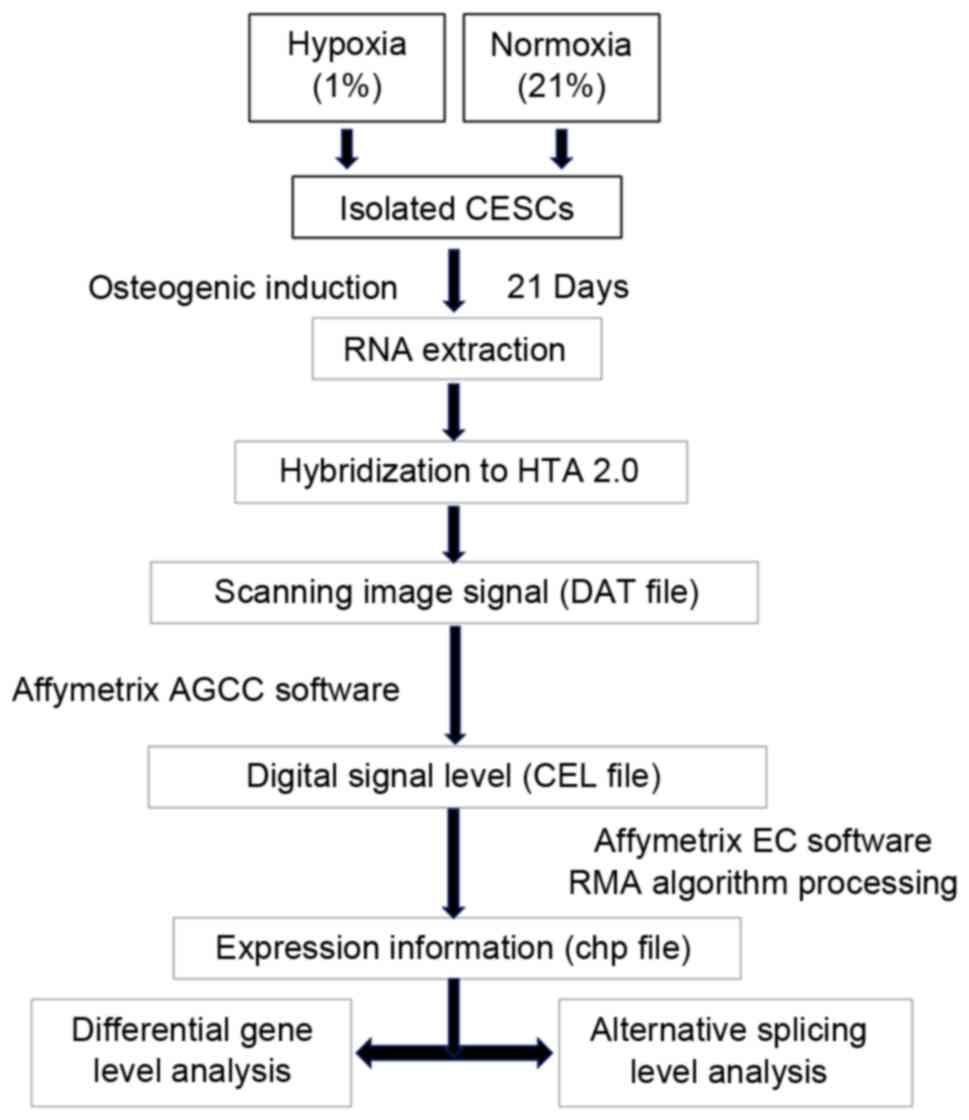
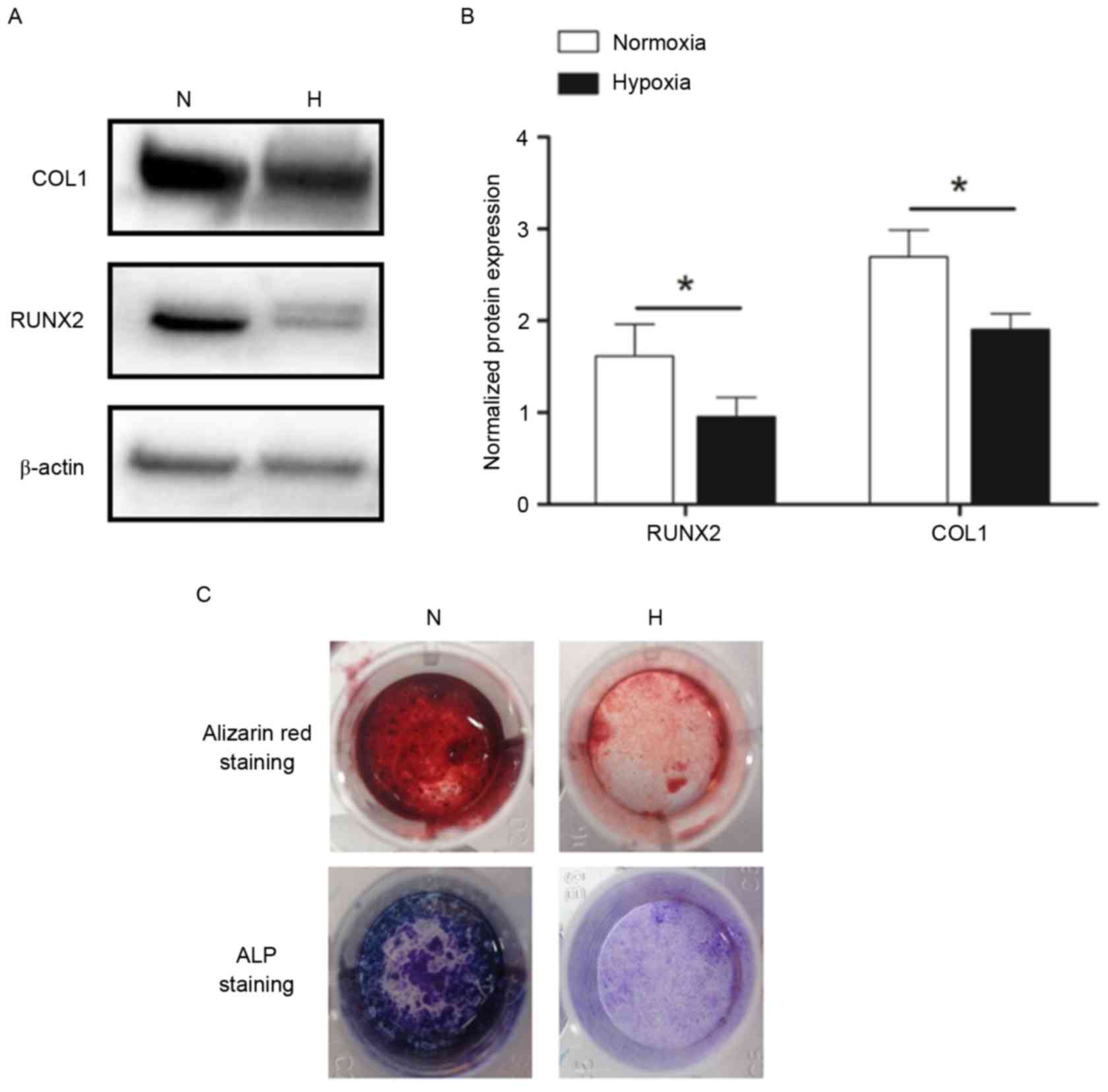
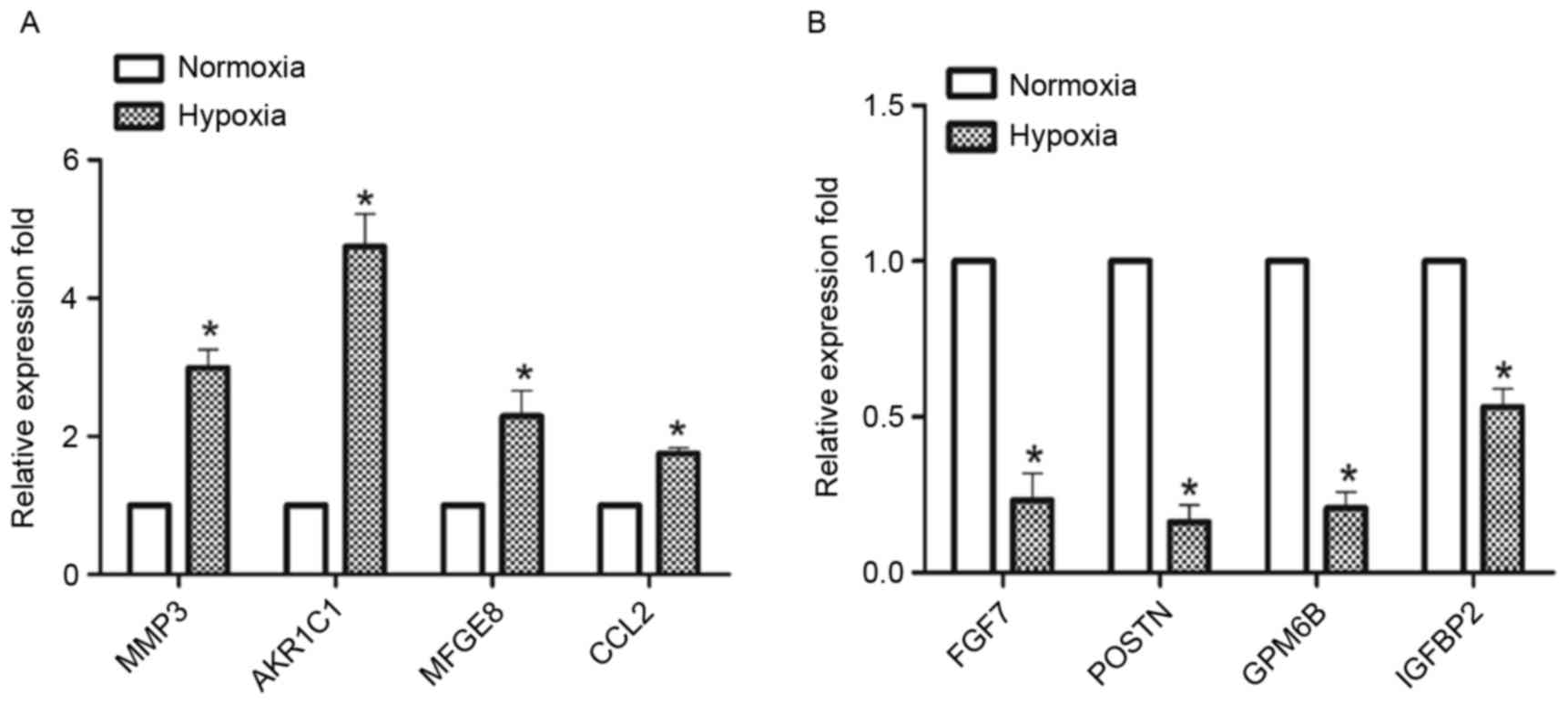
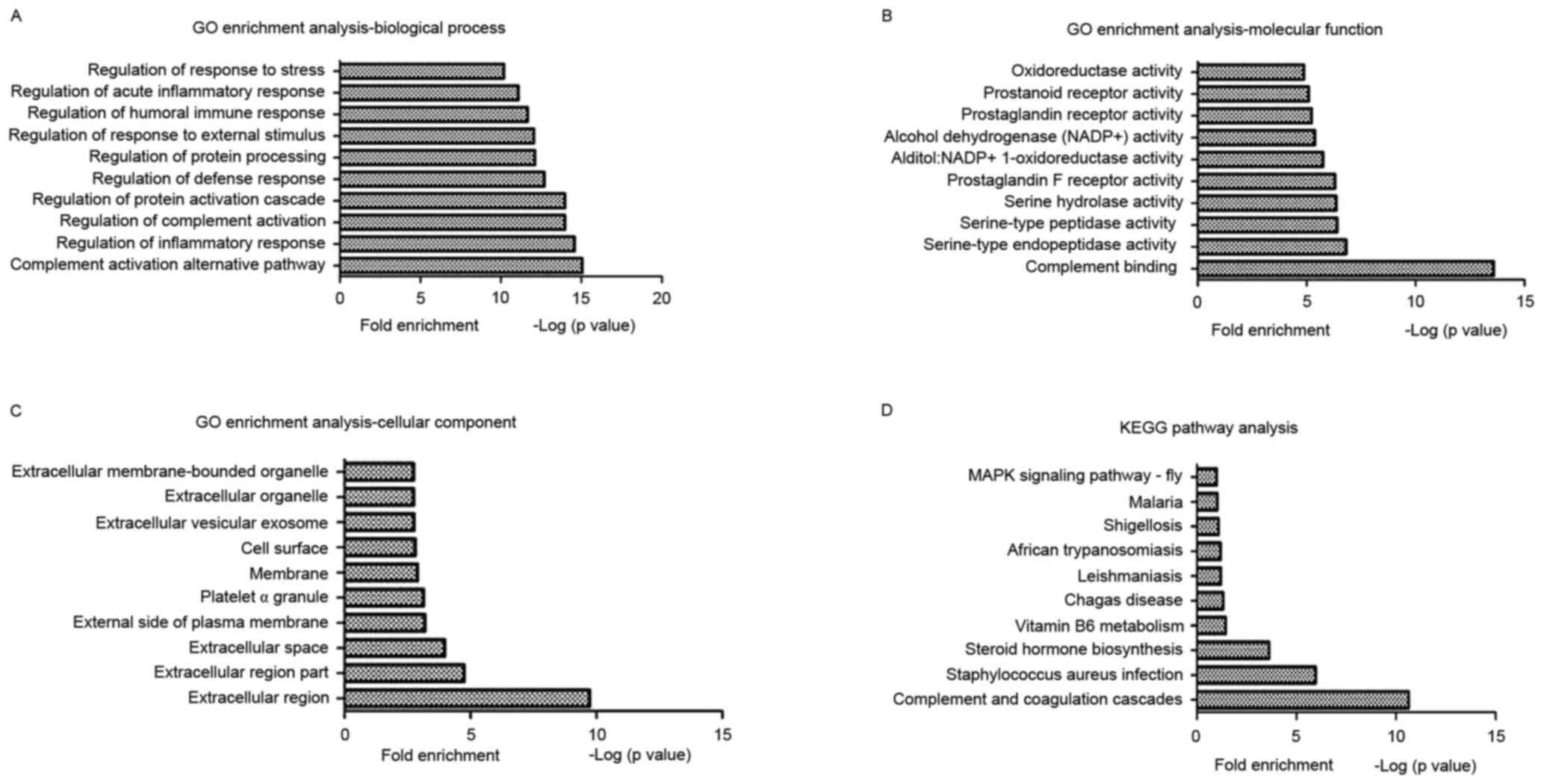
|
1
|
Andersson GB: Epidemiological features of
chronic low-back pain. Lancet. 354:581–585. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Freemont AJ: The cellular pathobiology of
the degenerate intervertebral disc and discogenic back pain.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 48:5–10. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stokes IA and Iatridis JC: Mechanical
conditions that accelerate intervertebral disc degeneration:
Overload versus immobilization. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
29:2724–2732. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Le Maitre CL, Freemont AJ and Hoyland JA:
