|
1
|
Rosell M, Jones MC and Parker MG: Role of
nuclear receptor corepressor RIP140 in metabolic syndrome. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1812:919–928. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
White R, Morganstein D, Christian M, Seth
A, Herzog B and Parker MG: Role of RIP140 in metabolic tissues:
Connections to disease. FEBS Lett. 582:39–45. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fritah A, Christian M and Parker MG: The
metabolic coregulator RIP140: An update. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 299:E335–E340. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chung HT: RIP140, a Janus metabolic switch
involved in defense functions. Cell Mol Immunol. 10:7–9. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ho PC, Chuang YS, Hung CH and Wei LN:
Cytoplasmic receptor-interacting protein 140 (RIP140) interacts
with perilipin to regulate lipolysis. Cell Signal. 23:1396–1403.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Powelka AM, Seth A, Virbasius JV, Kiskinis
E, Nicoloro SM, Guilherme A, Tang X, Straubhaar J, Cherniack AD,
Parker MG and Czech MP: Suppression of oxidative metabolism and
mitochondrial biogenesis by the transcriptional corepressor RIP140
in mouse adipocytes. J Clin Invest. 116:125–136. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Docquier A, Harmand PO, Fritsch S,
Chanrion M, Darbon JM and Cavaillès V: The transcriptional
coregulator RIP140 represses E2F1 activity and discriminates breast
cancer subtypes. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2959–2970. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lapierre M, Bonnet S, Bascoul-Mollevi C,
Ait-Arsa I, Jalaguier S, Del Rio M, Plateroti M, Roepman P, Ychou
M, Pannequin J, et al: RIP140 increases APC expression and controls
intestinal homeostasis and tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest.
124:1899–1913. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang D, Wang Y, Dai Y, Wang J, Suo T, Pan
H and Liu H, Shen S and Liu H: Downregulation of RIP140 in
hepatocellular carcinoma promoted the growth and migration of the
cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 36:2077–2085. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
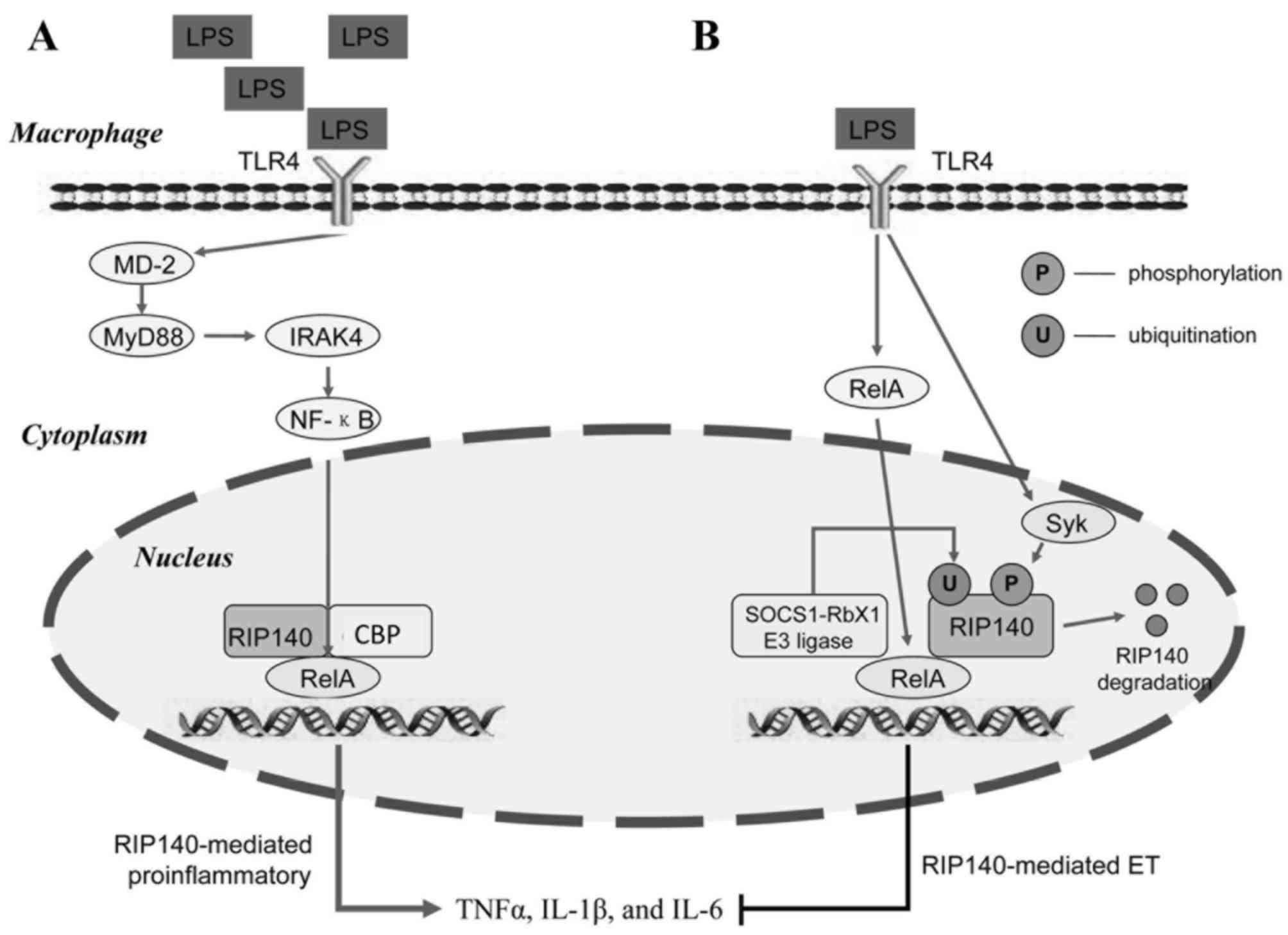
Zschiedrich I, Hardeland U, Krones-Herzig
A, Diaz M Berriel, Vegiopoulos A, Müggenburg J, Sombroek D, Hofmann
TG, Zawatzky R, Yu X, et al: Coactivator function of RIP140 for
NFkappaB/RelA-dependent cytokine gene expression. Blood.
112:264–276. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ho PC, Tsui YC, Feng X, Greaves DR and Wei
LN: NF-kB-mediated degradation of the co-activator RIP140 regulates
