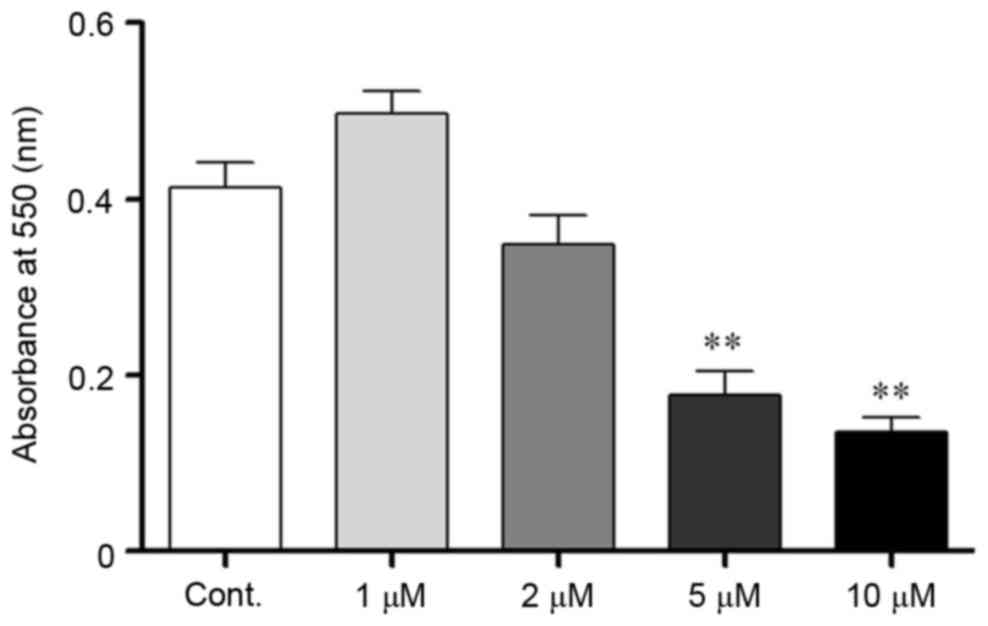
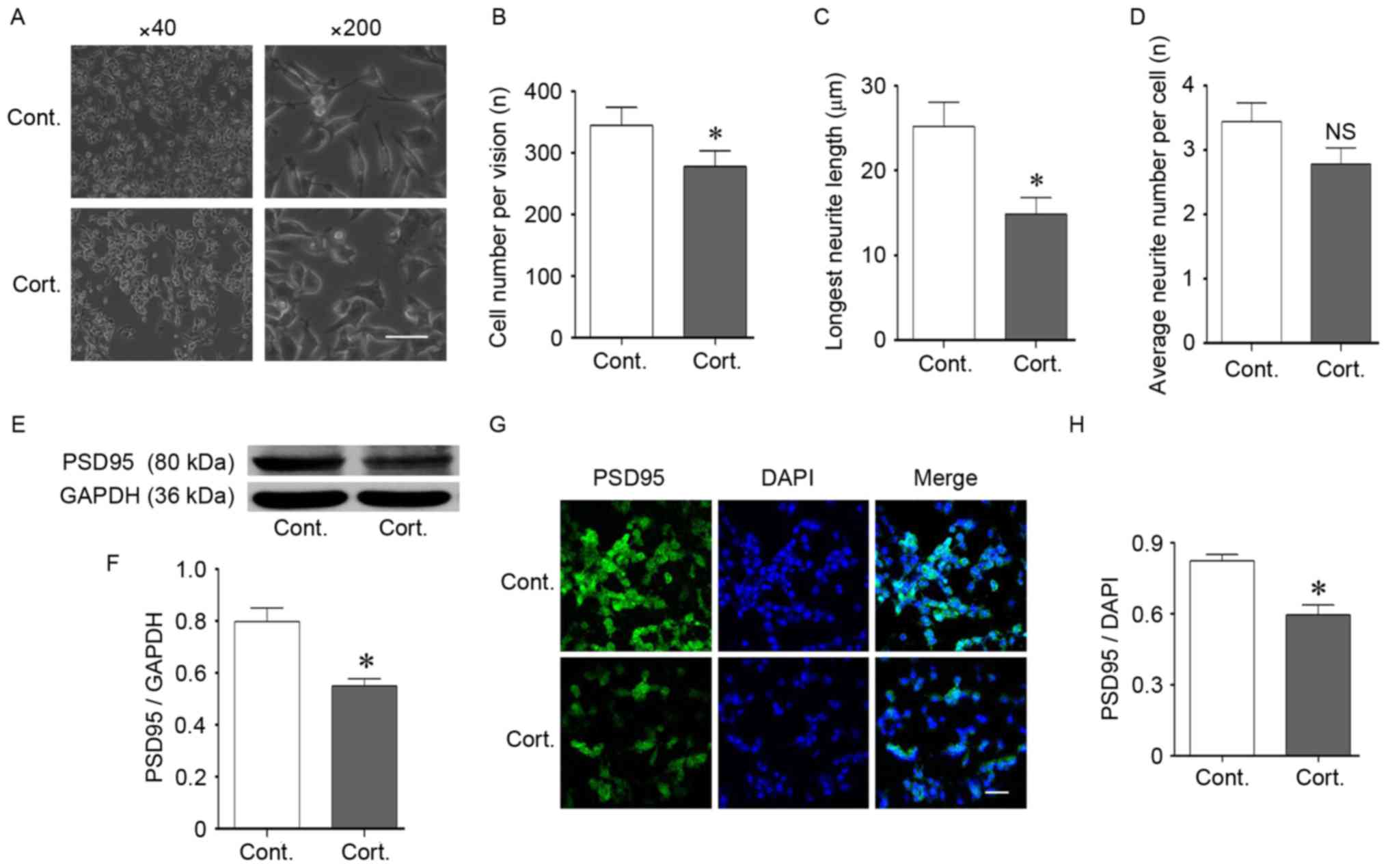
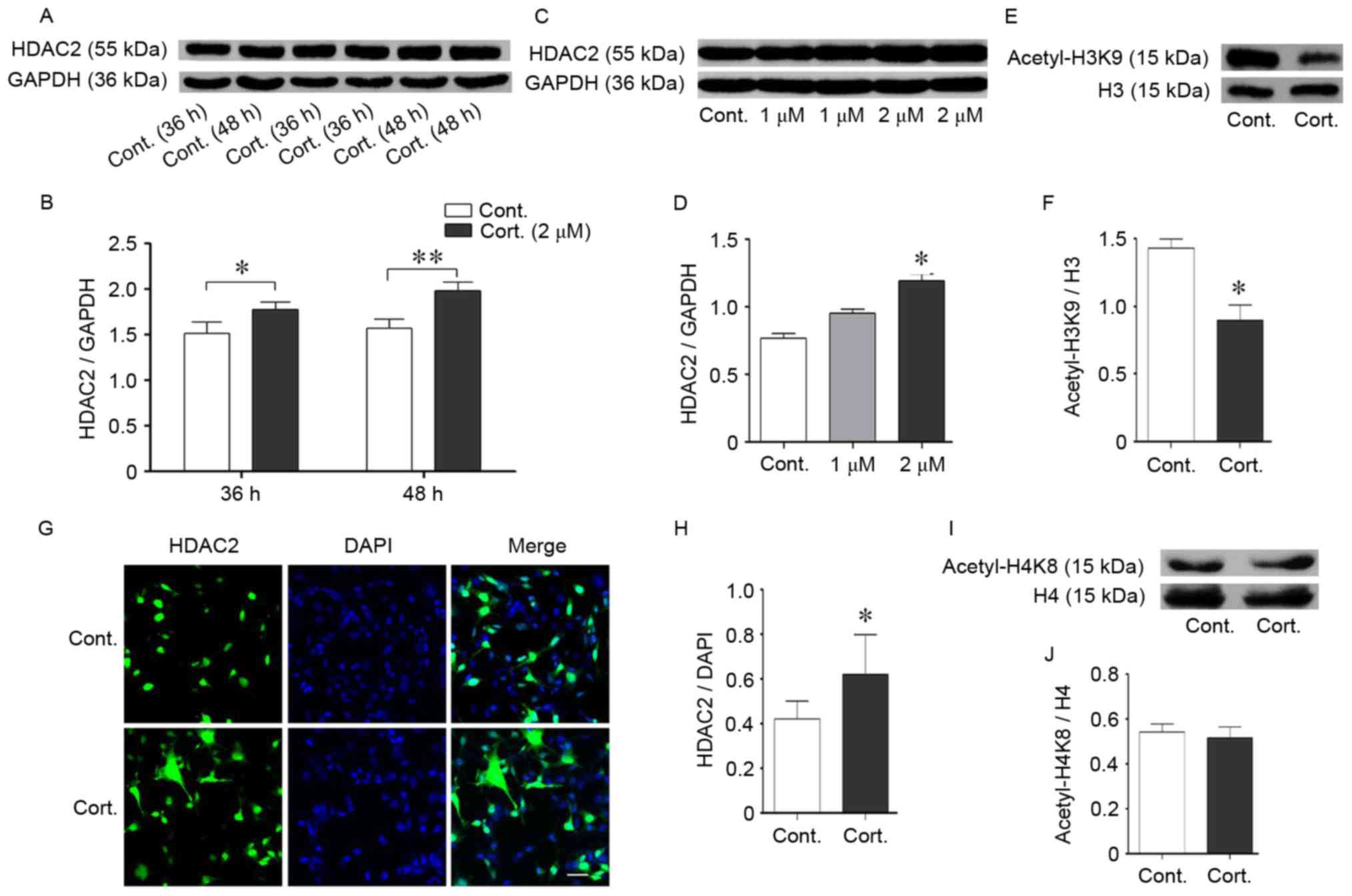
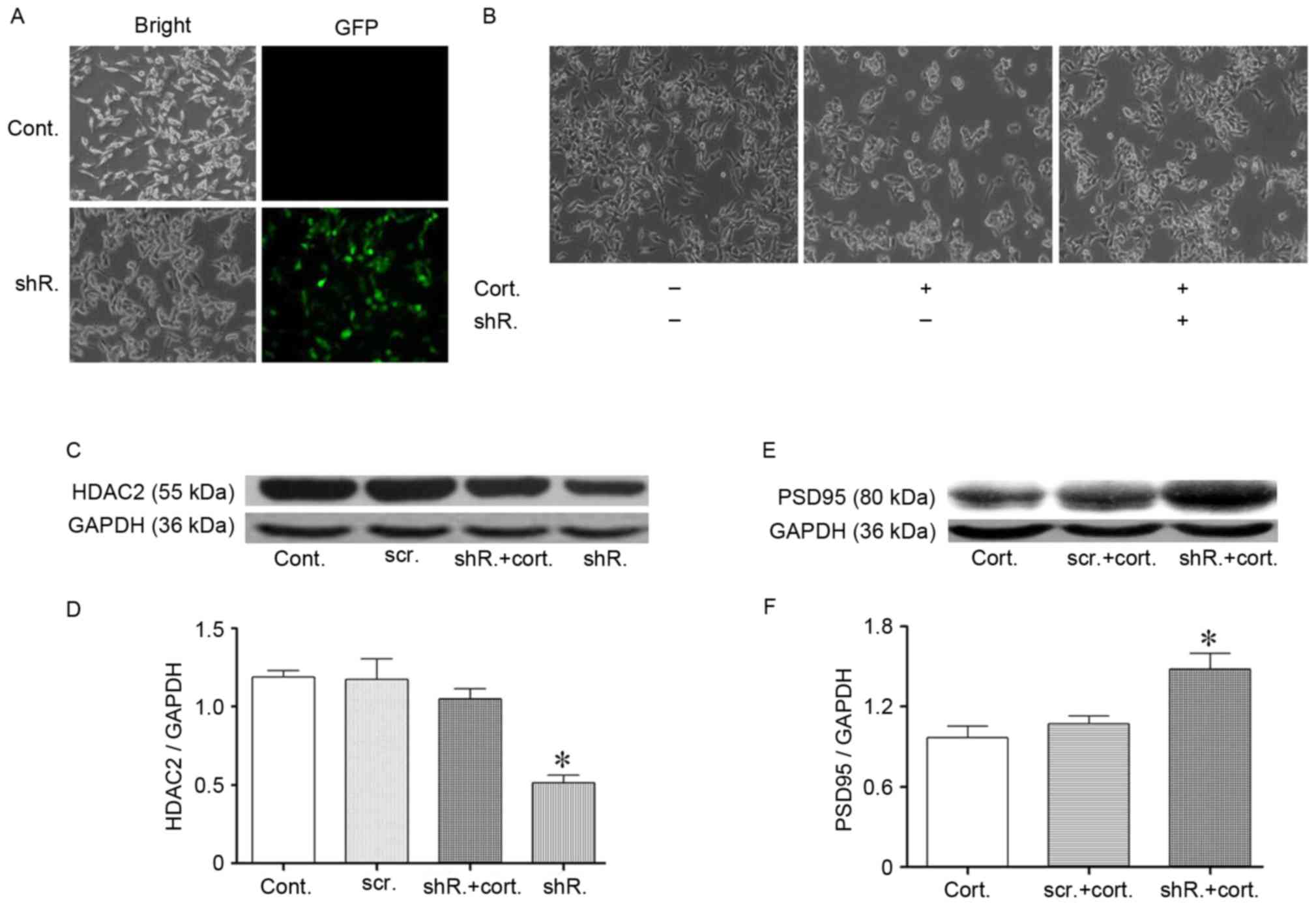
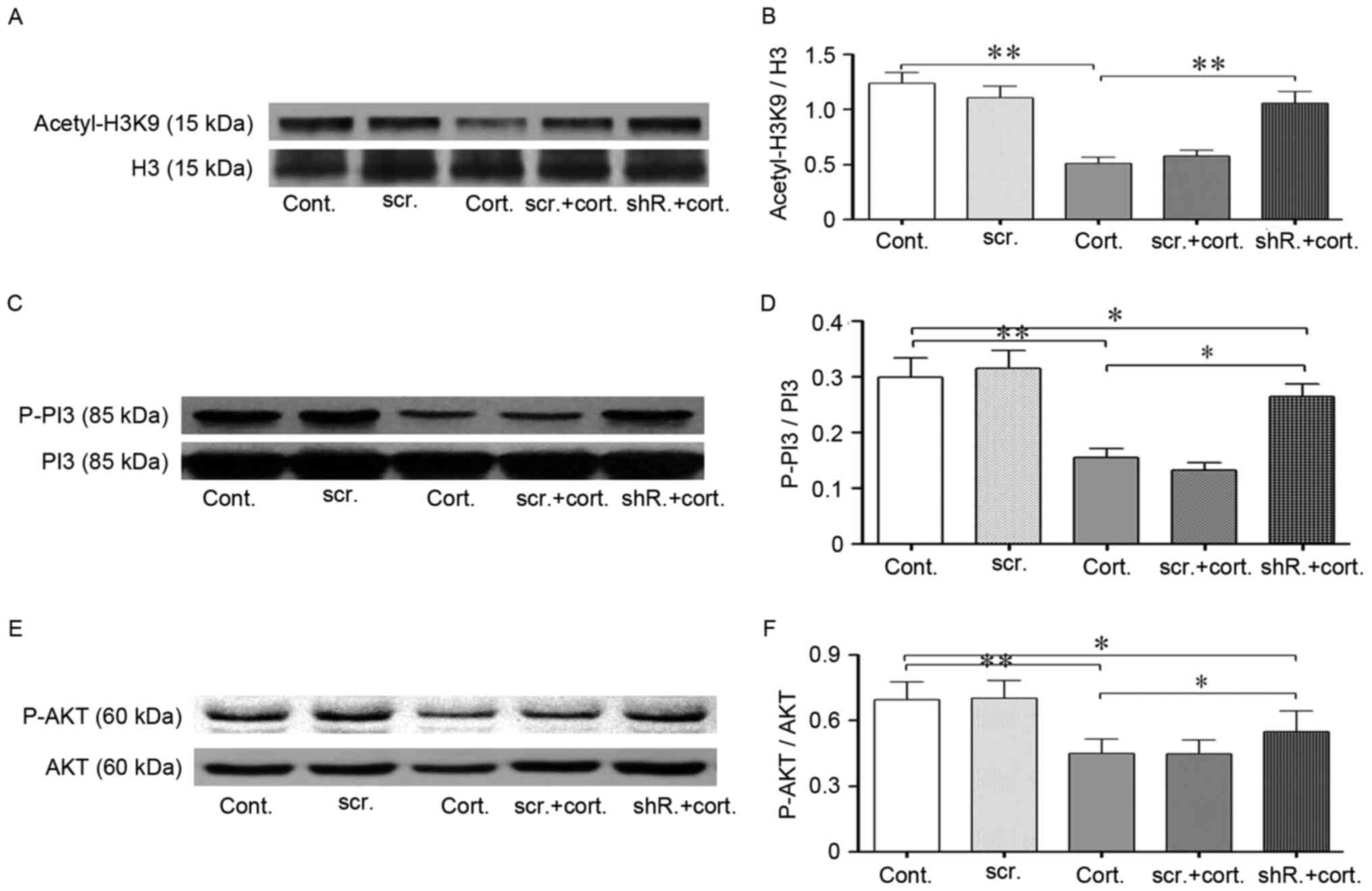
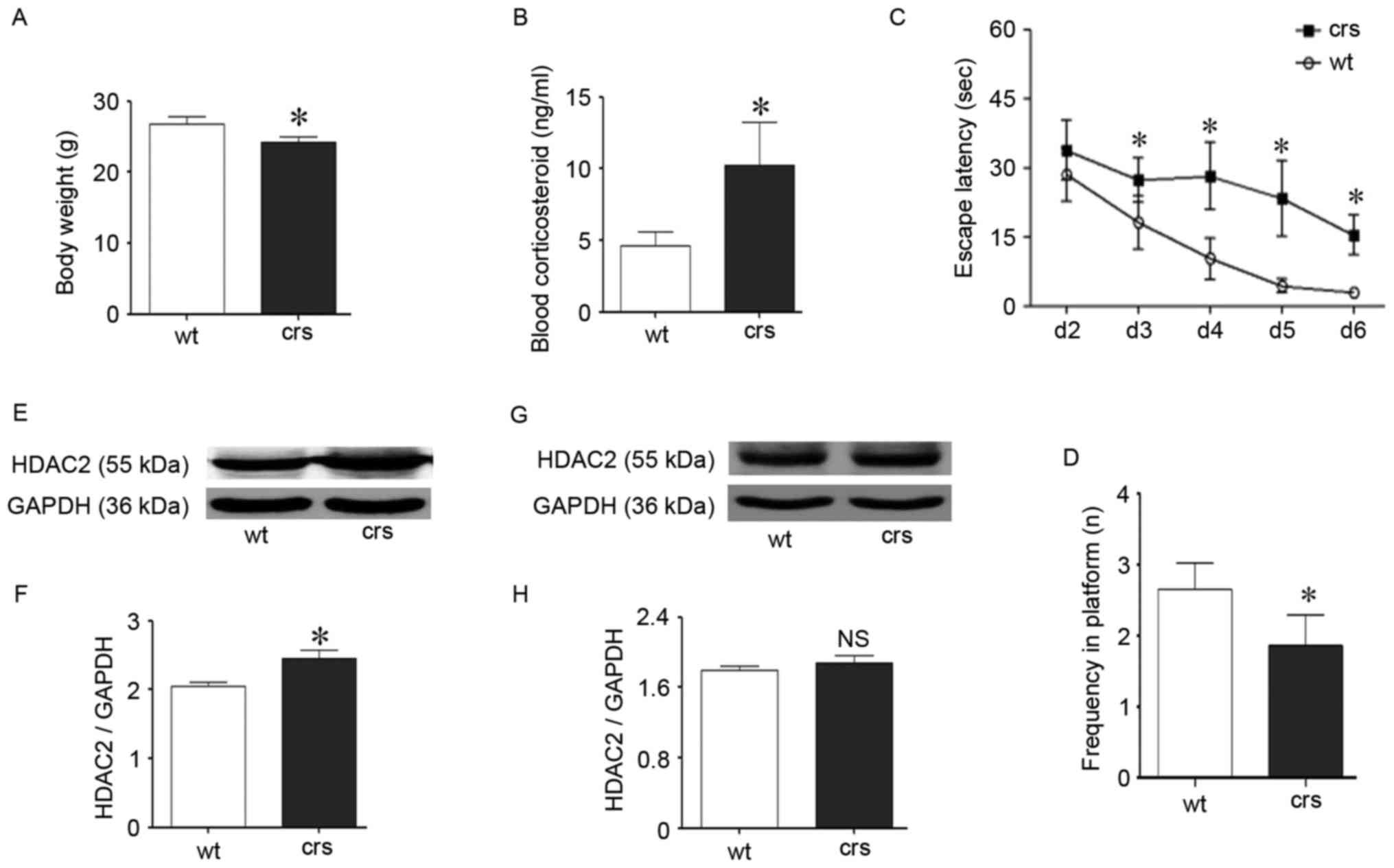
|
1
|
Nicolaides NC, Kyratzi E,
Lamprokostopoulou A, Chrousos GP and Charmandari E: Stress, the
stress system and the role of glucocorticoids.
Neuroimmunomodulation. 22:6–19. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang Q, van Heerikhuize J, Aronica E,
Kawata M, Seress L, Joels M, Swaab DF and Lucassen PJ:
Glucocorticoid receptor protein expression in human hippocampus;
stability with age. Neurobiol Aging. 34:1662–1673. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lucassen PJ, Pruessner J, Sousa N, Almeida
OF, van Dam AM, Rajkowska G, Swaab DF and Czéh B: Neuropathology of
stress. Acta Neuropathol. 127:109–135. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ferland CL and Schrader LA: Regulation of
histone acetylation in the hippocampus of chronically stressed
