Introduction
Dendritic cells (DCs) include a range of subtypes,
which can induce T cell immune responses, and are the key
regulators of the human immune system (1,2).
However, the origin of DCs and the growth factor requirements
during their development remain to be fully elucidated. Studies
have demonstrated that substantial numbers of functional DCs can be
obtained from the peripheral blood or bone marrow (BM) precursor
cells through the effects of different cytokines (3,4).
Additionally, DCs can also arise from intrathymic progenitor cells,
which are able to form T lymphocytes (5,6). In
the mouse, at least two DC subpopulations have been identified in
the thymus, based on the expression of CD11c and B220, which are
termed conventional DCs (cDCs;
CD11c+B220−DCs) and plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs;
CD11c+B220+DCs), respectively. Among these,
cDCs exhibit a high capacity for antigen processing and
presentation through major histocompatibility complex class I and
II molecules to T cells (7). In
addition pDCs are potent type I interferon (IFN) producers
(7–9), which are critical in protecting the
thymus against viral infection (10,11)
and thymocytes positive selection through the secretion of IFN-α
(12,13). However, the exact properties of
thymic DCs (TDCs) remain to be fully elucidated due to the current
limitations in the expansion method in vitro. In previous
years, considerable efforts have been made to improve this. Varas
et al (14) demonstrated
that interleukin (IL)-7 can increase the production of DCs using
fetal thymus organ culture (FTOC).
Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 ligand (Flt3L), also
termed fetal liver kinase-2, is a receptor tyrosine kinase
expressed on hematopoietic stem cells and early precursors
(15). Flt3L represents a key
factor in Type I IFN-producing cell (pDC precursor)
differentiation. Studies have demonstrated that Flt3L treatment can
significantly increase the number of CD11c+ myeloid DCs
and type I IFN-producing cells (16–18).
The Flt3L pathway is, therefore, critical in DC homeostasis.
However, few studies have focused on the effect of Flt3L in DC
differentiation and development in the thymus. In the present
study, FTOC was used to imitate the thymic micro-environment, in
which TDCs are required. Combined with the method of hanging drop
culture, the effect of Flt3L on the differentiation of BM-derived
hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs) into DCs in the thymus was
further examined. The present study hypothesized that a large
number of cDCs and pDCs may be routinely generated from a small
number of CD117+ HPCs by adding Flt3L. The investigation
aimed to provide novel insight into the differentiation and
development of TDCs, which may have significant potential in
translational medicine.
Materials and methods
Mice
C57BL/6 mice and BALB/c mice were purchased from the
Experimental Animal Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
(Shanghai, China). In all experiments, 8–12 week old mice (25–30 g)
were used. A total of 40 male mice and 60 female mice were used.
All mice were bred in the animal facility of the Institute of
Medical Biotechnology (Jiangsu, China) under pathogen-free
conditions (18–22°C/lighting 10–14 h with pelleted food). The
present study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Soochow
University (Suzhou, China). All methods were performed in
accordance with the approved guidelines and experimental protocols,
approved by the Ethical Review Board of Soochow University, and the
mice used in the present study were handled in strict accordance
with recomended animal practices. The day of identification of the
vaginal plug was designated as day 0 of gestation. Mouse fetuses at
day 15 of gestation were obtained from timed pregnancies.
FTOC
The thymic lobes were aseptically removed from
15-day-old mouse fetuses using a stereoscopic microscope (Olympus
SZX7; Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). The lobes were trimmed of
surrounding mesenchyme and were organ-cultured as follows: A total
of 4–6 individual thymic lobes were placed on the surface of
0.8-µm polycarbonate filters (EMD Millipore, Madrid, Spain),
which rested on stainless steel screen sections attached to the
central well of organ tissue culture dishes (BD Biosciences, San
Diego, CA, USA). The lobes were cultured in 2 ml RPMI 1640 medium
supplemented with sodium pyruvate (1 mmol/l), streptomycin (100
mg/ml) and penicillin (100 U/ml; all purchased from Invitrogen Life
Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA), and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS;
Gibco Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA). FTOC medium was also
added with 2-deoxyguanosine (2-dGuo; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO,
USA), which was used to remove thymocytes within the embryonic
thymic lobes. The organ cultures were treated at a concentration of
1.35 mmol/l 2-dGuo. The peripheral well of the culture dishes was
filled with 2 ml sterile distilled water. The cultures were
incubated at 37°C in a humidified incubator containing 5%
CO2, and the medium was replaced daily. The cultures
were incubated at 37°C for 5–7 days in a humidified incubator
containing 5% CO2, and the medium was replaced every 2
days.
HPC purification and hanging drop
culture
A total of six male C57BL/6 mice were sacrificed by
cervical dislocation. The BM cells from the 12 femurs and tibias of
the sacrificed mice were collected and centrifuged using
Ficoll-Paque centrifugation at 450 g for 20 min to pellet
granulocytes and erythrocytes at 25°C. The BM monocytes
(6–10×106) were washed twice with phosphate-buffered
saline (PBS). The HPCs were purified via magnetic-activated cell
sorting (MACS) using a MiniMacs equipment (Miltenyi Biotec GmbH,
Teterow, Germany). The cells were pelleted and incubated with
anti-CD117 phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated cross-reactive rat
anti-mouse monoclonal antibodies (clone 3C11; 20
µl/107 cells; Miltenyi Biotec GmbH) in the
presence of 0.5% FBS in PBS at 4°C for 15 min. The marked cells
were washed with PBS and incubated with anti-phycoerythrin (PE)
microbeads (100 µl/107 cells; Miltenyi Biotec
Inc, Auburn, CA, USA) in the presence of 0.5% FBS in PBS at 4°C for
15 min. The cells were washed, resuspended and purified via MACS.
The purity of the sorted cells was determined by re-analyzing a
small sample of collected cells and a purity of >95% was
observed. The sorted CD117+HPCs and embryonic thymic
lobes from the 2-dGuo-treated FTOC system were seeded in a Terasaki
plate (Sumitomo Bakelite Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Subsequently,
the plate was turned over and incubated for 48 h at 37°C in a
humidified incubator containing 5% CO2. After 48 h
culture, the lobes in each well were collected and cultured using
the FTOC system. For following experiments, the lobes were divided
into two groups, consisting of a control group and the Flt3L group.
