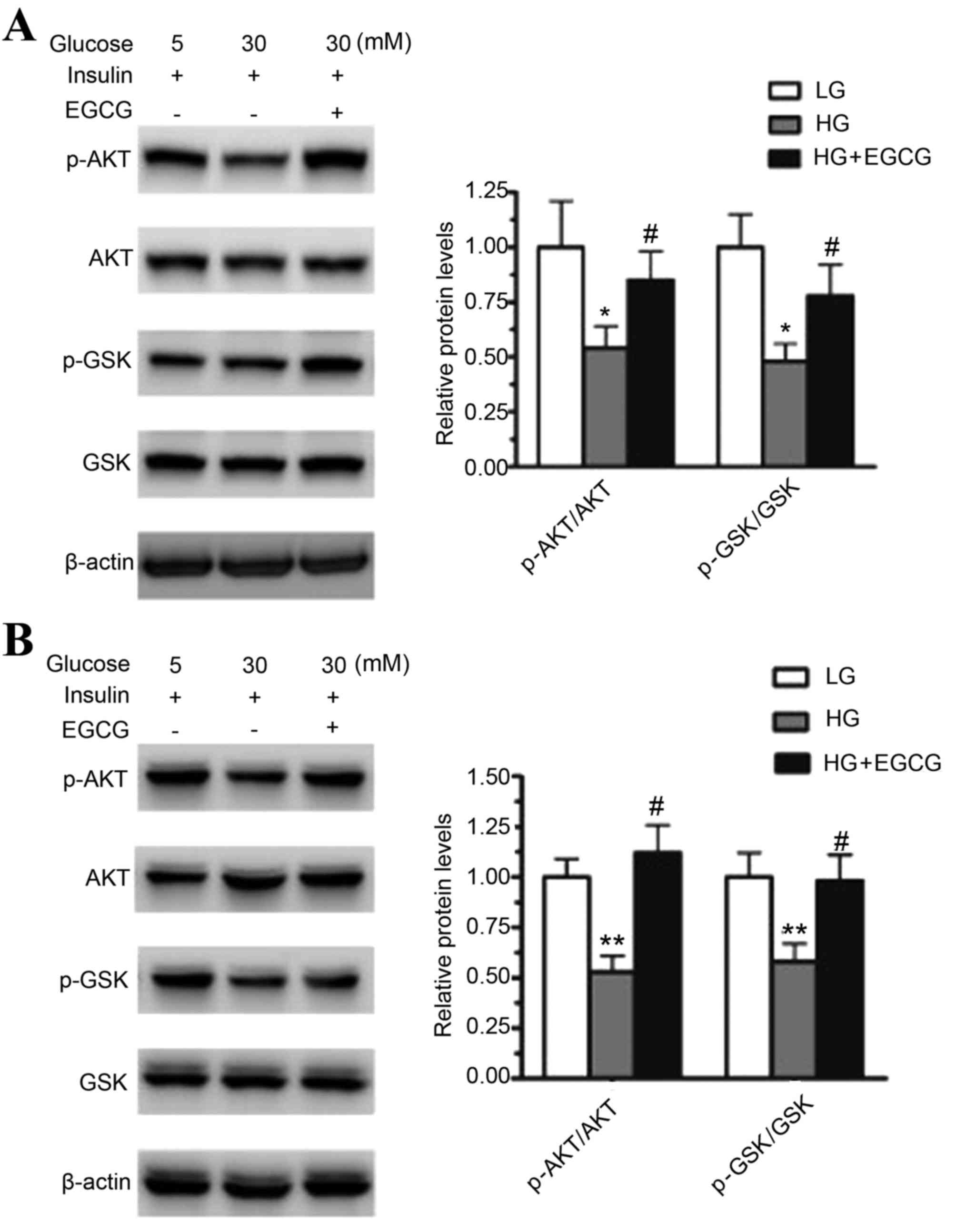
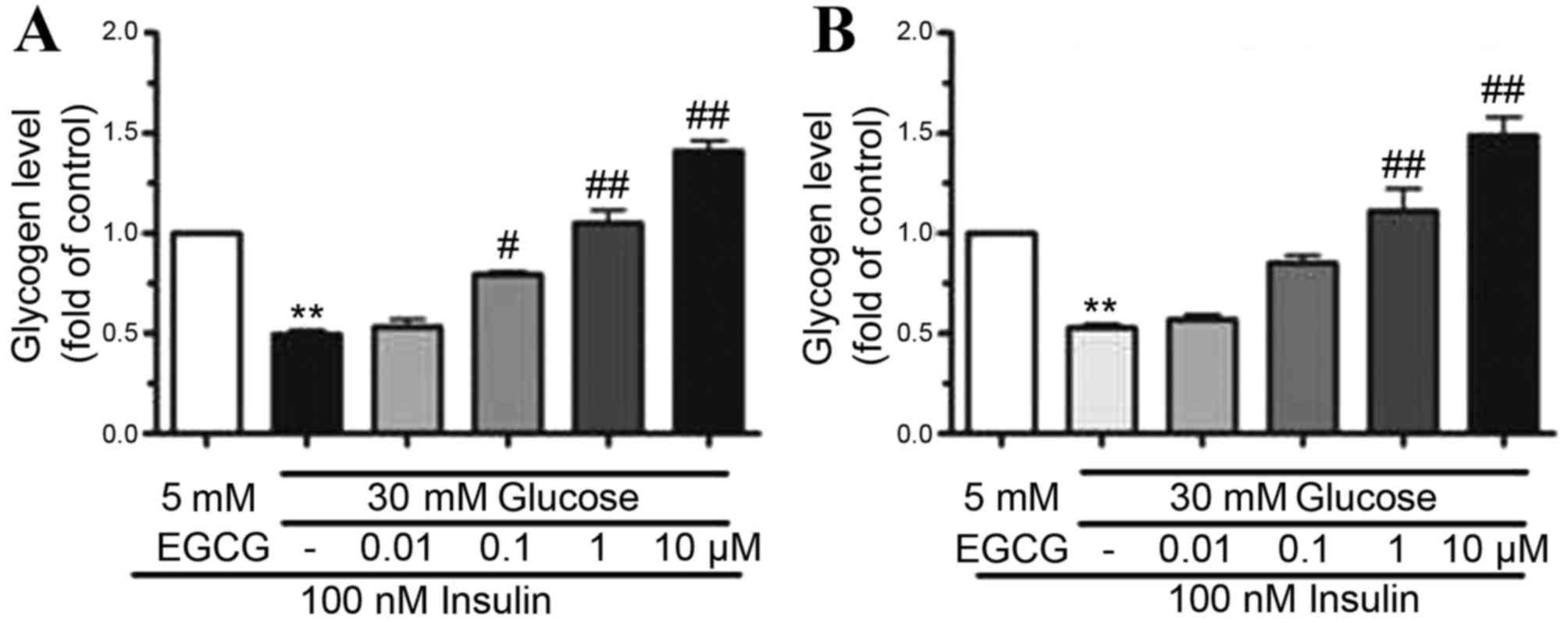
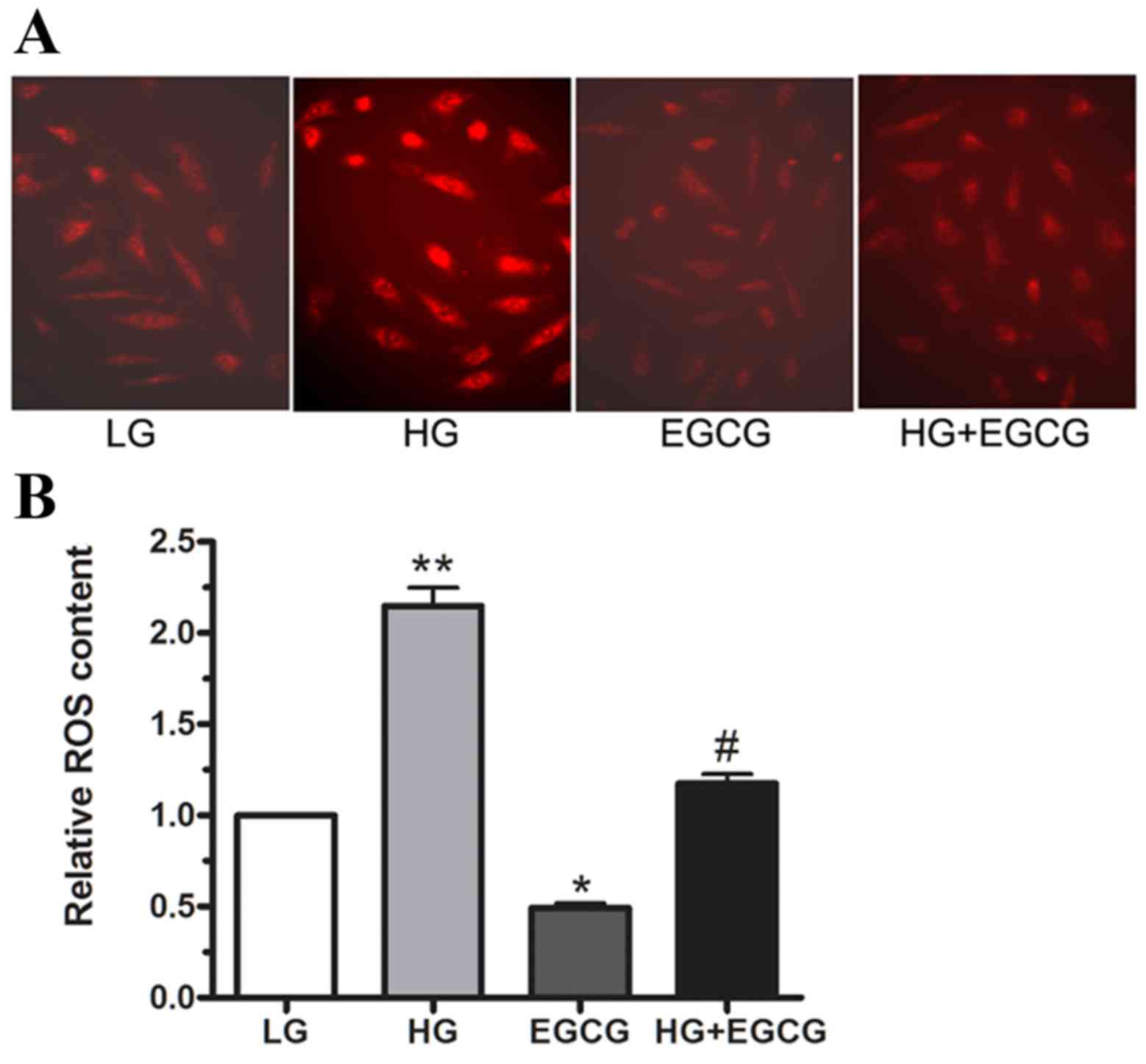
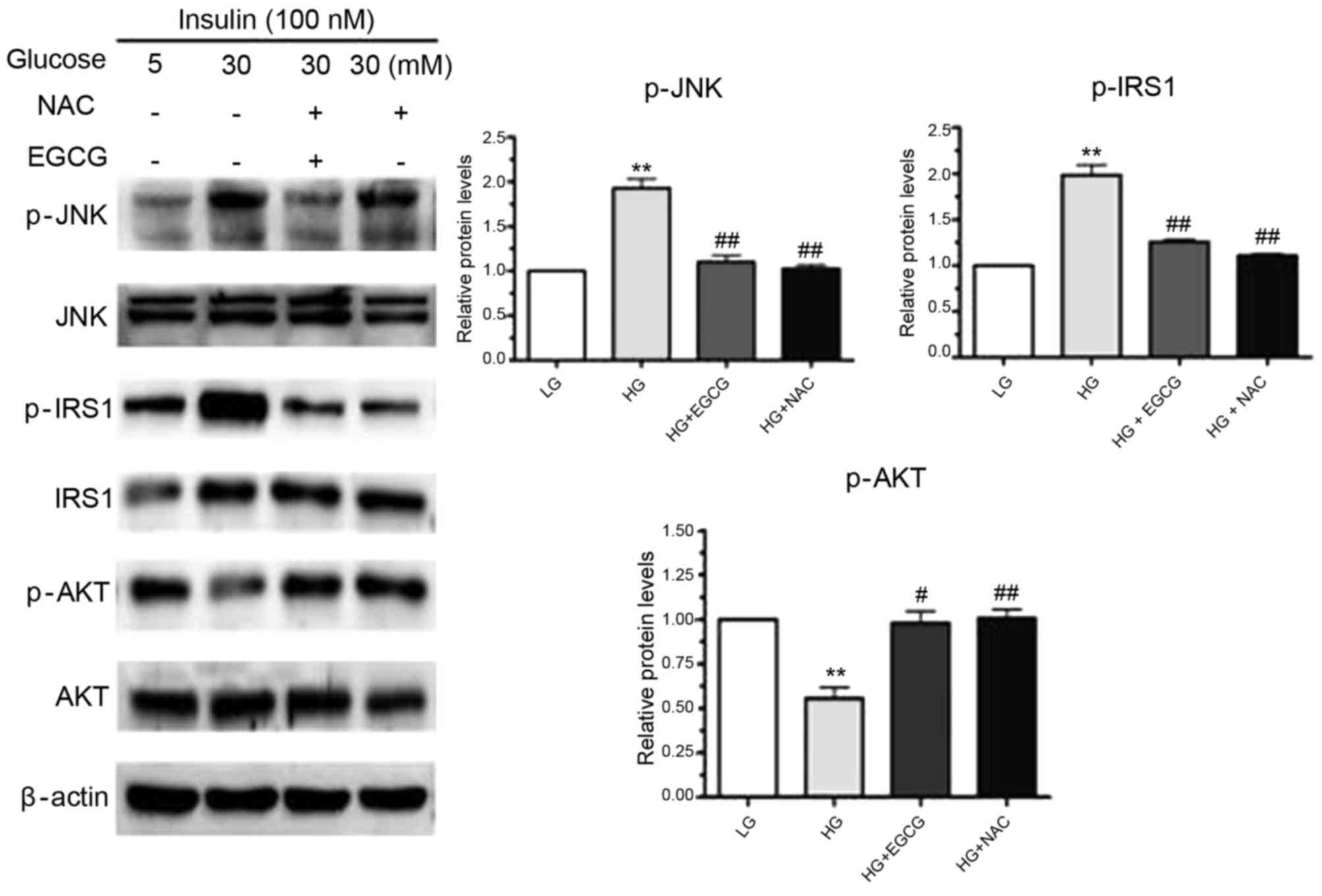
|
1
|
Ezenwaka CE, Okoye O, Esonwune C, Onuoha
P, Dioka C, Osuji C, Oguejiofor C and Meludu S: High prevalence of
abdominal obesity increases the risk of the metabolic syndrome in
Nigerian type 2 diabetes patients: Using the International diabetes
federation worldwide definition. Metab Syndr Relat Disord.
12:277–282. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cable JC, Tan GD, Alexander SP and
O'Sullivan SE: The effects of obesity, diabetes and metabolic
syndrome on the hydrolytic enzymes of the endocannabinoid system in
animal and human adipocytes. Lipids Health Dis. 13:432014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu CY, Huang CJ, Huang LH, Chen IJ, Chiu
