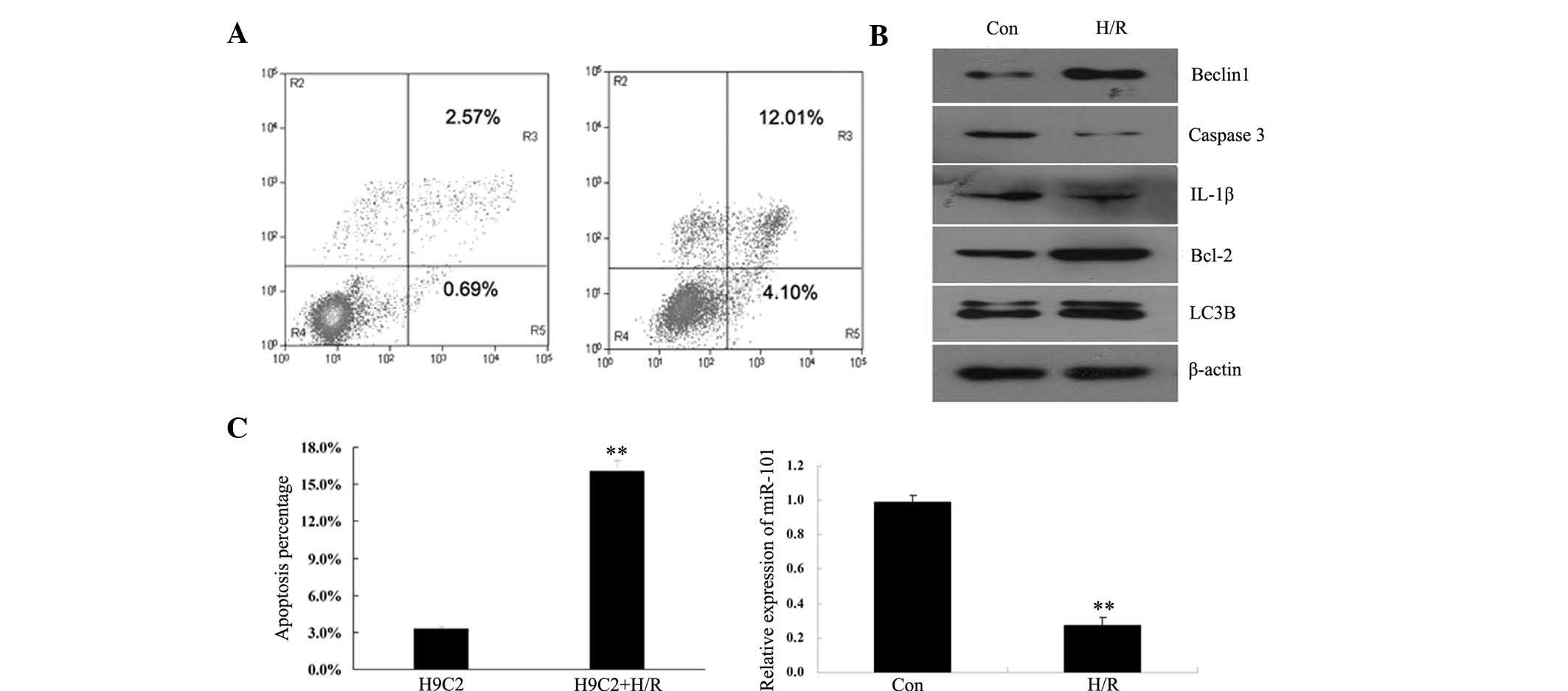
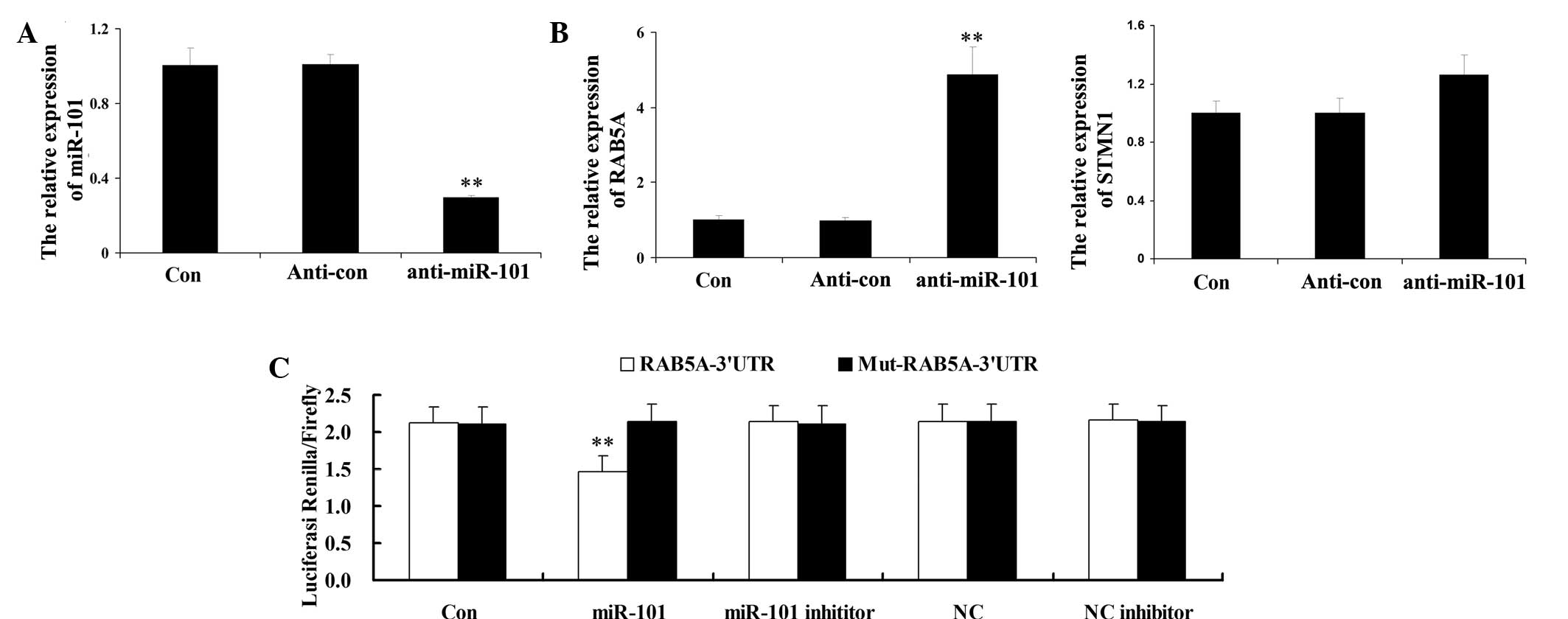
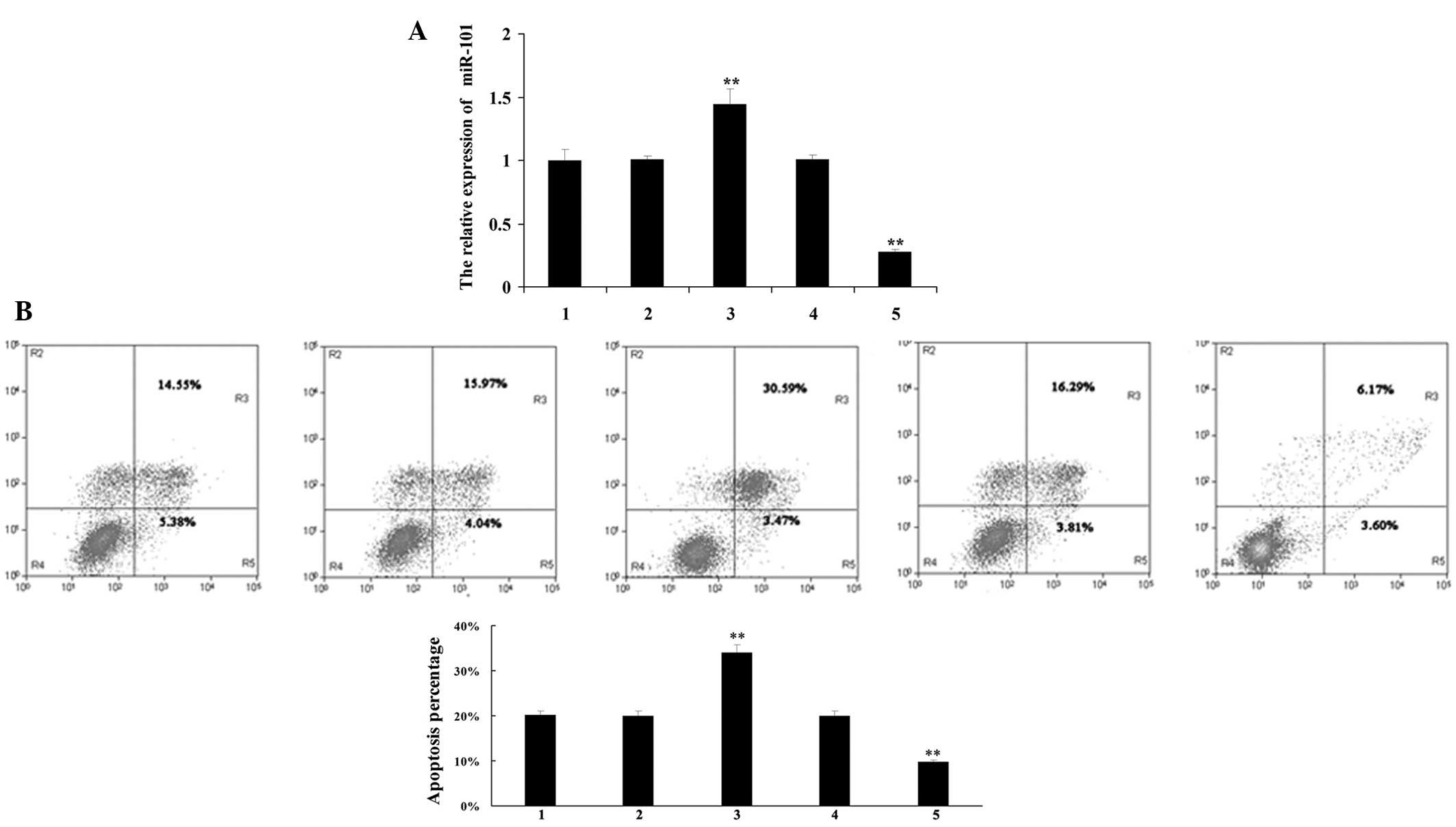
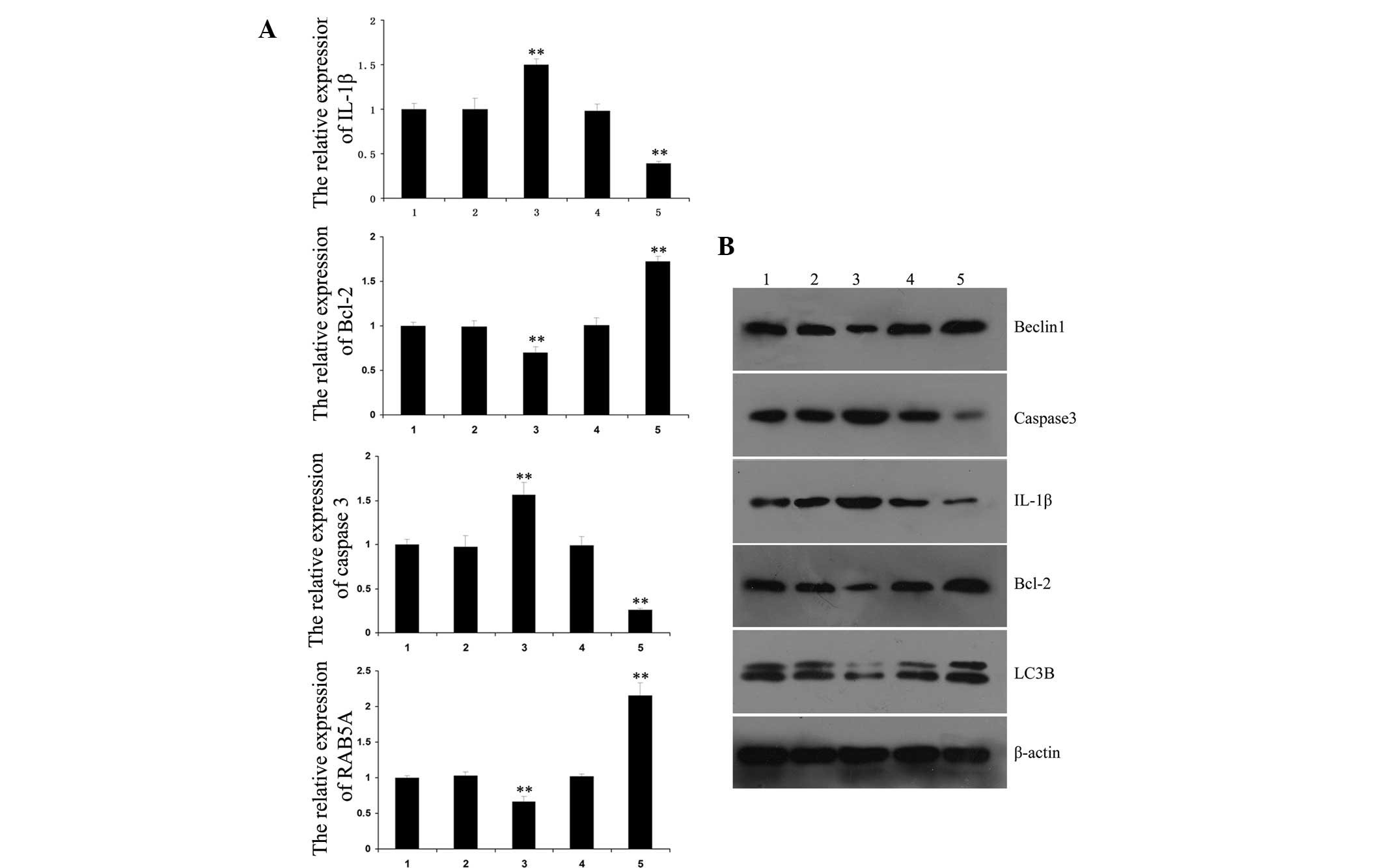
|
1
|
Oku M, Takano Y and Sakai Y: The emerging
role of autophagy in peroxisome dynamics and lipid metabolism of
phyllosphere microorganisms. Front Plant Sci. 5:812014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Petersen M, Hofius D and Andersen SU:
Signaling unmasked: Autophagy and catalase promote programmed cell
death. Autophagy. 10:2004.
|
|
3
