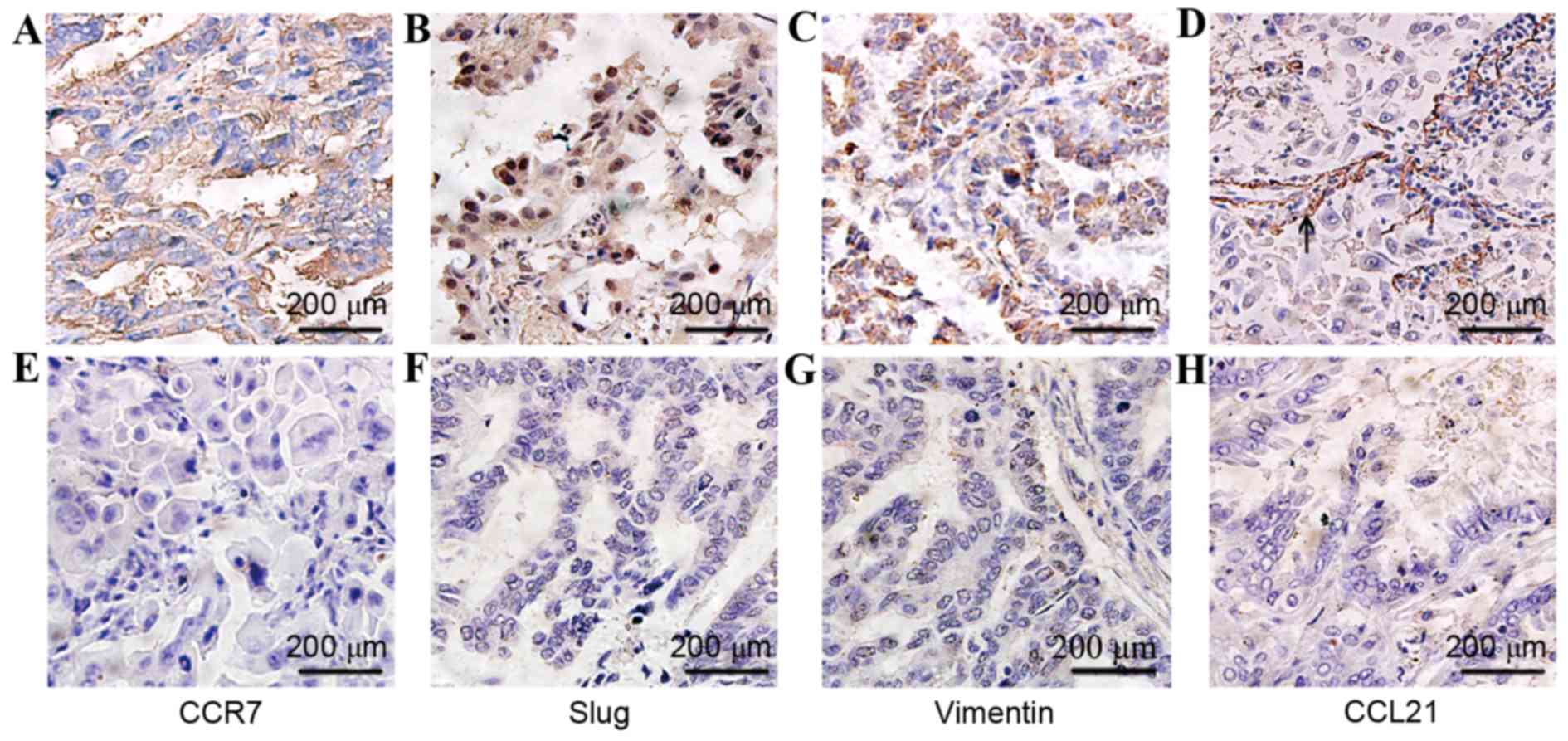
|
1
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
De Craene B and Berx G: Regulatory
networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat
Rev Cancer. 13:97–110. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mukaida N and Baba T: Chemokines in tumor
development and progression. Exp Cell Res. 318:95–102. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zlotnik A, Burkhardt AM and Homey B:
Homeostatic chemokine receptors and organ-specific metastasis. Nat
Rev Immunol. 11:597–606. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Förster R, Davalos-Misslitz AC and Rot A:
CCR7 and its ligands: Balancing immunity and tolerance. Nat Rev
Immunol. 8:362–371. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Carlsen HS, Haraldsen G, Brandtzaeg P and
Baekkevold ES: Disparate lymphoid chemokine expression in mice and
men: No evidence of CCL21 synthesis by human high endothelial
venules. Blood. 106:444–446. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Baekkevold ES, Yamanaka T, Palframan RT,
Carlsen HS, Reinholt FP, von Andrian UH, Brandtzaeg P and Haraldsen
G: The CCR7 ligand ELC (CCL19) is transcytosed in high endothelial
venules and mediates T cell recruitment. J Exp Med. 193:1105–1112.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Gunn MD, Tangemann K, Tam C, Cyster JG,
Rosen SD and Williams LT: A chemokine expressed in lymphoid high
endothelial venules promotes the adhesion and chemotaxis of naive T
lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:pp. 258–263. 1998;
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Sperveslage J, Frank S, Heneweer C,
Egberts J, Schniewind B, Buchholz M, Bergmann F, Giese N, Munding
J, Hahn SA, et al: Lack of CCR7 expression is rate limiting for
lymphatic spread of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer.