In the control group, the thymic lobes were cultured with complete
RPMI 1640 media (20 mmol/l HEPES buffer, 50 μmol/l 2-ME, 100 U/ml
penicillin, 100 mg/ml streptomycin, 2 mM gluta mine, 1 mmol/l
sodium pyruvate and 20% FBS) at 37°C in a humidified incubator
containing 5% CO2 for 12 days. In the Flt3L group, the
lobes were cultured with the aforementioned complete RPMI 640 media
containing Flt3L (R&D Systems Europe, Ltd., Abingdon, UK) at a
concentration of 100 ng/ml for 12 days. The medium was replaced
daily.
TDC isolation
Single cell suspensions were obtained by passing the
disrupted thymic lobes from the 12-day-FTOC system through a
25-gauge hypodermic needle (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ,
USA), and washed in PBS containing 1% FBS prior to use. A total of
1×106 thymocytes were incubated with rat anti-mouse
CD11c-PE monoclonal antibodies (clone N418;
10µl/107 cells; Miltenyi Biotec, Inc.) for 15 min
at 4°C. Following staining, the cells were washed once with PBS and
incubated with anti-PE microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec, Inc.) for 15
min at 4°C. The marked cells were washed, resuspended in PBS and
purified using MACS. Subsequently, the CD11c+ thymocytes
were resuspended in PBS containing 1% FBS prior to staining. The
CD11c+ thymocytes were separately incubated with
monoclonal Bio-conjugated mouse B220 antibody (clone RA3-6B2; 10
µl/107 cells; Miltenyi Biotec, Inc.) for ~20 min
and strepavidin-microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec, Inc.) for ~20 min at
4°C. Finally, the CD11c+B220− DCs (cDCs) and
CD11c+B220+ DCs (pDCs) were isolated using
MACS.
Immunofluorescence staining and flow
cytometric analysis
The thymic lobes from the 12-day-FTOC system were
homogenized in PBS, and a suspension of thymocytes was derived by
passing the sample through a cell filter. A total of
2×105 subsets of embryonic thymocyte cells were
incubated with saturating quantities of fluorescein isothiocyanate
(FITC)- and PE-labeled monoclonal antibodies for 30 min at 4°C. The
antibodies included anti-CD11c-FITC (clone N418), anti-CD4-PE
(clone GK1.5), anti-CD8-PE (clone 53-6.7), anti-CD117-PE (clone
2B8; anti-Ia-PE (clone NIMR-4), anti-CD8-FITC (clone 53-6.7) and
B220-biotin (clone RA3-6B2; all from eBioscience, San Diego, CA,
USA), anti-CD11c PE (clone HL3) and anti-B220 FITC (clone RA3-6B2;
BD Pharmingen, San Diego, CA, USA). Following staining, the cells
were washed twice and resuspended in PBS for analysis.
Subsequently, the cells were analyzed using a FACScalibur (BD
Biosciences, Mountain View, CA, USA).
Optical microscopy
The thymic lobes from the 12-day-FTOC system were
homogenized and sorted into cDCs(~5×105) and pDCs
(~5×105) using MACS. Subsequently, the cDCs and pDCs
were stimulated in vitro with CpG2006 (GenScript, Nanjing,
China) for 24 h at 37°C, in a humidified incubator containing 5%
CO2. Following culture for 24 h, the mature cDCs and
pDCs stained with Giemsa (Sigma-Aldrich) were observed and images
were captured under an optical microscope (Olympus CKX41; Olympus
Corporation, Tokyo, Japan).
Mixed leukocyte cultures for assaying DC
function
The culture system used in the present study has
been described previously (19).
Allogenic CD4+ T cells from the BALB/c mice were used as
responders (14). Briefly, the
adherent cells were initially removed by incubating splenic
mononuclear cells (MNCs) at 37°C for 2 h in RPMI 1640 containing
10% FBS. The nonadherent splenic MNCs (1×107) were
incubated with microbead-conjugated anti-mouse CD4 monoclonal
antibody (clone L3T4; 10 µl/107 cells; Miltenyi
Biotec GmbH) and the CD4+ T cells were separated using
MACS. The cDCs and pDCs from the FTOC system were used as
stimulators. Graded doses of stimulator cells (between 100 and
3×104 cells) were added to the T cells
(3×105) in a 96-well round-bottom tissue-culture plate
(Corning Incorporated, Corning, NY, USA). Following incubating with
or without CpG2006 at 37°C for 4 days, the cell proliferation was
determined using 3-(4,5-dimethyl
thiazolyl-2)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (Sigma-Aldrich). The
resultant absorbance at 490 nm was read using a Dynatech MR7000
microtiter plate reader (Dynatech Laboratories, Chantilly, VA,
USA).
Cytokine detection
The sorted cDCs (3×105) and pDCs
(3×105) were cultured with CpG2216 for 24 h to stimulate
cytokine production. Following the 24 h culture, the supernatants
were collected and quantified using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent
assays (ELISA). The color development was measured at 490 nm using
a Dynatech MR7000 microtiter plate reader. The mouse IL-12 p70
ELISA kit was purchased from BioSource International (Camarillo,
CA, USA), whereas the mouse IFN-α ELISA kit was purchased from PBL
Biomedical Laboratories (Piscataway, NJ, USA).
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain
reaction (RT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from 1×106 of the
indicated cells using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen Life
Technologies), according to the manufacturer's instructions.
First-strand complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized from 200 ng
total RNA in a 25 µl reaction volume with the use of random
primers (Takara Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Dalian, China) using
Bio-Rad gradient PCR (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA,
USA). Subsequently, the cDNA was amplified for 25 cycles consisting
of 94°C for 30 sec, 58°C for 30 sec and 72°C for 45 sec, with a
pair of oligonucleotide primers for the corresponding toll-like
receptor (TLR). A glyceralde-hyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH)
transcript was amplified in parallel as a control. The
corresponding oligonucleotide primer sequences were as follows:
TLR7, forward 5′-AGAGGCCCATGTGATCGTG-3′ and reverse
5′-CGAGGGCAATTTCCACTTAGG-3′; TLR9, forward
5′-AACATGGTTCTCCGTCGAAGG-3′ and reverse 5′-GTAGATGCAGTTCCCGTCC-3′;
and GAPDH, forward 5′-CCTAAGGCCAACCGTGAAAAG-3′ and reverse
5′-TCTTCATGGTGCTAGGAGCCA-3′. The PCR products were fractionated on
a 1.5% agarose gel (Sigma-Aldrich) and visualized using ethidium
bromide (0.5 µg/ml; Sigma-Aldrich) staining.
