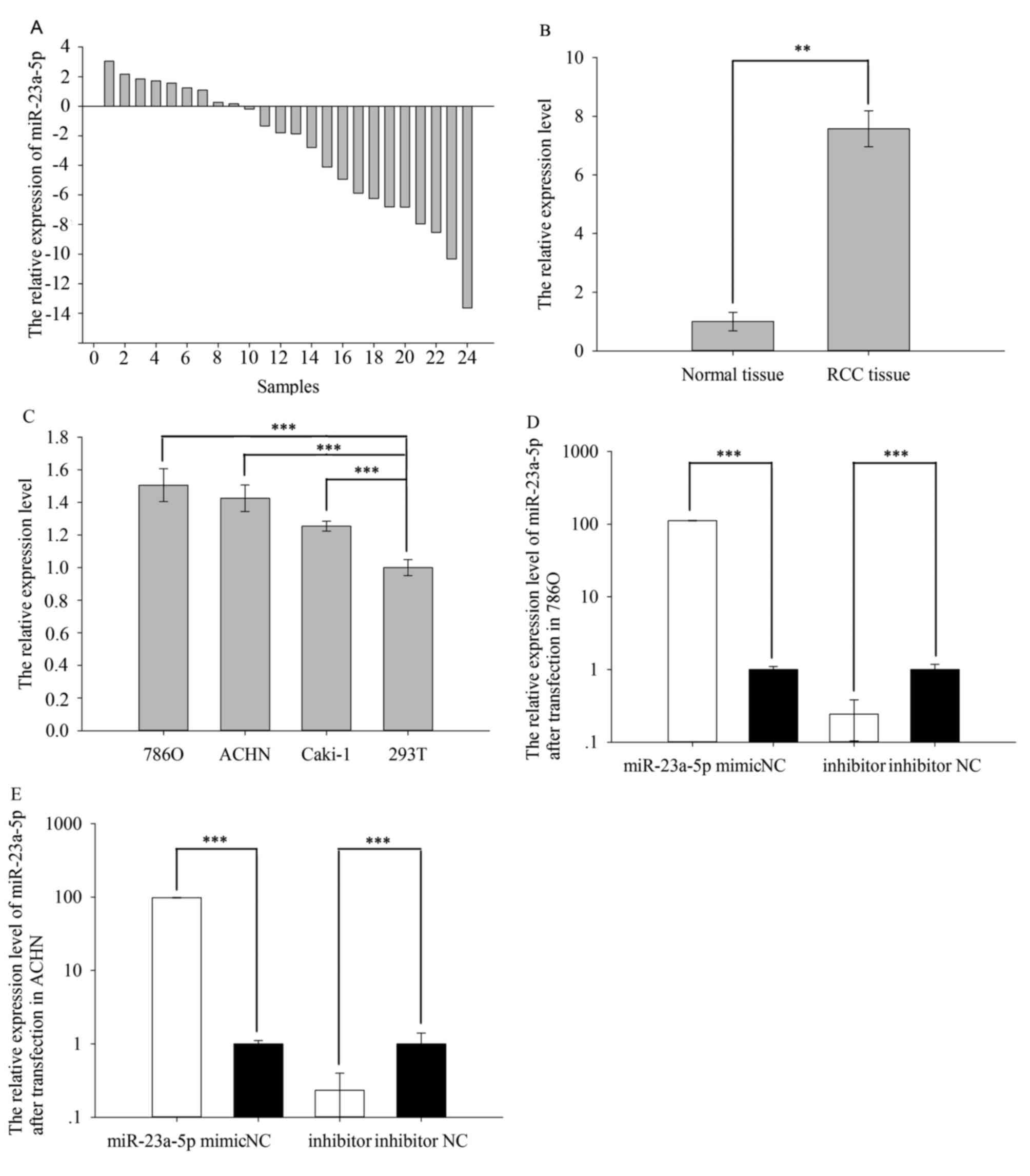
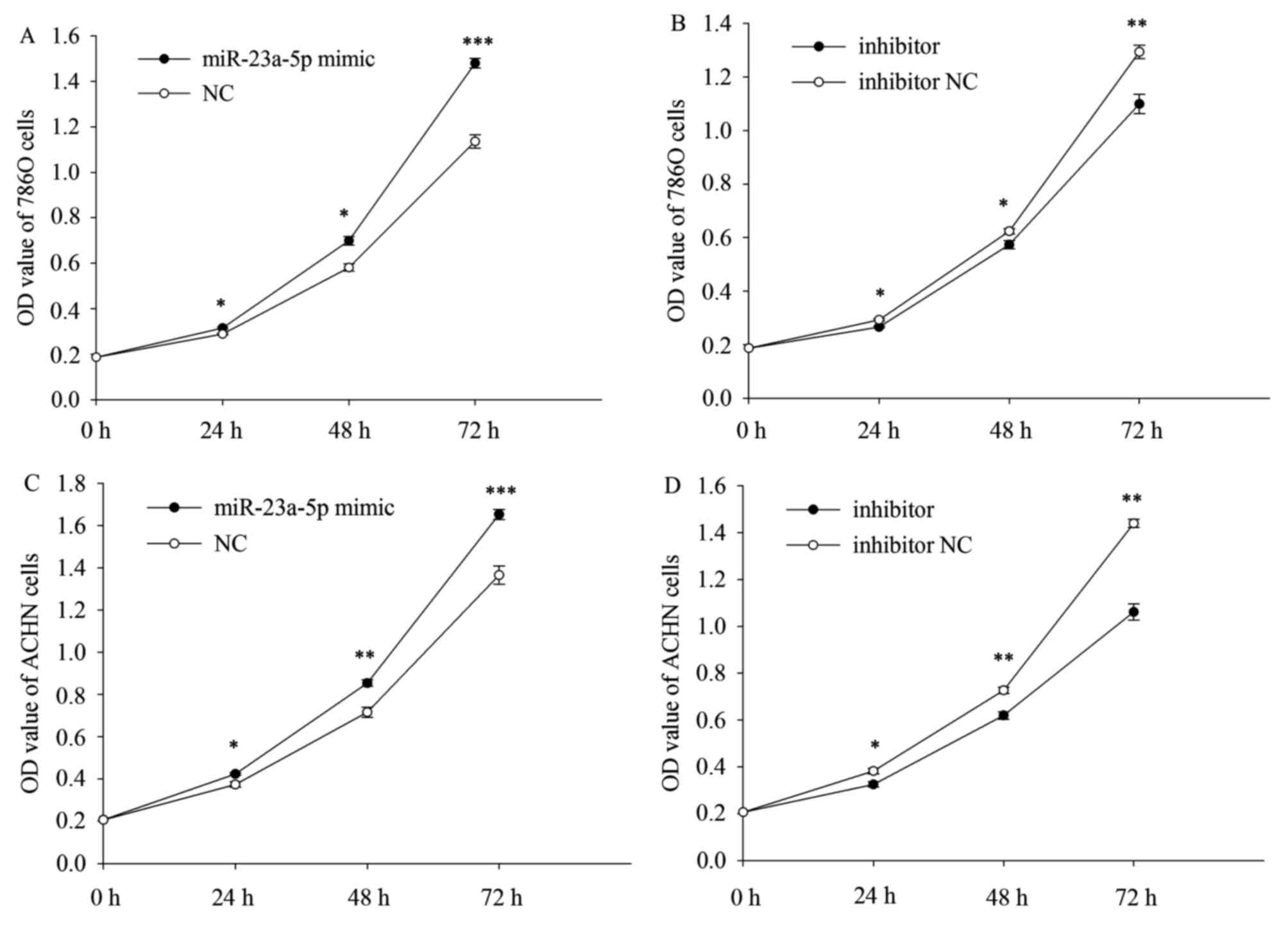
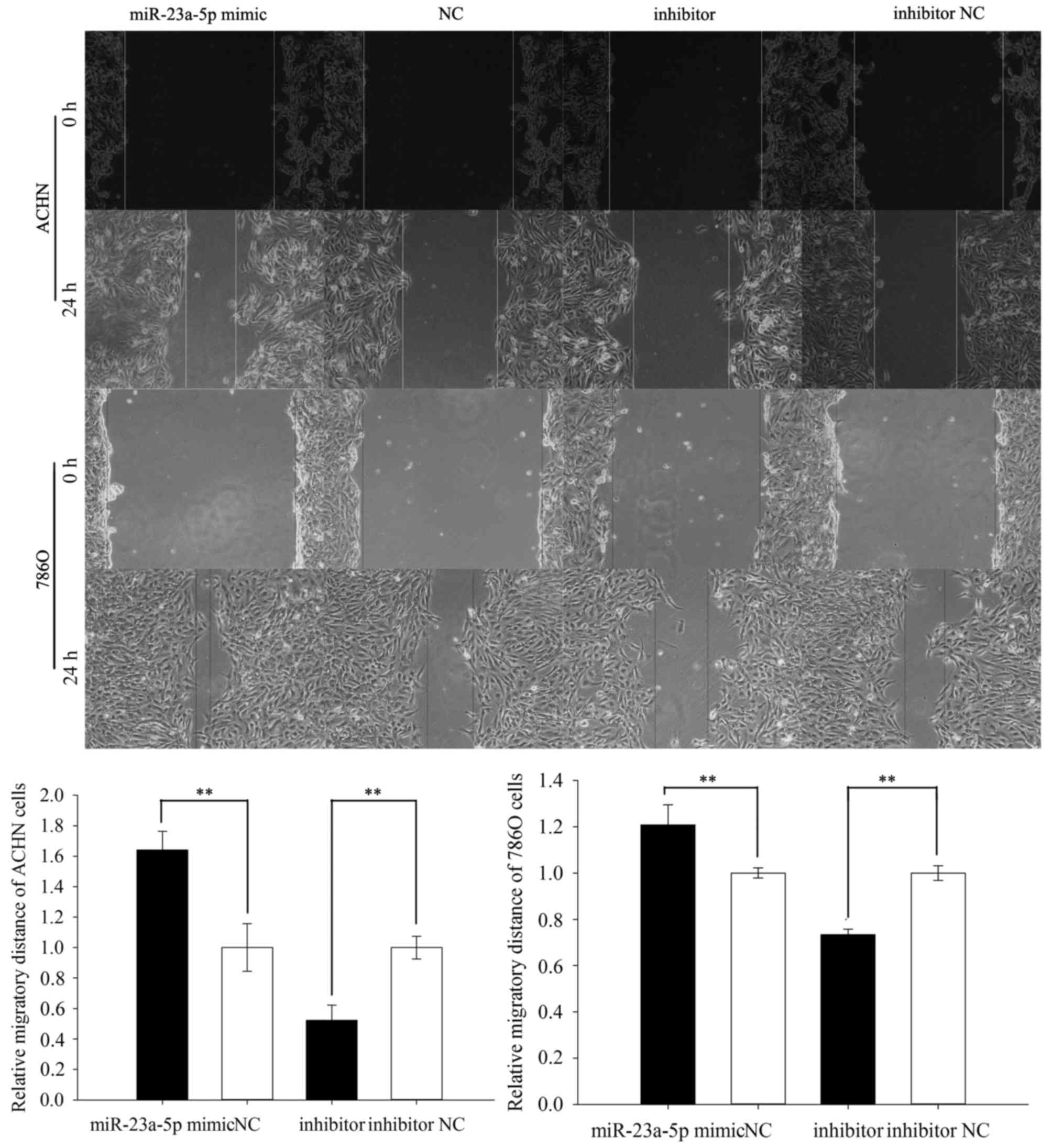
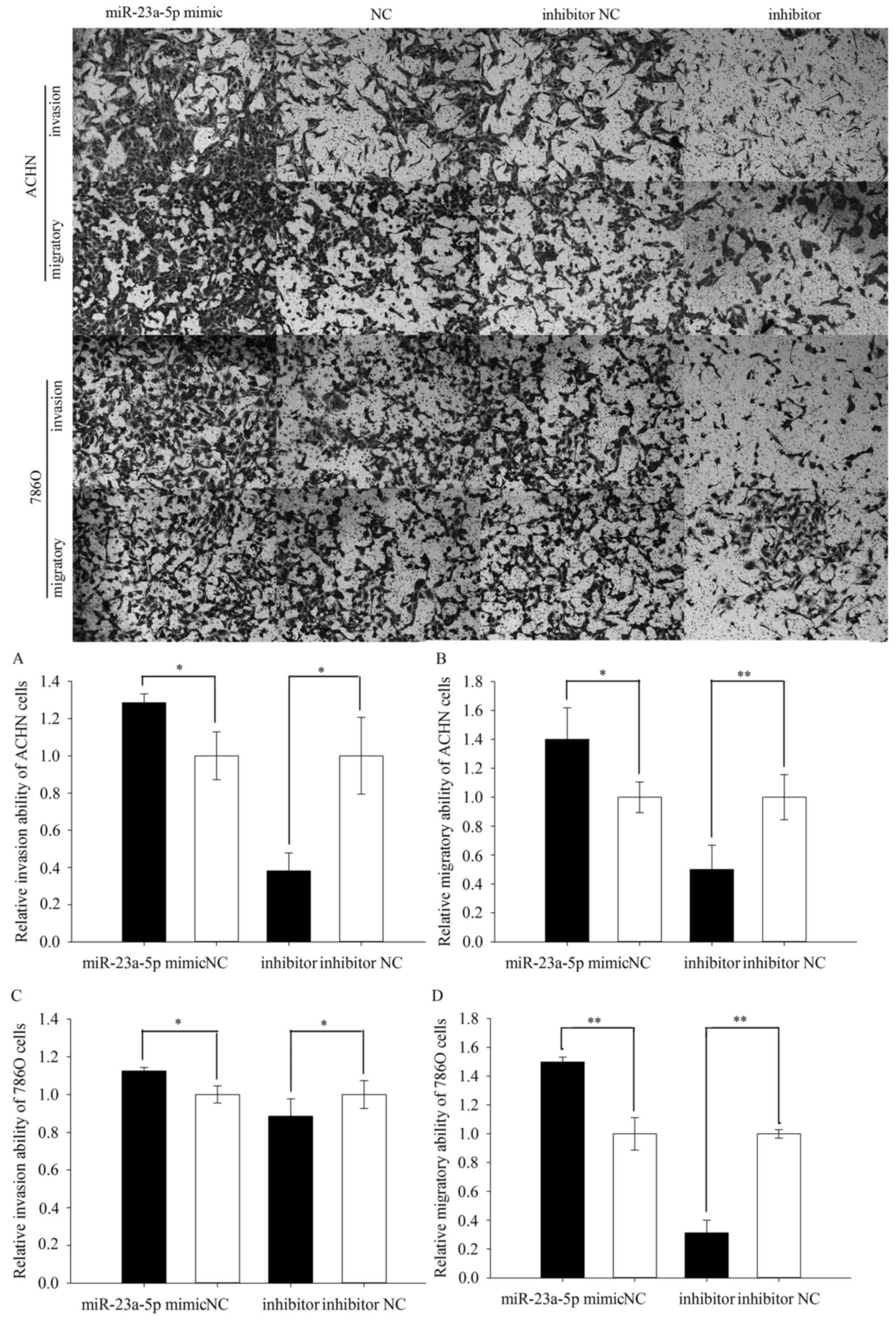
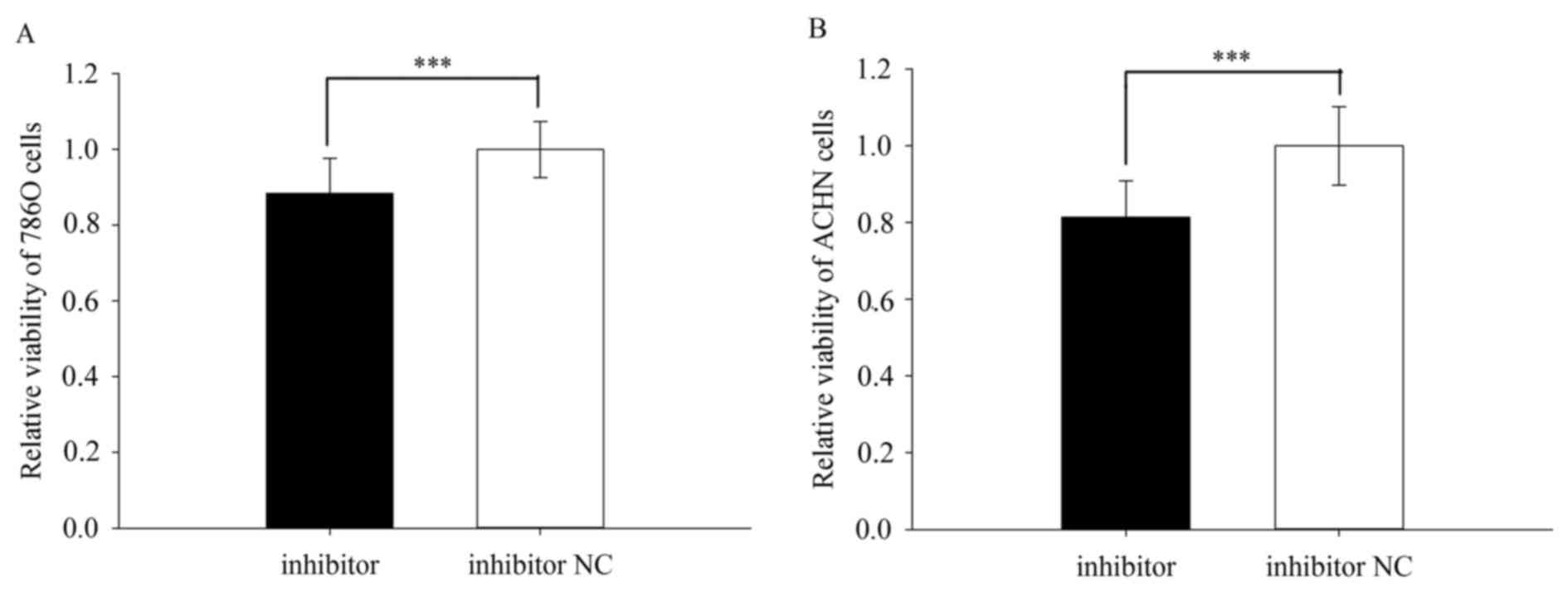
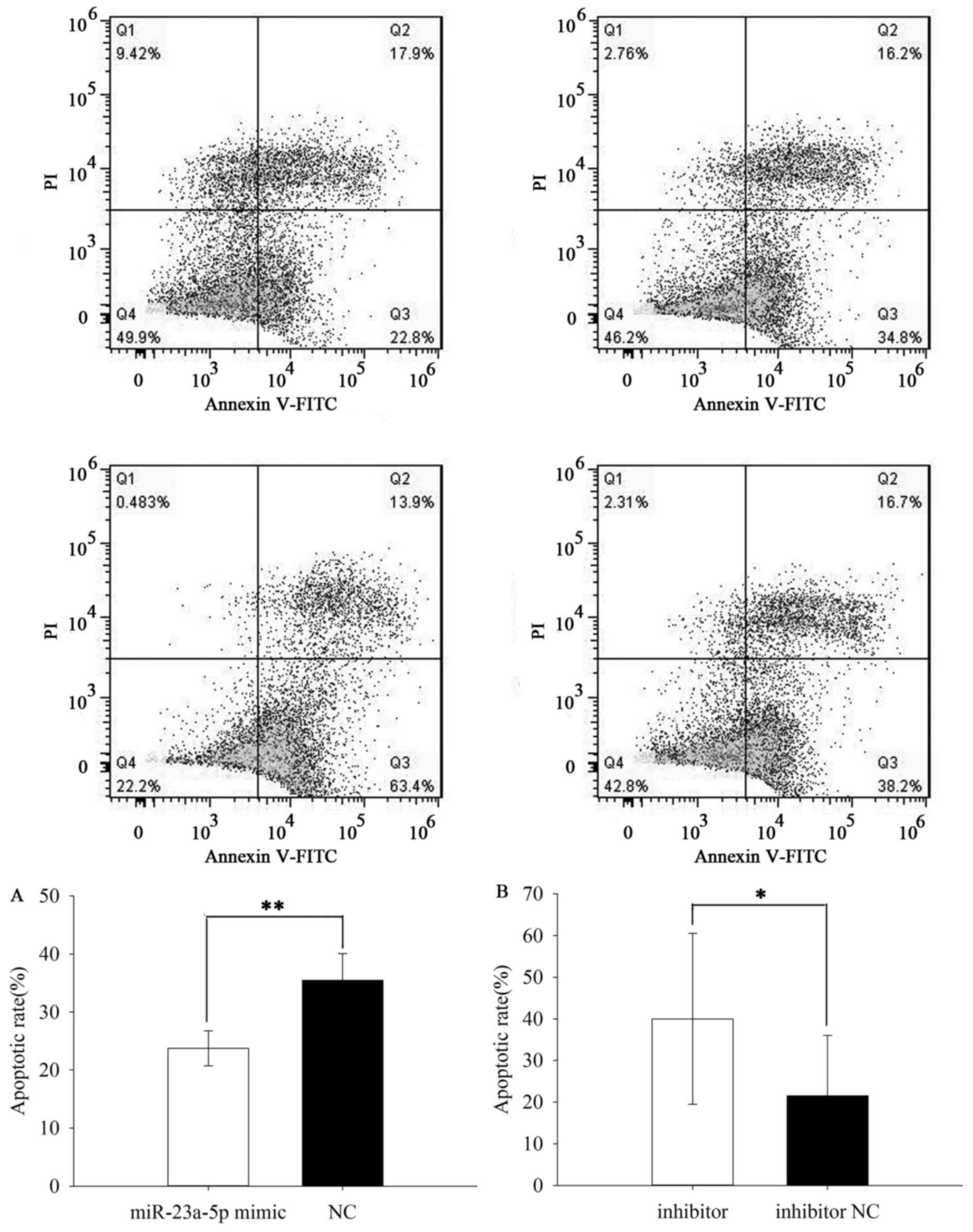
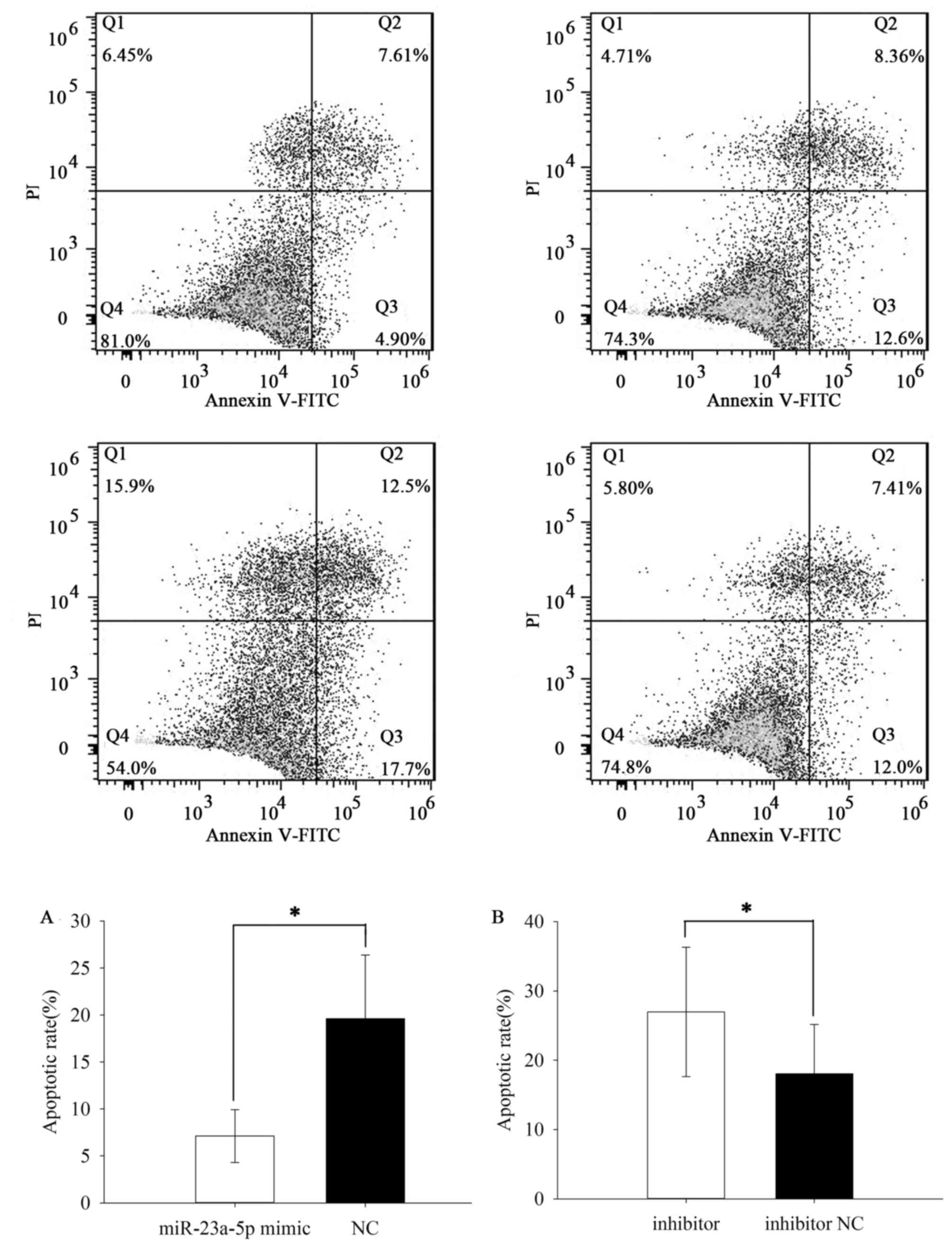
|
1
|
Kovacs G, Akhtar M, Beckwith BJ, Bugert P,
Cooper CS, Delahunt B, Eble JN, Fleming S, Ljungberg B, Medeiros
LJ, et al: The Heidelberg classification of renal cell tumours. J
Pathol. 183:131–133. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Patard JJ, Leray E, Rodriguez A,
Rioux-Leclercq N, Guillé F and Lobel B: Correlation between symptom
