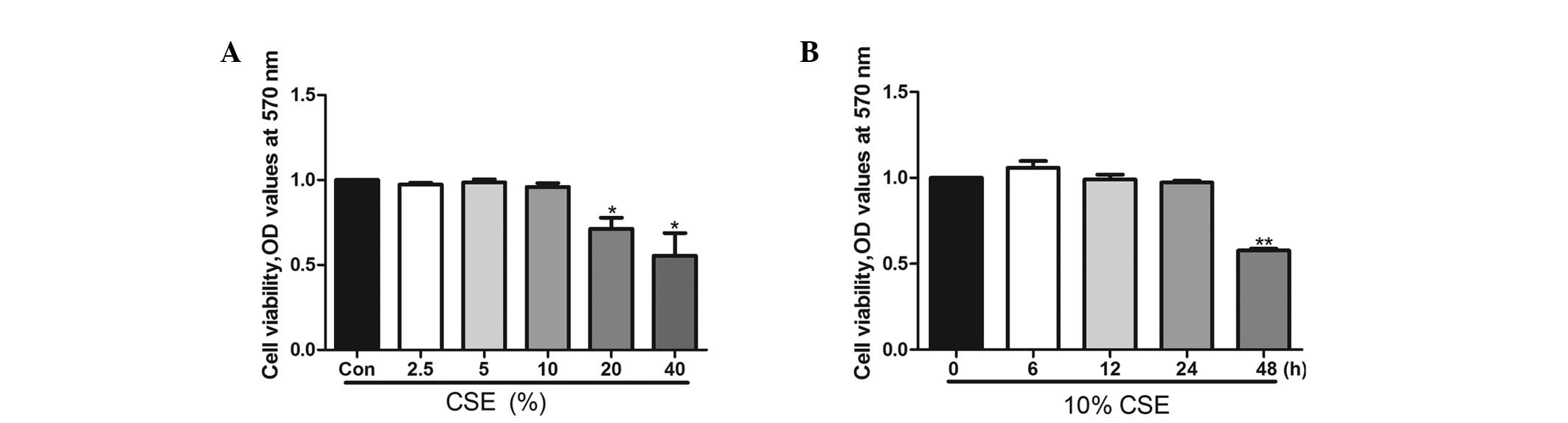
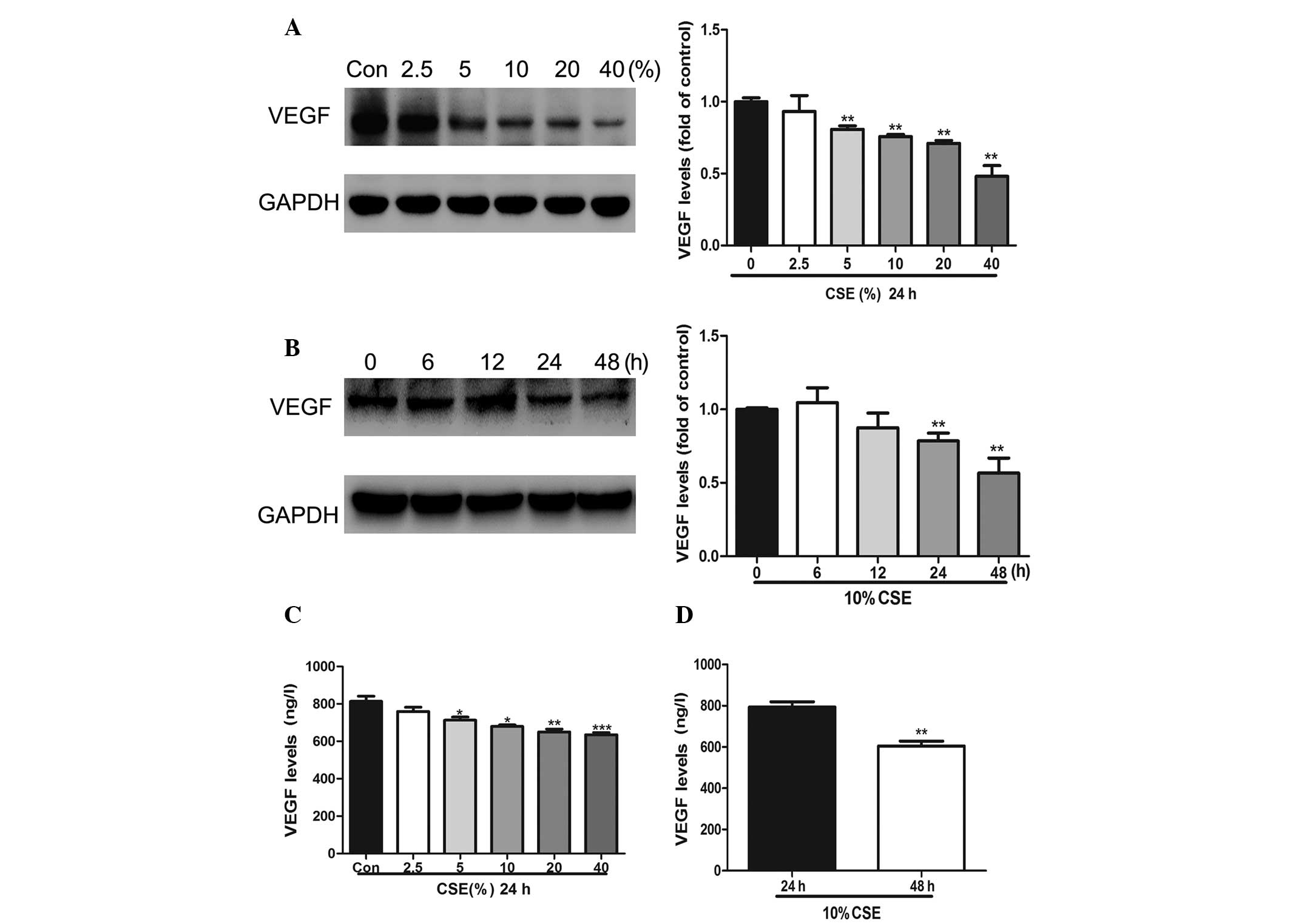
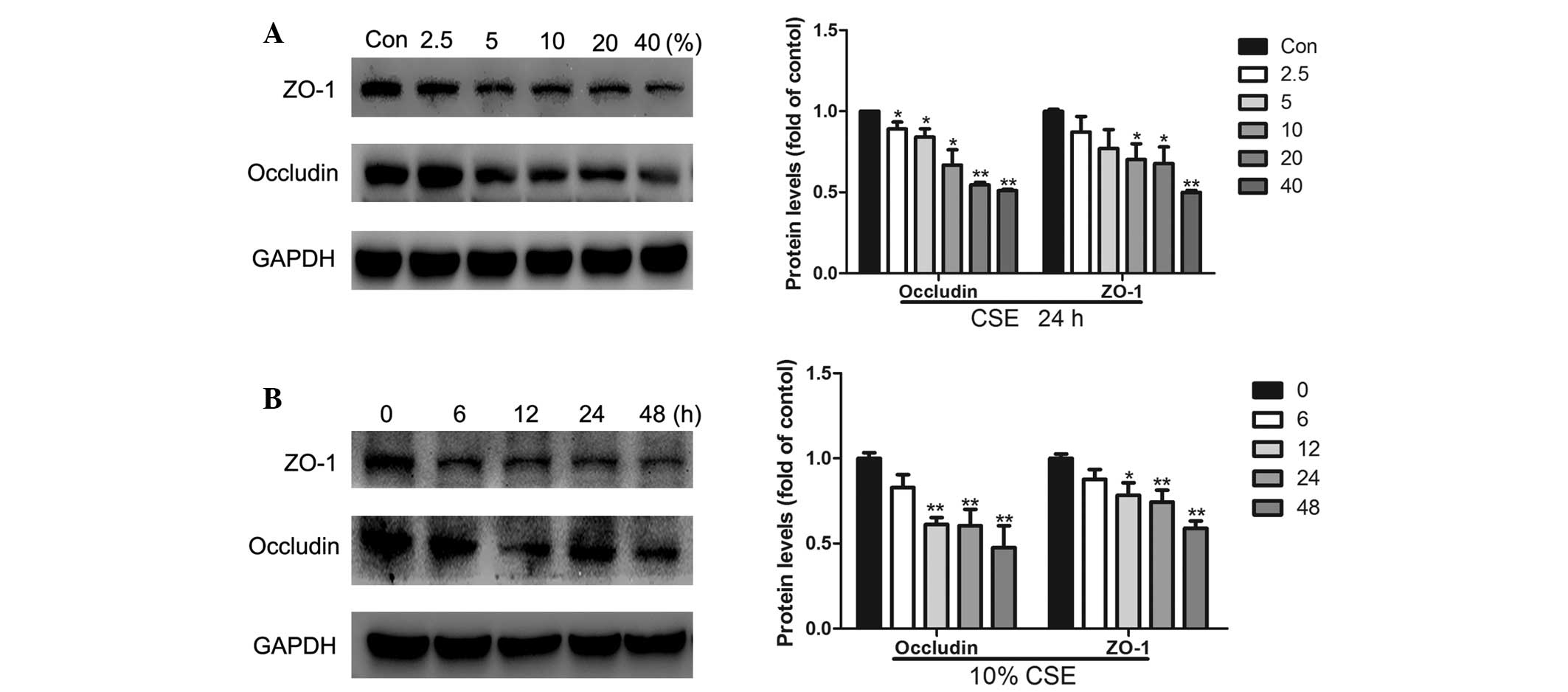