Statistical analysis
All data are expressed as the mean ± standard error
of the mean. Student's t-test and a one-way analysis of
variance were used to assess the difference between the two groups
or among multiple groups, respectively. All data were analyzed
using SPSS 16.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). P<0.05 was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
BM-derived CD117+ HPCs
differentiate into TDCs in the FTOC system in the presence of
Flt3L
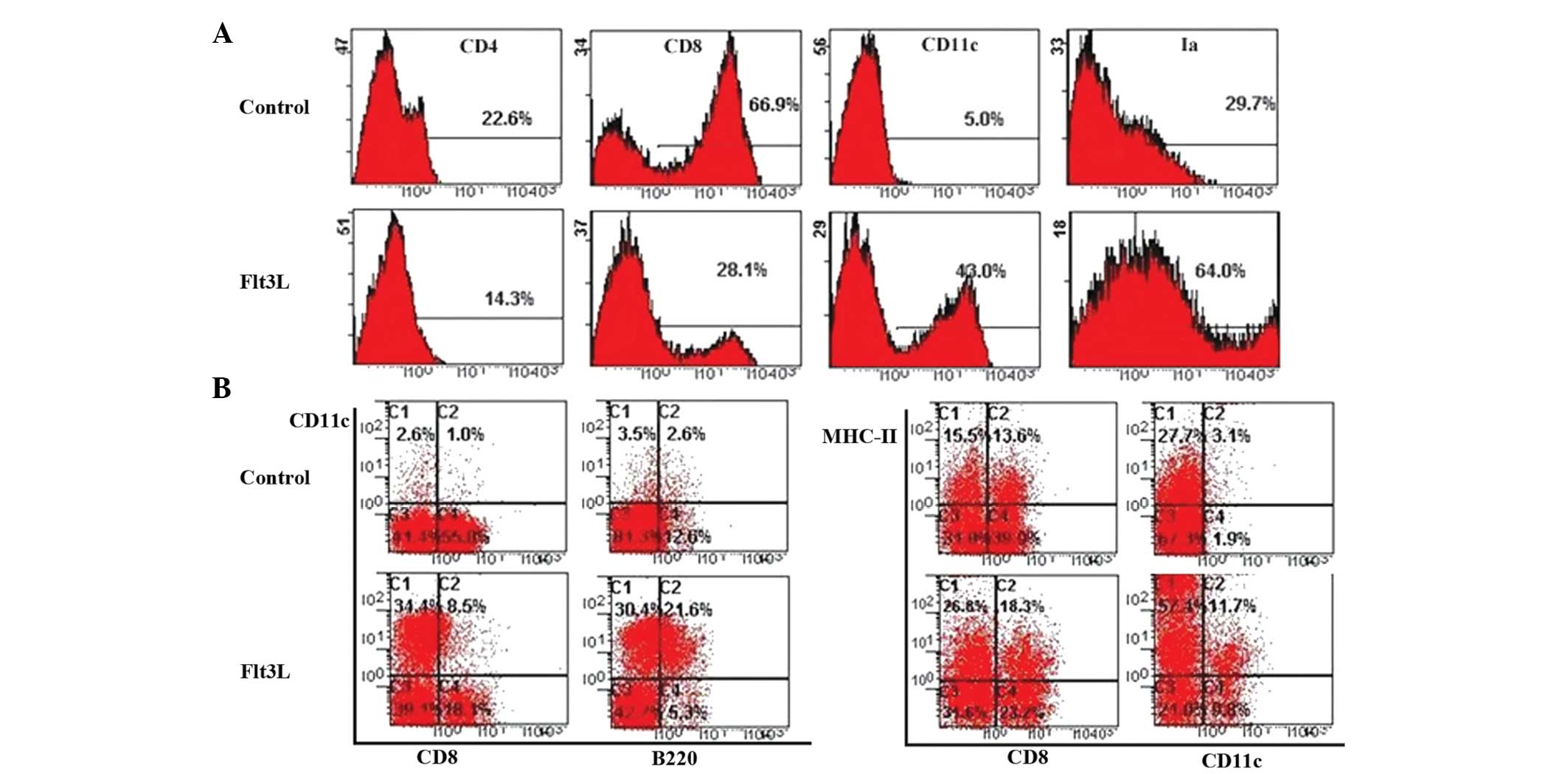
To determine the effect of Flt3L on the
differentiation of HPCs into TDCs, BM CD117+ HPCs were
cultured using the FTOC system in the presence of Flt3L. The number
of thymocytes from the Flt3L-treated group was twice the number
observed in the control group. This suggested that Flt3L
contributed to HPC proliferation in the FTOC system.
To further characterize the subset of proliferated
thymic cells, different cell surface markers on the thymocytes were
detected following 12 days of culture with or without Flt3L. Flow
cytometric analysis revealed that the expression of CD11c in the
Flt3L group was approximately nine times higher tha that in the
control group (Fig. 1A). The
proportion of CD8-CD11c+ thymocytes increased in the
presence of Flt3L (Fig. 1B).
Similarly, the Ia+CD11c+ thymocytes from the
Flt3L-treated FTOC proliferated faster than those in control
cultures. In addition, the proportion of cDCs was also nine times
higher in the Flt3L-treated group than in the control group, and
the proportion of pDCs was eight times higher (Fig. 1B). These results confirmed the
existence of a large number of TDCs (cDCs and pDCs) in the
Flt3L-treated group.