131:E371–E381. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Legler DF, Uetz-von Allmen E and Hauser
MA: CCR7: Roles in cancer cell dissemination, migration and
metastasis formation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 54:78–82. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li X, Ma Q, Xu Q, Liu H, Lei J, Duan W,
Bhat K, Wang F, Wu E and Wang Z: SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling induces
pancreatic cancer cell invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in vitro through non-canonical activation of Hedgehog
pathway. Cancer Lett. 322:169–176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Chen K, Li Z, Jiang P, Zhang X, Zhang Y,
Jiang Y, He Y and Li X: Co-expression of CD133, CD44v6 and human
tissue factor is associated with metastasis and poor prognosis in
pancreatic carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 32:755–763. 2014.
|
|
13
|
Lee SH, Kang HY, Kim KS, Nam BY, Paeng J,
Kim S, Li JJ, Park JT, Kim DK, Han SH, et al: The monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1)/CCR2 system is involved in
peritoneal dialysis-related epithelial-mesenchymal transition of
peritoneal mesothelial cells. Lab Invest. 92:1698–1711. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Marsigliante S, Vetrugno C and Muscella A:
Paracrine CCL20 loop induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
breast epithelial cells. Mol Carcinog. 55:1175–1186. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Li F, Zou Z, Suo N, Zhang Z, Wan F, Zhong
G, Qu Y, Ntaka KS and Tian H: CCL21/CCR7 axis activating chemotaxis
accompanied with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human breast
carcinoma. Med Oncol. 31:1802014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang J, Zhou Y and Yang Y: CCR7 pathway
induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition through up-regulation of
Snail signaling in gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 32:4672015.
|
|
17
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Goldstraw P, Chansky K, Crowley J,
Rami-Porta R, Asamura H, Eberhardt WE, Nicholson AG, Groome P,
Mitchell A, Bolejack V, et al: The IASLC lung cancer staging
project: proposals for revision of the TNM stage groupings in the
forthcoming (Eighth) edition of the TNM classification for lung
cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 11:39–51. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen X, Ye S, Xiao W, Wang W, Luo L and
Liu Y: ERK1/2 pathway mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition by
cross-interacting with TGFβ/Smad and Jagged/Notch signaling
pathways in lens epithelial cells. Int J Mol Med. 33:1664–1670.
2014.
|
|
21
|
Buonato JM and Lazzara MJ: ERK1/2 blockade
prevents epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells and
promotes their sensitivity to EGFR inhibition. Cancer Res.
74:309–319. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Maekawa S, Iwasaki A, Shirakusa T,
Kawakami T, Yanagisawa J, Tanaka T, Shibaguchi H, Kinugasa T and
Kuroki M and Kuroki M: Association between the expression of
chemokine receptors CCR7 and CXCR3, and lymph node metastatic
potential in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 19:1461–1468.
2008.
|
|
23
|
Shields JD, Fleury ME, Yong C, Tomei AA,
Randolph GJ and Swartz MA: Autologous chemotaxis as a mechanism of
tumor cell homing to lymphatics via interstitial flow and autocrine
CCR7 signaling. Cancer Cell. 11:526–538. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li Y, Zhang Q, Jiang L, Qiu X and Wang E:
Upregulation of the Chemokine Receptor CCR7 expression by
HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in non-small cell lung cancer. Zhongguo
Fei Ai Za Zhi. 11:724–728. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Li Y, Zhang Q, Wang Y, Qiu X and Wang E:
Effects of hypoxia on the expression of CCR7 and proliferation,
invasiveness of A549 cells. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 11:704–706.
2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Pang MF, Georgoudaki AM, Lambut L,
Johansson J, Tabor V, Hagikura K, Jin Y, Jansson M, Alexander JS,
Nelson CM, et al: TGF-β1-induced EMT promotes targeted migration of
breast cancer cells through the lymphatic system by the activation
of CCR7/CCL21-mediated chemotaxis. Oncogene. 35:748–760. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Papageorgis P: TGFβ signaling in tumor
initiation, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. J
Oncol. 2015:5871932015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|