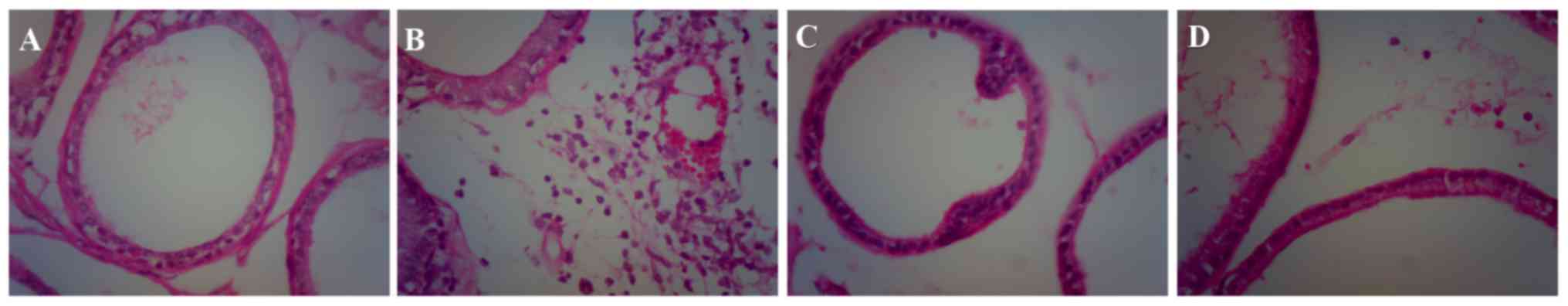
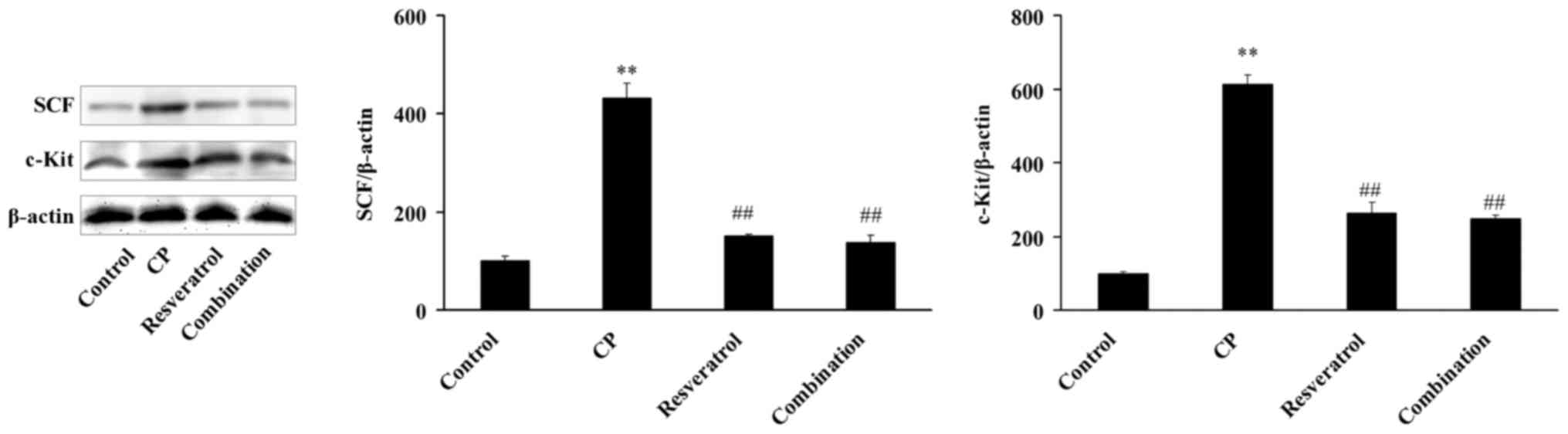
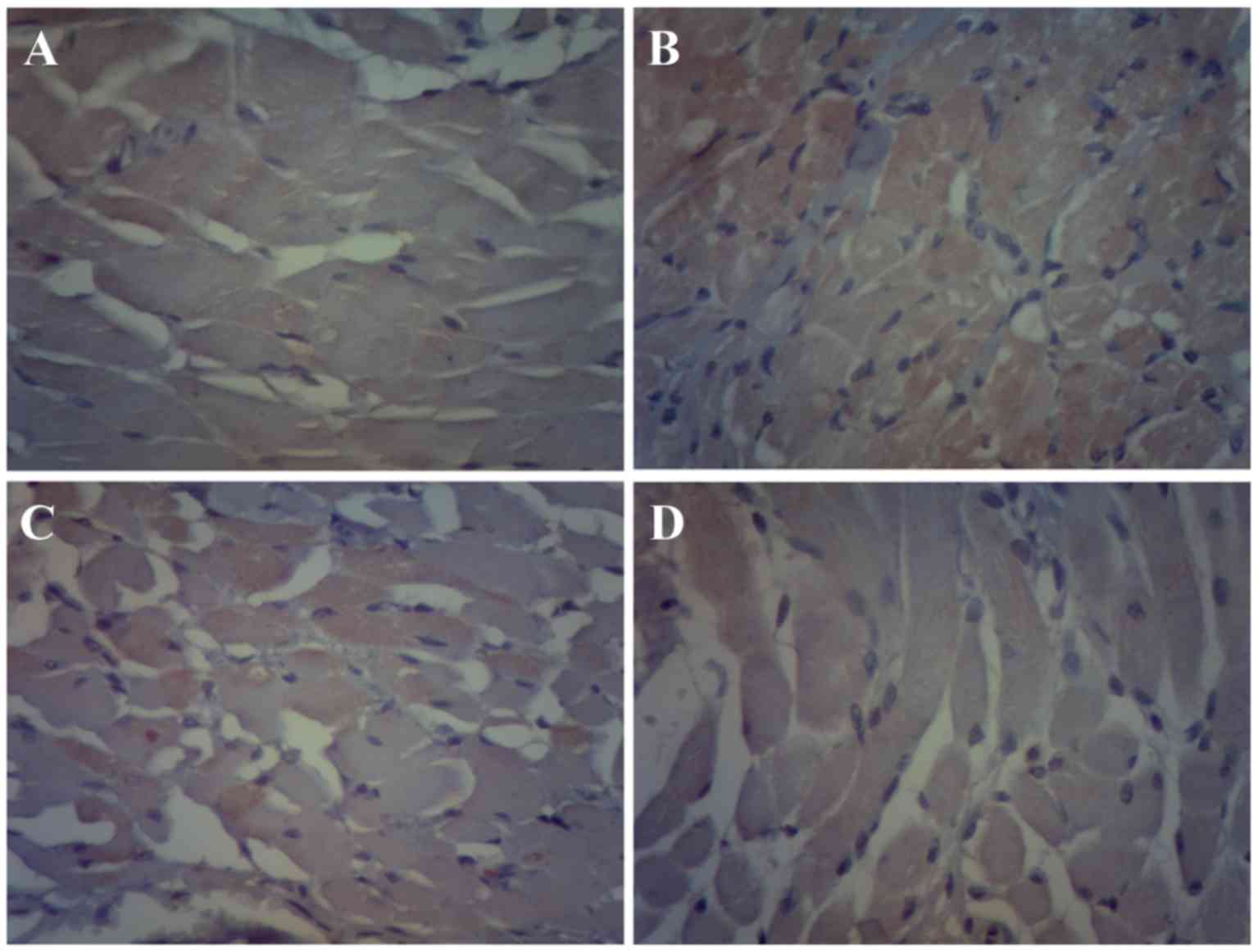
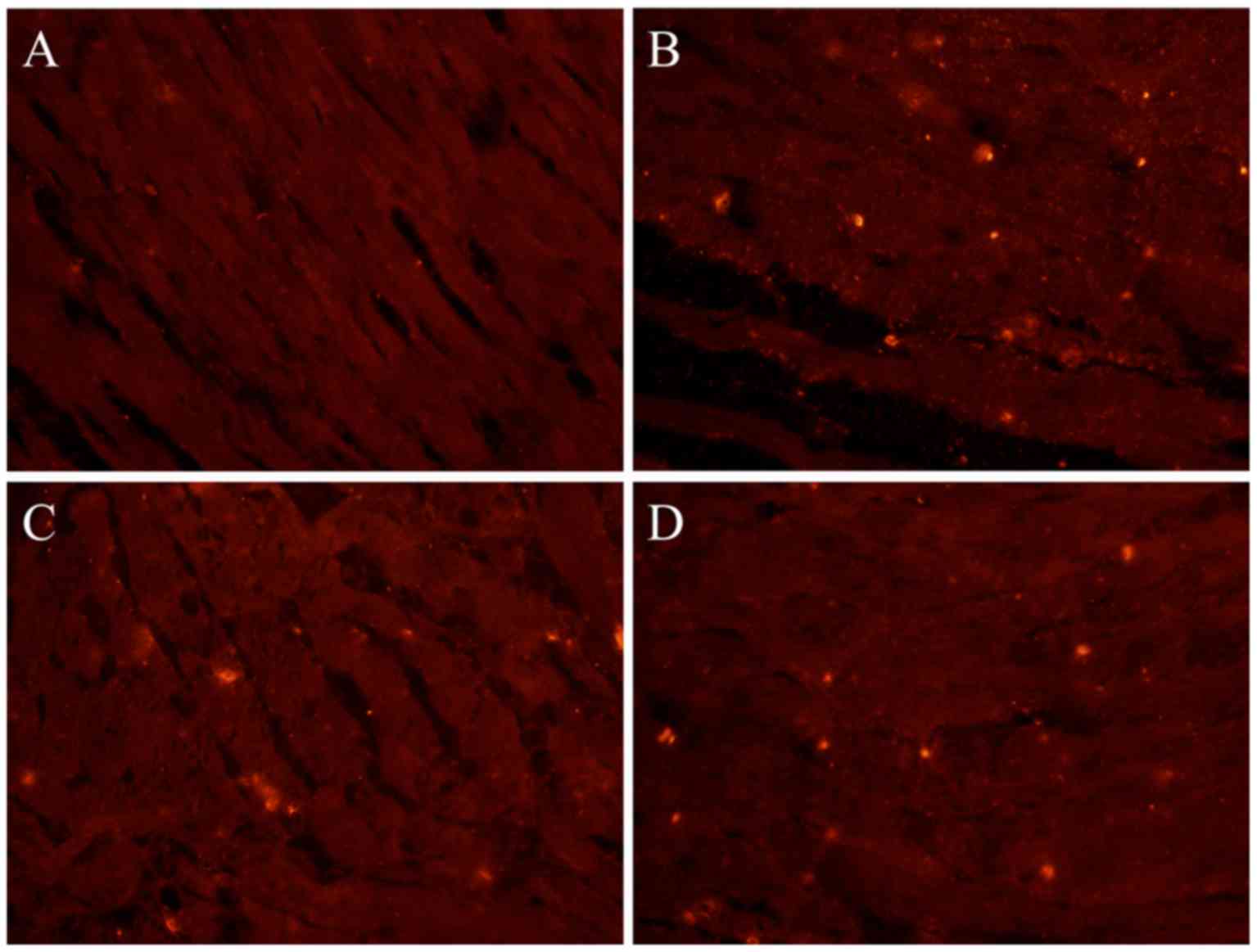
|
1
|
Cho DS, Choi JB, Kim YS, Joo KJ, Kim SH,
Kim JC and Kim HW: Heart rate variability in assessment of
autonomic dysfunction in patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic
pelvic pain syndrome. Urology. 78:1369–1372. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liao LM, Shi BY and Liang CQ: Ambulatory
urodynamic monitoring of external urethral sphincter behavior in
chronic prostatitis patients. Asian J Androl. 1:215–217.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wei J, Li N, Xia X, Chen X, Peng F, Besner
GE and Feng J: Effects of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation
on the interstitial cells of Cajal. Cell Tissue Res. 356:29–37.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shin DH, Lee MJ, Jiao HY, Choi S, Kim MW,
