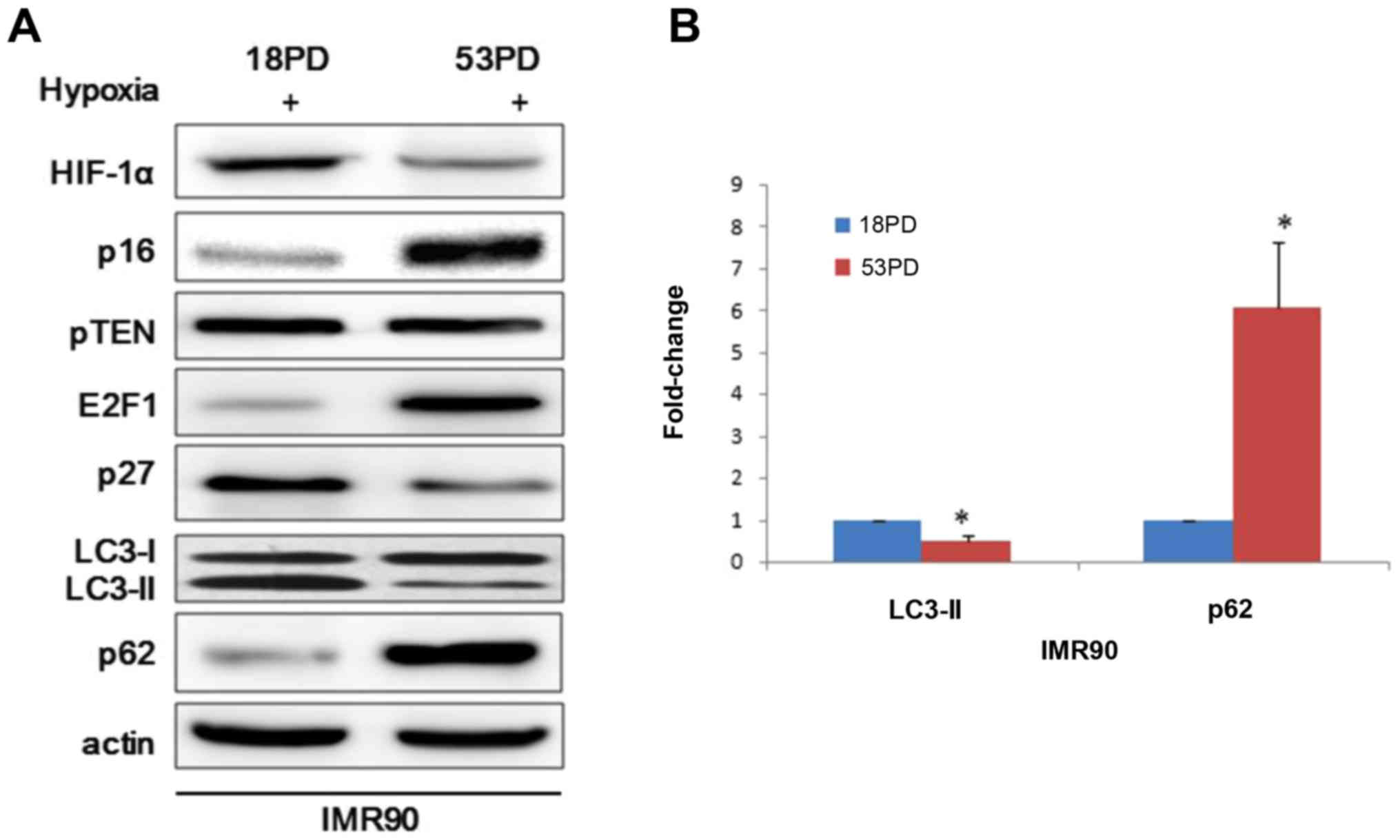
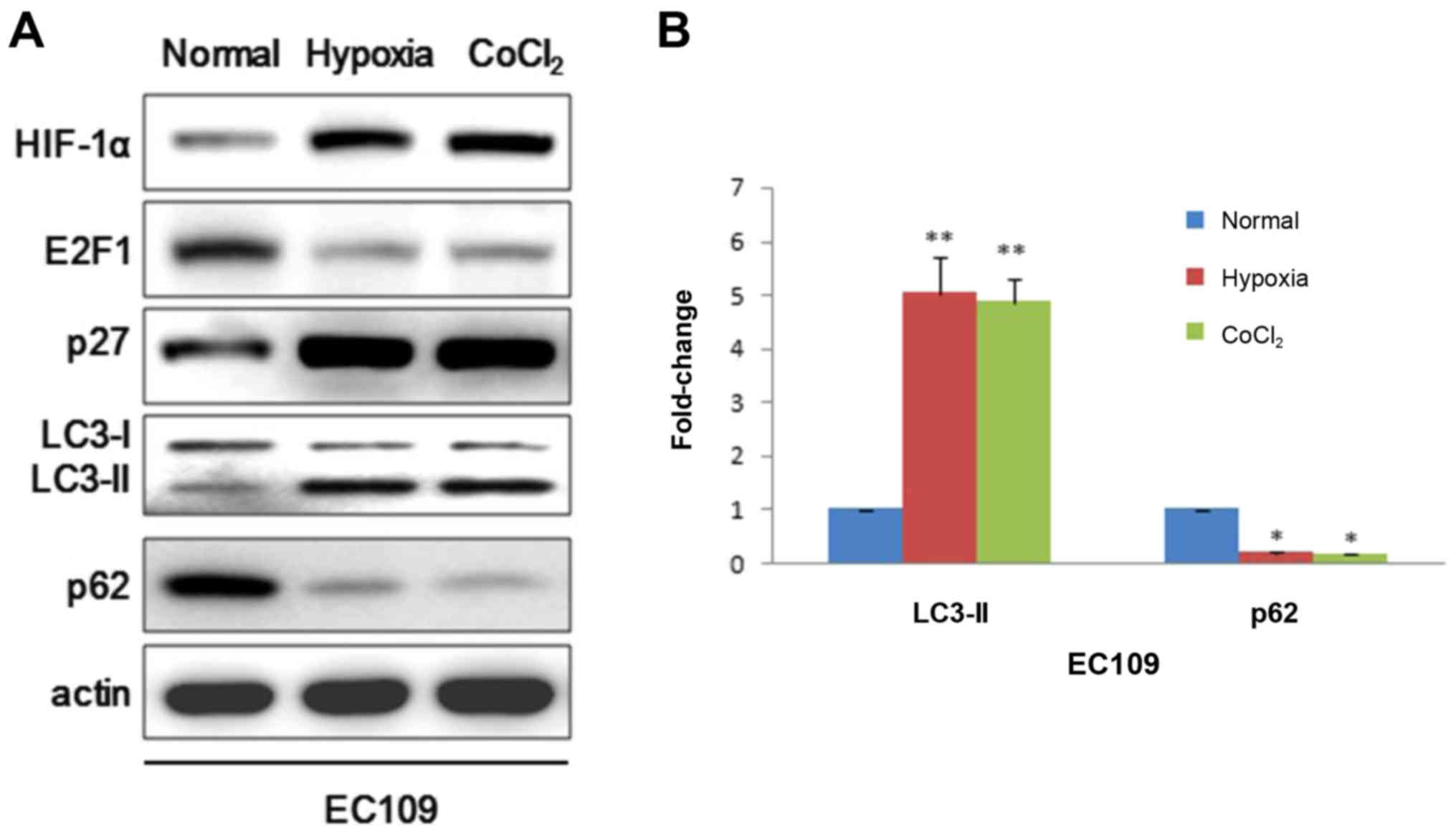
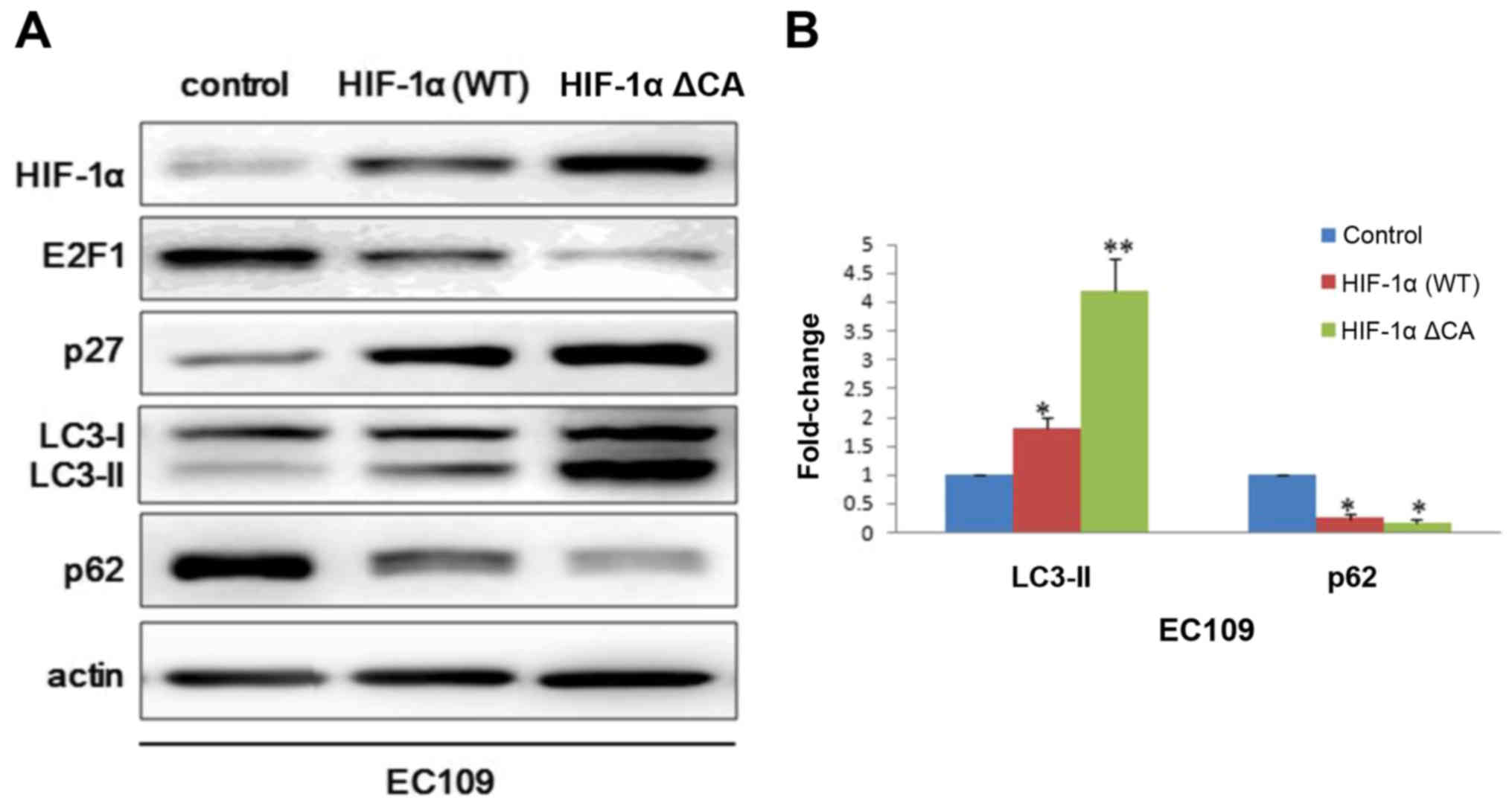
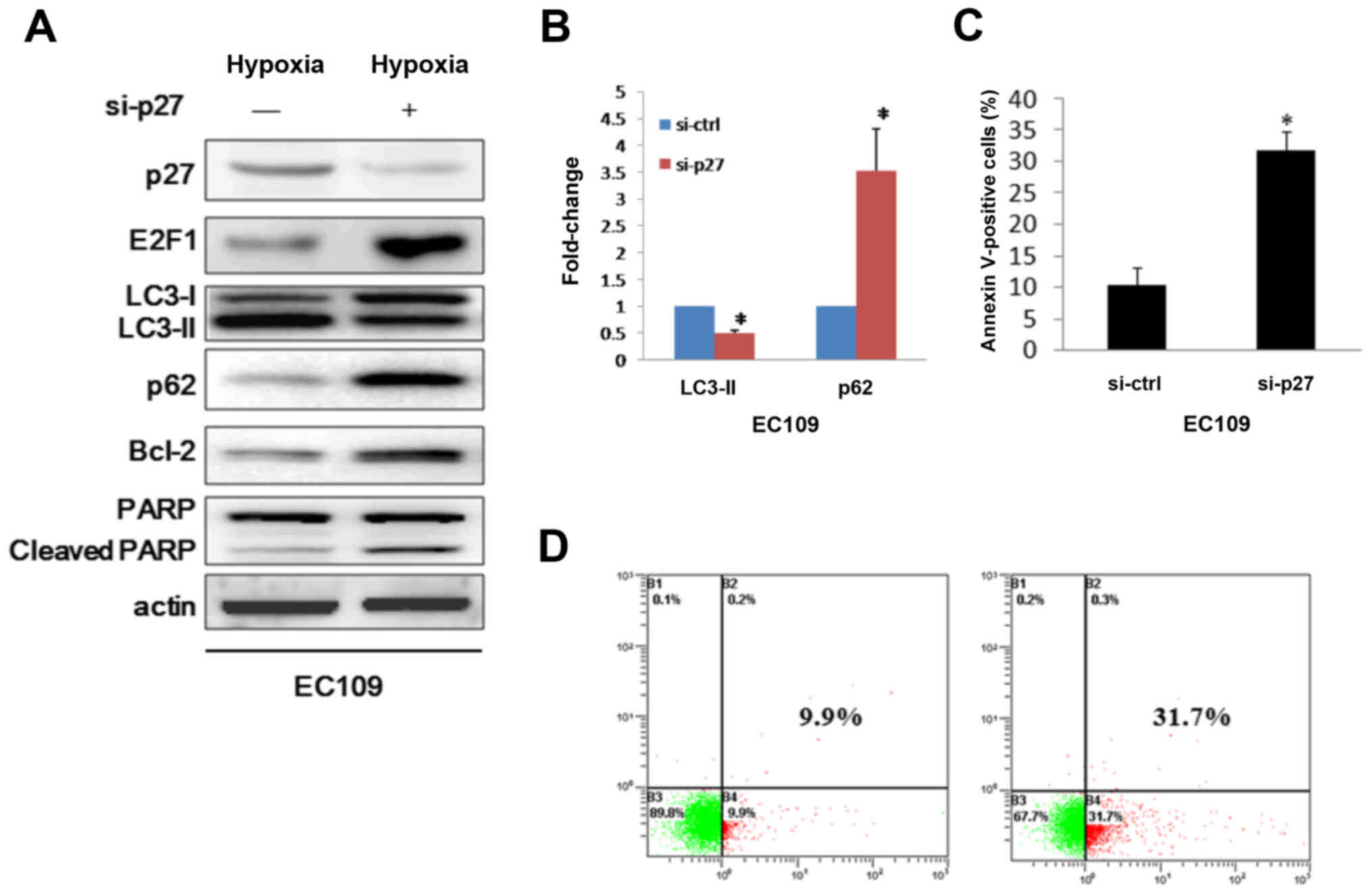
|
1
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cao J, Ying M, Xie N, Lin G, Dong R, Zhang
J, Yan H, Yang X, He Q and Yang B: The oxidation states of DJ-1
dictate the cell fate in response to oxidative stress triggered by
4-hpr: Autophagy or apoptosis? Antioxid Redox Signal. 21:1443–1459.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rubinsztein DC: The roles of intracellular
