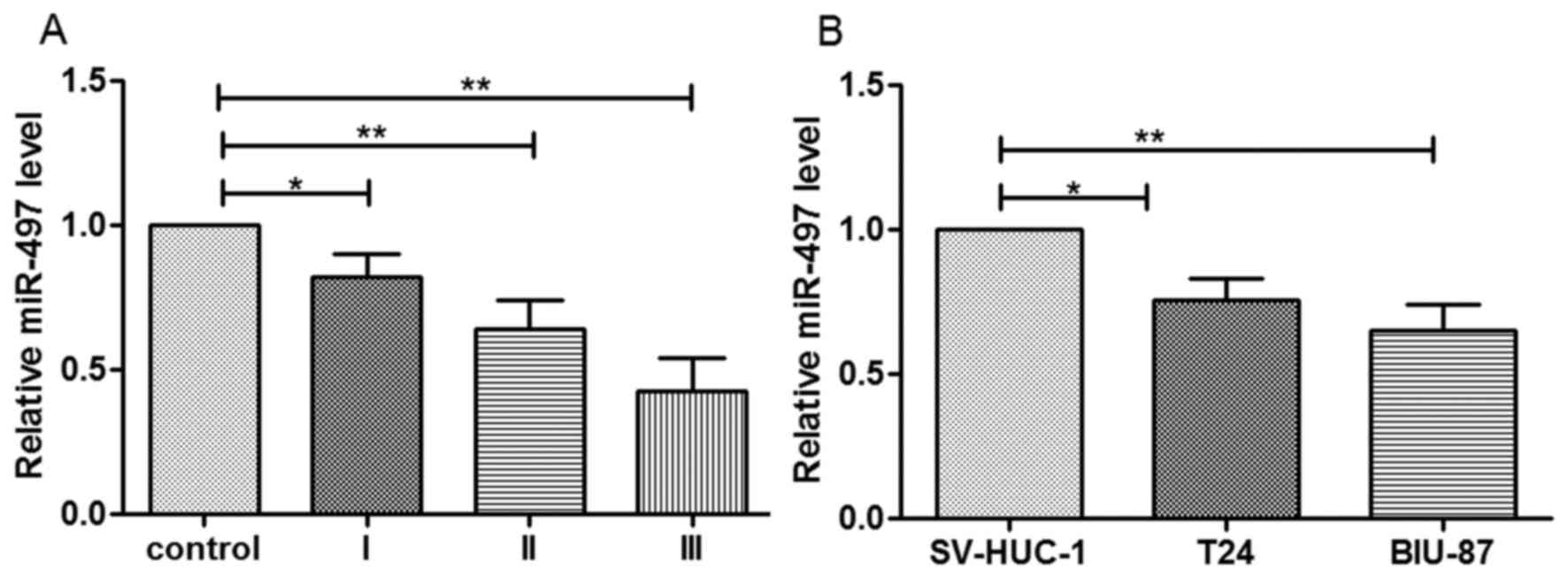
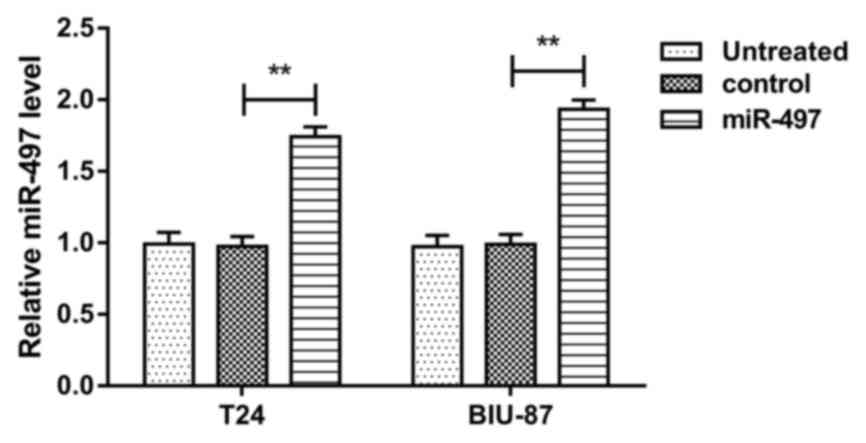
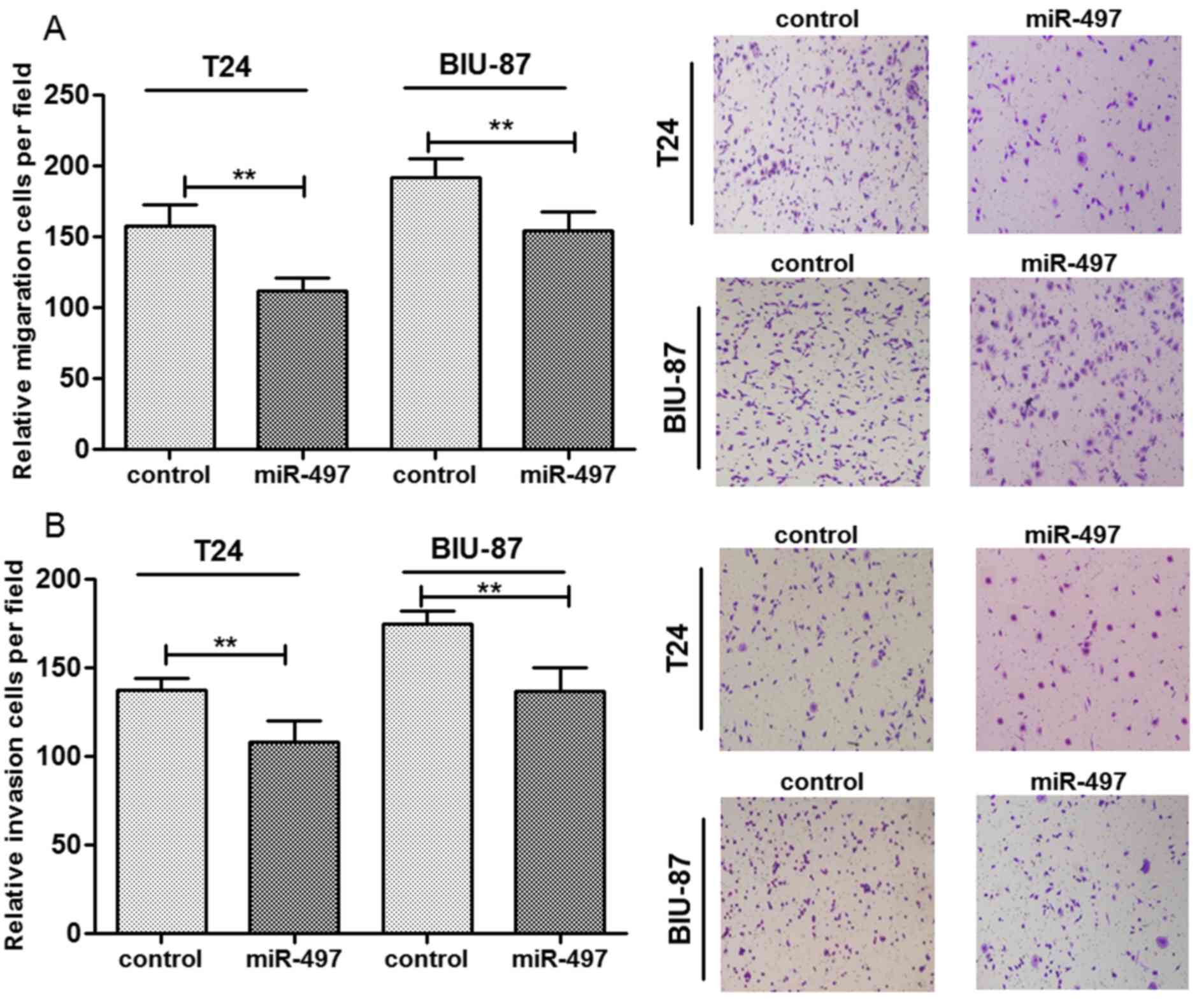
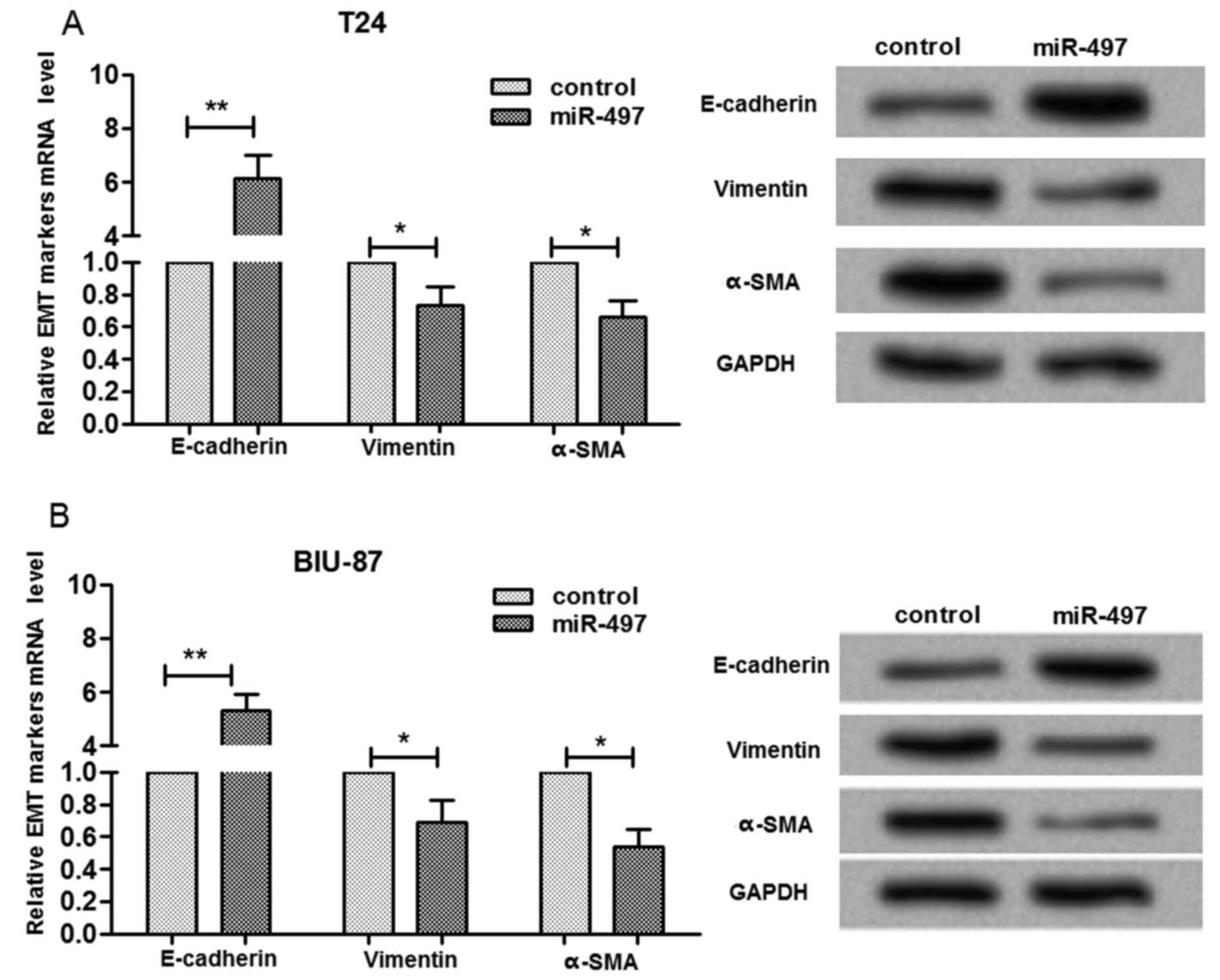
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang X and Zhang Y: Bladder cancer and
genetic mutations. Cell Biochem Biophys. 73:65–69. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Harshman LC, Preston MA, Bellmunt J and
Beard C: Diagnosis of bladder carcinoma: A clinician's perspective.
Surg Pathol Clin. 8:677–685. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheung G, Sahai A, Billia M, Dasgupta P
and Khan MS: Recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of
bladder cancer. BMC Med. 11:132013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aigner A: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in cancer
invasion and metastasis: Therapeutic approaches based on
metastasis-related miRNAs. J Mol Med (Berl). 89:445–457. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zheng N, Yang P, Wang Z and Zhou Q:
OncomicroRNAs-mediated tumorigenesis: Implication in cancer
diagnosis and targeted therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 17:40–47.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Medina PP and Slack FJ: MicroRNAs and
cancer: An overview. Cell Cycle. 7:2485–2492. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lan G, Yang L, Xie X, Peng L and Wang Y:
MicroRNA-490-5p is a novel tumor suppressor targeting c-FOS in
human bladder cancer. Arch Med Sci. 11:561–569. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Drayton RM, Dudziec E, Peter S, Bertz S,
Hartmann A, Bryant HE and Catto JW: Reduced expression of miRNA-27a
modulates cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer by targeting the
cystine/glutamate exchanger SLC7A11. Clin Cancer Res. 20:1990–2000.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yin KJ, Deng Z, Huang H, Hamblin M, Xie C,
Zhang J and Chen YE: miR-497 regulates neuronal death in mouse
brain after transient focal cerebral ischemia. Neurobiol Dis.
