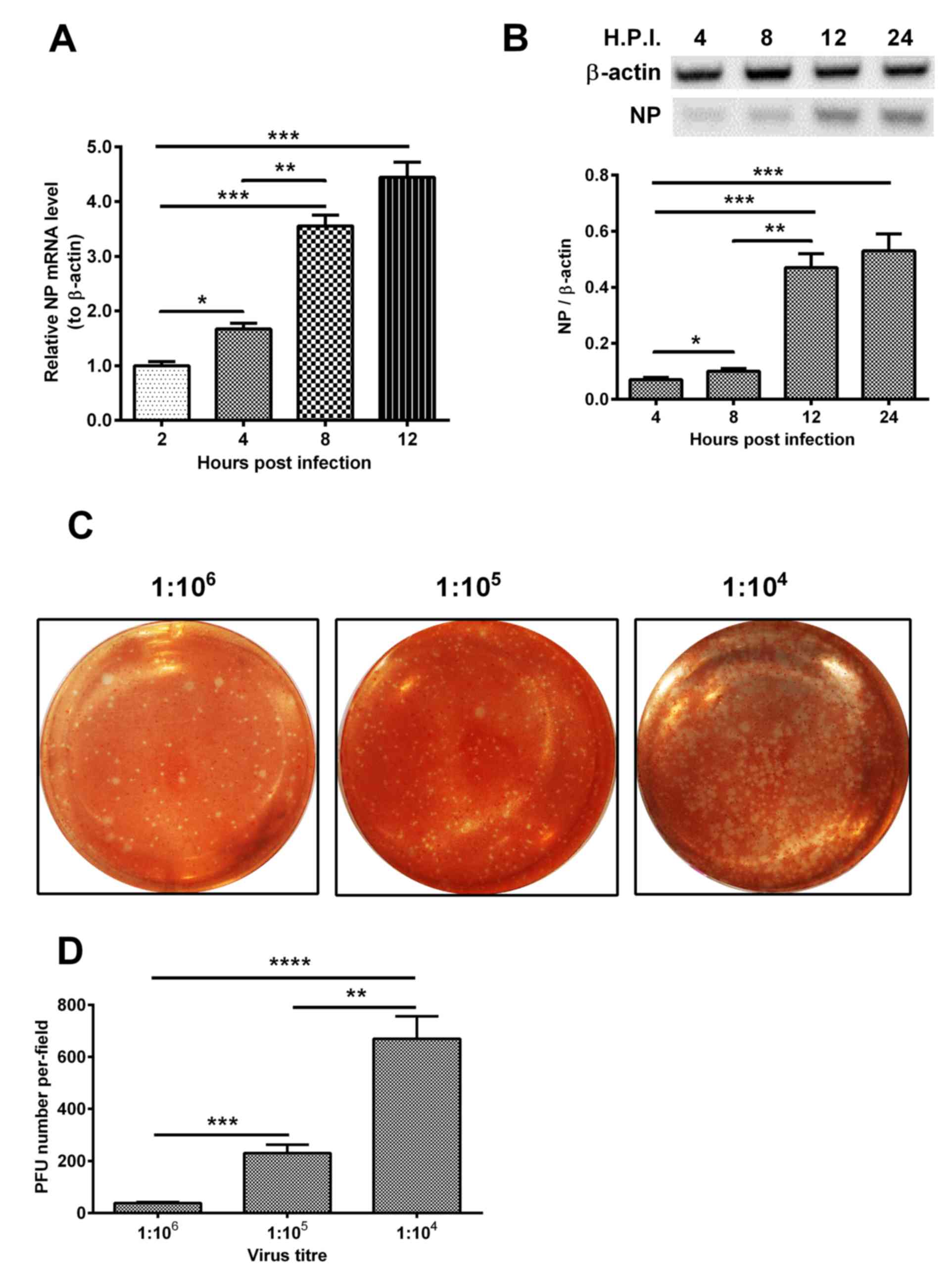
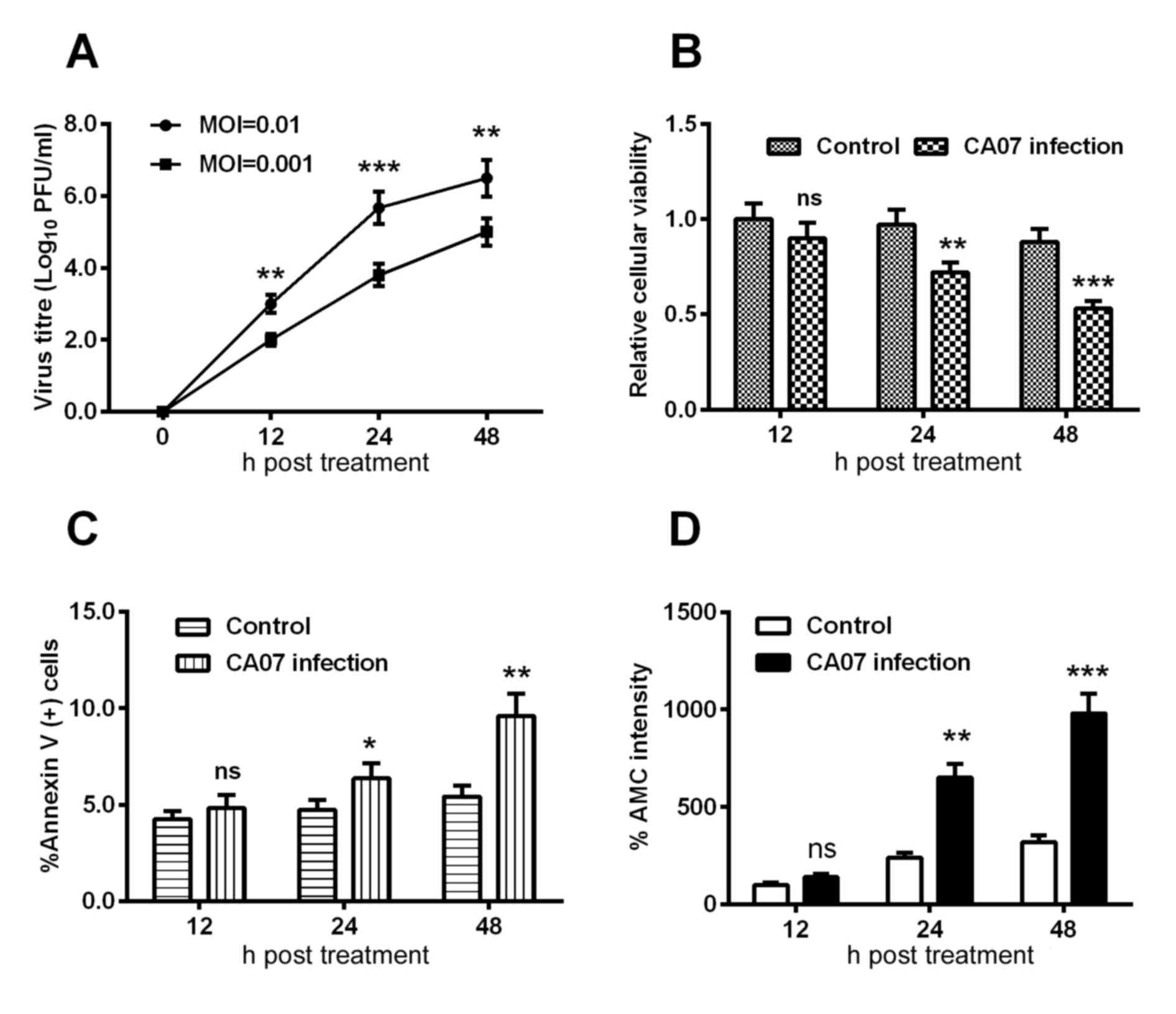
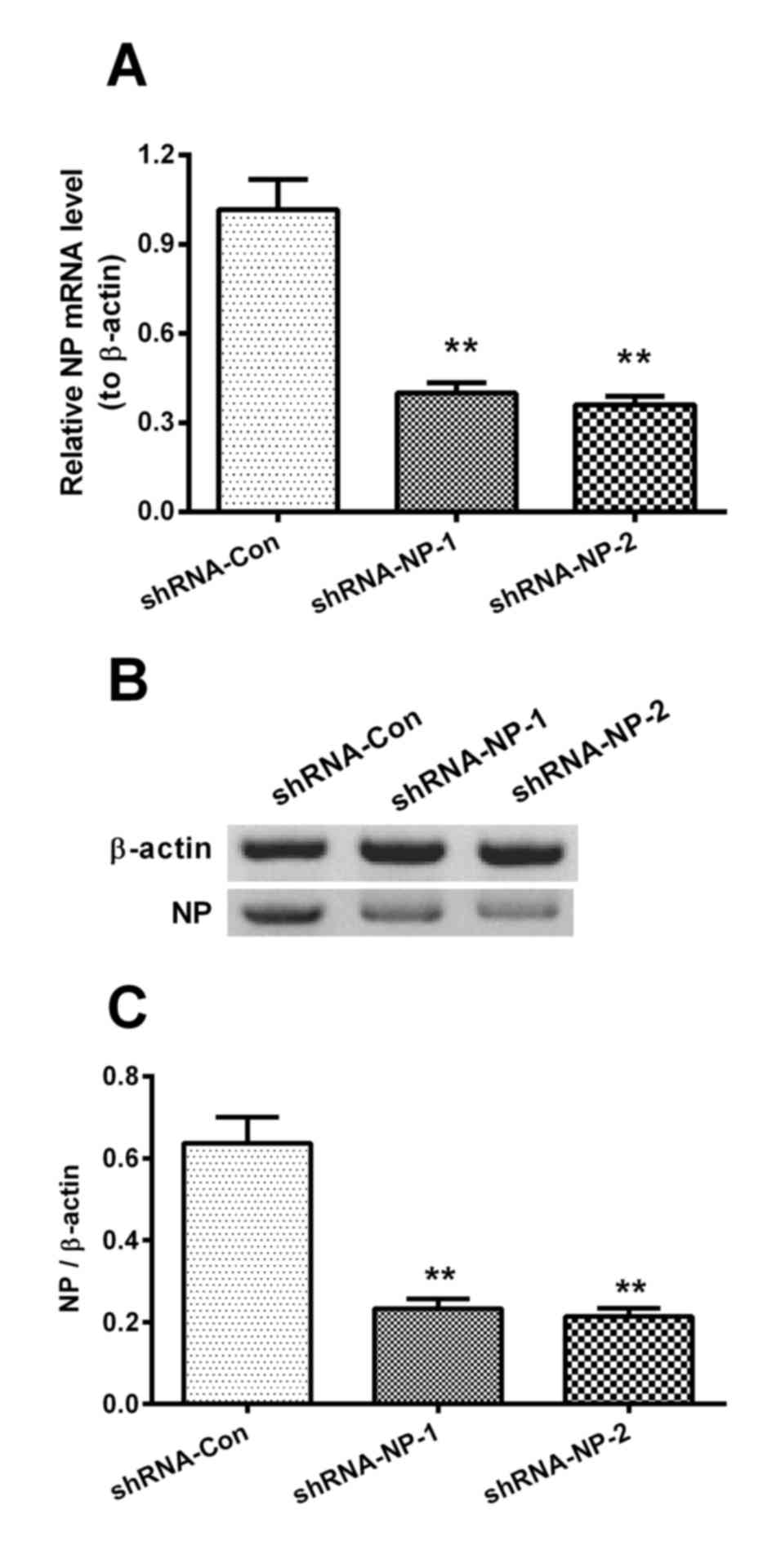
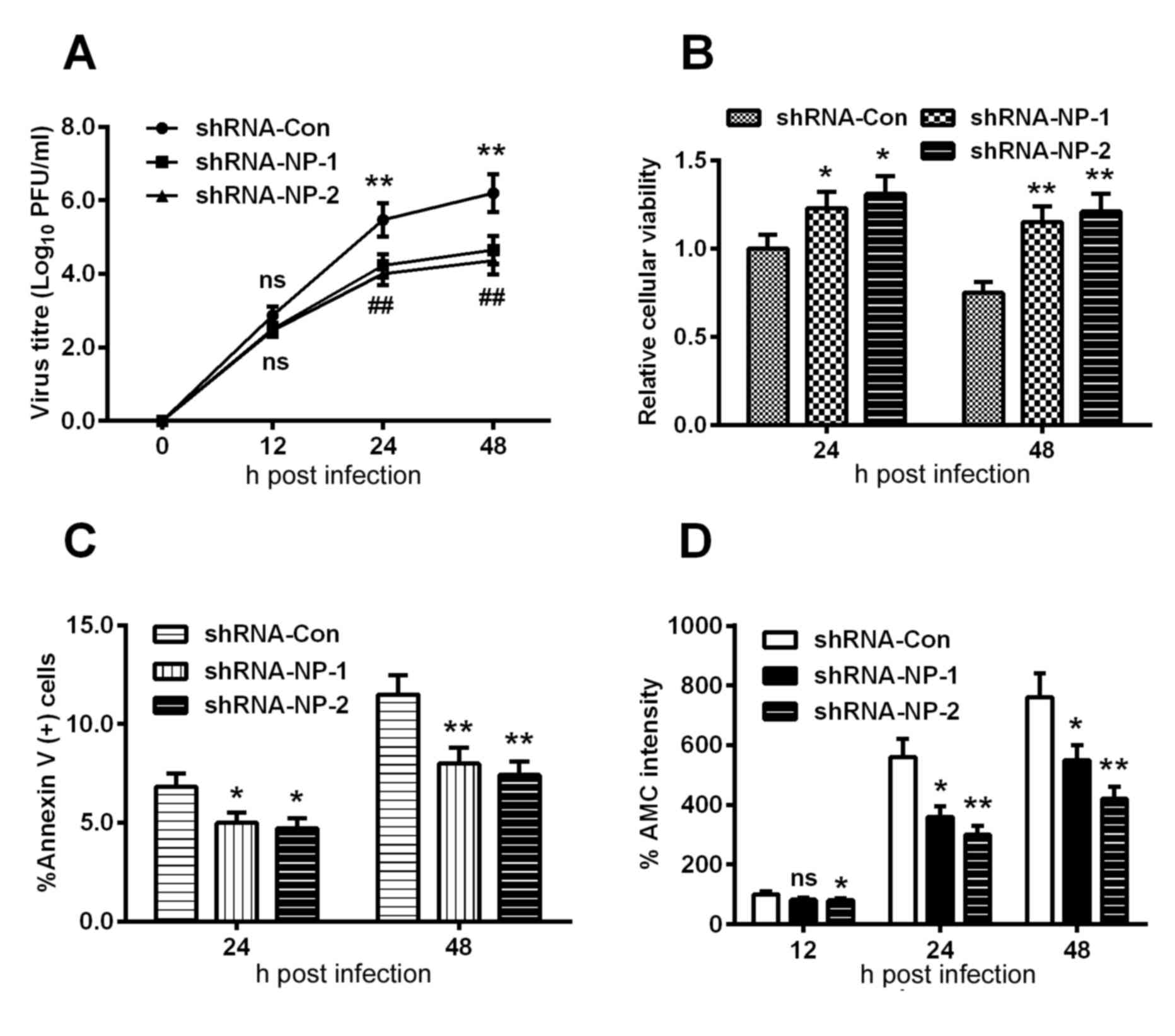
|
1
|
Fraser C, Donnelly CA, Cauchemez S, Hanage
WP, van Kerkhove MD, Hollingsworth TD, Griffin J, Baggaley RF,
Jenkins HE, Lyons EJ, et al: Pandemic potential of a strain of
influenza A (H1N1): Early findings. Science. 324:1557–1561. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pan HY, Yano M and Kido H: Effects of
inhibitors of Toll-like receptors, protease-activated receptor-2
signalings and trypsin on influenza A virus replication and
upregulation of cellular factors in cardiomyocytes. J Med Invest.
