibits transcription factor NF-kappaB and induces apoptosis of
multiple myeloma cells. Leuk Res. 29:99–105. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wichterman KA, Baue AE and Chaudry IH:
Sepsis and septic shock - a review of laboratory models and a
proposal. J Surg Res. 29:189–201. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Telford WG, King LE and Fraker PJ:
Comparative evaluation of several DNA binding dyes in the detection
of apoptosia-associated chromatin degradation by flow cytometry.
Cytometry. 13:137–143. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gurkan F, Alkaya A, Ece A, et al: Cardiac
troponin-I as a marker of myocardial dysfunction in children with
septic shock. Swiss Med Wkly. 134:593–596. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
ver Elst KM, Spapen HD, Nguyen DN, Garbar
C, Huyghens LP and Gorus FK: Cardiac troponins I and T are
biological markers of left ventricular dysfunction in septic shock.
Clin Chem. 46:650–657. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Turner A, Tsamitros M and Bellomo R:
Myocardial cell injury in septic shock. Crit Care Med.
27:1775–1780. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Besarab A, Bolton WK, Browne JK, et al:
The effects of normal as compared with low hematocrit values in
patients with cardiac disease who are receiving hemodialysis and
epoetin. N Engl J Med. 339:584–590. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Phrommintikul A, Haas SJ, Elsik M and Krum
H: Mortality and target haemoglobin concentrations in anaemic
patients with chronic kidney disease treated with erythropoietin: a
meta-analysis. Lancet. 369:381–388. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zarychanski R, Turgeon AF, McIntyre L and
Fergusson DA: Erythropoietin-receptor agonists in critically ill
patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. CMAJ.
177:725–734. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Arcasoy MO: The non-haematopoietic
biological effects of erythropoietin. Br J Haematol. 141:14–31.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bohlius J, Wilson J, Seidenfeld J, et al:
Erythropoietin or darbepoetin for patients with cancer. Cochrane
Database Syst Rev. 3:CD0034072006.PubMed/NCBI
|