rats: A potential role of sirtuins. Neuroscience. 174:104–114.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kenworthy CA, Sengupta A, Luz SM, Ver
Hoeve ES, Meda K, Bhatnagar S and Abel T: Social defeat induces
changes in histone acetylation and expression of histone modifying
enzymes in the ventral hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and dorsal
raphe nucleus. Neuroscience. 264:88–98. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ferland CL, Harris EP, Lam M and Schrader
LA: Facilitation of the HPA axis to a novel acute stress following
chronic stress exposure modulates histone acetylation and the
ERK/MAPK pathway in the dentate gyrus of male rats. Endocrinology.
155:2942–2952. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Radley JJ, Kabbaj M, Jacobson L,
Heydendael W, Yehuda R and Herman JP: Stress risk factors and
stress-related pathology: Neuroplasticity, epigenetics and
endophenotypes. Stress. 14:481–497. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Johnsson A, Durand-Dubief M, Xue-Franzen
Y, Rönnerblad M, Ekwall K and Wright A: HAT-HDAC interplay
modulates global histone H3K14 acetylation in gene-coding regions
during stress. EMBO Rep. 10:1009–1014. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hildmann C, Riester D and Schwienhorst A:
Histone deacetylases-an important class of cellular regulators with
a variety of functions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 75:487–497.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Clayton AL, Hazzalin CA and Mahadevan LC:
Enhanced histone acetylation and transcription: A dynamic
perspective. Mol Cell. 23:289–296. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yao ZG, Liu Y, Zhang L, Huang L, Ma CM, Xu
YF, Zhu H and Qin C: Co-location of HDAC2 and insulin signaling
components in the adult mouse hippocampus. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
32:1337–1342. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guan JS, Haggarty SJ, Giacometti E,
Dannenberg JH, Joseph N, Gao J, Nieland TJ, Zhou Y, Wang X,
Mazitschek R, et al: HDAC2 negatively regulates memory formation
and synaptic plasticity. Nature. 459:55–60. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gräff J, Rei D, Guan JS, Wang WY, Seo J,