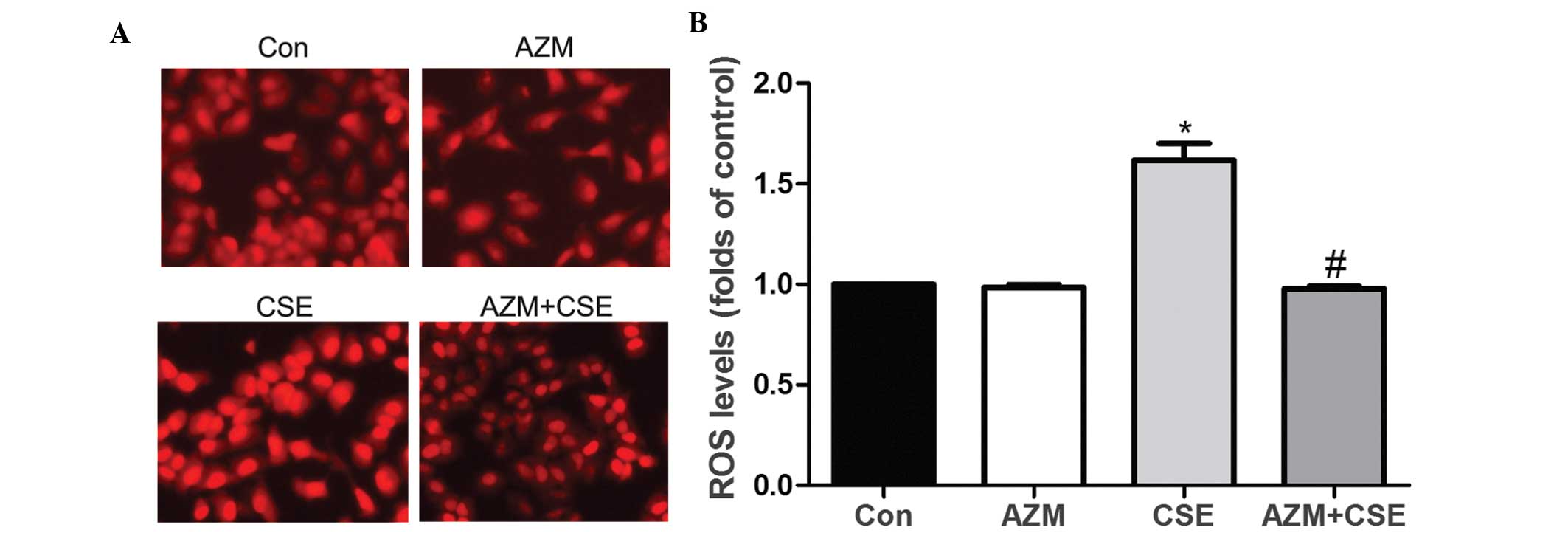
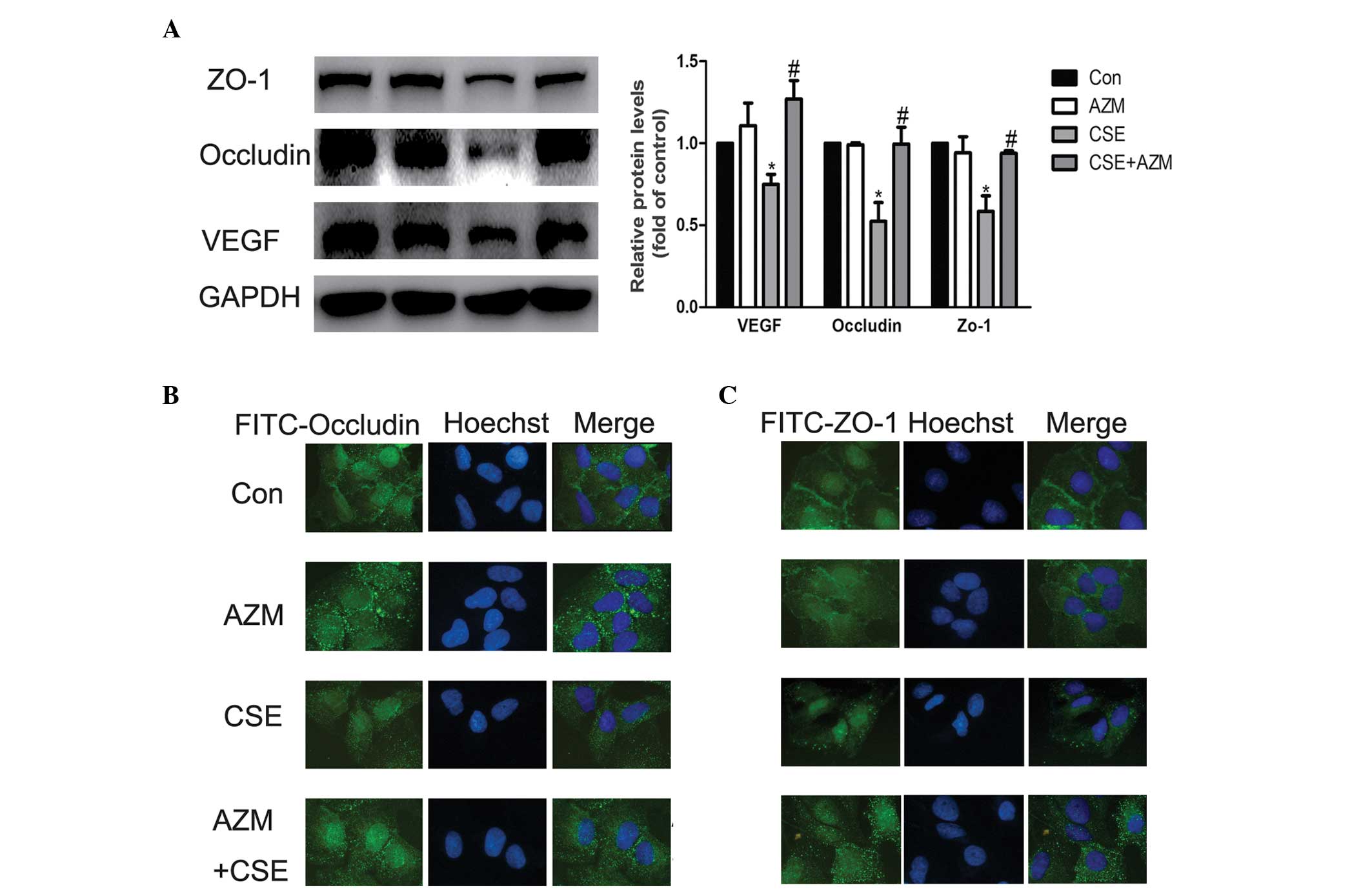
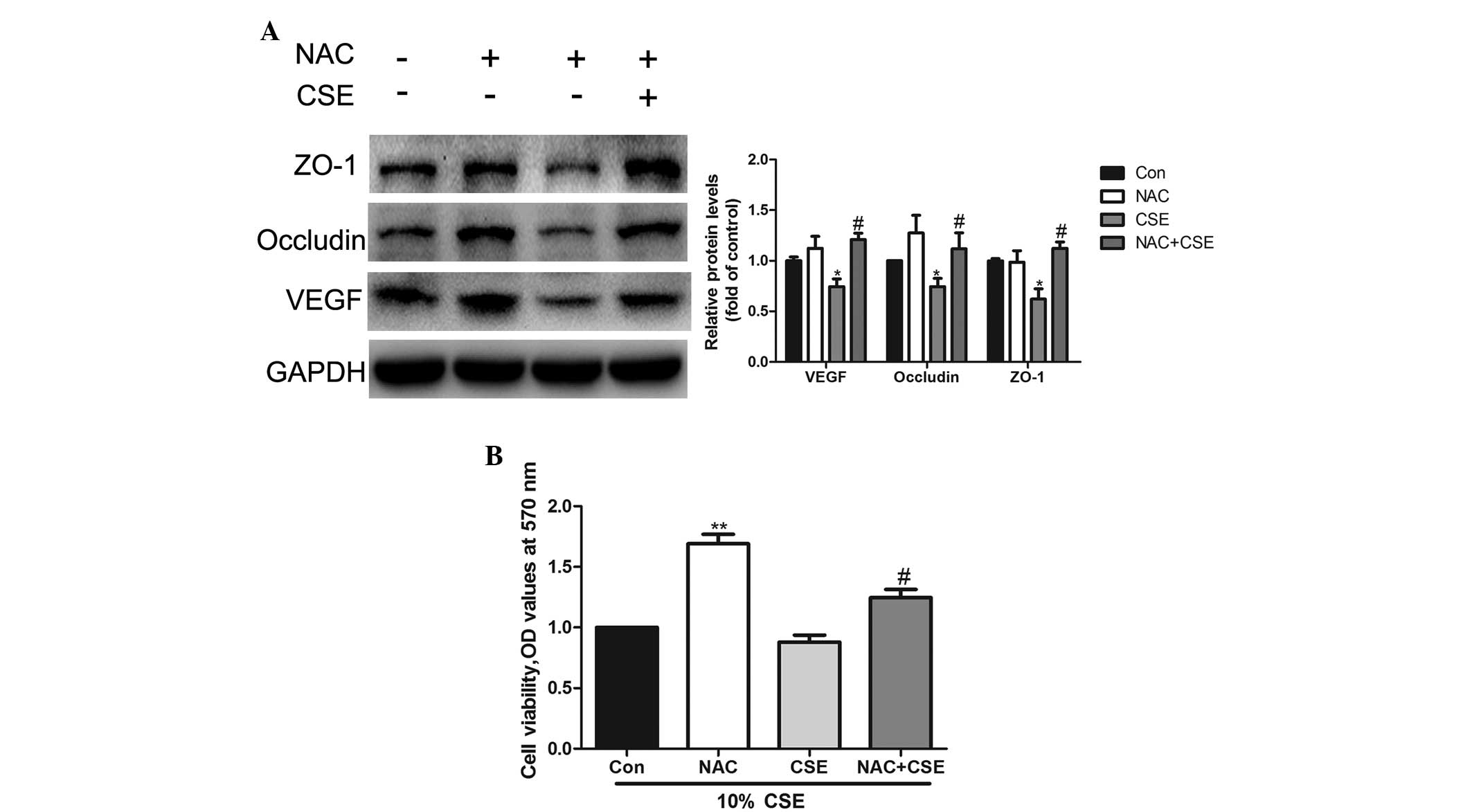
|
1
|
Hartman TE, Tazelaar HD, Swensen SJ and
Müller NL: Cigarette smoking: CT and pathologic findings of
associated pulmonary diseases. Radiographics. 17:377–390. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tuder RM, Wood K, Taraseviciene L, Flores
SC and Voekel NF: Cigarette smoke extract decreases the expression
of vascular endothelial growth factor by cultured cells and
triggers apoptosis of pulmonary endothelial cells. Chest.