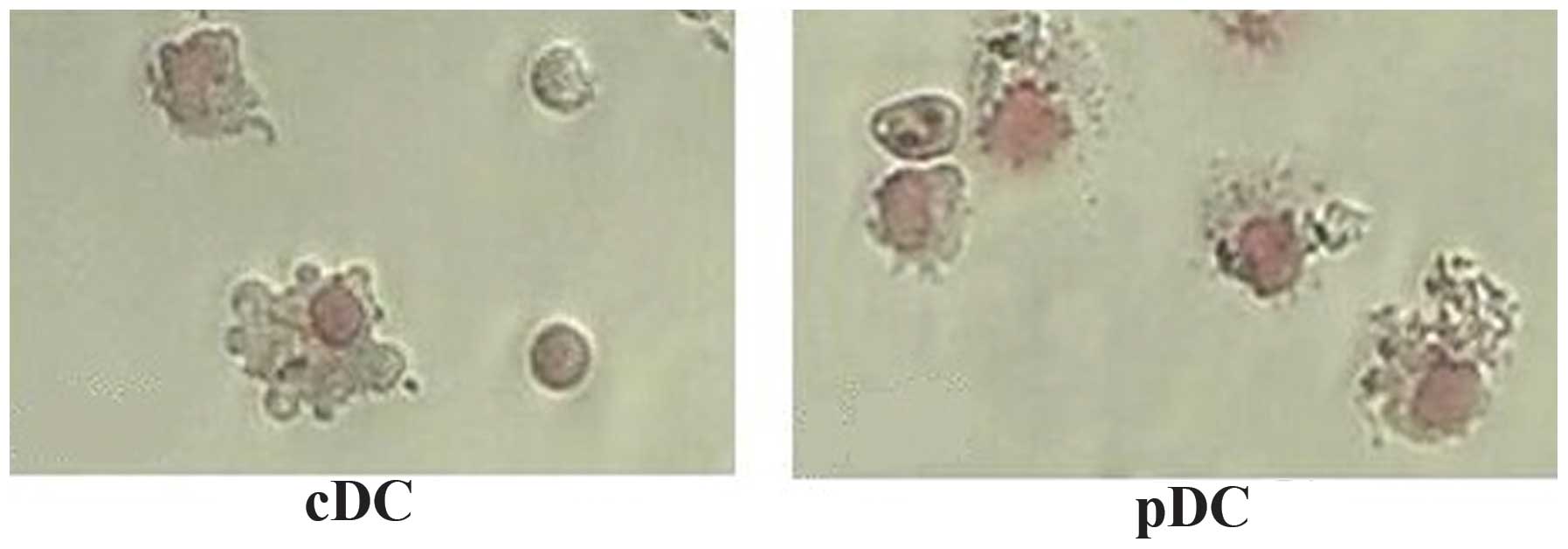
Morphological examination was performed to confirm
the nature of the identified cells. Freshly isolated
CD11c+B220+ pDCs from the FTOC system
exhibited a round shape with few membrane projections, whereas the
CD11c+B220-cDCs exhibited a large, cytoplasm-rich,
irregular shape with numerous membrane projections. Followin
overnught culture in the presence of CpG2006, these two types of
TDCs were observed to exhibit a typical DC morphology with
irregular membranes, bean-like nuclei and fine dendritic processes
(Fig. 2). The results of the
Giemsa staining indicated that the matured thymic cDCs and pDCs
presented with the specific morphology of DCs.
TDCs from Flt3L-administered FTOC promote
CD4+ T cell proliferation
To assess the functional properties of TDCs from
Flt3L-treated FTOC, purified CD4+T cells were used as
responder cells to evaluate the allostimulatory capacity of the
thymocytes generated in the 12-day Flt3L-treated FTOC system. As
shown in Fig. 3, the
CD11c+ DCs were capable of stimulating the proliferation
of allogeneic T cells with or without CpG2006 treatment. However,
CD11c+ DCs without Cp2006 treatment exhibited a
relatively poor stimulatory capacity. This indicated that the
thymocytes cultured in Flt3L-treated cultures were efficient
antigen-presenting cells.
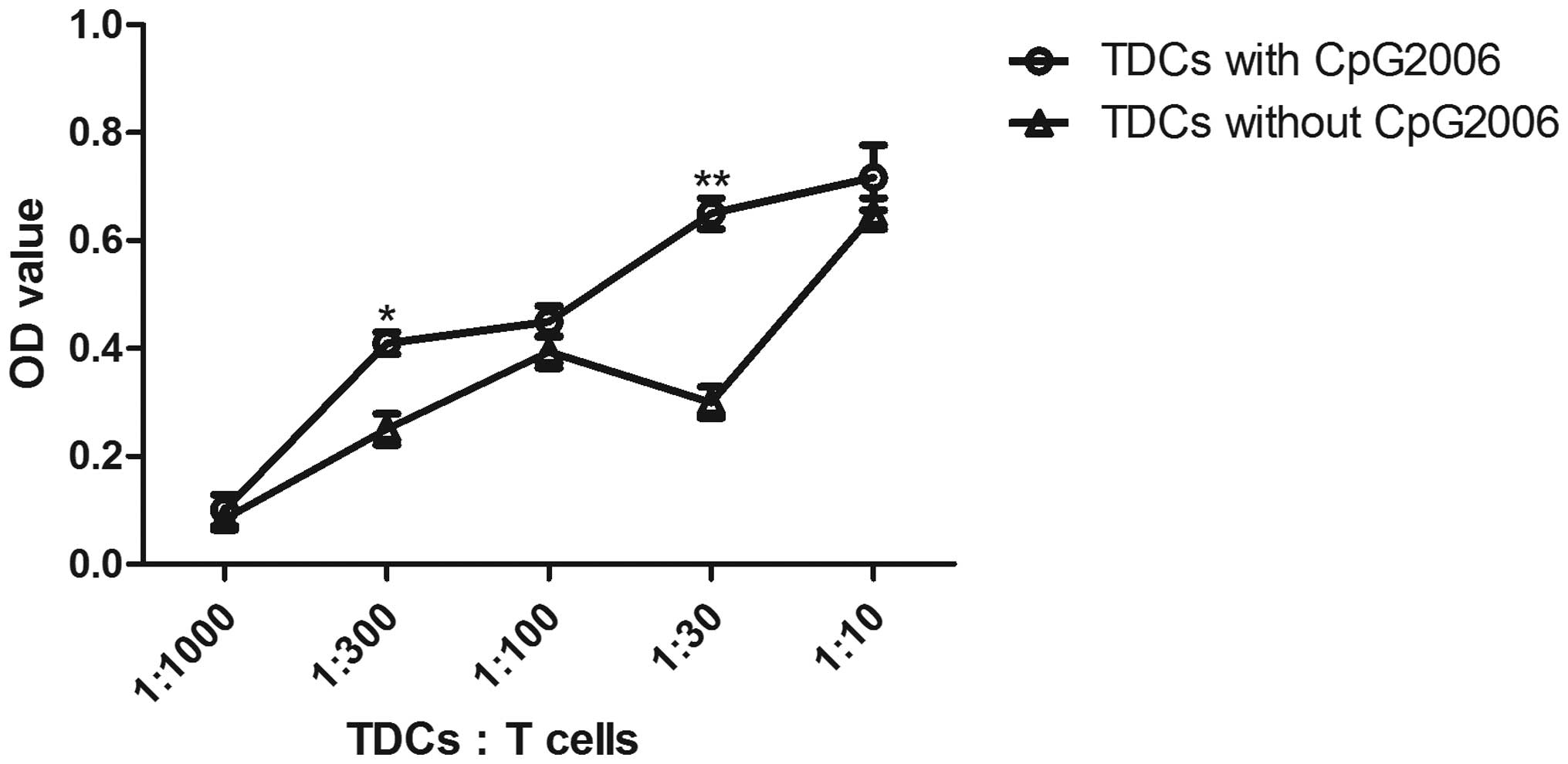
To further examine the potential of cDCs and pDCs in
stimulating the proliferation of allogeneic T cells, mixed
leukocyte cultures were performed. As shown in Fig. 4, the cDCs subjected to CpG2006
treatment proliferated faster than the pDCs. Therefore, cDCs and
pDCs from the Flt3L-administered FTOC system exhibited different
potentials in stimulating the proliferation of allogeneic T
cells.