Hennig KM, Nieland TJ, Fass DM, Kao PF, Kahn M, et al: An
epigenetic blockade of cognitive functions in the neurodegenerating
brain. Nature. 483:222–226. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xuan A, Long D, Li J, Ji W, Hong L, Zhang
M and Zhang W: Neuroprotective effects of valproic acid following
transient global ischemia in rats. Life Sci. 90:463–468. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hommet C, Mondon K, de Toffol B and
Constans T: Reversible cognitive and neurological symptoms during
valproic acid therapy. J Am Geriatr Soc. 55:6282007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Morris MJ, Mahgoub M, Na ES, Pranav H and
Monteggia LM: Loss of histone deacetylase 2 improves working memory
and accelerates extinction learning. J Neurosci. 33:6401–6411.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim HS, Chang YG, Bae HJ, Eun JW, Shen Q,
Park SJ, Shin WC, Lee EK, Park S, Ahn YM, et al: Oncogenic
potential of CK2α and its regulatory role in EGF-induced HDAC2
expression in human liver cancer. FEBS J. 281:851–861. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nott A, Watson PM, Robinson JD, Crepaldi L
and Riccio A: S-Nitrosylation of histone deacetylase 2 induces
chromatin remodelling in neurons. Nature. 455:411–415. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Saaltink DJ and Vreugdenhil E: Stress,
glucocorticoid receptors, and adult neurogenesis: A balance between
excitation and inhibition? Cell Mol Life Sci. 71:2499–2515. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kolber BJ and Muglia LJ: Defining brain
region-specific glucocorticoid action during stress by conditional
gene disruption in mice. Brain Res. 1293:85–90. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang P, Jiang S, Cui Y, Yue Z, Su C, Sun
J, Sheng S and Tian J: The n-terminal 5-MER peptide analogue P165
of amyloid precursor protein exerts protective effects on SH-SY5Y
cells and rat hippocampus neuronal synapses. Neuroscience.
173:169–178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Scott HJ, Stebbing MJ, Walters CE,
McLenachan S, Ransome MI, Nichols NR and Turnley AM: Differential
