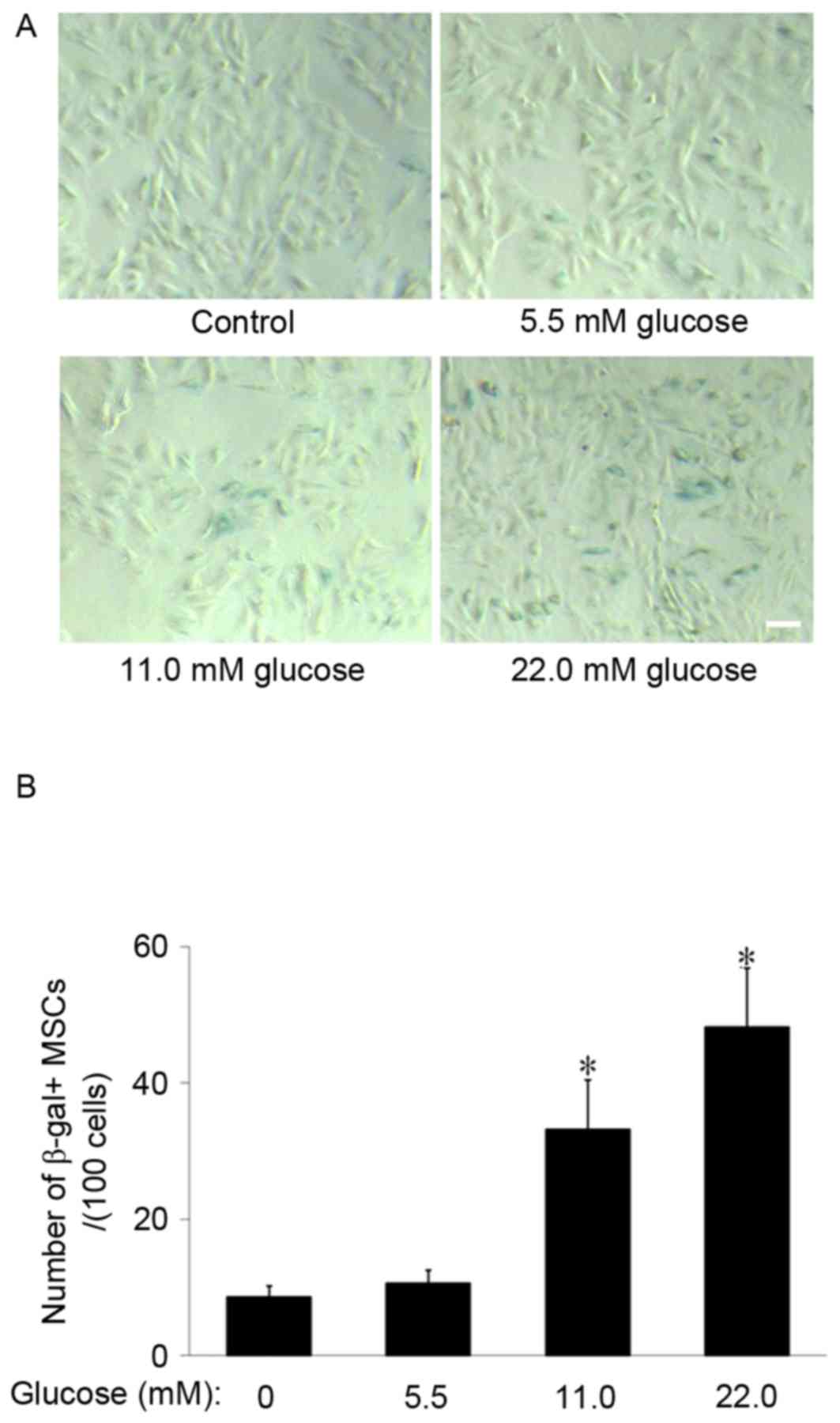
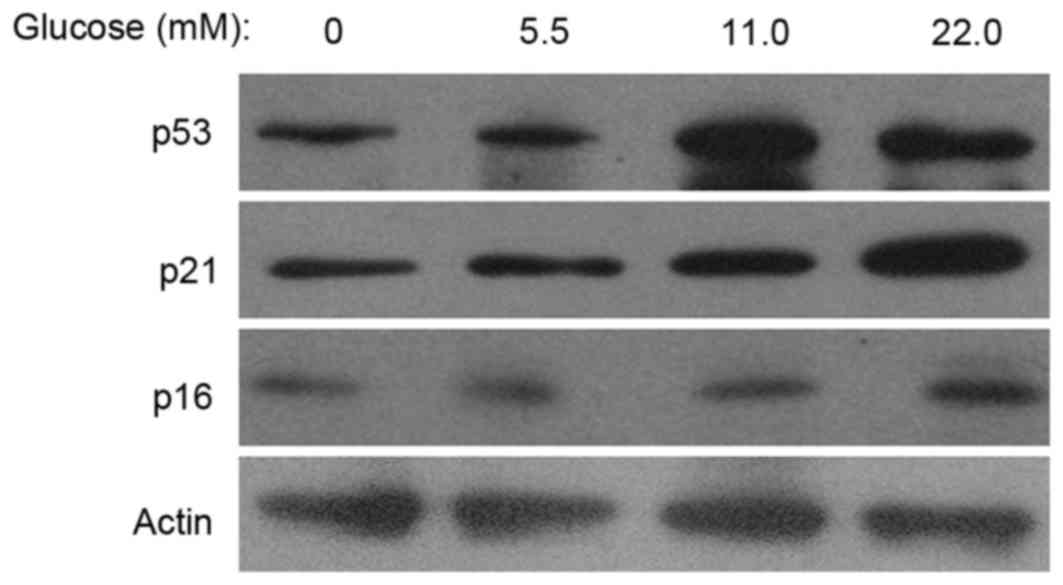
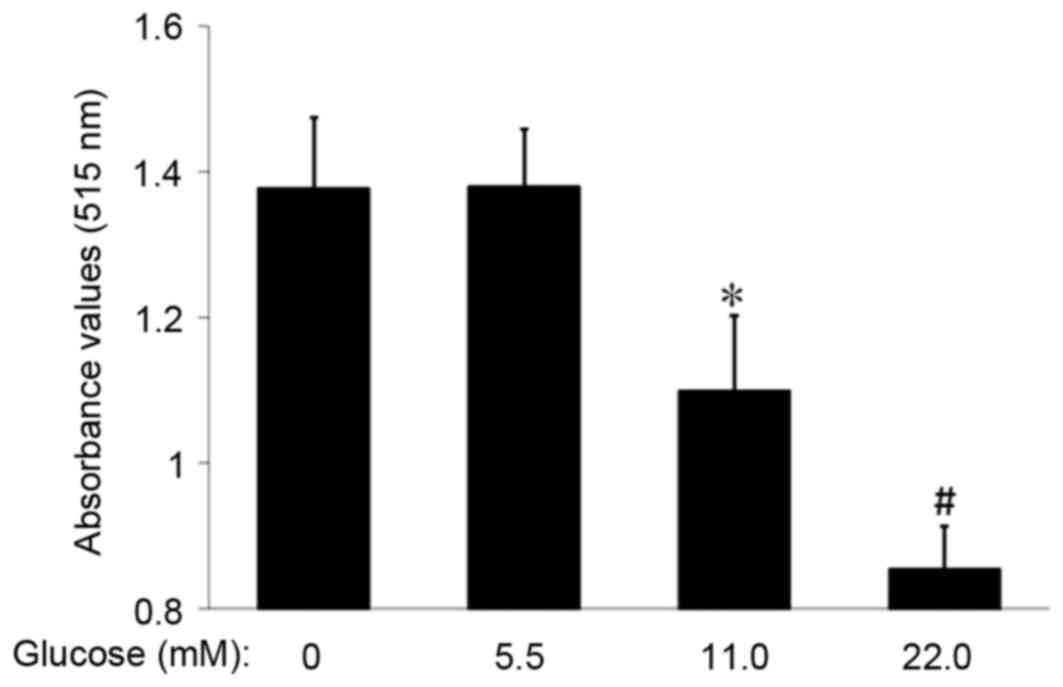
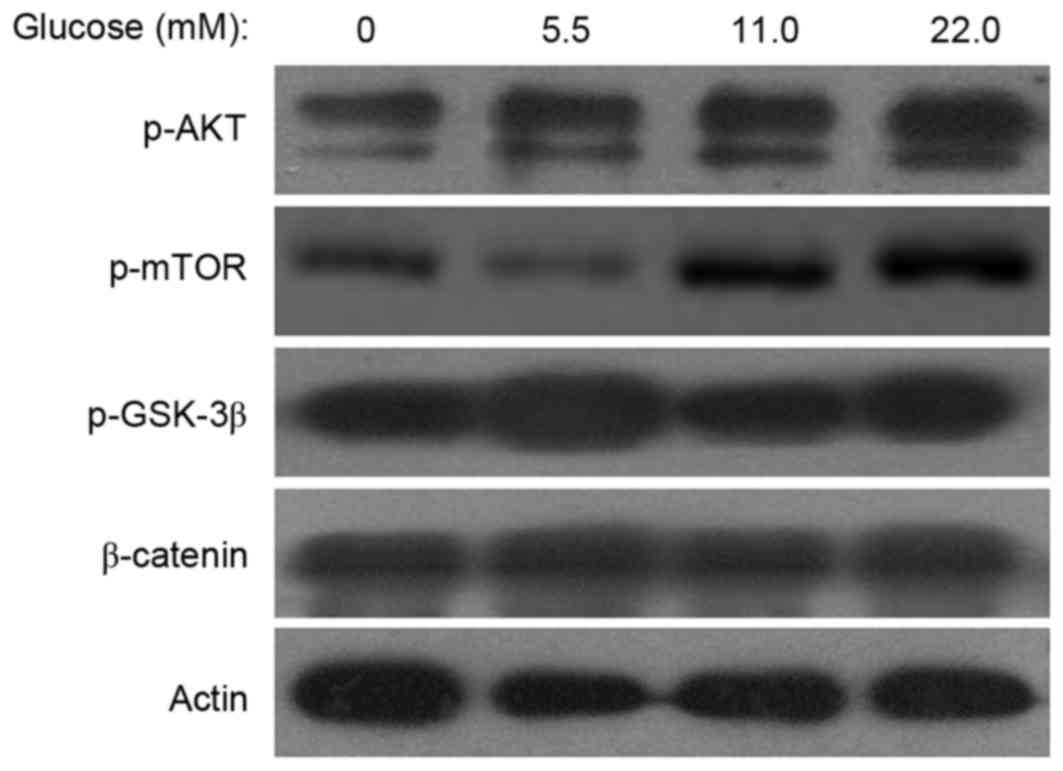
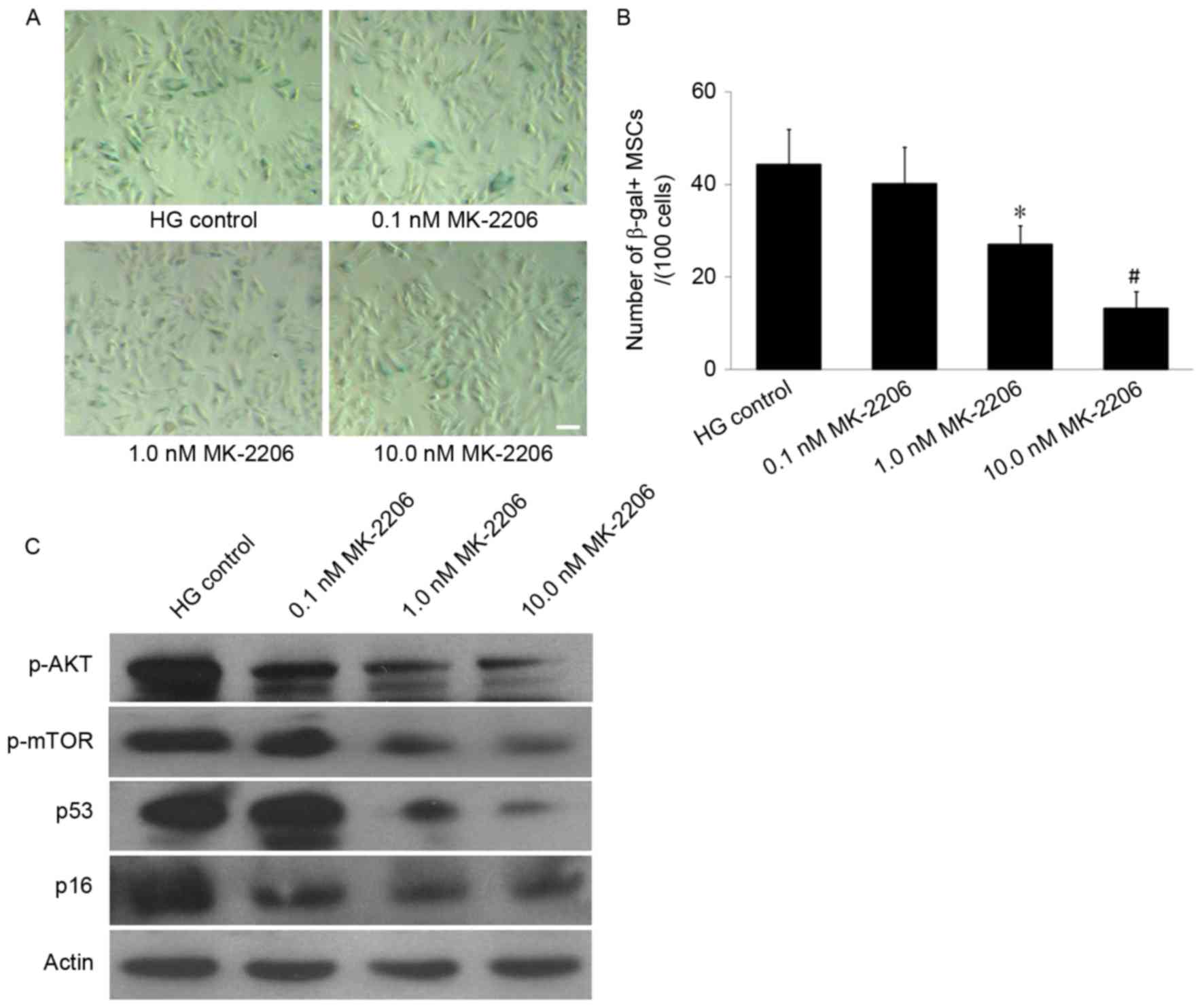
|
1
|
Schultz MB and Sinclair DA: When stem
cells grow old: Phenotypes and mechanisms of stem cell aging.
Development. 143:3–14. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brunauer R and Kennedy BK: Medicine.
Progeria accelerates adult stem cell aging. Science. 348:1093–1094.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Miura Y: Guest editorial: Human
mesenchymal stromal/stem cell (MSC). Int J Hematol. 103:119–121.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Asumda FZ: Age-associated changes in the
ecological niche: Implications for mesenchymal stem cell aging.
Stem Cell Res Ther. 4:472013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
de Miguel MP, Fuentes-Julián S,
Blázquez-Martínez A, Pascual CY, Aller MA, Arias J and
Arnalich-Montiel F: Immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal
stem cells: Advances and applications. Curr Mol Med. 12:574–591.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ankrum J and Karp JM: Mesenchymal stem
cell therapy: Two steps forward, one step back. Trends Mol Med.
16:203–209. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Alt EU, Senst C, Murthy SN, Slakey DP,
Dupin CL, Chaffin AE, Kadowitz PJ and Izadpanah R: Aging alters
tissue resident mesenchymal stem cell properties. Stem Cell Res.