inflammatory response and contributes to endotoxin tolerance. Nat
Immunol. 13:379–386. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kopanakis K, Tzepi IM, Pistiki A, Carrer
DP, Netea MG, Georgitsi M, Lymperi M, Droggiti DI, Liakakos T,
Machairas A and Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ: Pre-treatment with
low-dose endotoxin prolongs survival from experimental lethal
endotoxic shock: Benefit for lethal peritonitis by Escherichia
coli. Cytokine. 62:382–388. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guilherme A, Virbasius JV, Puri V and
Czech MP: Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin
resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:367–377.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang X, Huang L and Xing D:
Photoactivation of Dok1/ERK/PPARγ signaling axis inhibits excessive
lipolysis in insulin-resistant adipocytes. Cell Signal.
27:1265–1275. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kelley DE, Mokan M, Simoneau JA and
Mandarino LJ: Interaction between glucose and free fatty acid
metabolism in human skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest. 92:91–98. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Barma P and Bhattacharya S, Bhattacharya
A, Kundu R, Dasgupta S, Biswas A and Bhattacharya S, Roy SS and
Bhattacharya S: Lipid induced overexpression of NF-kappaB in
skeletal muscle cells is linked to insulin resistance. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1792:190–200. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Unger RH: Lipotoxic diseases. Annu Rev
Med. 53:319–336. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Santomauro AT, Boden G, Silva ME, Rocha
DM, Santos RF, Ursich MJ, Strassmann PG and Wajchenberg BL:
Overnight lowering of free fatty acids with Acipimox improves
insulin resistance and glucose tolerance in obese diabetic and
nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes. 48:1836–1841. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Savage DB, Petersen KF and Shulman GI:
Disordered lipid metabolism and the pathogenesis of insulin
resistance. Physiol Rev. 87:507–520. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Christianson JL, Nicoloro S, Straubhaar J
and Czech MP: Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 2 is required for peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma expression and adipogenesis
in cultured 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 283:2906–2916. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum
M, Leibel RL and Ferrante AW Jr: Obesity is associated with
macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest.