Park CG, Na J, Kim SW, Park IK, So I and Jun JY: Regulatory roles
of endogenous mitogen-activated protein kinases and tyrosine
kinases in the pacemaker activity of colonic interstitial cells of
cajal. Pharmacology. 96:16–24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li J, Kong D, He Y, Wang X, Gao L, Li J,
Yan M, Liu D, Wang Y, Zhang L and Jin X: The impact of inflammatory
cells in malignant ascites on small intestinal ICCs' morphology and
function. J Cell Mol Med. 19:2118–2127. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sergeant GP, Hollywood MA, McCloskey KD,
Thornbury KD and McHale NG: Specialised pacemaking cells in the
rabbit urethra. J Physiol. 526:359–366. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Faussone-Pellegrini MS, Serni S and Carini
M: Distribution of ICC and motor response characteristics in
urinary bladders reconstructed from human ileum. Am J Physiol.
273:G147–G157. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shafik A, El Sibai O and Ahmed I: The
identification of specialized pacemaking cells in the anal
sphincters. Int J Colorectal Dis. 21:453–457. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thornbury KD, Hollywood MA, McHale NG and
Sergeant GP: Cajal beyond the gut: Interstitial cells in the
urinary system-towards general regulatory mechanisms of smooth
muscle contractility? Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 74:536–542.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hashitani H and Lang RJ: Functions of
ICC-like cells in the urinary tract and male genital organs. J Cell
Mol Med. 14:1199–1211. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lang RJ and Klemm MF: Interstitial cell of
Cajal-like cells in the upper urinary tract. J Cell Mol Med.
9:543–556. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lennartsson J and Rönnstrand L: Stem cell
factor receptor/c-Kit: From basic science to clinical implications.
Physiol Rev. 92:1619–1649. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Abu-Duhier FM, Goodeve AC, Care RS, Gari
M, Wilson GA, Peake IR and Reilly JT: Mutational analysis of class
III receptor tyrosine kinases (C-KIT, C-FMS, FLT3) in idiopathic
myelofibrosis. Br J Haematol. 120:464–470. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Biers SM, Reynard JM, Doore T and Brading
AF: The functional effects of a c-kit tyrosine inhibitor on
guinea-pig and human detrusor. BJU Int. 97:612–616. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Roskoski R Jr: Structure and regulation of
Kit protein-tyrosine kinase-the stem cell factor receptor. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 338:1307–1315. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yuksel O Haki, Urkmez A and Verit A: The
role of Cajal cells in chronic prostatitis. Arch Ital UrolAndrol.