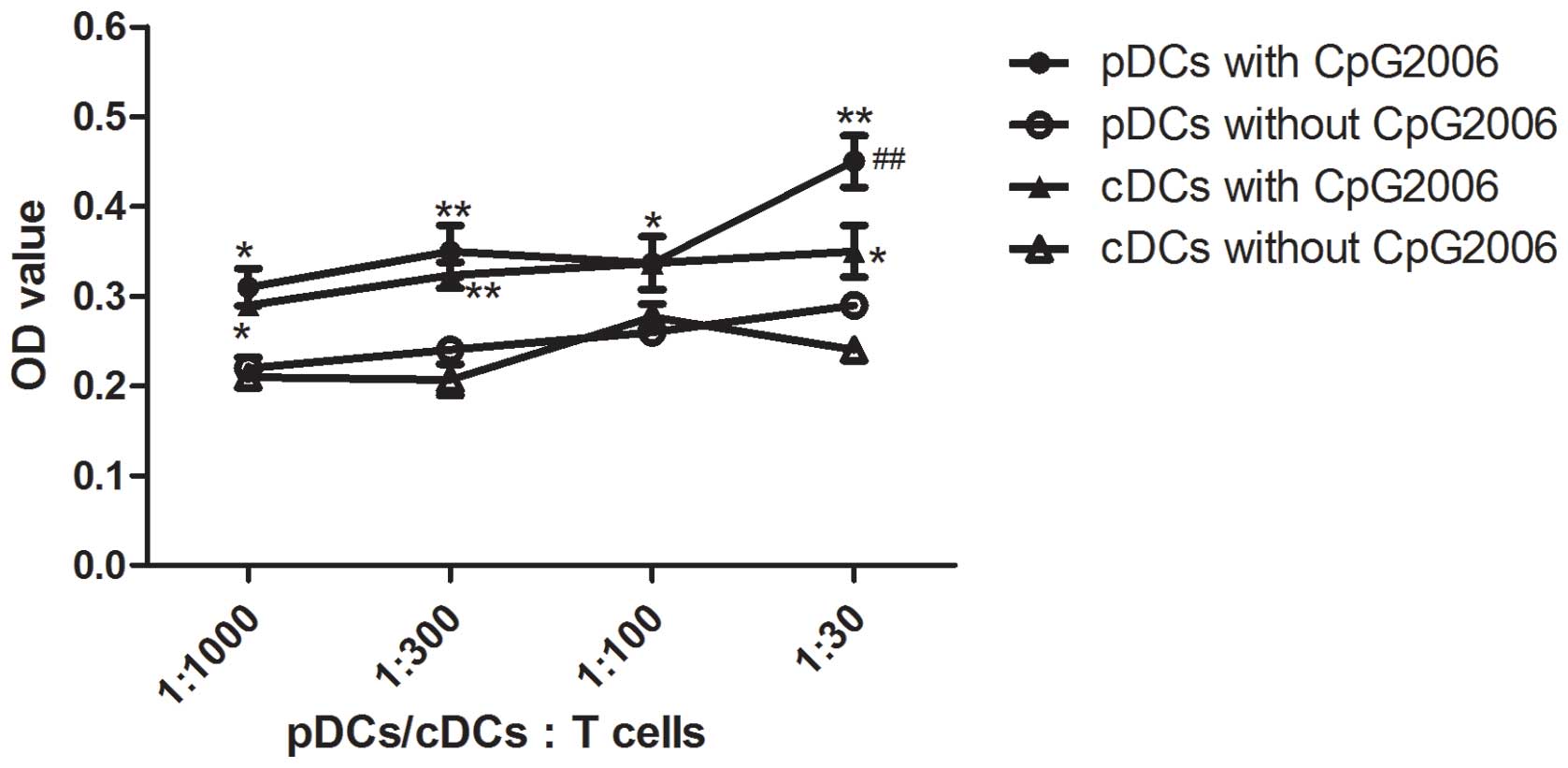 | Figure 4Allogenic mixed lymphocyte reaction.