|
Tessitore A, Cicciarelli G, Del Vecchio F,
et al: MicroRNAs in the DNA Damage/Repair Network and Cancer. Int J
Genomics. 2014:8202482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen LJ, Lim SH, Yeh YT, Lien SC and Chiu
JJ: Roles of microRNAs in atherosclerosis and restenosis. J Biomed
Sci. 19:792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu T, Li D and Jiang D: Targeting cell
signaling and apoptotic pathways by luteolin: cardioprotective role
in rat cardiomyocytes following ischemia/reperfusion. Nutrients.
4:2008–2019. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Morita K: Surgical reoxygenation injury of
the myocardium in cyanotic patients: clinical relevance and
therapeutic strategies by normoxic management during
cardiopulmonary bypass. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 60:549–556.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu LF, Liang Z, Lv ZR, et al:
MicroRNA-15a/b are up-regulated in response to myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Geriatr Cardiol. 9:28–32. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qin Y, Yu Y, Dong H, Bian X, Guo X and
Dong S: MicroRNA 21 inhibits left ventricular remodeling in the
early phase of rat model with ischemia-reperfusion injury by
suppressing cell apoptosis. Int J Med Sci. 9:413–423. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu L, Zhang G, Liang Z, et al:
MicroRNA-15b enhances hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis of
cardiomyocytes via a mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Apoptosis.