JP and Hsu CH: Effects of green tea extract on insulin resistance
and glucagon-like peptide 1 in patients with type 2 diabetes and
lipid abnormalities: A randomized, double-blinded, and
placebo-controlled trial. PLoS One. 9:e911632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gilbert RE: The endothelium in diabetic
nephropathy. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 16:4102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Crespy V and Williamson G: A review of the
health effects of green tea catechins in in vivo animal models. J
Nutr. 134 Suppl 12:S3431–S3440. 2004.
|
|
6
|
Basu A, Sanchez K, Leyva MJ, Wu M, Betts
NM, Aston CE and Lyons TJ: Green tea supplementation affects body
weight, lipids, and lipid peroxidation in obese subjects with
metabolic syndrome. J Am Coll Nutr. 29:31–40. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sae-Tan S, Grove KA and Lambert JD: Weight
control and prevention of metabolic syndrome by green tea.
Pharmacol Res. 64:146–154. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ihm SH, Jang SW, Kim OR, Chang K, Oak MH,
Lee JO, Lim DY and Kim JH: Decaffeinated green tea extract improves
hypertension and insulin resistance in a rat model of metabolic
syndrome. Atherosclerosis. 224:377–383. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sae-Tan S, Rogers CJ and Lambert JD:
Voluntary exercise and green tea enhance the expression of genes
related to energy utilization and attenuate metabolic syndrome in
high fat fed mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 58:1156–1159. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thielecke F and Boschmann M: The potential
role of green tea catechins in the prevention of the metabolic
syndrome-A review. Phytochemistry. 70:11–24. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Senger AE Vieira, Schwanke CH, Gomes I and
Gottlieb MG Valle: Effect of green tea (Camellia sinensis)
consumption on the components of metabolic syndrome in elderly. J
Nutr Health Aging. 16:738–742. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cia D, Vergnaud-Gauduchon J, Jacquemot N
and Doly M: Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) prevents H2O2-induced
oxidative stress in primary rat retinal pigment epithelial cells.
Curr Eye Res. 39:944–952. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang EJ, Lee J, Lee SY, Kim EK, Moon YM,
Jung YO, Park SH and Cho ML: EGCG attenuates autoimmune arthritis
by inhibition of STAT3 and HIF-1α with Th17/Treg control. PLoS One.