Accelerated cellular senescence in degenerate intervertebral discs:
A possible role in the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc
degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 9:R452007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhao CQ, Wang LM, Jiang LS and Dai LY: The
cell biology of intervertebral disc aging and degeneration. Ageing
Res Rev. 6:247–261. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Urban JP, Smith S and Fairbank JC:
Nutrition of the intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
29:2700–2709. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Buckwalter JA: Aging and degeneration of
the human intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 20:1307–1314.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Holm S, Maroudas A, Urban JP, Selstam G
and Nachemson A: Nutrition of the intervertebral disc: Solute
transport and metabolism. Connect Tissue Res. 8:101–119. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Raj PP: Intervertebral disc:
Anatomy-physiology- pathophysiology-treatment. Pain Pract. 8:18–44.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li FC, Zhang N, Chen WS and Chen QX:
Endplate degeneration may be the origination of the vacuum
phenomenon in intervertebral discs. Med Hypotheses. 75:169–171.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jackson AR, Huang CY and Gu WY: Effect of
endplate calcification and mechanical deformation on the
distribution of glucose in intervertebral disc: A 3D finite element
study. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 14:195–204. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Roberts S, Urban JP, Evans H and
Eisenstein SM: Transport properties of the human cartilage endplate
in relation to its composition and calcification. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 21:415–420. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu LT, Huang B, Li CQ, Zhuang Y, Wang J
and Zhou Y: Characteristics of stem cells derived from the
degenerated human intervertebral disc cartilage endplate. PLoS One.
6:e262852011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Boskey AL: Signaling in response to
hypoxia and normoxia in the intervertebral disc. Arthritis Rheum.