112:1796–1808. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
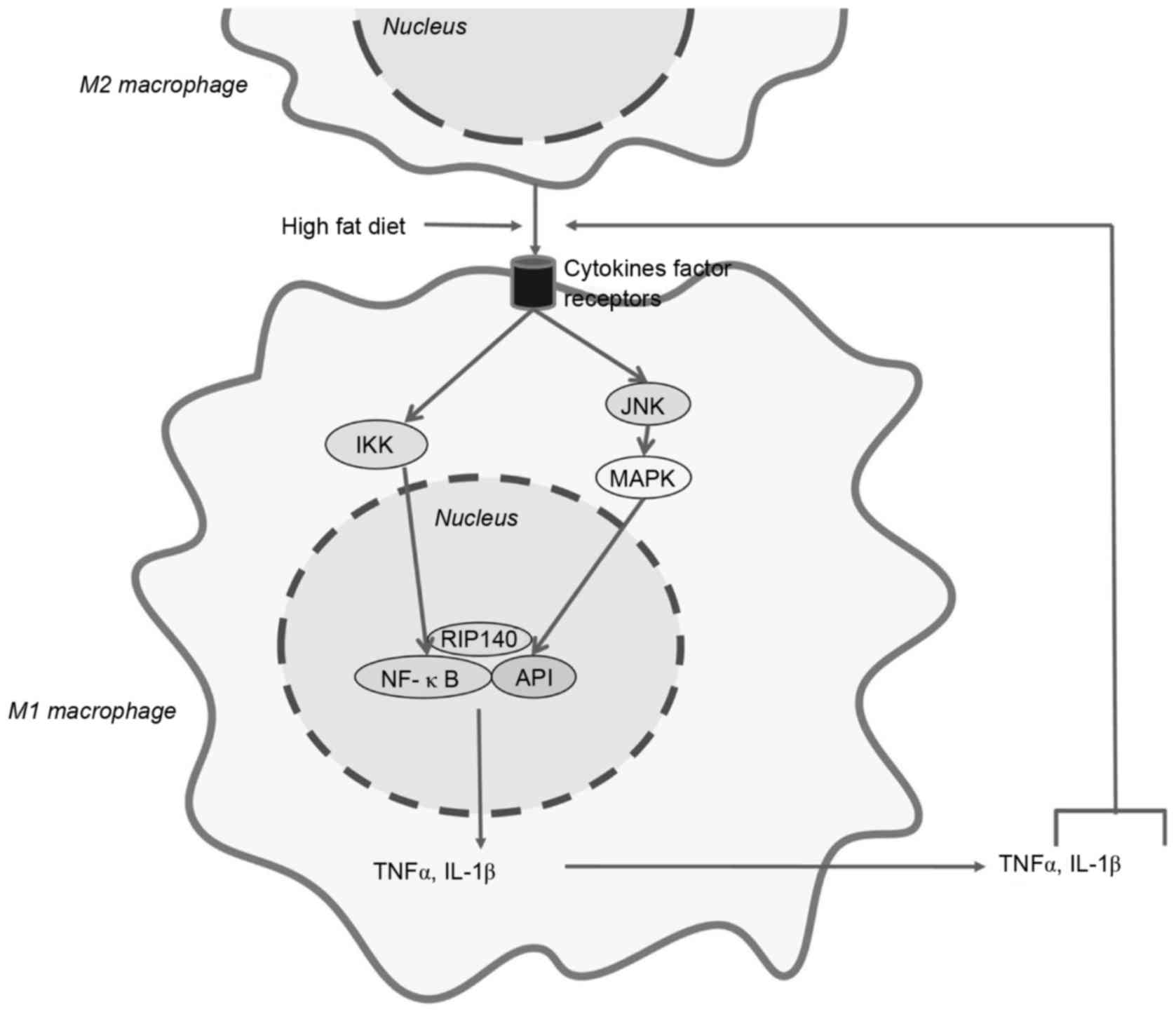
Liu PS, Lin YW, Burton FH and Wei LN:
M1-M2 balancing act in white adipose tissue browning-a new role for
RIP140. Adipocyte. 4:146–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu PS, Lin YW, Lee B, McCrady-Spitzer SK,
Levine JA and Wei LN: Reducing RIP140 expression in macrophage
alters ATM infiltration, facilitates white adipose tissue browning,
and prevents high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes.