The allogenic mixed lymphocytes reaction was performed using
purified CD4+ T cells (3×105 cells/well in
96-round-well plate) as responder cells. Thymic pDCs from
Flt3L-treated FTOC with and without CpG2006 stimulation, and thymic
cDCs from Flt3L-treatd FTOC with and without CpG2006, stimulation
were examined. All the indicated cell subpopulations were purified
or generated. The results are representative of three independent
experiments. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01, pDCs
with CpG2006, vs. pDCs without CpG2006; *P<0.05 and
**P<0.01, cDCs with CpG2006, vs. cDCs without
CpG2006. ##P<0.01, pDCs with CpG2006, vs. cDCs with
CpG2006. FTOC, fetal thymus organ culture; Flt3L, Fms-like tyrosine
kinase 3 ligand; cDC, conventional dendritic cell; pDC,
plasmacytoid dendritic cell; OD, optical density. |
Cytokine production by thymic cDCs and
pDCs
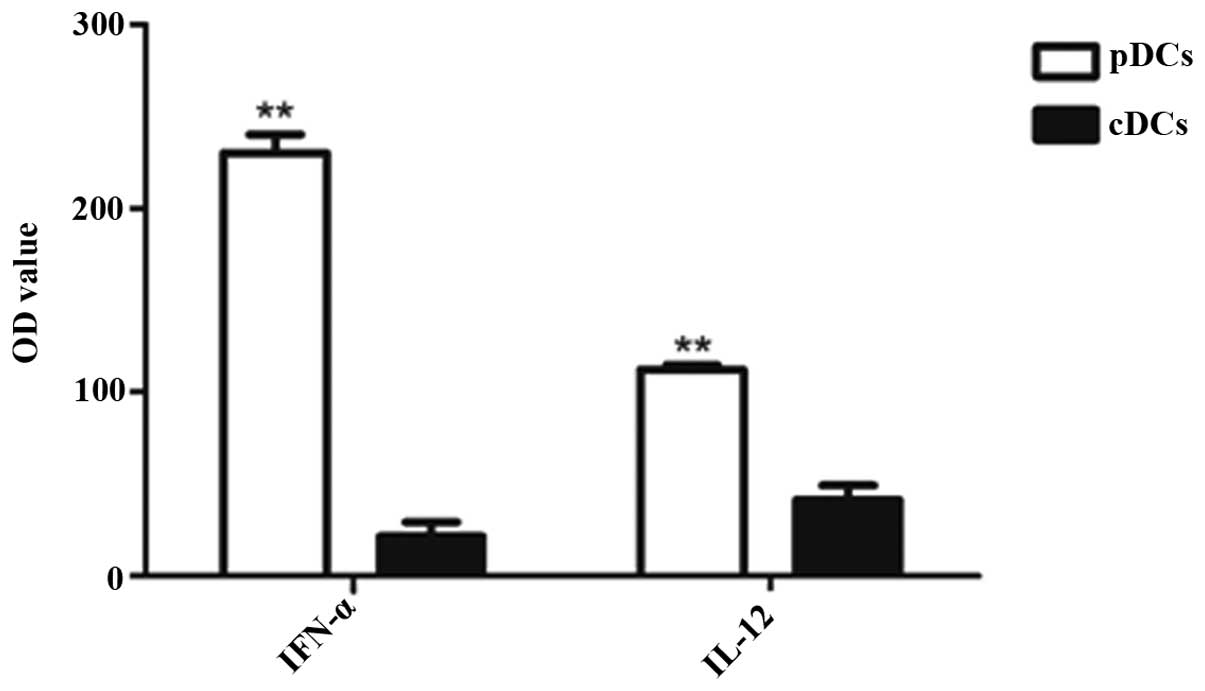
The production of particular cytokines is an
indication of the intrathymic role of TDCs, aside from antigen
presentation. However, only a small number of cytokines produced by
TDCs in situ in a steady state have been observed until now.
In the present study, thymic cDCs and pDCs were stimulated with CpG
oligonucleotides (CpG2216) to assess their cytokine secretion
capacities. As shown in Fig. 5,
the cDCs secreted a low level of IL-12 and IFN-α, whereas the pDCs
secreted substantial quantities of IFN-α, but not IL-12. This
indicated that the thymic pDCs and cDCs exhibited diverse
capacities in IFN-α and IL-12 production.
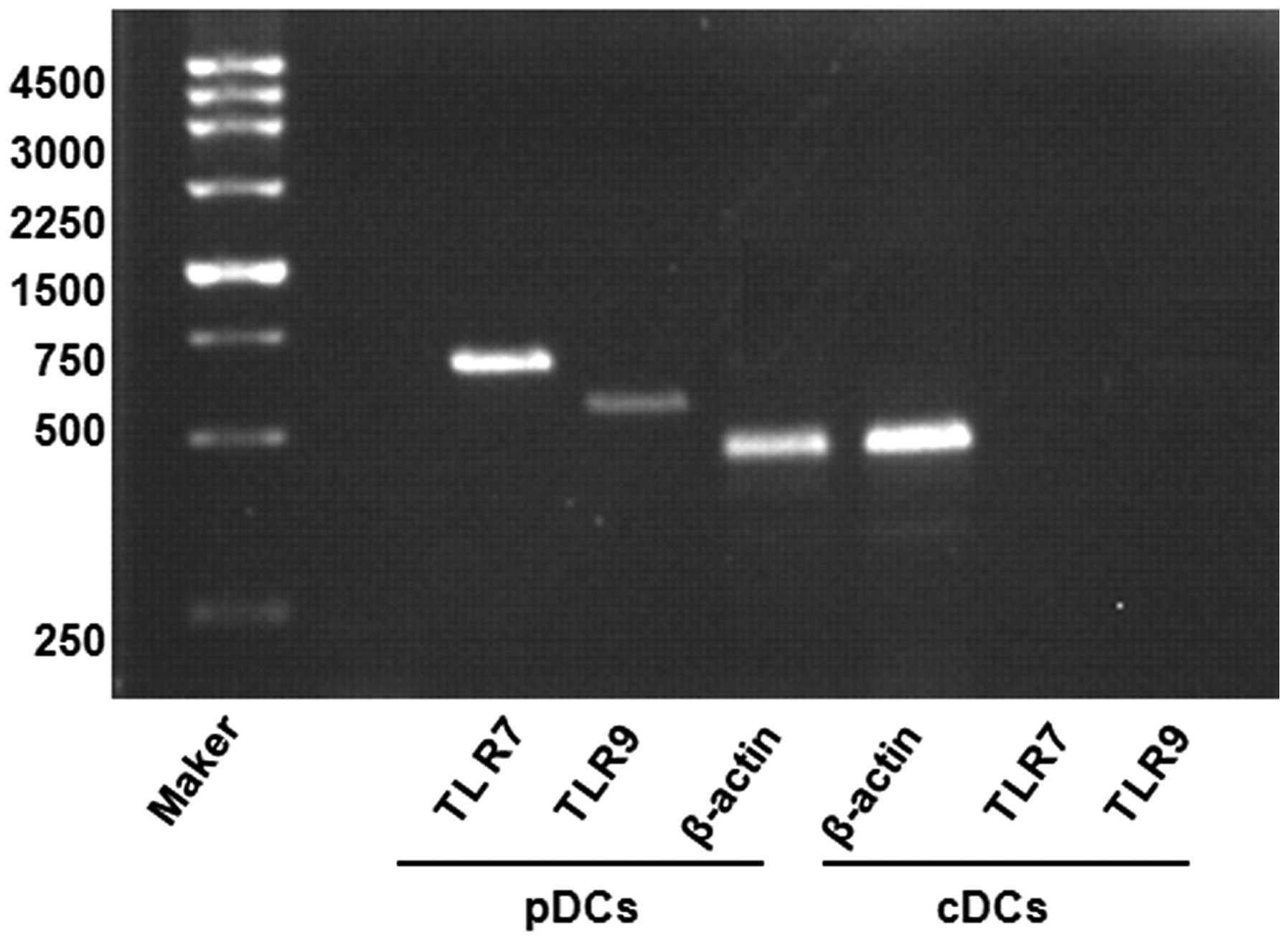
In addition, RT-PCR was applied to assess the
expression of levels of TLR7 and TLR9 in the thymic cDCs and pDCs
stimulated by CpG2216. It was found that the thymic pDCs, but not
the cDCs, expressed high levels of TLR7 and TLR9 (Fig. 6). These results are consistent with
those of previous studies (20).