8:215–225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ting CH, Ho PJ and Yen BL: Age-related
decreases of serum-response factor levels in human mesenchymal stem
cells are involved in skeletal muscle differentiation and
engraftment capacity. Stem Cells Dev. 23:1206–1216. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Khan M, Mohsin S, Khan SN and Riazuddin S:
Repair of senescent myocardium by mesenchymal stem cells is
dependent on the age of donor mice. J Cell Mol Med. 15:1515–1527.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang DY, Wang HJ and Tan YZ:
Wnt/β-catenin signaling induces the aging of mesenchymal stem cells
through the DNA damage response and the p53/p21 pathway. PLoS One.
6:e213972011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang E, Guo Q, Gao H, Xu R, Teng S and Wu
Y: Metformin and resveratrol inhibited high glucose-induced
metabolic memory of endothelial senescence through
SIRT1/p300/p53/p21 pathway. PLoS One. 10:e01438142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
del Nogal M, Troyano N, Calleros L, Griera
M, Rodriguez-Puyol M, Rodriguez-Puyol D and Ruiz-Torres MP:
Hyperosmolarity induced by high glucose promotes senescence in
human glomerular mesangial cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
54:98–110. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Güemes M, Rahman SA and Hussain K: What is
a normal blood glucose? Arch Dis Child. 101:569–574. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cheng NC, Hsieh TY, Lai HS and Young TH:
High glucose-induced reactive oxygen species generation promotes
stemness in human adipose-derived stem cells. Cytotherapy.
18:371–383. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ferraro F, Lymperi S, Méndez-Ferrer S,
Saez B, Spencer JA, Yeap BY, Masselli E, Graiani G, Prezioso L,
Rizzini EL, et al: Diabetes impairs hematopoietic stem cell
mobilization by altering niche function. Sci Transl Med.
3:104ra1012011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kočí Z, Turnovcová K, Dubský M,
Baranovičová L, Holáň V, Chudíčková M, Syková E and Kubinová S:
Characterization of human adipose tissue-derived stromal cells
isolated from diabetic patient's distal limbs with critical
ischemia. Cell Biochem Funct. 32:597–604. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stolzing A, Coleman N and Scutt A:
Glucose-induced replicative senescence in mesenchymal stem cells.
Rejuvenation Res. 9:31–35. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Parsch D, Fellenberg J, Brummendorf TH,
Eschlbeck AM and Richter W: Telomere length and telomerase activity
during expansion and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem
cells and chondrocytes. J Mol Med (Berl). 82:49–55. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Estrada JC, Torres Y, Benguría A, Dopazo
A, Roche E, Carrera-Quintanar L, Pérez RA, Enríquez JA, Torres R,
Ramírez JC, et al: Human mesenchymal stem cell-replicative
senescence and oxidative stress are closely linked to aneuploidy.
Cell Death Dis. 4:e6912013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu S, Liu S, Wang X, Zhou J, Cao Y, Wang
F and Duan E: The PI3K-Akt pathway inhibits senescence and promotes
self-renewal of human skin-derived precursors in vitro. Aging Cell.
10:661–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Iglesias-Bartolome R, Patel V, Cotrim A,
Leelahavanichkul K, Molinolo AA, Mitchell JB and Gutkind JS: mTOR
inhibition prevents epithelial stem cell senescence and protects
from radiation-induced mucositis. Cell Stem Cell. 11:401–414. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang D, Yan B, Yu S, Zhang C, Wang B,
Wang Y, Wang J, Yuan Z, Zhang L and Pan J: Coenzyme Q10 inhibits
the aging of mesenchymal stem cells induced by D-galactose through
Akt/mTOR signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015:8672932015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang XM, Yao M, Liu SX, Hao J, Liu QJ and
Gao F: Interplay between the notch and PI3K/Akt pathways in high
glucose-induced podocyte apoptosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
306:F205–F213. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Montes DK, Brenet M, Muñoz VC, Burgos PV,
Villanueva CI, Figueroa CD and González CB: Vasopressin activates
Akt/mTOR pathway in smooth muscle cells cultured in high glucose
concentration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 441:923–928. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guan G, Han H, Yang Y, Jin Y, Wang X and
Liu X: Neferine prevented hyperglycemia-induced endothelial cell
apoptosis through suppressing ROS/Akt/NF-κB signal. Endocrine.