58:19–28. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mamas MA, Fraser D and Neyses L:
Cardiovascular manifestations associated with influenza virus
infection. Int J Cardiol. 130:304–309. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Warren-Gash C, Smeeth L and Hayward AC:
Influenza as a trigger for acute myocardial infarction or death
from cardiovascular disease: A systematic review. Lancet Infect
Dis. 9:601–610. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Davis MM, Taubert K, Benin AL, Brown DW,
Mensah GA, Baddour LM, Dunbar S and Krumholz HM; American Heart
Association, : American College of Cardiology: Influenza
vaccination as secondary prevention for cardiovascular disease: A
science advisory from the American Heart Association/American
College of Cardiology. Circulation. 114:1549–1553. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Steinhauer DA, Domingo E and Holland JJ:
Lack of evidence for proofreading mechanisms associated with an RNA
virus polymerase. Gene. 122:281–288. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ludwig S, Planz O, Pleschka S and Wolff T:
Influenza-virus-induced signaling cascades: Targets for antiviral
therapy? Trends Mol Med. 9:46–52. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ludwig S, Pleschka S, Planz O and Wolff T:
Ringing the alarm bells: Signalling and apoptosis in influenza
virus infected cells. Cell Microbiol. 8:375–386. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhirnov OP, Konakova TE, Wolff T and Klenk
HD: NS1 protein of influenza A virus down-regulates apoptosis. J
Virol. 76:1617–1625. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mohsin MA, Morris SJ, Smith H and Sweet C:
Correlation between levels of apoptosis, levels of infection and
haemagglutinin receptor binding interaction of various subtypes of
influenza virus: Does the viral neuraminidase have a role in these
associations. Virus Res. 85:123–131. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schultz-Cherry S and Hinshaw VS: Influenza
virus neuraminidase activates latent transforming growth factor
beta. J Virol. 70:8624–8629. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Morris SJ, Nightingale K, Smith H and
Sweet C: Influenza A virus-induced apoptosis is a multifactorial
process: Exploiting reverse genetics to elucidate the role of
influenza A virus proteins in virus-induced apoptosis. Virology.
335:198–211. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhirnov O and Bukrinskaya AG:
Nucleoproteins of animal influenza viruses, in contrast to those of
human strains, are not cleaved in infected cells. J Gen Virol.
65:1127–1134. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhirnov OP and Bukrinskaya AG: Two forms
of influenza virus nucleoprotein in infected cells and virions.
Virology. 109:174–179. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ludwig S, Pleschka S and Wolff T: A fatal
relationship-influenza virus interactions with the host cell. Viral
Immunol. 12:175–196. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pleschka S, Wolff T, Ehrhardt C, Hobom G,
Planz O, Rapp UR and Ludwig S: Influenza virus propagation is
impaired by inhibition of the Raf/MEK/ERK signalling cascade. Nat
Cell Biol. 3:301–305. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mori I, Komatsu T, Takeuchi K, Nakakuki K,
Sudo M and Kimura Y: In vivo induction of apoptosis by influenza
virus. J Gen Virol. 76:2869–2873. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Roulston A, Marcellus RC and Branton PE:
Viruses and apoptosis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 53:577–628. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chanturiya AN, Basañez G, Schubert U,
Henklein P, Yewdell JW and Zimmerberg J: PB1-F2, an influenza A
virus-encoded proapoptotic mitochondrial protein, creates variably
sized pores in planar lipid membranes. J Virol. 78:6304–6312. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stasakova J, Ferko B, Kittel C, Sereinig
S, Romanova J, Katinger H and Egorov A: Influenza A mutant viruses
with altered NS1 protein function provoke caspase-1 activation in
primary human macrophages, resulting in fast apoptosis and release
of high levels of interleukins 1beta and 18. J Gen Virol.
86:185–195. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Han X, Li Z, Chen H, Wang H, Mei L, Wu S,
Zhang T, Liu B and Lin X: Influenza virus A/Beijing/501/2009(H1N1)
NS1 interacts with β-tubulin and induces disruption of the
microtubule network and apoptosis on A549 cells. PloS One.
7:e483402012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wurzer WJ, Planz O, Ehrhardt C, Giner M,
Silberzahn T, Pleschka S and Ludwig S: Caspase 3 activation is
essential for efficient influenza virus propagation. EMBO J.
22:2717–2728. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhirnov OP, Konakova TE, Garten W and
Klenk H: Caspase-dependent N-terminal cleavage of influenza virus
nucleocapsid protein in infected cells. J Virol. 73:10158–10163.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yajima T and Knowlton KU: Viral
myocarditis: From the perspective of the virus. Circulation.
119:2615–2624. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Balachandran S, Roberts PC, Kipperman T,
Bhalla KN, Compans RW, Archer DR and Barber GN: Alpha/beta
interferons potentiate virus-induced apoptosis through activation
of the FADD/Caspase-8 death signaling pathway. J Virol.
74:1513–1523. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|