19:19–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Frankel LB, Wen J, Lees M, et al:
microRNA-101 is a potent inhibitor of autophagy. EMBO J.
30:4628–4641. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin X, Guan H, Li H, et al: miR-101
inhibits cell proliferation by targeting Rac1 in papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Biomed Rep. 2:122–126. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yin J, Wang M, Jin C and Qi Q: miR-101
sensitizes A549 NSCLC cell line to CDDP by activating caspase
3-dependent apoptosis. Oncol Lett. 7:461–465. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gong JS and Kim GJ: he role of autophagy
in the placenta as a regulator of cell death. Clin Exp Reprod Med.
41:97–107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hou C, Zhu M, Sun M and Lin Y: MicroRNA
let-7i induced autophagy to protect T cell from apoptosis by
targeting IGF1R. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 453:728–734. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gustafsson AB and Gottlieb RA: Recycle or
die: the role of autophagy in cardioprotection. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
44:654–661. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu Y, An Y, Wang Y, et al: miR-101
inhibits autophagy and enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 29:2019–2024.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li Y, Zhao Y, Hu J, et al: A novel
ER-localized transmembrane protein, EMC6, interacts with RAB5A and
regulates cell autophagy. Autophagy. 9:150–163. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Sybers HD, Ingwall J and DeLuca M:
Autophagy in cardiac myocytes. Recent Adv Stud Cardiac Struct
Metab. 12:453–463. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang ZL, Fan Y and Liu ML: Ginsenoside
Rg1 inhibits autophagy in H9c2 cardiomyocytes exposed to
hypoxia/reoxygenation. Mol Cell Biochem. 365:243–250. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cao X, Chen A, Yang P, et al: Alpha-lipoic
acid protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury
by inhibiting autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 441:935–940.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang JH, Behrns KE, Leeuwenburgh C and Kim
JS: Critical role of autophage in ischemia/reperfusion injury to
aged livers. Autophagy. 8:140–141. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Han Z, Cao J, Song D, et al: Autophagy is
involved in the cardioprotection effect of remote limb ischemic
postconditioning on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in
normal mice, but not diabetic mice. PLoS One. 9:e868382014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kang JW, Cho H and Lee SM: Melatonin
inhibits mTOR-dependent autophagy during liver
ischemia/reperfusion. Cell Physiol Biochem. 33:23–36. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y and Ren J: Targeting autophagy for
the therapeutic application of histone deacetylase inhibitors in
ischemia/reperfusion heart injury. Circulation. 129:1088–1091.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zeng M, Wei X, Wu Z, et al: NF-κB-mediated
induction of autophagy in cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 436:180–185. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hamacher-Brady A, Brady NR and Gottlieb
RA: The interplay between pro-death and pro-survival signaling
pathways in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: apoptosis meets
autophagy. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 20:445–462. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu G, Wang T, Song J and Zhou Z: Effects
of apoptosis-related proteins caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 on cerebral
ischemia rats. Biomed Rep. 1:861–867. 2013.
|
|
28
|
Ni Z, Wang B, Dai X, et al: HCC cells with
high levels of Bcl-2 are resistant to ABT-737 via activation of the
ROS-JNK-autophagy pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 70:194–203. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Heath-Engel HM, Chang NC and Shore GC: The
endoplasmic reticulum in apoptosis and autophagy: role of the BCL-2
protein family. Oncogene. 27:6419–6433. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liang XH, Kleeman LK, Jiang HH, et al:
Protection against fatal Sindbis virus encephalitis by beclin, a
novel Bcl-2-interacting protein. J Virol. 72:8586–8596.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, et al: Bcl-2
antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell.
122:927–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|