graduation, tumor characteristics and survival in renal cell
carcinoma. Eur Urol. 44:226–232. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ljungberg B, Bensalah K, Canfield S,
Dabestani S, Hofmann F, Hora M, Kuczyk MA, Lam T, Marconi L,
Merseburger AS, et al: EAU guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: 2014
update. Eur Urol. 67:913–924. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Massari F, Bria E, Maines F, Milella M,
Giannarelli D, Cognetti F, Pappagallo G, Tortora G and Porta C:
Adjuvant treatment for resected renal cell carcinoma: Are all
strategies equally negative? Potential implications for trial
design with targeted agents. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 11:471–476.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mlcochova H, Machackova T, Rabien A,
Radova L, Fabian P, Iliev R, Slaba K, Poprach A, Kilic E, Stanik M,
et al: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-associated microRNA/mRNA
signature is linked to metastasis and prognosis in clear-cell renal
cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. 6:318522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yamamoto H and Mori M: MicroRNAs as
therapeutic targets and colorectal cancer therapeutics. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 937:239–247. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
He Y, Meng C, Shao Z, Wang H and Yang S:
miR-23a functions as a tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 34:1485–1496. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shang X, Li G, Liu H, Li T, Liu J, Zhao Q
and Wang C: Comprehensive Circular RNA profiling reveals that
hsa_circ_0005075, a new circular RNA biomarker, Is Involved in
hepatocellular crcinoma development. Medicine (Baltimore).
95:e38112016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu L, Li L, Li J, Li H, Shen Q, Ping J, Ma
Z, Zhong J and Dai L: Overexpression of miR-1260b in non-small cell