protein-degradation pathways in neurodegeneration. Nature.
443:780–786. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang Z and Klionsky DJ: Eaten alive: A
history of macroautophagy. Nat Cell Biol. 12:814–822. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mijaljica D, Prescott M and Devenish RJ:
Microautophagy in mammalian cells: Revisiting a 40-year-old
conundrum. Autophagy. 7:673–682. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jiang P and Mizushima N: Autophagy and
human diseases. Cell Res. 24:69–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
White E: Deconvoluting the
context-dependent role for autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
12:401–410. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Burada F, Nicoli ER, Ciurea ME, Uscatu DC,
Ioana M and Gheonea DI: Autophagy in colorectal cancer: An
important switch from physiology to pathology. World J Gastrointest
Oncol. 7:271–284. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cecconi F and Jäättelä M: Targeting
ions-induced autophagy in cancer. Cancer cell. 26:599–600. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shintani T and Klionsky DJ: Autophagy in
health and disease: A double-edged sword. Science. 306:990–995.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sena P, Mariani F, Mancini S, Benincasa M,
Magnani G, Pedroni M, Palumbo C and Roncucci L: Autophagy is
upregulated during colorectal carcinogenesis, and in DNA
microsatellite stable carcinomas. Oncol Rep. 34:3222–3230.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shelby SJ, Angadi PS, Zheng QD, Yao J, Jia
L and Zacks DN: Hypoxia inducible factor 1α contributes to
regulation of autophagy in retinal detachment. Exp Eye Res.