Therefore, the thymic cDCs and pDCs from the culture system
presented with functional capacities in cytokine production.
Discussion
DCs are critical in immunotherapy against
infections. However, the limited availability of DCs is the
predominant restriction in biological or clinical investigations.
Several reports have used in vitro differentiated
myeloid-derived DCs (21), which
are induced principally by granulocyte-macrophage
colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) in combination with other
cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-4 and stem cell
factor (16,22,23).
Flt3L and GM-CSF are important cytokines during DC development in a
steady state, and the two are expressed in DC progenitors (24). Notably, GM-CSF is expressed
predominantly in monocytes, cDCs and skin DCs, whereas Flt3 is
expressed in cDCs and pDCs (25).
In the thymus, Flt3 is expressed by a subset of early T lineage
progenitors (ETPs), and these Flt3+ ETPs represent the
earliest intrathymic T lineage progenitors identified thus far
(26) In addition, HPCs exhibit
different mobilization kinetics in response to Flt3L, resulting in
the preferential mobilization of HPCs at day 5 followed by HPC
mobilization at day 10 (27).
Although DCs are traditionally generated in vitro with
cytokine cocktails containing GM-CSF, with or without IL-4, the
in vivo expansion of DC populations is usually accomplished
through the administration of the Flt3L growth factor (3,4).
Additionally, DCs can arise from lymphoid- and myeloid-committed BM
precursors, which lack markers of differentiated immune lineage
cells and express the Flt3 receptor (lin-flt3+)
(28). Few studies have used Flt3L
in DC expansion in vitro.
In the present study, comprehensive analysis of the
role of Flt3L on the development of thymic DCs (cDCs and pDCs) from
BM-derived HPCs was performed. In order to remove pre-thymocytes in
the embryonic thymic lobes, freshly collected thymic lobes were
treated with 2-dGuo prior to seeding the BM-derived HPCs within a
hanging drop culture system. In the Flt3L-FTOC system, two distinct
DC subsets (cDCs and pDCs) were characterized from the BM-derived
HPCs, which were separately identified as
CD11c+B220− and
CD11c+B220+ in the mouse thymus. Notably,
Flt3L treatment was capable of expanding cDCs and pDCs,
particularly, pDCs. Following overnight culture in the presence of
CpG2006, the cDCs and pDCs generated by the Flt3L-FTOC system
exhibited a typical DC morphology with irregular membranes,
bean-like nuclei and fine dendritic projections. Functionally,
these TDCs (cDCs and pDCs) from the Flt3L-FTOC system stimulated
allogenic T cell proliferation.
The present study also observed that the pDCs, but
not the cDCs, from the Flt3L-FTOC system expressed high levels of
TLR7 and TLR9. This suggested that thymic pDCs are a major
component of TLR7- and TLR9-dependent inflammation. The
TLR7/9-dependent pathway appears to be a predominant mode of
nucleic acid sensing in pDCs, although additional DNA sensors,
including DHX9/DHX36 have been suggested (29). pDCs are innate immune cells, which
circulate in the blood and lymphoid tissues and, upon stimulation
by unmethylated CpG DNA through the engagement of TLR7 and TLR9,
pDCs can be specialized to produce substantial quantities of IFN-α
(30,31). The present study also observed that
these pDCs secreted higher levels of IL-12 and IFN-α, compared with
the cDCs following stimulation with CpG2216. These findings
suggested that pDCs are more important in protecting the thymus
against viral infection than cDCs.
In conclusion, the current limitations in isolating
large numbers of DCs has been the predominant obstacle in
investigating the biological functions and clinical applications of
DCs. The present study demonstrated that the Flt3L-FTOC system was
able to support in vitro expansion of a novel TDC lineage in
culture from a number of CD117+ HPCs. Notably, this
culture system provided the distinct expansion of thymic pDCs,
however, it was not able to produce pure cDCs or pDCs. Therefore,
this culture system requires improvement to produce a single subset
of DCs. These findings have important implications for the current
opinion that in vitro-generated pDCs may offer potential in
translational medicine.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural
Science Foundation of China Grants (grant nos. 30400395 and
31500718) and the Projects of Soochow Science And Technology Plans
(grant no. SYS201438).
References
|
1
|
Lee HK and Iwasaki A: Innate control of
adaptive immunity: Dendritic cells and beyond. Semin Immunol.
19:48–55. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shortman K and Naik SH: Steady-state and
inflammatory dendritic-cell development. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:19–30.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gilliet M, Boonstra A, Paturel C,
Antonenko S, Xu XL, Trinchieri G, O'Garra A and Liu YJ: The
development of murine plasmacytoid dendritic cell precursors is
differentially regulated by FLT3-ligand and granulocyte/macrophage
colony-stimulating factor. J Exp Med. 195:953–958. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Miller G, Pillarisetty VG, Shah AB, Lahrs
S and DeMatteo RP: Murine Flt3 ligand expands distinct dendritic
cells with both tolerogenic and immunogenic properties. J Immunol.
170:3554–3564. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Luche H, Ardouin L, Teo P, See P, Henri S,
Merad M, Ginhoux F and Malissen B: The earliest intrathymic
precursors of CD8alpha (+) thymic dendritic cells correspond to
myeloid-type double-negative 1c cells. Eur J Immunol. 41:2165–2175.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ardavin C, Wu L, Li CL and Shortman K:
Thymic dendritic cells and T cells develop simultaneously in the
thymus from a common precursor population. Nature. 362:761–763.
1993. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kadowaki N, Antonenko S and Liu YJ:
Distinct CpG DNA and polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid
double-stranded RNA, respectively, stimulate CD11c-type 2 dendritic
cell precursors and CD11c+ dendritic cells to produce type I IFN. J
Immunol. 166:2291–2295. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Diebold SS, Kaisho T, Hemmi H, Akira S and
Reis e Sousa C: Innate antiviral responses by means of
TLR7-mediated recognition of single-stranded RNA. Science.