58:3637–3639. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Merceron C, Vinatier C, Portron S, Masson
M, Amiaud J, Guigand L, Chérel Y, Weiss P and Guicheux J:
Differential effects of hypoxia on osteochondrogenic potential of
human adipose-derived stem cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
298:C355–C364. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Makino Y, Kanopka A, Wilson WJ, Tanaka H
and Poellinger L: Inhibitory PAS domain protein (IPAS) is a
hypoxia-inducible splicing variant of the hypoxia-inducible
factor-3alpha locus. J Biol Chem. 277:32405–32408. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tacconelli A, Farina AR, Cappabianca L,
Desantis G, Tessitore A, Vetuschi A, Sferra R, Rucci N, Argenti B,
Screpanti I, et al: TrkA alternative splicing: A regulated
tumor-promoting switch in human neuroblastoma. Cancer Cell.
6:347–360. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kazantseva J, Kivil A, Tints K, Kazantseva
A, Neuman T and Palm K: Alternative splicing targeting the
hTAF4-TAFH domain of TAF4 represses proliferation and accelerates
chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS
One. 8:e747992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kazantseva J, Kivil A, Tints K, Kazantseva
A, Neuman T and Palm K: PTHrP in differentiating human mesenchymal
stem cells: Transcript isoform expression, promoter methylation,
and protein accumulation. Biochimie. 95:1888–1896. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hang X, Li P, Li Z, Qu W, Yu Y, Li H, Shen
Z, Zheng H, Gao Y, Wu Y, et al: Transcription and splicing
regulation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells under hypoxic
stress conditions by exon array. BMC Genomics. 10:1262009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Moller-Levet CS, Betts GN, Harris AL,
Homer JJ, West CM and Miller CJ: Exon array analysis of head and
neck cancers identifies a hypoxia related splice variant of LAMA3
associated with a poor prognosis. PLoS Comput Biol. 5:e10005712009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ducy P, Zhang R, Geoffroy V, Ridall AL and
Karsenty G: Osf2/Cbfa1: A transcriptional activator of osteoblast
differentiation. Cell. 89:747–754. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lynch MP, Stein JL, Stein GS and Lian JB:
The influence of type I collagen on the development and maintenance
of the osteoblast phenotype in primary and passaged rat calvarial
osteoblasts: Modification of expression of genes supporting cell
growth, adhesion, and extracellular matrix mineralization. Exp Cell
Res. 216:35–45. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Andrianarivo AG, Robinson JA, Mann KG and
Tracy RP: Growth on type I collagen promotes expression of the
osteoblastic phenotype in human osteosarcoma MG-63 cells. J Cell
Physiol. 153:256–265. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu N, Shi S, Deng M, Tang L, Zhang G, Liu
N, Ding B, Liu W, Liu Y, Shi H, et al: High levels of β-catenin
signaling reduce osteogenic differentiation of stem cells in
inflammatory microenvironments through inhibition of the
noncanonical Wnt pathway. J Bone Miner Res. 26:2082–2095. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Derveaux S, Vandesompele J and Hellemans
J: How to do successful gene expression analysis using real-time
PCR. Methods. 50:227–230. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schiller ZA, Schiele NR, Sims JK, Lee K
and Kuo CK: Adipogenesis of adipose-derived stem cells may be
regulated via the cytoskeleton at physiological oxygen levels in
vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 4:792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Redshaw Z and Loughna PT: Oxygen
concentration modulates the differentiation of muscle stem cells
toward myogenic and adipogenic fates. Differentiation. 84:193–202.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Khan WS, Adesida AB, Tew SR, Lowe ET and
Hardingham TE: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells express
the pericyte marker 3G5 in culture and show enhanced chondrogenesis
in hypoxic conditions. J Orthop Res. 28:834–840. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang DC, Yang MH, Tsai CC, Huang TF, Chen
YH and Hung SC: Hypoxia inhibits osteogenesis in human mesenchymal
stem cells through direct regulation of RUNX2 by TWIST. PLoS One.
6:e239652011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Martin-Rendon E, Hale SJ, Ryan D, Baban D,
Forde SP, Roubelakis M, Sweeney D, Moukayed M, Harris AL, Davies K
and Watt SM: Transcriptional profiling of human cord blood
CD133+ and cultured bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
in response to hypoxia. Stem Cells. 25:1003–1012. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim JH, Kim SH, Song SY, Kim WS, Song SU,
Yi T, Jeon MS, Chung HM, Xia Y and Sung JH: Hypoxia induces
adipocyte differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells by
triggering reactive oxygen species generation. Cell Biol Int.