63:4021–4031. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cancello R, Henegar C, Viguerie N, Taleb
S, Poitou C, Rouault C, Coupaye M, Pelloux V, Hugol D, Bouillot JL,
et al: Reduction of macrophage infiltration and chemoattractant
gene expression changes in white adipose tissue of morbidly obese
subjects after surgery-induced weight loss. Diabetes. 54:2277–2786.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sartipy P and Loskutoff DJ: Monocyte
chemoattractant protein 1 in obesity and insulin resistance. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:7265–7270. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rull A, Camps J, Alonso-Villaverde C and
Joven J: Insulin resistance, inflammation, and obesity: Role of
monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (or CCL2) in the regulation of
metabolism. Mediators Inflamm. 2010:pii: 3265802010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Uchida Y, Takeshita K, Yamamoto K, Kikuchi
R, Nakayama T, Nomura M, Cheng XW, Egashira K, Matsushita T,
Nakamura H and Murohara T: Stress augments insulin resistance and
prothrombotic state: Role of visceral adipose-derived monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1. Diabetes. 61:1552–1561. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Solinas G, Vilcu C, Neels JG,
Bandyopadhyay GK, Luo JL, Naugler W, Grivennikov S, Wynshaw-Boris
A, Scadeng M, Olefsky JM and Karin M: JNK1 in hematopoietically
derived cells contributes to diet-induced inflammation and insulin
resistance without affecting obesity. Cell Metab. 6:386–397. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tang X, Guilherme A, Chakladar A, Powelka
AM, Konda S, Virbasius JV, Nicoloro SM, Straubhaar J and Czech MP:
An RNA interference-based screen identifies MAP4K4/NIK as a
negative regulator of PPAR gamma, adipogenesis, and
insulin-responsive hexose transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:2087–2092. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shulman GI: Cellular mechanisms of insulin
resistance. J Clin Invest. 106:171–176. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
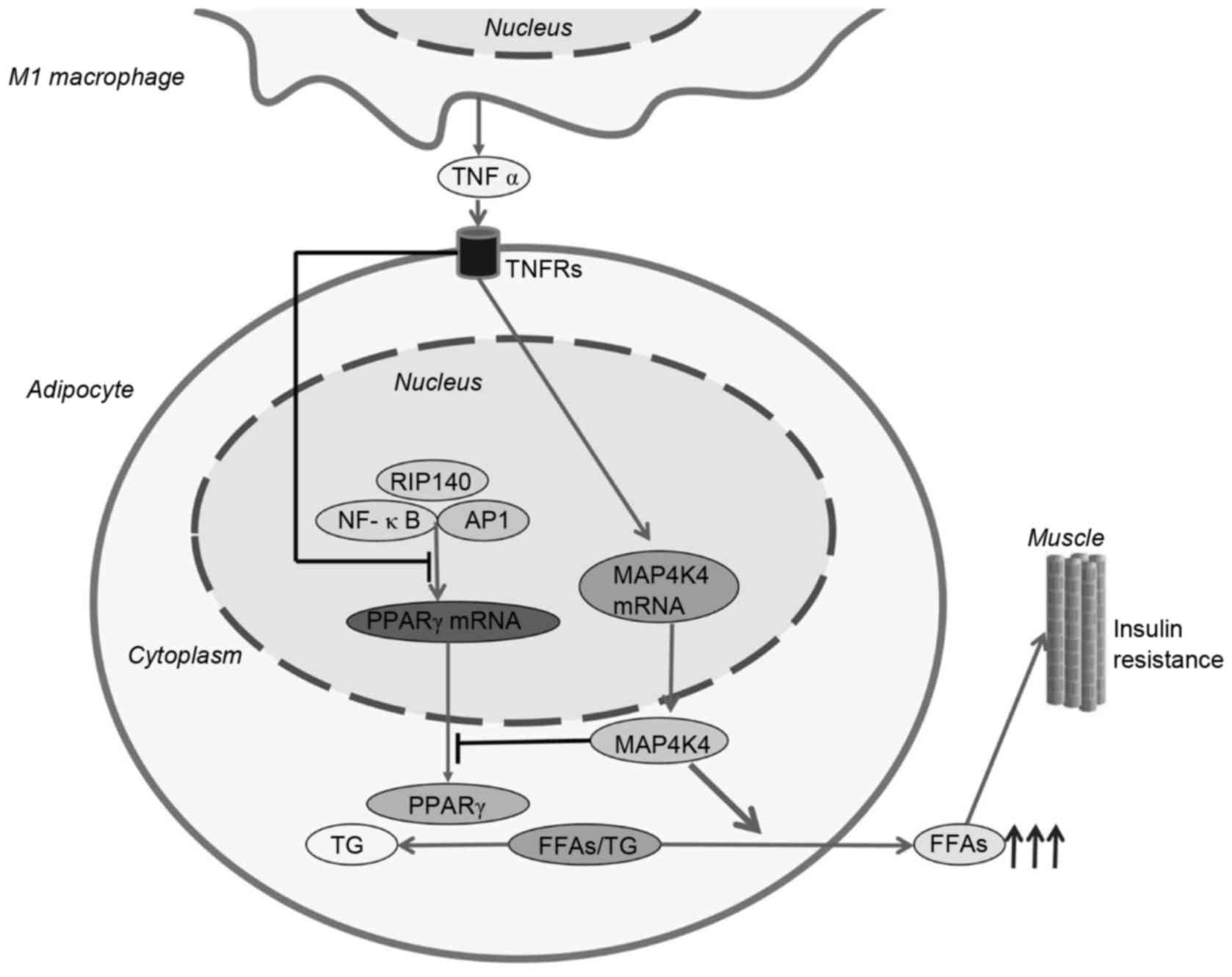
Tesz GJ, Guilherme A, Guntur KV, Hubbard
AC, Tang X, Chawla A and Czech MP: Tumor necrosis factor alpha
(TNFalpha) stimulates Map4k4 expression through TNFalpha receptor 1
signaling to c-Jun and activating transcription factor 2. J Biol