137:84–93. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang H, Bosch-Marce M, Shimoda LA, Tan
YS, Baek JH, Wesley JB, Gonzalez FJ and Semenza GL: Mitochondrial
autophagy is an HIF-1-dependent adaptive metabolic response to
hypoxia. J Biol Chem. 283:10892–10903. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu H, Wang D, Zhang L, Xie X, Wu Y, Liu
Y, Shao G and Su Z: Upregulation of autophagy by hypoxia-inducible
factor-1α promotes EMT and metastatic ability of CD133+
pancreatic cancer stem-like cells during intermittent hypoxia.
Oncol Rep. 32:935–942. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA and Semenza GL:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS
heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 92:5510–5514. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Blagosklonny MV: Antiangiogenic therapy
and tumor progression. Cancer cell. 5:13–17. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Semenza GL: HIF-1 and mechanisms of
hypoxia sensing. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 13:167–171. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Seeber LM, Horrée N, Vooijs MA, Heintz AP,
van der Wall E, Verheijen RH and van Diest PJ: The role of hypoxia
inducible factor-1alpha in gynecological cancer. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 78:173–184. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tittarelli A, Janji B, van Moer K, Noman
MZ and Chouaib S: The selective degradation of synaptic connexin 43
protein by Hypoxia-induced autophagy impairs natural killer
cell-mediated tumor cell killing. J Biol Chem. 290:23670–23679.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jiang H, Martin V, Gomez-Manzano C,
Johnson DG, Alonso M, White E, Xu J, McDonnell TJ, Shinojima N and
Fueyo J: The RB-E2F1 pathway regulates autophagy. Cancer Res.
70:7882–7893. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen T, Xue L, Niu J, Ma L, Li N, Cao X,
Li Q, Wang M, Zhao W, Li G, et al: The retinoblastoma protein
selectively represses E2F1 targets via a TAAC DNA element during
cellular senescence. J Biol Chem. 287:37540–37551. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Polager S and Ginsberg D: E2F-at the
crossroads of life and death. Trends Cell Biol. 18:528–535. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R,
Liang XH, Mizushima N, Packer M, Schneider MD and Levine B: Bcl-2
antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell.
122:927–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Luo S and Rubinsztein DC: Apoptosis blocks
Beclin 1-dependent autophagosome synthesis: An effect rescued by
Bcl-xL. Cell Death Differ. 17:268–277. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chagin AS: Effectors of mTOR-autophagy
pathway: Targeting cancer, affecting the skeleton. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 28:1–7. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pei Y, Wang P, Liu H, He F and Ming L:
FOXQ1 promotes esophageal cancer proliferation and metastasis by
negatively modulating CDH1. Biomed Pharmacother. 74:89–94. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kirschner K, Samarajiwa SA, Cairns JM,
Menon S, Pérez-Mancera PA, Tomimatsu K, Bermejo-Rodriguez C, Ito Y,
Chandra T, Narita M, et al: Phenotype specific analyses reveal
distinct regulatory mechanism for chronically activated p53. PLoS
Genet. 11:e10050532015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vaupel P: The role of hypoxia-induced
factors in tumor progression. Oncologist. 9 Suppl 5:S10–S17. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Unruh A, Ressel A, Mohamed HG, Johnson RS,
Nadrowitz R, Richter E, Katschinski DM and Wenger RH: The
hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha is a negative factor for tumor
therapy. Oncogene. 22:3213–3220. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Clarke HJ, Chambers JE, Liniker E and
Marciniak SJ: Endoplasmic reticulum stress in malignancy. Cancer
Cell. 25:563–573. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu Y, Zhao T, Itasaka S, Zeng L, Yeom CJ,
Hirota K, Suzuki K, Morinibu A, Shinomiya K, Ou G, et al:
Involvement of decreased hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activity and
resultant G1-S cell cycle transition in radioresistance of
perinecrotic tumor cells. Oncogene. 32:2058–2068. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|