effects of SOCS2 on neuronal differentiation and morphology. Brain
Res. 1067:138–145. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Baumann VR: Stress sensitivity and
adaptation. Z Gesamte Inn Med. 30:15–16, passim. 1975.(In German).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang X, Han ZP, Zhang SS, Zhu PX, Hao C,
Fan TT, Yang Y, Li L, Shi YF and Wei LX: Chronic restraint stress
decreases the repair potential from mesenchymal stem cells on liver
injury by inhibiting TGF-β1 generation. Cell Death Dis.
5:e13082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li S, He Z, Guo L, Huang L, Wang J and He
W: Behavioral alterations associated with a down regulation of HCN1
mRNA in hippocampal cornus ammon 1 region and neocortex after
chronic incomplete global cerebral ischemia in rats. Neuroscience.
165:654–661. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ricobaraza A, Cuadrado-Tejedor M,
Pérez-Mediavilla A, Frechilla D, Del Rio J and Garcia-Osta A:
Phenylbutyrate ameliorates cognitive deficit and reduces tau
pathology in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model.
Neuropsychopharmacology. 34:1721–1732. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gräff J, Kim D, Dobbin MM and Tsai LH:
Epigenetic regulation of gene expression in physiological and
pathological brain processes. Physiol Rev. 91:603–649. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stankiewicz AM, Swiergiel AH and Lisowski
P: Epigenetics of stress adaptations in the brain. Brain Res Bull.
98:76–92. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Buttrick GJ and Wakefield JG: PI3-K and
GSK-3: Akting together with microtubules. Cell Cycle. 7:2621–2625.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu N, Wang LH, Guo LL, Wang GQ, Zhou XP,
Jiang Y, Shang J, Murao K, Chen JW, Fu WQ and Zhang GX: Chronic
restraint stress inhibits hair growth via substance P mediated by
reactive oxygen species in mice. PLoS One. 8:e615742013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jeong JY, Lee DH and Kang SS: Effects of
chronic restraint stress on body weight, food intake, and
hypothalamic gene expressions in mice. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul).