Chem. 282:19302–19312. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS and
Spiegelman BM: Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha:
Direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science.
259:87–91. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Odegaard JI, Ricardo-Gonzalez RR, Goforth
MH, Morel CR, Subramanian V, Mukundan L, Red Eagle A, Vats D,
Brombacher F, Ferrante AW and Chawla A: Macrophage-specific
PPARgamma controls alternative activation and improves insulin
resistance. Nature. 447:1116–1120. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yamaguchi Y, Cavallero S, Patterson M,
Shen H, Xu J, Kumar SR and Sucov HM: Adipogenesis and epicardial
adipose tissue: A novel fate of the epicardium induced by
mesenchymal transformation and PPARγ activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 112:2070–2075. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Imai T, Takakuwa R, Marchand S, Dentz E,
Bornert JM, Messaddeq N, Wendling O, Mark M, Desvergne B, Wahli W,
et al: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma is required
in mature white and brown adipocytes for their survival in the
mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:4543–4547. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Loft A, Forss I, Siersbæk MS, Schmidt SF,
Larsen AS, Madsen JG, Pisani DF, Nielsen R, Aagaard MM, Mathison A,
et al: Browning of human adipocytes requires KLF11 and
reprogramming of PPARγ superenhancers. Genes Dev. 29:7–22. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Siersbæk MS, Loft A, Aagaard MM, Nielsen
R, Schmidt SF, Petrovic N, Nedergaard J and Mandrup S: Genome-wide
profiling of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ in
primary epididymal, inguinal, and brown adipocytes reveals
depot-selective binding correlated with gene expression. Mol Cell
Biol. 32:3452–3463. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ait-Lounis A and Laraba-Djebari F:
TNF-alpha modulates adipose macrophage polarization to M1 phenotype
in response to scorpion venom. Inflamm Res. 64:929–936. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bing C: Is interleukin-1β a culprit in
macrophage-adipocyte cross talk in obesity? Adipocyte. 4:149–152.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
McLaren JE, Michael DR, Ashlin TG and
Ramji DP: Cytokines, macrophage lipid metabolism and foam cells:
Implications for cardiovascular disease therapy. Prog Lipid Res.