38:32–40. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang QB, Zhang ZQ, Fang SL, Liu YR, Jiang
G and Li KF: Effects of hypoxia on proliferation and osteogenic
differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells: An in vitro and
in vivo study. Genet Mol Res. 13:10204–10214. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang B, Liu LT, Li CQ, Zhuang Y, Luo G,
Hu SY and Zhou Y: Study to determine the presence of progenitor
cells in the degenerated human cartilage endplates. Eur Spine J.
21:613–622. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
D'Ippolito G, Diabira S, Howard GA, Roos
BA and Schiller PC: Low oxygen tension inhibits osteogenic
differentiation and enhances stemness of human MIAMI cells. Bone.
39:513–522. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Choi JR, Pingguan-Murphy B, Wan Abas WA,
Azmi MA Noor, Omar SZ, Chua KH and Wan Safwani WK: Impact of low
oxygen tension on stemness, proliferation and differentiation
potential of human adipose-derived stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 448:218–224. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Brock M, Haider TJ, Vogel J, Gassmann M,
Speich R, Trenkmann M, Ulrich S, Kohler M and Huber LC: The
hypoxia-induced microRNA-130a controls pulmonary smooth muscle cell
proliferation by directly targeting CDKN1A. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 61:129–137. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Leszczynska KB, Foskolou IP, Abraham AG,
Anbalagan S, Tellier C, Haider S, Span PN, O'Neill EE, Buffa FM and
Hammond EM: Hypoxia-induced p53 modulates both apoptosis and
radiosensitivity via AKT. J Clin Invest. 125:2385–2398. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nerlich AG, Schaaf R, Wälchli B and Boos
N: Temporo-spatial distribution of blood vessels in human lumbar
intervertebral discs. Eur Spine J. 16:547–555. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee DC, Adams CS, Albert TJ, Shapiro IM,
Evans SM and Koch CJ: In situ oxygen utilization in the rat
intervertebral disc. J Anat. 210:294–303. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Freemont AJ, Watkins A, Le Maitre C, Baird
P, Jeziorska M, Knight MT, Ross ER, O'Brien JP and Hoyland JA:
Nerve growth factor expression and innervation of the painful
intervertebral disc. J Pathol. 197:286–292. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Walsh DA, McWilliams DF, Turley MJ, Dixon
MR, Fransès RE, Mapp PI and Wilson D: Angiogenesis and nerve growth
factor at the osteochondral junction in rheumatoid arthritis and
osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 49:1852–1861. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Babadagli ME, Tezcan B, Yilmaz ST and
Tufan AC: Matrilin-3 as a putative effector of C-type natriuretic
peptide signaling during TGF-β induced chondrogenic differentiation
of mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Biol Rep. 41:5549–5555. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fernandes AM, Herlofsen SR, Karlsen TA,
Küchler AM, Fløisand Y and Brinchmann JE: Similar properties of
chondrocytes from osteoarthritis joints and mesenchymal stem cells
from healthy donors for tissue engineering of articular cartilage.
PLoS One. 8:e629942013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Herlofsen SR, Bryne JC, Høiby T, Wang L,
Issner R, Zhang X, Coyne MJ, Boyle P, Gu H, Meza-Zepeda LA, et al:
Genome-wide map of quantified epigenetic changes during in vitro
chondrogenic differentiation of primary human mesenchymal stem
cells. BMC Genomics. 14:1052013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Weber M, Sotoca AM, Kupfer P, Guthke R and
van Zoelen EJ: Dynamic modelling of microRNA regulation during
mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. BMC Syst Biol. 7:1242013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Blencowe BJ: Alternative splicing: New
insights from global analyses. Cell. 126:37–47. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jeon YM, Kook SH, Rho SJ, Lim SS, Choi KC,
Kim HS, Kim JG and Lee JC: Fibroblast growth factor-7 facilitates
osteogenic differentiation of embryonic stem cells through the
activation of ERK/Runx2 signaling. Mol Cell Biochem. 382:37–45.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Drabek K, van de Peppel J, Eijken M and
van Leeuwen JP: GPM6B regulates osteoblast function and induction
of mineralization by controlling cytoskeleton and matrix vesicle
release. J Bone Miner Res. 26:2045–2051. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hamidouche Z, Fromigué O, Ringe J, Häupl T
and Marie PJ: Crosstalks between integrin alpha 5 and IGF2/IGFBP2
signalling trigger human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal
osteogenic differentiation. BMC Cell Biol. 11:442010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Schraufstatter IU, Khaldoyanidi SK and
DiScipio RG: Complement activation in the context of stem cells and
tissue repair. World J Stem Cells. 7:1090–1108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lee DS, Yi TG, Lee HJ, Kim SN, Park S,
Jeon MS and Song SU: Mesenchymal stem cells infected with
Mycoplasma arginini secrete complement C3 to regulate
immunoglobulin production in B lymphocytes. Cell Death Dis.