117:241S–242S. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hoshino Y, Mio T, Nagai S, Miki H, Ito I
and Izumi T: Cytotoxic effects of cigarette smoke extract on an
alveolar type II cell-derived cell line. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 281:L509–L516. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kasahara Y, Tuder RM,
Taraseviciene-Stewart L, et al: Inhibition of VEGF receptors causes
lung cell apoptosis and emphysema. J Clin Invest. 106:1311–1319.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chung KF and Adcock IM: Multifaceted
mechanisms in COPD: inflammation, immunity and tissue repair and
destruction. Eur Respir J. 31:1334–1356. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Park JW, Ryter SW and Choi AM: Functional
significance of apoptosis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
COPD. 4:347–353. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Van Driessche W, Kreindler JL, Malik AB,
Margulies S, Lewis SA and Kim KJ: Interrelations/cross talk between
transcellular transport function and paracellular tight junctional
properties in lung epithelial and endothelial barriers. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 293:L520–L524. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li XY, Rahman I, Donaldson K and MacNee W:
Mechanisms of cigarette smoke induced increased airspace
permeability. Thorax. 51:465–471. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Serikov VB, Leutenegger C, Krutilina R, et
al: Cigarette smoke extract inhibits expression of peroxiredoxin V
and increases airway epithelial permeability. Inhal Toxicol.
18:79–92. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Oshitani N, Watanabe K, Nakamura S,
Fujiwara Y, Higuchi K and Arakawa T: Dislocation of tight junction
proteins without F-actin disruption in inactive Crohn’s disease.
Int J Mol Med. 15:407–410. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mankertz J, Tavalali S, Schmitz H, et al:
Expression from the human occludin promoter is affected by tumor
necrosis factor alpha and interferon gamma. J Cell Sci. 113(Pt 11):
2085–2090. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
van Baarlen P, Troost FJ, van Hemert S, et
al: Differential NF-kappaB pathways induction by Lactobacillus
plantarum in the duodenum of healthy humans correlating with immune
tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:2371–2376. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fanning AS, Jameson BJ, Jesaitis LA and
Anderson JM: The tight junction protein ZO-1 establishes a link
between the transmembrane protein occludin and the actin
cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem. 273:29745–29753. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yadav UC, Naura AS, Aguilera-Aguirre L, et
al: Aldose reductase inhibition prevents allergic airway remodeling
through PI3K/AKT/GSK3beta pathway in mice. PLoS one. 8:e574422013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Azghani AO: Pseudomonas aeruginosa and
epithelial permeability: role of virulence factors elastase and
exotoxin A. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 15:132–140. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Olivera D, Knall C, Boggs S and Seagrave
J: Cytoskeletal modulation and tyrosine phosphorylation of tight
junction proteins are associated with mainstream cigarette
smoke-induced permeability of airway epithelium. Exp Toxicol
Pathol. 62:133–143. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Voelkel NF, Vandivier RW and Tuder RM:
Vascular endothelial growth factor in the lung. Am J Physiol Lung
Cell Mol Physiol. 290:L209–L221. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mura M, Han B, Andrade CF, et al: The
early responses of VEGF and its receptors during acute lung injury:
implication of VEGF in alveolar epithelial cell survival. Crit
Care. 10:R1302006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thaikoottathil JV, Martin RJ, Zdunek J,
Weinberger A, Rino JG and Chu HW: Cigarette smoke extract reduces
VEGF in primary human airway epithelial cells. Eur Respir J.
33:835–843. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kasahara Y, Tuder RM, Cool CD, Lynch DA,
Flores SC and Voelkel NF: Endothelial cell death and decreased
expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor 2 in emphysema. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 163:737–744. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Marwick JA, Stevenson CS, Giddings J, et
al: Cigarette smoke disrupts VEGF165-VEGFR-2 receptor signaling
complex in rat lungs and patients with COPD: morphological impact
of VEGFR-2 inhibition. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
290:L897–L908. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Culić O, Eraković V and Parnham MJ:
Anti-inflammatory effects of macrolide antibiotics. Eur J
Pharmacol. 429:209–229. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Shinkai M, Henke MO and Rubin BK:
Macrolide antibiotics as immunomodulatory medications: proposed
mechanisms of action. Pharmacol Ther. 117:393–405. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vanaudenaerde BM, Vos R, Meyts I, et al:
Macrolide therapy targets a specific phenotype in respiratory
medicine: from clinical experience to basic science and back.
Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 7:279–287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rubin BK: Immunomodulatory properties of
macrolides: overview and historical perspective. Am J Med.
117(Suppl 9A): 2S–4S. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zuckerman JM: The newer macrolides:
azithromycin and clarithromycin. Infect Dis Clin North Am.
14:449–462. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Levert H, Gressier B, Moutard I, et al:
Azithromycin impact on neutrophil oxidative metabolism depends on
exposure time. Inflammation. 22:191–201. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bergamini G, Cigana C, Sorio C, et al:
Effects of azithromycin on glutathione S-transferases in cystic
fibrosis airway cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 41:199–206. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Popovic M, Janicijevic-Hudomal S,
Kaurinovic B, Rasic J and Trivic S: Antioxidant effects of some
drugs on ethanol-induced ulcers. Molecules. 14:816–826. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saint-Criq V, Rebeyrol C, Ruffin M, et al:
Restoration of chloride efflux by azithromycin in airway epithelial
cells of cystic fibrosis patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
55:1792–1793. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Faux SP, Tai T, Thorne D, Xu Y, Breheny D
and Gaca M: The role of oxidative stress in the biological
responses of lung epithelial cells to cigarette smoke. Biomarkers.
14(Suppl 1): 90–96. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rao R: Oxidative stress-induced disruption
of epithelial and endothelial tight junctions. Front Biosci.
13:7210–7226. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
You K, Xu X, Fu J, et al: Hyperoxia
disrupts pulmonary epithelial barrier in newborn rats via the
deterioration of occludin and ZO-1. Respir Res. 13:362012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schweitzer KS, Hatoum H, Brown MB, et al:
Mechanisms of lung endothelial barrier disruption induced by
cigarette smoke: role of oxidative stress and ceramides. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 301:L836–L846. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Willis BC and Borok Z: TGF-beta-induced
EMT: mechanisms and implications for fibrotic lung disease. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 293:L525–L534. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pierson T, Learmonth-Pierson S, Pinto D
and van Hoek ML: Cigarette smoke extract induces differential
expression levels of beta-defensin peptides in human alveolar
epithelial cells. Tob Induc Dis. 11:102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Noriyasu A, Konishi T, Mochizuki S, et al:
Menthol-enhanced cytotoxicity of cigarette smoke demonstrated in
two bioassay models. Tob Induc Dis. 11:182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fukano Y, Yoshimura H and Yoshida T: Heme
oxygenase-1 gene expression in human alveolar epithelial cells
(A549) following exposure to whole cigarette smoke on a direct in
vitro exposure system. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 57:411–418. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang T, Chen M and Sun T: Simvastatin
attenuates TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
human alveolar epithelial cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 31:863–874.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Heijink IH, Brandenburg SM, Postma DS and
van Oosterhout AJ: Cigarette smoke impairs airway epithelial
barrier function and cell-cell contact recovery. Eur Respir J.