303:1529–1531. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jarrossay D, Napolitani G, Colonna M,
Sallusto F and Lanzavecchia A: Specialization and complementarity
in microbial molecule recognition by human myeloid and
plasma-cytoid dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. 31:3388–3393. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bendriss-Vermare N, Barthélémy C, Durand
I, Bruand C, Dezutter-Dambuyant C, Moulian N, Berrih-Aknin S, Caux
C, Trinchieri G and Brière F: Human thymus contains
IFN-alpha-producing CD11c (−), myeloid CD11c (+) and mature
interdigitating dendritic cells. J Clin Invest. 107:8358442001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gurney KB, Colantonio AD, Blom B, Spits H
and Uittenbogaart CH: Endogenous IFN-alpha production by
plasmacytoid dendritic cells exerts an antiviral effect on thymic
HIV-1 infection. J Immunol. 173:7269–7276. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fohrer H, Audit IM, Sainz A, Schmitt C,
Dezutter-Dambuyant C and Dalloul AH: Analysis of transcription
factors in thymic and CD34+ progenitor-derived plasmacytoid and
myeloid dendritic cells: Evidence for distinct expression profiles.
Exp Hematol. 32:104–112. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Keir ME, Stoddart CA, Linquist-Stepps V,
Moreno ME and McCune JM: IFN-alpha secretion by type 2 predendritic
cells up-regulates MHC class I in the HIV-1-infected thymus. J
Immunol. 168:325–331. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Varas A, Vicente A, Sacedón R and Zapata
AG: Interleukin-7 influences the development of thymic dendritic
cells. Blood. 92:93–100. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Adolfsson J, Borge OJ, Bryder D,
Theilgaard-Mönch K, Astrand-Grundström I, Sitnicka E, Sasaki Y and
Jacobsen SE: Upregulation of Flt3 expression within the bone marrow
Lin (−) Sca1 (+) c-kit (+) stem cell compartment is accompanied by
loss of self-renewal capacity. Immunity. 15:659–669. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Maraskovsky E, Brasel K, Teepe M, Roux ER,
Lyman SD, Shortman K and McKenna HJ: Dramatic increase in the
numbers of functionally mature dendritic cells in Flt3
ligand-treated mice: Multiple dendritic cell subpopulations
identified. J Exp Med. 184:1953–1962. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
O'Keeffe M, Hochrein H, Vremec D, Pooley
J, Evans R, Woulfe S and Shortman K: Effects of administration of
progeni-poietin 1, Flt-3 ligand, granulocyte colony-stimulating
factor and pegylated granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating
factor on dendritic cell subsets in mice. Blood. 99:2122–2130.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen W, Antonenko S, Sederstrom JM, Liang
X, Chan AS, Kanzler H, Blom B, Blazar BR and Liu YJ: Thrombopoietin
cooperates with FLT3-ligand in the generation of plasma-cytoid
dendritic cell precursors from human hematopoietic progenitors.
Blood. 103:2547–2553. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Suss G and Shortman K: A subclass of
dendritic cells kills CD4 T cells via Fas/Fas-ligand-induced
apoptosis. J Exp Med. 183:1789–1796. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ganguly D, Chamilos G, Lande R, Gregorio
J, Meller S, Facchinetti V, Homey B, Barrat FJ, Zal T and Gilliet
M: Self-RNA-antimicrobial peptide complexes activate human
dendritic cells through TLR7 and TLR8. J Exp Med. 206:1983–1994.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cella M, Sallusto F and Lanzavecchia A:
Origin, maturation and antigen presenting function of dendritic
cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 9:10–16. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Romani N, Reider D, Heuer M, Ebner S,
Kämpgen E, Eibl B, Niederwieser D and Schuler G: Generation of
mature dendritic cells from human blood. An improved method with
special regard to clinical applicability. J Immunol Methods.
196:137–151. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou LJ and Tedder TF: CD14+ blood
monocytes can differentiate into functionally mature CD83+
dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:2588–2592. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kingston D, Schmid MA, Onai N, Obata-Onai
A, Baumjohann D and Manz MG: The concerted action of GM-CSF and
Flt3-ligand on in vivo dendritic cell homeostasis. Blood.
114:835–843. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
McKenna HJ, Stocking KL, Miller RE, Brasel
K, De Smedt T, Maraskovsky E, Maliszewski CR, Lynch DH, Smith J,
Pulendran B, et al: Mice lacking flt3 ligand have deficient
hematopoiesis affecting hematopoietic progenitor cells, dendritic
cells and natural killer cells. Blood. 95:3489–3497.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sambandam A, Maillard I, Zediak VP, Xu L,
Gerstein RM, Aster JC, Pear WS and Bhandoola A: Notch signaling
controls the generation and differentiation of early T lineage
progenitors. Nat Immunol. 6:663–670. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
de Kruijf EJ, Hagoort H, Velders GA, Fibbe
WE and van Pel M: Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells are
differentially mobilized depending on the duration of Flt3-ligand
administration. Haematologica. 95:1061–1067. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Karsunky H, Merad M, Cozzio A, Weissman IL
and Manz MG: Flt3 ligand regulates dendritic cell development from
Flt3+ lymphoid and myeloid-committed progenitors to Flt3+ dendritic
cells in vivo. J Exp Med. 198:305–313. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim T, Pazhoor S, Bao M, Zhang Z,
Hanabuchi S, Facchinetti V, Bover L, Plumas J, Chaperot L, Qin J
and Liu YJ: Aspartate-g lutamate-alanine-histidine box motif
(DEAH)/RNA helicase A helicases sense microbial DNA in human
plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:15181–15186. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Beignon AS, McKenna K, Skoberne M, Manches
O, DaSilva I, Kavanagh DG, Larsson M, Gorelick RJ, Lifson JD and
Bhardwaj N: Endocytosis of HIV-1 activates plasmacytoid dendritic
cells via Toll-like receptor-viral RNA interactions. J Clin Invest.
115:3265–3275. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Heil F, Hemmi H, Hochrein H, Ampenberger
F, Kirschning C, Akira S, Lipford G, Wagner H and Bauer S:
Species-specific recognition of single-stranded RNA via toll-like
receptor 7 and 8. Science. 303:1526–1529. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|