5:e11922014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Soland MA, Bego M, Colletti E, Zanjani ED,
St Jeor S, Porada CD and Almeida-Porada G: Mesenchymal stem cells
engineered to inhibit complement-mediated damage. PLoS One.
8:e604612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ignatius A, Ehrnthaller C, Brenner RE,
Kreja L, Schoengraf P, Lisson P, Blakytny R, Recknagel S, Claes L,
Gebhard F, et al: The anaphylatoxin receptor C5aR is present during
fracture healing in rats and mediates osteoblast migration in
vitro. J Trauma. 71:952–960. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Collard CD, Väkevä A, Morrissey MA, Agah
A, Rollins SA, Reenstra WR, Buras JA, Meri S and Stahl GL:
Complement activation after oxidative stress: Role of the lectin
complement pathway. Am J Pathol. 156:1549–1556. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Cowell RM, Plane JM and Silverstein FS:
Complement activation contributes to hypoxic-ischemic brain injury
in neonatal rats. J Neurosci. 23:9459–9468. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Altare F, Jouanguy E, Lamhamedi-Cherradi
S, Fondanéche MC, Fizame C, Ribiérre F, Merlin G, Dembic Z,
Schreiber R, Lisowska-Grospierre B, et al: A causative relationship
between mutant IFNgR1 alleles and impaired cellular response to
IFNgamma in a compound heterozygous child. Am J Hum Genet.
62:723–726. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Duque G, Huang DC, Macoritto M, Rivas D,
Yang XF, Ste-Marie LG and Kremer R: Autocrine regulation of
interferon gamma in mesenchymal stem cells plays a role in early
osteoblastogenesis. Stem Cells. 27:550–558. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Duque G, Huang DC, Dion N, Macoritto M,
Rivas D, Li W, Yang XF, Li J, Lian J, Marino FT, et al:
Interferon-γ plays a role in bone formation in vivo and rescues
osteoporosis in ovariectomized mice. J Bone Miner Res.
26:1472–1483. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Dighe AS, Yang S, Madhu V, Balian G and
Cui Q: Interferon gamma and T cells inhibit osteogenesis induced by
allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells. J Orthop Res. 31:227–234.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Olszowski T, Poziomkowska-Gęsicka I,
Jensenius JC and Adler G: Lectin pathway of complement activation
in a Polish woman with MASP-2 deficiency. Immunobiology.
219:261–262. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Choung HW, Lee DS, Lee HK, Shon WJ and
Park JC: Preameloblast-derived factors mediate osteoblast
differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by
Runx2-Osterix-BSP signaling. Tissue Eng Part A. 22:93–102. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Haddad JJ: Endotoxin-mediated regulation
of nuclear factor-kappaB nuclear translocation and activation in
the hippocampus of the central nervous system: Modulation by
intracerebroventricular treatment with thymulin and the
immunomodulatory role of the IkappaB-alpha/pIkappaB-alpha pathway.
Neuroscience. 164:1509–1520. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Nguyen TL Xuan, Choi JW, Lee SB, Ye K, Woo
SD, Lee KH and Ahn JY: Akt phosphorylation is essential for nuclear
translocation and retention in NGF-stimulated PC12 cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 349:789–798. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Mathieu J, Zhang Z, Nelson A, Lamba DA,
Reh TA, Ware C and Ruohola-Baker H: Hypoxia induces re-entry of
committed cells into pluripotency. Stem Cells. 31:1737–1748. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Cramer T, Schipani E, Johnson RS, Swoboda
B and Pfander D: Expression of VEGF isoforms by epiphyseal
chondrocytes during low-oxygen tension is HIF-1 alpha dependent.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 12:433–439. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|