9:e860622014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou J, Farah BL, Sinha RA, Wu Y, Singh
BK, Bay BH, Yang CS and Yen PM: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG),
a green tea polyphenol, stimulates hepatic autophagy and lipid
clearance. PLoS One. 9:e871612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Benelli R, Venè R, Bisacchi D, Garbisa S
and Albini A: Anti-invasive effects of green tea polyphenol
epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), a natural inhibitor of metallo
and serine proteases. Biol Chem. 383:101–105. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao C, She T, Wang L, Su Y, Qu L, Gao Y,
Xu S, Cai S and Shou C: Daucosterol inhibits cancer cell
proliferation by inducing autophagy through reactive oxygen
species-dependent manner. Life Sci. 137:37–43. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Saltiel AR: Insulin signaling in the
control of glucose and lipid homeostasis. Handb Exp Pharmacol.
233:51–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hendriksen PH, Oey PL, Wieneke GH,
Bravenboer B and Banga JD: Subclinical diabetic neuropathy:
Similarities between electrophysiological results of patients with
type 1 (insulin-dependent) and type 2 (non-insulin-dependent)
diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 35:690–695. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Eddouks M, Maghrani M and Michel JB:
Hypoglycaemic effect of Triticum repens P. Beauv. in normal and
diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 102:228–232. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Stefano GB, Challenger S and Kream RM:
Hyperglycemia-associated alterations in cellular signaling and
dysregulated mitochondrial bioenergetics in human metabolic
disorders. Eur J Nutr. 55:2339–2345. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bukhari SA, Naqvi SA, Nagra SA, Anjum F,
Javed S and Farooq M: Assessing of oxidative stress related
parameters in diabetes mellitus type 2: Cause excessive damaging to
DNA and enhanced homocysteine in diabetic patients. Pak J Pharm
Sci. 28:483–491. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tsuneki H, Ishizuka M, Terasawa M, Wu JB,
Sasaoka T and Kimura I: Effect of green tea on blood glucose levels
and serum proteomic patterns in diabetic (db/db) mice and on
glucose metabolism in healthy humans. BMC Pharmacol. 4:182004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hirsch N, Konstantinov A, Anavi S, Aronis
A, Hagay Z, Madar Z and Tirosh O: Prolonged feeding with green tea
polyphenols exacerbates cholesterol-induced fatty liver disease in
mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 60:2542–2553. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Weisburger JH and Chung FL: Mechanisms of
chronic disease causation by nutritional factors and tobacco
products and their prevention by tea polyphenols. Food Chem
Toxicol. 40:1145–1154. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Raederstorff DG, Schlachter MF, Elste V
and Weber P: Effect of EGCG on lipid absorption and plasma lipid
levels in rats. J Nutr Biochem. 14:326–332. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rösen P, Nawroth PP, King G, Moller W,
Tritschler HJ and Packer L: The role of oxidative stress in the
onset and progression of diabetes and its complications: A summary
of a congress series sponsored by UNESCO-MCBN, the American
diabetes association and the German diabetes society. Diabetes
Metab Res Rev. 17:189–212. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nishikawa T, Edelstein D and Brownlee M:
The missing link: A single unifying mechanism for diabetic
complications. Kidney Int Suppl. 77:S26–S30. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Paolisso G and Giugliano D: Oxidative
stress and insulin action: Is there a relationship? Diabetologia.
39:357–363. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rudich A, Kozlovsky N, Potashnik R and
Bashan N: Oxidant stress reduces insulin responsiveness in 3T3-L1
adipocytes. Am J Physiol. 272:E935–E940. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kyriakis JM and Avruch J: Sounding the
alarm: Protein kinase cascades activated by stress and
inflammation. J Biol Chem. 271:24313–24316. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Blair AS, Hajduch E, Litherland GJ and
Hundal HS: Regulation of glucose transport and glycogen synthesis
in L6 muscle cells during oxidative stress. Evidence for cross-talk
between the insulin and SAPK2/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 274:36293–36299. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Birnbaum MJ: Turning down insulin
signaling. J Clin Invest. 108:655–659. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu K, Zhao W, Gao X, Huang F, Kou J and
Liu B: Diosgenin ameliorates palmitate-induced endothelial
dysfunction and insulin resistance via blocking IKKβ and IRS-1
pathways. Atherosclerosis. 223:350–358. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Katakam AK, Chipitsyna G, Gong Q, Vancha
AR, Gabbeta J and Arafat HA: Streptozotocin (STZ) mediates acute
upregulation of serum and pancreatic osteopontin (OPN): A novel
islet-protective effect of OPN through inhibition of STZ-induced
nitric oxide production. J Endocrinol. 187:237–247. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chu J, Zhang H, Huang X, Lin Y, Shen T,
Chen B, Man Y, Wang S and Li J: Apelin ameliorates TNF-α-induced
reduction of glycogen synthesis in the hepatocytes through G
protein-coupled receptor APJ. PLoS One. 8:e572312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|