50:331–347. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qiu Y, Yanase T, Hu H, Tanaka T, Nishi Y,
Liu M, Sueishi K, Sawamura T and Nawata H: Dihydrotestosterone
suppresses foam cell formation and attenuates atherosclerosis
development. Endocrinology. 151:3307–3316. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yvan-Charvet L, Ranalletta M, Wang N, Han
S, Terasaka N, Li R, Welch C and Tall AR: Combined deficiency of
ABCA1 and ABCG1 promotes foam cell accumulation and accelerates
atherosclerosis in mice. J Clin Invest. 117:3900–3908.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wei H, Tarling EJ, McMillen TS, Tang C and
LeBoeuf RC: ABCG1 regulates mouse adipose tissue macrophage
cholesterol levels and the ratio of M1 to M2 cells during obesity
and caloric restriction. J Lipid Res. 56:2337–2347. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lin YW, Liu PS, Adhikari N, Hall JL and
Wei LN: RIP140 contributes to foam cell formation and
atherosclerosis by regulating cholesterol homeostasis in
macrophages. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 79:287–294. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dawson MI and Xia Z: The retinoid X
receptors and their ligands. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1821:21–56.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Calkin AC and Tontonoz P: Liver X receptor
signaling pathways and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 30:1513–1518. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
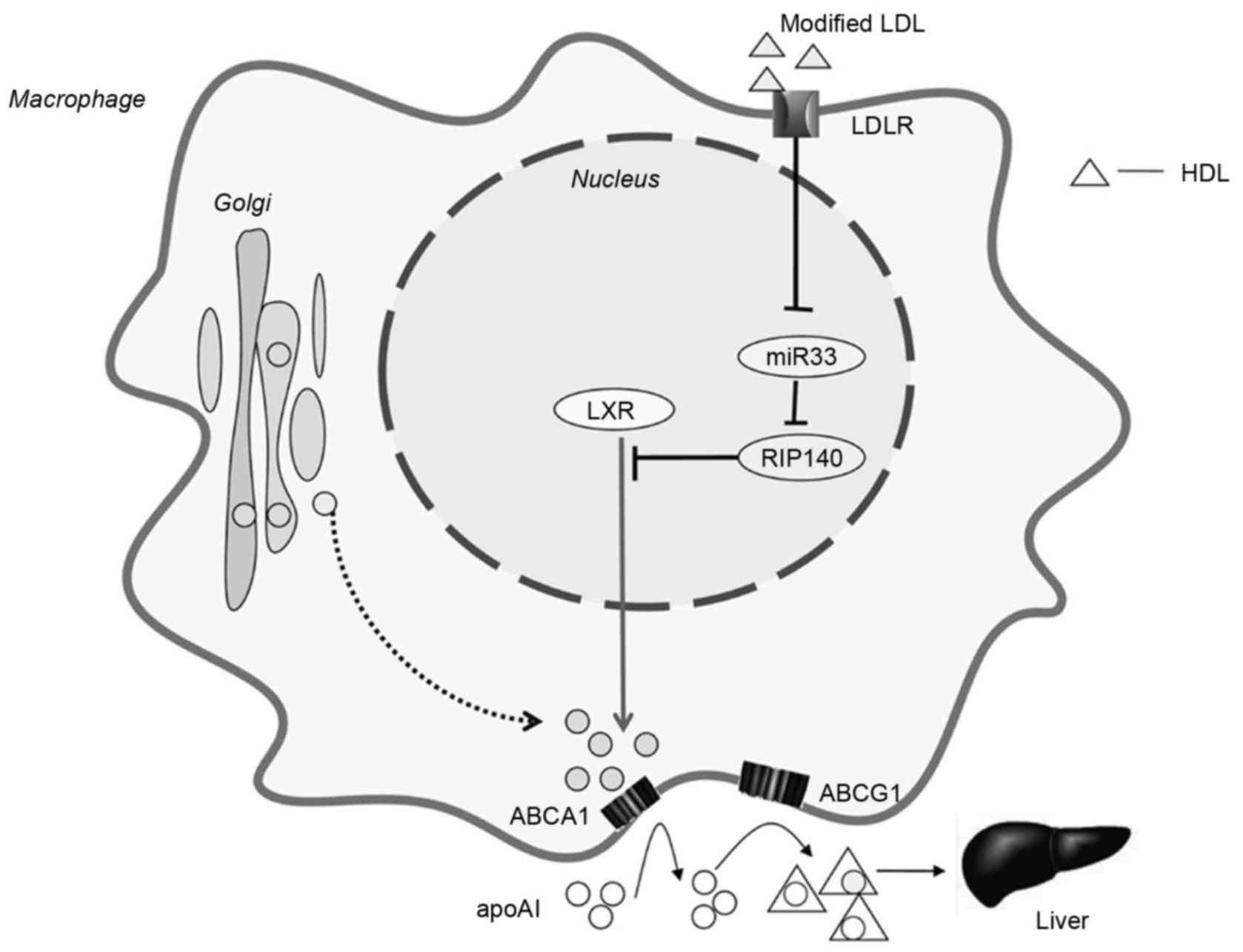
He Y, Zhang L, Li Z, Gao H, Yue Z, Liu Z,
Liu X, Feng X and Liu P: RIP140 triggers foam-cell formation by
repressing ABCA1/G1 expression and cholesterol efflux via liver X
receptor. FEBS Lett. 589:455–460. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Calkin AC and Tontonoz P: Transcriptional
integration of metabolism by the nuclear sterol-activated receptors
lXR and FXR. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:213–224. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ho PC, Chang KC, Chuang YS and Wei LN:
Cholesterol regulation of receptor-interacting protein 140 via
microRNA-33 in inflammatory cytokine production. FASEB J.
25:1758–1766. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rayner KJ, Sheedy FJ, Esau CC, Hussain FN,
Temel RE, Parathath S, van Gils JM, Rayner AJ, Chang AN, Suarez Y,
et al: Antagonism of mir-33 in mice promotes reverse cholesterol
transport and regression of atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest.
121:2921–2931. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Dávalos A and Fernández-Hernando C: From