28:288–296. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mustafa T, Jiang SZ, Eiden AM, Weihe E,
Thistlethwaite I and Eiden LE: Impact of PACAP and PAC1 receptor
deficiency on the neurochemical and behavioral effects of acute and
chronic restraint stress in male C57BL/6 mice. Stress. 18:408–418.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cuadrado-Tejedor M, Ricobaraza A, Del Rio
J, Frechilla D, Franco R, Pérez-Mediavilla A and Garcia-Osta A:
Chronic mild stress in mice promotes cognitive impairment and
CDK5-dependent tau hyperphosphorylation. Behav Brain Res.
220:338–343. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Finsterwald C and Alberini CM: Stress and
glucocorticoid receptor-dependent mechanisms in long-term memory:
From adaptive responses to psychopathologies. Neurobiol Learn Mem.
112:17–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chakravarty S, Pathak SS, Maitra S,
Khandelwal N, Chandra KB and Kumar A: Epigenetic regulatory
mechanisms in stress-induced behavior. Int Rev Neurobiol.
115:117–154. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gutièrrez-Mecinas M, Trollope AF, Collins
A, Morfett H, Hesketh SA, Kersanté F and Reul JM: Long-lasting
behavioral responses to stress involve a direct interaction of
glucocorticoid receptors with ERK1/2-MSK1-Elk-1 signaling. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:13806–13811. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dombrowsky H and Uhlig S: Steroids and
histone deacetylase in ventilation-induced gene transcription. Eur
Respir J. 30:865–877. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brownell JE and Allis CD: Special HATs for
special occasions: Linking histone acetylation to chromatin
assembly and gene activation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 6:176–184. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shibasaki M, Mizuno K, Kurokawa K and
Ohkuma S: Enhancement of histone acetylation in midbrain of mice
with ethanol physical dependence and its withdrawal. Synapse.
65:1244–1250. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang L, Lv Z, Hu Z, Sheng J, Hui B, Sun J
and Ma L: Chronic cocaine-induced H3 acetylation and
transcriptional activation of CaMKIIalpha in the nucleus accumbens
is critical for motivation for drug reinforcement.
Neuropsychopharmacology. 35:913–928. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
de Kloet ER, Karst H and Joëls M:
Corticosteroid hormones in the central stress response:
Quick-and-slow. Front Neuroendocrinol. 29:268–272. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Beato M and Sánchez-Pacheco A: Interaction
of steroid hormone receptors with the transcription initiation
complex. Endocr Rev. 17:587–609. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Revollo JR and Cidlowski JA: Mechanisms
generating diversity in glucocorticoid receptor signaling. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1179:167–178. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen Y, Li J, Dunn S, Xiong S, Chen W,
Zhao Y, Chen BB, Mallampalli RK and Zou C: Histone deacetylase 2
(HDAC2) protein-dependent deacetylation of mortality factor 4-like
1 (MORF4L1) protein enhances its homodimerization. J Biol Chem.
289:7092–7098. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hou N, Gong M, Bi Y, Zhang Y, Tan B, Liu
Y, Wei X, Chen J and Li T: Spatiotemporal expression of HDAC2
during the postnatal development of the rat hippocampus. Int J Med
Sci. 11:788–795. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Spencer JP: The impact of fruit flavonoids
on memory and cognition. Br J Nutr. 104 Suppl 3:40–47. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lee CC, Huang CC and Hsu KS: Insulin
promotes dendritic spine and synapse formation by the PI3K/Akt/mTOR
and Rac1 signaling pathways. Neuropharmacology. 61:867–879. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang X, Hu J and Price SR: Inhibition of
PI3-kinase signaling by glucocorticoids results in increased
branched-chain amino acid degradation in renal epithelial cells. Am
J Physiol Cell Physiol. 292:C1874–C1879. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Noh JH, Bae HJ, Eun JW, Shen Q, Park SJ,
Kim HS, Nam B, Shin WC, Lee EK, Lee K, et al: HDAC2 provides a
critical support to malignant progression of hepatocellular
carcinoma through feedback control of mTORC1 and AKT. Cancer Res.
74:1728–1738. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sun C and Zhou J: Trichostatin A improves
insulin stimulated glucose utilization and insulin signaling
transduction through the repression of HDAC2. Biochem Pharmacol.
76:120–127. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|