lung cancer is associated with lymph node metastasis. Aging Dis.
6:478–485. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E,
Lortet-Tieulent J, Rosso S, Coebergh JW, Comber H, Forman D and
Bray F: Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe:
estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer. 49:1374–1403.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Varela I, Tarpey P, Raine K, Huang D, Ong
CK, Stephens P, Davies H, Jones D, Lin ML, Teague J, et al: Exome
sequencing identifies frequent mutation of the SWI/SNF complex gene
PBRM1 in renal carcinoma. Nature. 469:539–542. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen L, Xia G, Qiu F, Wu C, Denmon AP and
Zi X: Physapubescin selectively induces apoptosis in VHL-null renal
cell carcinoma cells through down-regulation of HIF-2α and inhibits
tumor growth. Sci Rep. 6:325822016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mai H, Xu X, Mei G, Hong T, Huang J, Wang
T, Yan Z, Li Y, Liang Y, Li L, et al: The interplay between HPIP
and casein kinase 1α promotes renal cell carcinoma growth and
metastasis via activation of mTOR pathway. Oncogenesis. 5:e2602016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chowdhury B, Porter EG, Stewart JC,
Ferreira CR, Schipma MJ and Dykhuizen EC: PBRM1 regulates the
expression of genes involved in metabolism and cell adhesion in
renal clear cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 11:e01537182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Moch H, Montironi R, Lopez-Beltran A,
Cheng L and Mischo A: Oncotargets in different renal cancer
subtypes. Curr Drug Targets. 16:125–135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao D, Lin M, Chen J, Pedrosa E,
Hrabovsky A, Fourcade HM, Zheng D and Lachman HM: MicroRNA
profiling of neurons generated using induced pluripotent stem cells
derived from patients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective
disorder, and 22q11.2 Del. PLoS One. 10:e01323872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Roncon P, Soukupovà M, Binaschi A,
Falcicchia C, Zucchini S, Ferracin M, Langley SR, Petretto E,
Johnson MR, Marucci G, et al: MicroRNA profiles in hippocampal
granule cells and plasma of rats with pilocarpine-induced
epilepsy-comparison with human epileptic samples. Sci Rep.
5:141432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu S, Liu C, Wang Z, Huang J and Zeng Q:
microRNA-23a-5p acts as a potential biomarker for sepsis-induced
acute respiratory distress syndrome in early stage. Cell Mol Biol
(Noisy-le-grand). 62:31–37. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|