88:133–135. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Torres P, Poveda A, Jimenez-Barbero J,
Ballesteros A and Plou FJ: Regioselective lipase-catalyzed
synthesis of 3-o-acyl derivatives of resveratrol and study of their
antioxidant properties. J Agric Food Chem. 58:807–813. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sharma S, Anjaneyulu M, Kulkarni SK and
Chopra K: Resveratrol, a polyphenolic phytoalexin, attenuates
diabetic nephropathy in rats. Pharmacology. 76:69–75. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Csiszar A: Anti-inflammatory effects of
resveratrol: Possible role in prevention of age-related
cardiovascular disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1215:117–122. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang F, Wu XN, Chen J, Wang WX and Lu ZF:
Resveratrol reverses multidrug resistance in human breast cancer
doxorubicin-resistant cells. Exp Ther Med. 7:1611–1616.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Poolman TM, Ng LL, Farmer PB and Manson
MM: Inhibition of the respiratory burst by resveratrol in human
monocytes: Correlation with inhibition of PI3K signaling. Free
Radic Biol Med. 39:118–132. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vajravelu BN, Hong KU, Al-Maqtari T, Cao
P, Keith MC, Wysoczynski M, Zhao J, JB IV Moore and Bolli R: C-Kit
promotes growth and migration of human cardiac progenitor cells via
the PI3K-AKT and MEK-ERK pathways. PloS One. 10:e01407982015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee SH, Byun SS, Lee SJ, Kim KH and Lee
JY: Effects of initial combined tamsulosin and solifenacin therapy
for overactive bladder and bladder outlet obstruction secondary to
benign prostatic hyperplasia: A prospective, randomized,
multicenter study. Int Urol Nephrol. 46:523–529. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guohong S, Qiumei Z, Baozhen P, Lijuan H,
Julaiti S, Aisikeer T, Xuan G, Lina Y, Reyihan W, Wentao Z and
Qingyang P: Effects of different Chinese herbal prescriptions on
cytokines in au- toimmune prostatitis rats. J Tradit Chin Med.
35:211–217. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cheng PW, Ho WY, Su YT, Lu PJ, Chen BZ,
Cheng WH, Lu WH, Sun GC, Yeh TC, Hsiao M and Tseng CJ: Resveratrol
decreases fructose-induced oxidative stress, mediated by NADPH
oxidase via an AMPK-dependent mechanism. Br J Pharmacol.
171:2739–2750. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Suzuki M, Ohtake A, Yoshino T, Yuyama H,
Hayashi A, Ukai M, Okutsu H, Noguchi Y, Sato S and Sasamata M:
Effects of solifenacin succinate (YM905) on detrusor overactivity
in conscious cerebral infarcted rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 512:61–66.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang X, Yuan L, Chen J, Xiong C and Ruan
J: Multitargeted protective effect of Abacopteris penangiana
against carrageenan-induced chronic prostatitis in rats. J
Ethnopharmacol. 151:343–351. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rivera RS, Nagatsuka H, Gunduz M, Cengiz
B, Gunduz E, Siar CH, Tsujigiwa H, Tamamura R, Han KN and Nagai N:
C-kit protein expression correlated with activating mutations in
KIT gene in oral mucosal melanoma. Virchows Arch. 452:27–32. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Metzger R, Schuster T, Till H, Franke FE
and Dietz HG: Cajal-like cells in the upper urinary tract:
Comparative study in various species. Pediatr Surg Int. 21:169–174.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Johnston L, Woolsey S, Cunningham RM,
O'Kane H, Duggan B, Keane P and McCloskey KD: Morphological
expression of KIT positive interstitial cells of Cajal in human
bladder. J Urol. 184:370–377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
McCloskey KD: Interstitial cells in the
urinary bladder-localization and function. Neurourol Urodyn.
29:82–87. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bashamboo A, Taylor AH, Samuel K, Panthier
JJ, Whetton AD and Forrester LM: The survival of differentiating
embryonic stem cells is dependent on the SCF-KIT pathway. J Cell
Sci. 119:3039–3046. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fraser L, Taylor AH and Forrester LM:
SCF/KIT inhibition has a cumulative but reversible effect on the
self-renewal of embryonic stem cells and on the survival of
differentiating cells. Cell Reprogram. 15:259–268. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lorincz A, Redelman D, Horvath VJ,
Bardsley MR, Chen H and Ordog T: Progenitors of interstitial cells
of cajal in the postnatal murine stomach. Gastroenterology.
134:1083–1093. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Taylor ML and Metcalfe DD: Kit signal
transduction. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 14:517–535. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|