47:764–771. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wakao S, Kuroda Y, Ogura F, Shigemoto T
and Dezawa M: Regenerative effects of mesenchymal stem cells:
Contribution of muse cells, a novel pluripotent stem cell type that
resides in mesenchymal cells. Cells. 1:1045–1060. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tomé M, Sepúlveda JC, Delgado M, Andrades
JA, Campisi J, González MA and Bernad A: miR-335 correlates with
senescence/aging in human mesenchymal stem cells and inhibits their
therapeutic actions through inhibition of AP-1 activity. Stem
Cells. 32:2229–2244. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Raggi C and Berardi AC: Mesenchymal stem
cells, aging and regenerative medicine. Muscles Ligaments Tendons
J. 2:239–242. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rachmiel M, Cohen M, Heymen E, Lezinger M,
Inbar D, Gilat S, Bistritzer T, Leshem G, Kan-Dror E, Lahat E and
Ekstein D: Hyperglycemia is associated with simultaneous
alterations in electrical brain activity in youths with type 1
diabetes mellitus. Clin Neurophysiol. 127:1188–1195. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Galindo RJ and Wallia A: Hyperglycemia and
diabetes mellitus following organ transplantation. Curr Diab Rep.
16:142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kojima H, Kim J and Chan L: Emerging roles
of hematopoietic cells in the pathobiology of diabetic
complications. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 25:178–187. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chang TC, Hsu MF and Wu KK: High glucose
induces bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell senescence by
upregulating autophagy. PLoS One. 10:e01265372015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang DY, Pan Y, Zhang C, Yan BX, Yu SS,
Wu DL, Shi MM, Shi K, Cai XX, Zhou SS, et al: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling induces the aging of mesenchymal stem cells through
promoting the ROS production. Mol Cell Biochem. 374:13–20. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu L, Hu X, Cai GY, Lv Y, Zhuo L, Gao JJ,
Cui SY, Feng Z, Fu B and Chen XM: High glucose-induced hypertrophy
of mesangial cells is reversed by connexin43 overexpression via
PTEN/Akt/mTOR signaling. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 27:90–100. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Montani MS Gilardini, Granato M, Cuomo L,
Valia S, Di Renzo L, D'Orazi G, Faggioni A and Cirone M: High
glucose and hyperglycemic sera from type 2 diabetic patients impair
DC differentiation by inducing ROS and activating Wnt/β-catenin and
p38 MAPK. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1862:805–813. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mehrfarjam Z, Esmaeili F, Shabani L and
Ebrahimie E: Induction of pancreatic β cell gene expression in
mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Biol Int. 40:486–500. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sun Y, Chen L, Hou XG, Hou WK, Dong JJ,
Sun L, Tang KX, Wang B, Song J, Li H and Wang KX: Differentiation
of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells from diabetic
patients into insulin-producing cells in vitro. Chin Med J (Engl).
120:771–776. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hashemian SJ, Kouhnavard M and
Nasli-Esfahani E: Mesenchymal stem cells: Rising concerns over
their application in treatment of type one diabetes mellitus. J
Diabetes Res. 2015:6751032015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rekittke NE, Ang M, Rawat D, Khatri R and
Linn T: Regenerative therapy of type 1 diabetes mellitus: From
pancreatic islet transplantation to mesenchymal stem cells. Stem
Cells Int. 2016:37646812016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fadini GP, Sartore S, Schiavon M, Albiero
M, Baesso I, Cabrelle A, Agostini C and Avogaro A: Diabetes impairs
progenitor cell mobilisation after hindlimb ischaemia-reperfusion
injury in rats. Diabetologia. 49:3075–3084. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shin L and Peterson DA: Impaired
therapeutic capacity of autologous stem cells in a model of type 2
diabetes. Stem Cells Transl Med. 1:125–135. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|