evolution to revolution: miRNAs as pharmacological targets for
modulating cholesterol efflux and reverse cholesterol transport.
Pharmacol Res. 75:60–72. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Karasawa T and Takahashi M: RIP140 as a
novel therapeutic target in the treatment of atherosclerosis. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 81:136–138. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jawad I, Lukšić I and Rafnsson SB:
Assessing available information on the burden of sepsis: Global
estimates of incidence, prevalence and mortality. J Glob Health.
2:0104042012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Charchaflieh J, Wei J, Labaze G, Hou YJ,
Babarsh B, Stutz H, Lee H, Worah S and Zhang M: The role of
complement system in septic shock. Clin Dev Immunol.
2012:4073242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang X and Quinn PJ: Lipopolysaccharide:
Biosynthetic pathway and structure modification. Prog Lipid Res.
49:97–107. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Xiong Y, Pennini M, Vogel SN and Medvedev
AE: IRAK4 kinase activity is not required for induction of
endotoxin tolerance but contributes to TLR2-mediated tolerance. J
Leukoc Biol. 94:291–300. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Laird MH, Rhee SH, Perkins DJ, Medvedev
AE, Piao W, Fenton MJ and Vogel SN: TLR4/MyD88/PI3K interactions
regulate TLR4 signaling. J Leukoc Biol. 85:966–977. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Nahid MA, Satoh M and Chan EK: MicroRNA in
TLR signaling and endotoxin tolerance. Cell Mol Immunol. 8:388–403.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Liew FY, Xu D, Brint EK and O'Neill LA:
Negative regulation of Toll-like receptor-mediated immune
responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 5:446–458. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Park SH, Park-Min KH, Chen J, Hu X and
Ivashkiv LB: Tumor necrosis factor induces GSK3 kinase-mediated
cross-tolerance to endotoxin in macrophages. Nat Immunol.
12:607–615. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Chen J and Ivashkiv LB: IFN-γ abrogates
endotoxin tolerance by facilitating Toll-like receptor induced
chromatin remodeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:19438–19443.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chen Y, Liu Z, Liang S, Luan X, Long F,
Chen J, Peng Y, Yan L and Gong J: Role of Kupffer cells in the
induction of tolerance of orthotopic liver transplantation in rats.
Liver Transpl. 14:823–836. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|