38:17–26. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li D, Zhao Y, Liu C, Chen X, Qi Y, Jiang
Y, Zou C, Zhang X, Liu S, Wang X, et al: Analysis of MiR-195 and
MiR-497 expression, regulation and role in breast cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 17:1722–1730. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yan JJ, Zhang YN, Liao JZ, Ke KP, Chang Y,
Li PY, Wang M, Lin JS and He XX: MiR-497 suppresses angiogenesis
and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting VEGFA and
AEG-1. Oncotarget. 6:29527–29542. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Li Z, Gong D, Zhan B,
Man X and Kong C: MicroRNA-497 inhibits the proliferation,
migration and invasion of human bladder transitional cell carcinoma
cells by targeting E2F3. Oncol Rep. 36:1293–1300. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Du M, Shi D, Lin Y, Yuan L, Li P, Chu H,
Qin C, Yin C, Zhang Z and Wang M: Circulating miR-497 and miR-663b
in plasma are potential novel biomarkers for bladder cancer. Sci
Rep. 5:104372015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mostofi FK, Davis CJ and Sesterhenn IA:
WHO histological typing of urinary bladder tumors. Springer;
Berlin: 1973
|
|
16
|
Union for International Cancer Control
(UICC), . TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. Sobin LH and
Wittekind CH: 6th. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ: 2002
|
|
17
|
Brackenbury WJ and Djamgoz MB: Nerve
growth factor enhances voltage-gated Na+ channel activity and
transwell migration in Mat-LyLu rat prostate cancer cell line. J
Cell Physiol. 210:602–608. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin Y, Yue B, Xiang H, Liu Y, Ma X and
Chen B: Survivin is expressed in degenerated nucleus pulposus cells
and is involved in proliferation and the prevention of apoptosis in
vitro. Mol Med Rep. 13:1026–1032. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yan JJ, Zhang YN, Liao JZ, Ke KP, Chang Y,
Li PY, Wang M, Lin JS and He XX: MiR-497 suppresses angiogenesis
and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting VEGFA and
AEG-1. Oncotarget. 6:29527–29542. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhu W, Zhu D, Lu S, Wang T, Wang J, Jiang
B, Shu Y and Liu P: miR-497 modulates multidrug resistance of human
cancer cell lines by targeting BCL2. Med Oncol. 29:384–391. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ruan WD, Wang P, Feng S, Xue Y and Zhang
B: MicroRNA-497 inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and
invasion by targeting AMOT in human osteosarcoma cells. Onco
Targets Ther. 9:303–313. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Luo Q, Li X, Gao Y, Long Y, Chen L, Huang
Y and Fang L: MiRNA-497 regulates cell growth and invasion by
targeting cyclin E1 in breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 13:952013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhu QS, Rosenblatt K, Huang KL, Lahat G,
Brobey R, Bolshakov S, Nguyen T, Ding Z, Belousov R, Bill K, et al:
Vimentin is a novel AKT1 target mediating motility and invasion.
Oncogene. 30:457–470. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
McInroy L and Määttä A: Down-regulation of
vimentin expression inhibits carcinoma cell migration and adhesion.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 360:109–114. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Peng RY, Zhou GH and Chun LI: Expression
of E-cadherin in Bladder Cancer. Prac J Cancer. 15:87–88. 2000.
|
|
27
|
Kumar CC, Kim JH, Bushel P, Armstrong L
and Catino JJ: Activation of smooth muscle alpha-actin promoter in
ras-transformed cells by treatments with antimitotic agents:
Correlation with stimulation of SRF:SRE mediated gene
transcription. J Biochem. 118:1285–1292. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kojc N, Zidar N, Vodopivec B and Gale N:
Expression of CD34, alpha-smooth muscle actin, and transforming
growth factor beta1 in squamous intraepithelial lesions and
squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx and hypopharynx. Hum Pathol.
36:16–21. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Duan LJ, Qi J, Kong XJ, Huang T, Qian XQ,
Xu D, Liang JH and Kang J: miR-133 modulates TGF-β1-induced bladder
smooth muscle cell hypertrophic and fibrotic response: Implication
for a role of microRNA in bladder wall remodeling caused by bladder
outlet obstruction. Cell Signal. 27:215–227. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang M, Shan LP and Zhang H: Expression
of Snail and E-cadherin in bladder urothelial carcinoma and their
relation with tumor recurrence. J Mod Oncol. 18:2422–2425.
2010.
|
|
31
|
Lewis SA, Traub P and Spilker CM: The
N-terminal domain of vimentin alters bladder permeability. J Urol.
170:2091–2094. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|