39:419–428. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Milara J, Peiró T, Serrano A and Cortijo
J: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is increased in patients
with COPD and induced by cigarette smoke. Thorax. 68:410–420. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Han X, Fink MP, Yang R and Delude RL:
Increased iNOS activity is essential for intestinal epithelial
tight junction dysfunction in endotoxemic mice. Shock. 21:261–270.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mazzon E and Cuzzocrea S: Role of
TNF-alpha in lung tight junction alteration in mouse model of acute
lung inflammation. Respir Res. 8:752007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Noth R, Lange-Grumfeld J, Stuber E, et al:
Increased intestinal permeability and tight junction disruption by
altered expression and localization of occludin in a murine graft
versus host disease model. BMC Gastroenterol. 11:1092011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Asgrimsson V, Gudjonsson T, Gudmundsson GH
and Baldursson O: Novel effects of azithromycin on tight junction
proteins in human airway epithelia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
50:1805–1812. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Halldorsson S, Gudjonsson T, Gottfredsson
M, Singh PK, Gudmundsson GH and Baldursson O: Azithromycin
maintains airway epithelial integrity during Pseudomonas aeruginosa
infection. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 42:62–68. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Banerjee B, Musk M, Sutanto EN, et al:
Regional differences in susceptibiity of bronchial epithelium to
mesenchymal transition and inhibition by the macrolide antibiotic
azithromycin. PLoS one. 7:e523092012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
McCall IC, Betanzos A, Weber DA, Nava P,
Miller GW and Parkos CA: Effects of phenol on barrier function of a
human intestinal epithelial cell line correlate with altered tight
junction protein localization. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 241:61–70.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Leung JC, Chan LY, Li FF, et al: Glucose
degradation products downregulate ZO-1 expression in human
peritoneal mesothelial cells: the role of VEGF. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 20:1336–1349. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Suzuki M, Betsuyaku T, Nagai K, et al:
Decreased airway expression of vascular endothelial growth factor
in cigarette smoke-induced emphysema in mice and COPD patients.
Inhal Toxicol. 20:349–359. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mura M, dos Santos CC, Stewart D and Liu
M: Vascular endothelial growth factor and related molecules in
acute lung injury. J Appl Physiol 1985. 97:1605–1617. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kasahara Y, Iwai K, Yachie A, et al:
Involvement of reactive oxygen intermediates in spontaneous and
CD95 (Fas/APO-1)-mediated apoptosis of neutrophils. Blood.
89:1748–1753. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tuder RM, Zhen L, Cho CY, et al: Oxidative
stress and apoptosis interact and cause emphysema due to vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor blockade. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 29:88–97. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tang K, Rossiter HB, Wagner PD and Breen
EC: Lung-targeted VEGF inactivation leads to an emphysema phenotype
in mice. J Appl Physiol 1985. 97:1559–1566. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Onoue S, Ohmori Y, Endo K, Yamada S,
Kimura R and Yajima T: Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary
adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide attenuate the cigarette
smoke extract-induced apoptotic death of rat alveolar L2 cells. Eur
J Biochem. 271:1757–1767. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chatterjee S, Heukamp LC, Sioba M, et al:
Tumor VEGF:VEGFR2 autocrine feed-forward loop triggers angiogenesis
in lung cancer. J Clin Invest. 123:1732–1740. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
González-Mariscal L, Quirós M and
Diaz-Coránguez M: ZO proteins and redox-dependent processes.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 15:1235–1253. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Blasig IE, Bellmann C, Cording J, et al:
Occludin protein family: oxidative stress and reducing conditions.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 15:1195–1219. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chen RM, Chou MW and Ueng TH: Induction of
cytochrome P450 1A1 in human hepatoma HepG2 cells by
6-nitrochrysene. Toxicol Lett. 117:69–77. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Winton HL, Wan H, Cannell MB, et al: Cell
lines of pulmonary and non-pulmonary origin as tools to study the
effects of house dust mite proteinases on the regulation of
epithelial permeability. Clin Exp Allergy. 28:1273–1285. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Fu LS, Ko YH, Lin KW, Hsu JY, Chu JJ and
Chi CS: Dioscorin protects tight junction protein expression in
A549 human airway epithelium cells from dust mite damage. J
Microbiol Immunol Infect. 42:457–463. 2009.
|
|
62
|
Li XY, Donaldson K, Rahman I and MacNee W:
An investigation of the role of glutathione in increased epithelial
permeability induced by cigarette smoke in vivo and in vitro. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 149:1518–1525. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Puig F, Fuster G, Adda M, et al:
Barrier-protective effects of activated protein C in human alveolar
epithelial cells. PLoS one. 8:e569652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Tischer E, Mitchell R, Hartman T, et al:
The human gene for vascular endothelial growth factor. Multiple
protein forms are encoded through alternative exon splicing. J Biol
Chem. 266:11947–11954. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|